The index finger is composed of three bones. Cuticles are the tissues along the sides and the base of nails.
 Surface Anatomy Hand Surgery Source
Surface Anatomy Hand Surgery Source
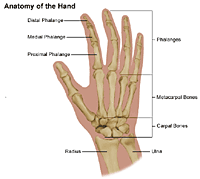
The distal phalanx intermediate phalanx and proximal phalanx.
Index finger anatomy. The pointer finger is the second digit and first finger of the human hand. The index finger does not contain any muscles but is controlled by muscles in the hand by attachments of tendons to the bones. The thumb has a distal and proximal phalanx as well as an interphalangeal and mcp joint.
Fingers have a complex anatomy. The index finger is the second digit of the hand. Distal interphalangeal dip proximal interphalangeal pip and metacarpophalangeal mcp.
Nails are comprised of a hard protein called keratin which is also a component of hair and skin. The ability to flex the fingers consists of a system of flexor muscles in the forearm and their tendons are inserted into the bones of the fingers. The lunula is the visible half moon at the base of the nail.
Finger injuries have the potential to slow down anyone. This usually takes the form of non verbal hand gestures. This finger has practical applications of both sensory touch and grasp but it is often used for expressive purposes as well.
Fingers are easily injured and broken fingers are some of the most common traumatic injuries seen in an emergency room. Fingers are one of the most used appendages and the most delicate so they are prone to injury. The matrix is the tissue from which the nails grow.
This finger often possesses the largest amount of sensitivity and greatest dexterity of any of the fingers. Picture of fingernail anatomy. It lies under the cuticle.
Each finger has 3 phalanges bones and 3 hinged joints. Ligaments connect finger bones and help keep them in place. Finger fractures may account for up to 10 of all bone fractures.
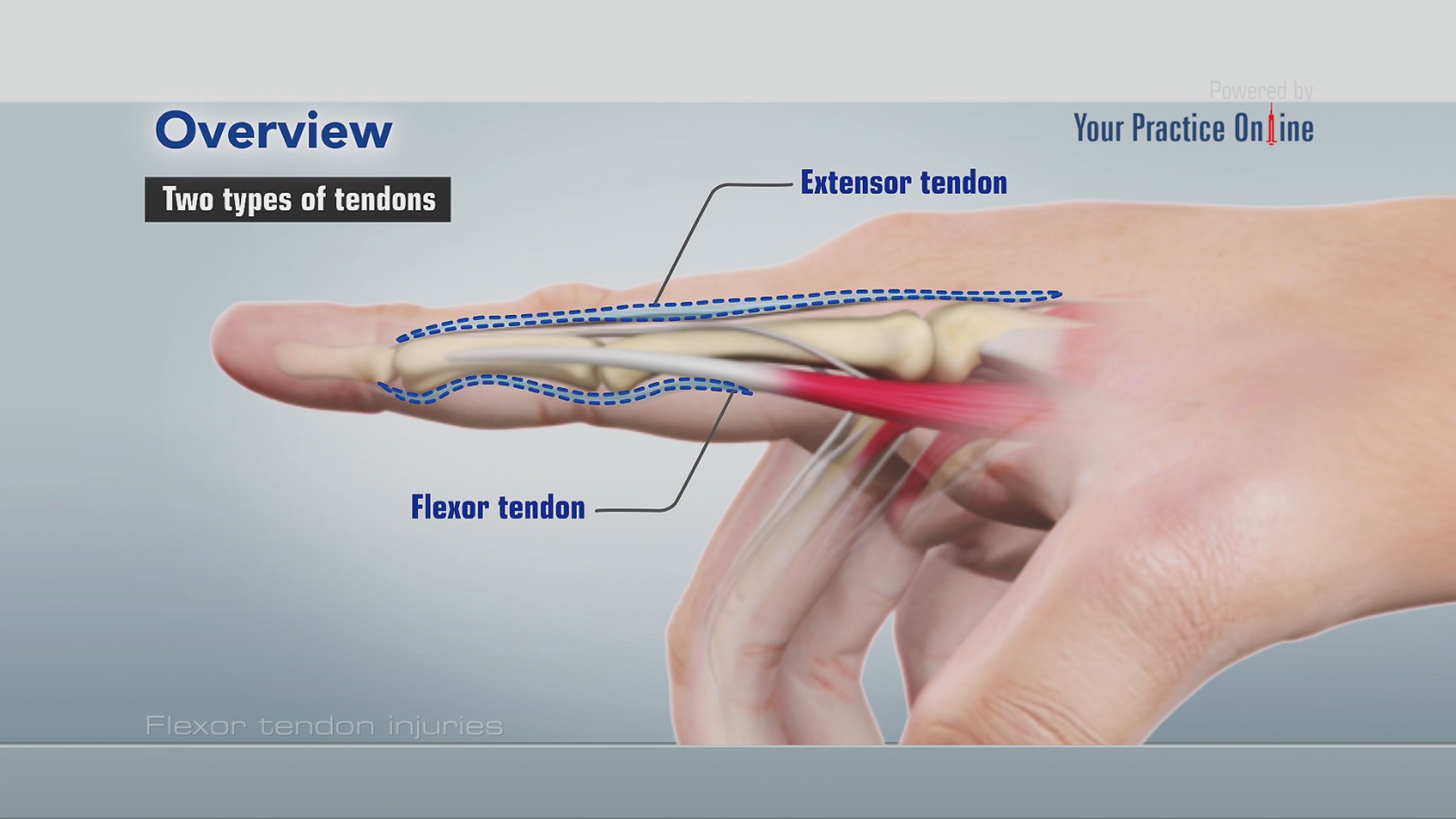
A flexor tendon injury can cause loss of flexion. Skin folds anchor the nails to the fingers. It is also called the index finger or the forefinger.
A digit includes the hand bones but these bones are not separated into individual appendages like a finger. The thumb has two of each. The index finger has three phalanges.
Along with the thumb and middle finger it is one of the most often used digits. The index middle ring and fifth digits have proximal middle and distal phalanges and three hinged joints. Anatomy of the fingers the human finger is mainly a bony structure with multiple joints giving it strength and flexibility.
Basic anatomy of the finger.
 Anatomy Of The Index Finger 18 Download Scientific Diagram
Anatomy Of The Index Finger 18 Download Scientific Diagram
 A Arterial Anatomy At The Fingertip B Dorsal Venous
A Arterial Anatomy At The Fingertip B Dorsal Venous
 Finger Names What Are Fingers Called
Finger Names What Are Fingers Called
 Extensor Tendon Injuries Florida Bone And Joint
Extensor Tendon Injuries Florida Bone And Joint
 How To Avoid Sore Hands From Mountain Biking Total
How To Avoid Sore Hands From Mountain Biking Total
 Illustration Picture Of Hand Structures Finger Anatomy
Illustration Picture Of Hand Structures Finger Anatomy
 Finger Injury Pictures Types Treatment Symptoms Diagnosis
Finger Injury Pictures Types Treatment Symptoms Diagnosis
 Hand Bones And Wrist Bones Mnemonics Anatomy And Physiology
Hand Bones And Wrist Bones Mnemonics Anatomy And Physiology
 Modern Human Thumb And Index Finger Right Hand During Pad
Modern Human Thumb And Index Finger Right Hand During Pad
 Index Finger Fixation Medical Illustration Human Anatomy
Index Finger Fixation Medical Illustration Human Anatomy
 What Peculiarities Of The Anatomy Of Hands Should Be Taken
What Peculiarities Of The Anatomy Of Hands Should Be Taken
 Our Index Finger Pointing To The Creator Answers In Genesis
Our Index Finger Pointing To The Creator Answers In Genesis
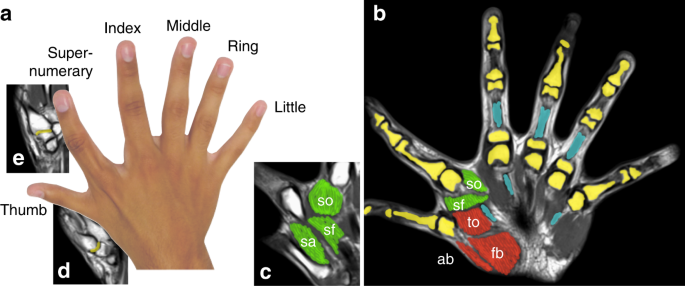
 Augmented Manipulation Ability In Humans With Six Fingered
Augmented Manipulation Ability In Humans With Six Fingered
 Diagram Of The Fingers Reading Industrial Wiring Diagrams
Diagram Of The Fingers Reading Industrial Wiring Diagrams
 Our Index Finger Pointing To The Creator Answers In Genesis
Our Index Finger Pointing To The Creator Answers In Genesis
 Figure 2 From An Under Actuated Mechanism For A Robotic
Figure 2 From An Under Actuated Mechanism For A Robotic
 Notes On Anatomy And Physiology The Hand And The Tiger S
Notes On Anatomy And Physiology The Hand And The Tiger S
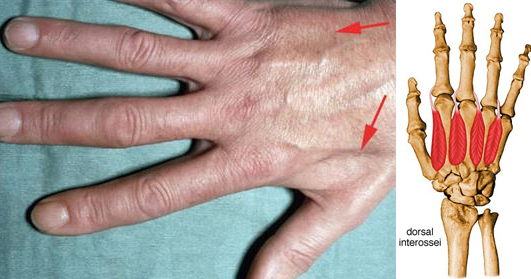 Physical Exam Of The Hand Hand Orthobullets
Physical Exam Of The Hand Hand Orthobullets

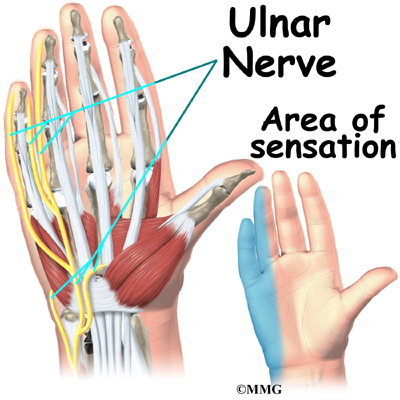


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar