Fruits contain seeds and a number of protective outer layers. Fruits are the seed containing reproductive organs including nuts and grains produced by angiosperms flowering plants.
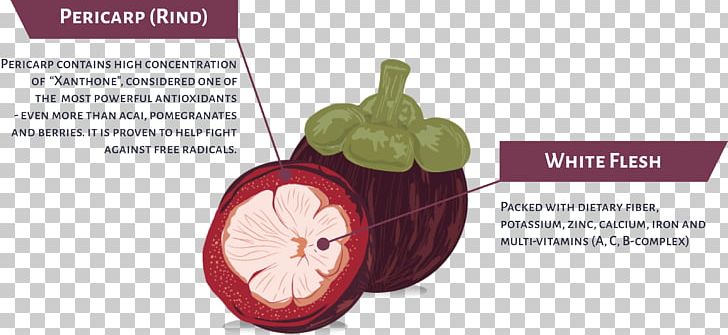 Fruit Anatomy Juice Purple Mangosteen Cocktail Png Clipart
Fruit Anatomy Juice Purple Mangosteen Cocktail Png Clipart
The anatomy of fruits and vegetables.

Anatomy of fruit. Fruit as a food source. When most people think of a fruit what typically comes to mind is a juicy edible object such as an apple orange or banana. They can be fleshy or dry.
Peach nectarine almond cherry plum prune apricot and olive all fall within the common peach type fruit figure 8. Conflict of interest statement the authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. In fleshy fruits the outer and often edible layer is the pericarp which is the tissue that develops from the ovary wall of the flower and surrounds the seeds.
Each one comes compact with nutrition ranging from body building energy giving and body regulating elements. What makes fruits and vegetables relevant to weight management is the array of nutritional elements such as vitamins minerals carbohydrates fats and proteins. Longitudinal sections of peach a plum b cherry c and olive d fruit.
Fruit anatomy is the internal structure of fruit the mature ovary or ovaries from one or more flowers. Fruit anatomy is the plant anatomy of the internal structure of fruit. Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers.
Pericarp all three carpi regions collectively. Exocarp skin or rind of a fruit. Fruit is arguably one of the.
It usually contains seeds which have developed from the enclosed ovule after fertilization although development without fertilization called parthenocarpy is known for example in bananas. Botanically a fruit is a mature ovary and its associated parts. The main purpose of fruit is to protect seeds during development.
So vascular anatomy of kiwi fruit wall shows a midway between axis and leaf and thus sheds some new light on the derivation of leaves. Once pollination and fertilization occur the ovary of the plant becomes the fruit and the ovules become the seeds. Fruit purpose of a fruit.
Anatomy of a fruit seed endocarp immediately around seed may be hard stony or papery. Mesocarp fleshy tissue in fleshy fruits between endo and exocarp. Peach type fruit develop from a single carpel and contain one or two seeds.
There is a massive variety of different types of fruit. Fruits are a characteristic of flowering plants. In fleshy fruits the outer layer which is often edible is the pericarp which is the tissue that develops from the ovary wall of the flower and surrounds the seeds.
 The Anatomy Of A Stone Fruit The Produce Moms
The Anatomy Of A Stone Fruit The Produce Moms
Citrus Citrus Clementina Clementine Mandarine And Citrus
Classification Anatomy And Function
Animal Plant Soil Science E2 5 Fruit Function And Anatomy
 The Anatomy Of A Stone Fruit The Produce Moms
The Anatomy Of A Stone Fruit The Produce Moms
 Fruit Botanical Anatomy Kitchen Art Print Pear Shaped Botany Art Surreal Medical Anatomical Surrealism Muscles Buttocks Pear Shaped Body
Fruit Botanical Anatomy Kitchen Art Print Pear Shaped Botany Art Surreal Medical Anatomical Surrealism Muscles Buttocks Pear Shaped Body
Fruit Anatomy Fruit Nut Research Information Center
 Coffee Cherry Fruit Anatomy Stock Image Image Of Berry
Coffee Cherry Fruit Anatomy Stock Image Image Of Berry
Fruit Anatomy Fruit Nut Research Information Center
 Fruit Function And Anatomy Ppt Download
Fruit Function And Anatomy Ppt Download
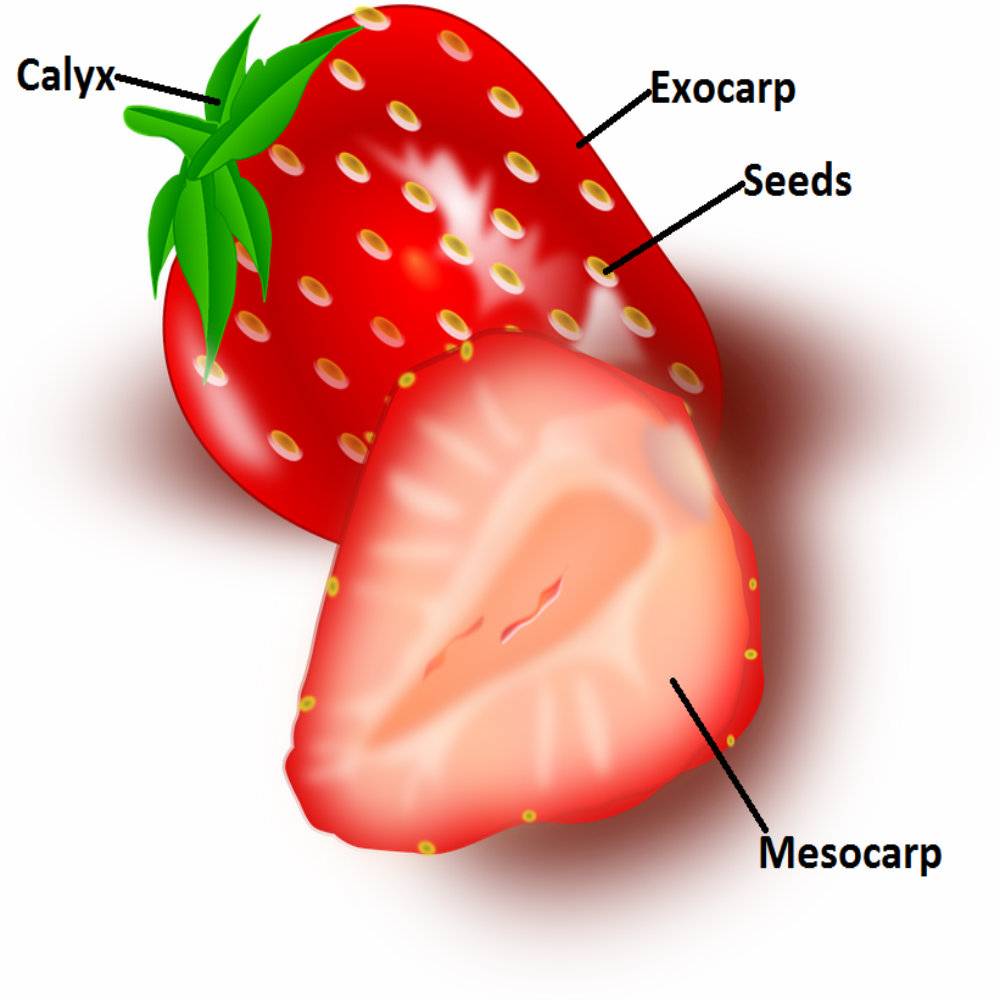 Berry Anatomy And Botanical Uses
Berry Anatomy And Botanical Uses

Fruit Anatomy Fruit Nut Research Information Center
 Fruit Fly Anatomy Basic Electrical Wiring Theory
Fruit Fly Anatomy Basic Electrical Wiring Theory
 Frontiers Vascular Anatomy Of Kiwi Fruit And Its
Frontiers Vascular Anatomy Of Kiwi Fruit And Its
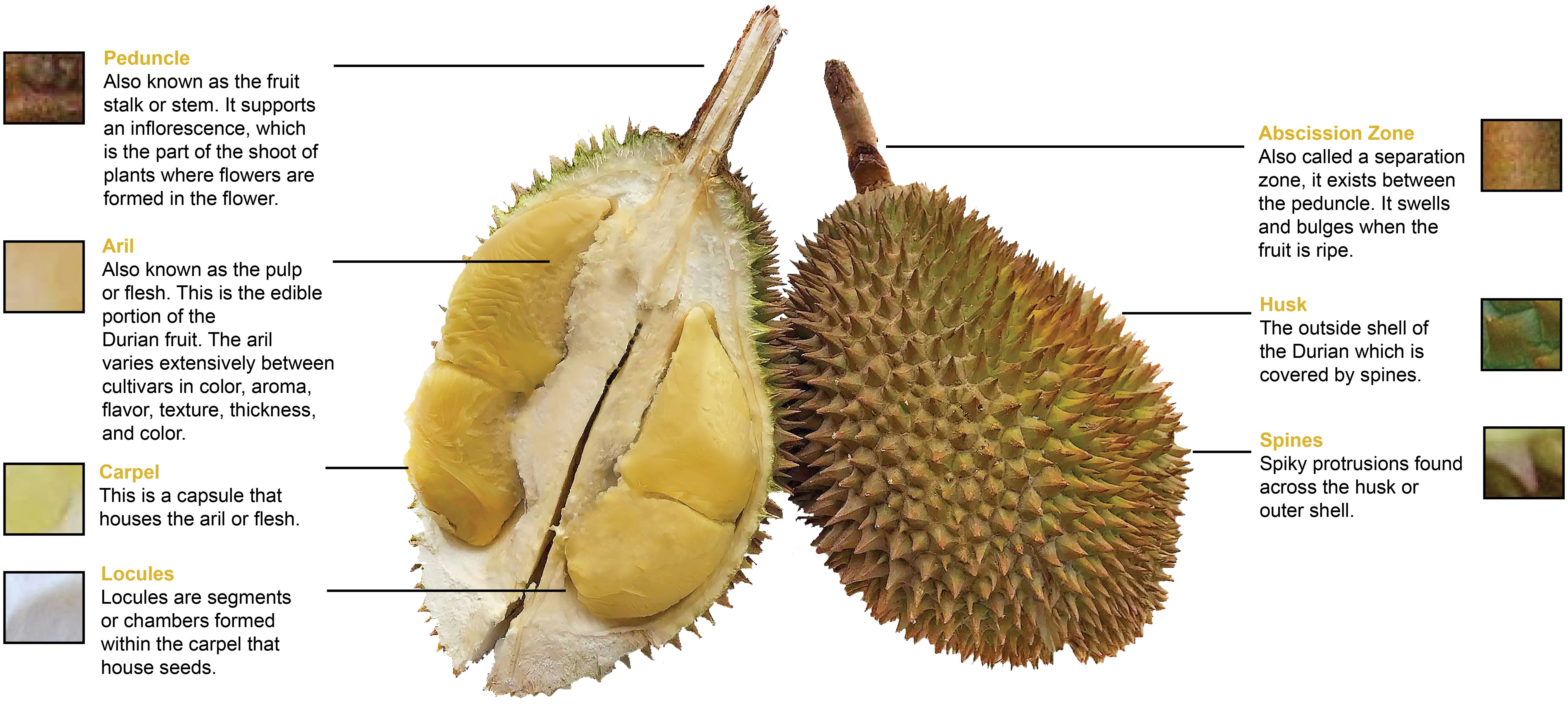 Durian Harvests Home Of The Musang King Durian
Durian Harvests Home Of The Musang King Durian
 22 Botanical Terms For Fruits Awkward Botany
22 Botanical Terms For Fruits Awkward Botany
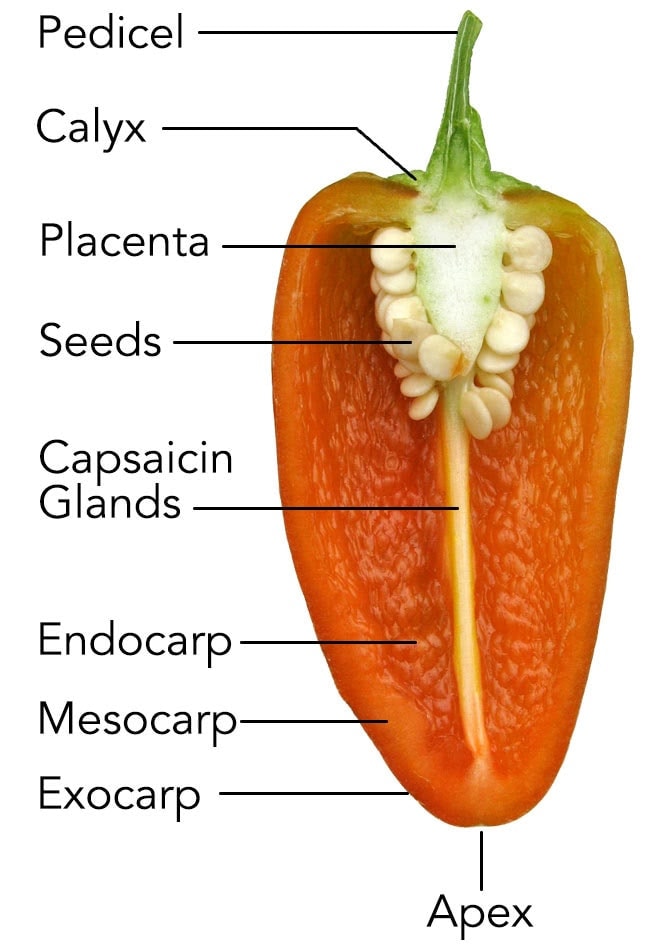 Anatomy Of A Chile Pepper Cayenne Diane
Anatomy Of A Chile Pepper Cayenne Diane
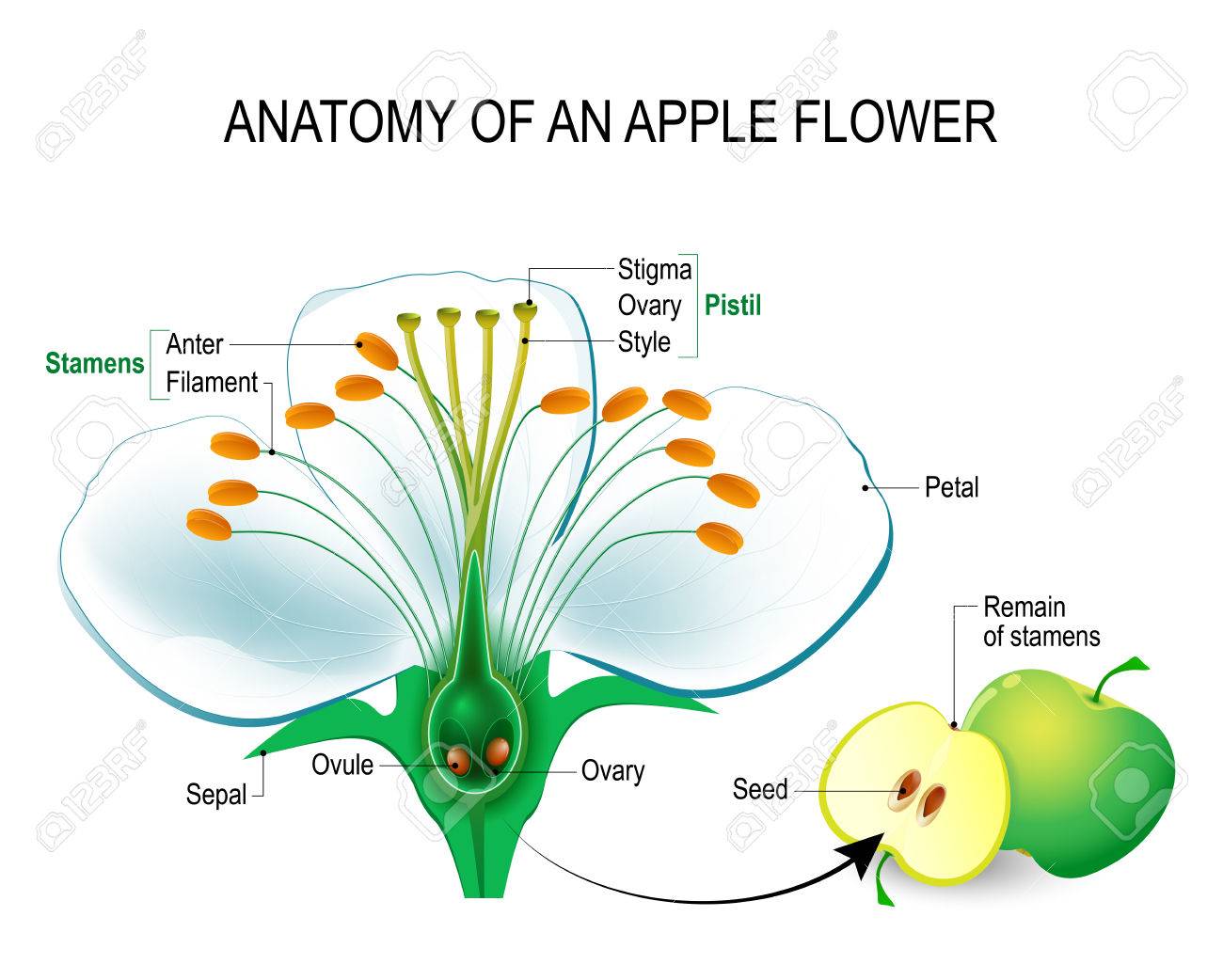 Anatomy Of An Apple Flower Flower Parts Detailed Diagram With
Anatomy Of An Apple Flower Flower Parts Detailed Diagram With
Anatomy Of Fruit Science Investigation Pre K Printable Fun
 Citrus Citrus Clementina Clementine Mandarine And Citrus
Citrus Citrus Clementina Clementine Mandarine And Citrus
 Morphology And Anatomy Of Tomato Ripe Red Fruit Tomato
Morphology And Anatomy Of Tomato Ripe Red Fruit Tomato
 Figure 4 From Fruit Morphology Anatomy And Mixocarpy
Figure 4 From Fruit Morphology Anatomy And Mixocarpy



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar