Canal for pharyngotympanic auditory tube. Canal anatomy canal debridement.
 Root Canal High Impact Visual Litigation Strategies
Root Canal High Impact Visual Litigation Strategies
Canal wall up mastoidectomy.

Canal anatomy. Canal wall down mastoidectomy. The inguinal canal is a short passage that extends inferiorly and medially through the inferior part of the abdominal wall. It is situated between the rectum and anus below the level of the pelvic diaphragm.
The vagina connects the uterus to the outside world. The canal serves as a pathway by which structures can pass from the abdominal wall to the external genitalia. The vagina is an elastic muscular canal with a soft flexible lining that provides lubrication and sensation.
It is superior and parallel to the inguinal ligament. The anal canal is the final segment of the gastrointestinal tract. The anal canal is the terminal part of the large intestine.
It has an important role in defecation and maintaining faecal continence. The description in this topic is from below upwards as that is how this region is usually examined in clinical practice. Canal of stapedius muscle.
The upper region has 5 to 10 rectal columns each column containing a small artery and vein. Gross anatomy dorello canal is found at the medial most end of the petrous ridge at the confluence of the inferior petrosal basal and cavernou. In this article we shall look at the anatomy of the anal canal its position structure relations and neurovascular supply.
Canal for pharyngotympanic tube. The anal canal is divided into three parts. Canal for tensor tympani muscle canal for vertebral artery.
Canal anatomy in anatomy a canal or canalis in latin is a tubular passage or channel which connects different regions of the body. The anal canal is the most terminal part of the lower gi tractlarge intestine which lies between the anal verge anal orifice anus in the perineum below and the rectum above. Dorello canal channels the abducens nerve cn vi from the pontine cistern to the cavernous sinus.
Dorlands illustrated medical dictionary 27th ed. The internal anatomy of the mesiobuccal root mb of maxillary molars is complex and commonly presents 2 main root canals named mb1 and mb2 but also a high incidence of fine anatomical structures which may include the presence of a middle mesial canal the so called mb3. The anal canal connects with the rectum at the point where it passes through a muscular pelvic diaphragm.
It lies in the anal triangle of perineum in between the right and left ischioanal fossa.
 Molar Root Canal Anatomy Springerlink
Molar Root Canal Anatomy Springerlink
 Maxillary Molar Root Canal Morphology And Anatomy Key
Maxillary Molar Root Canal Morphology And Anatomy Key
 Variations In Root Canal Anatomy Part 2 Mandibular 2nd
Variations In Root Canal Anatomy Part 2 Mandibular 2nd
 Saphenous Nerve Block At The Adductor Canal Nysora
Saphenous Nerve Block At The Adductor Canal Nysora
 Pdf Saphenous And Infrapatellar Nerves At The Adductor
Pdf Saphenous And Infrapatellar Nerves At The Adductor
 02 Root Canal Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
02 Root Canal Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
Scripps Mesa Endodontics Scripps Mesa Endodontics
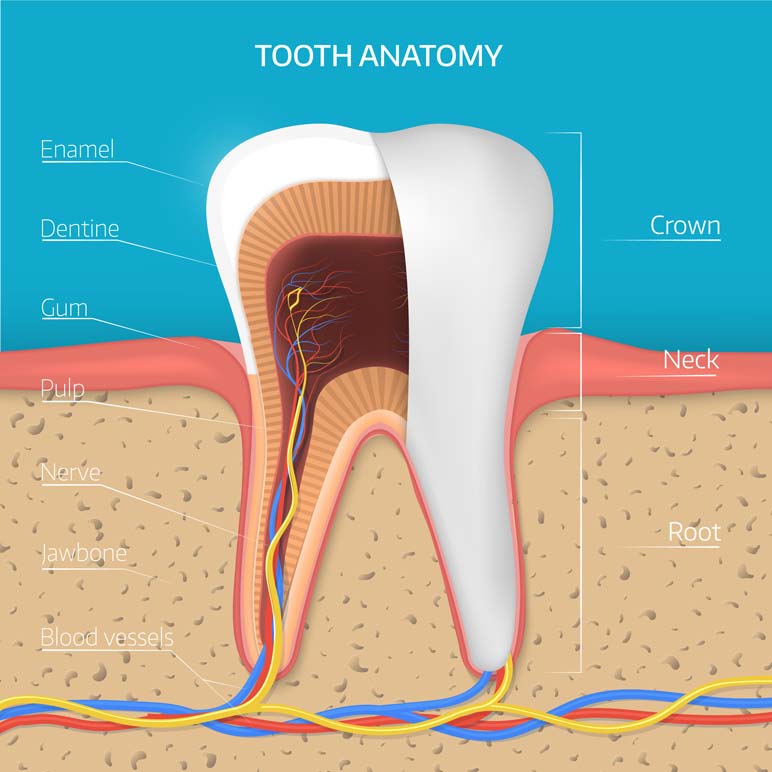 Root Canal Therapy Bronx Ny Your Bronx Dentist
Root Canal Therapy Bronx Ny Your Bronx Dentist
 The Root Canal Anatomy Project Single File Preparation
The Root Canal Anatomy Project Single File Preparation
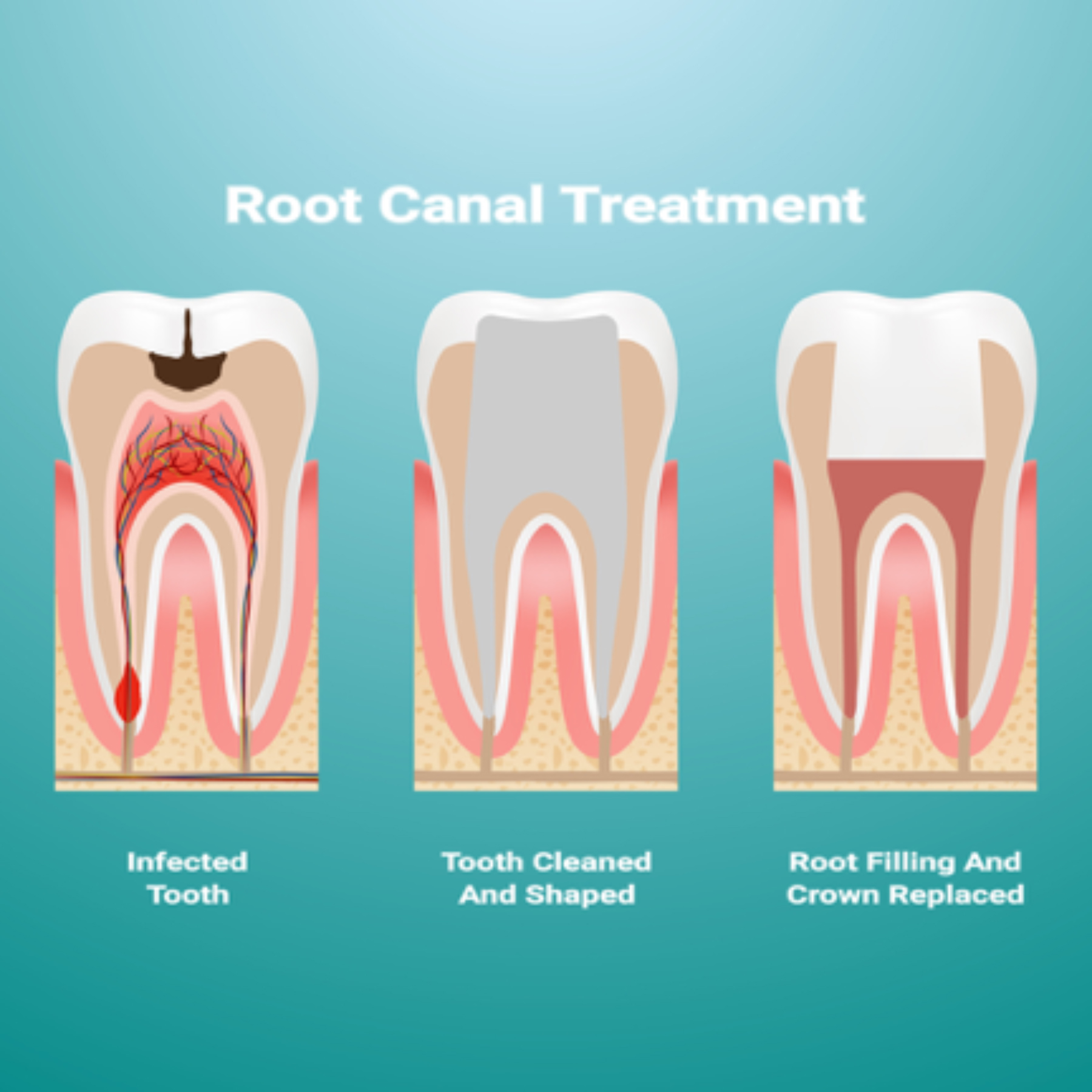 Root Canal Knoxville Therapy In One Visit Dr Jack Haney
Root Canal Knoxville Therapy In One Visit Dr Jack Haney
 Preserve The Canal Anatomy Online Presentation
Preserve The Canal Anatomy Online Presentation
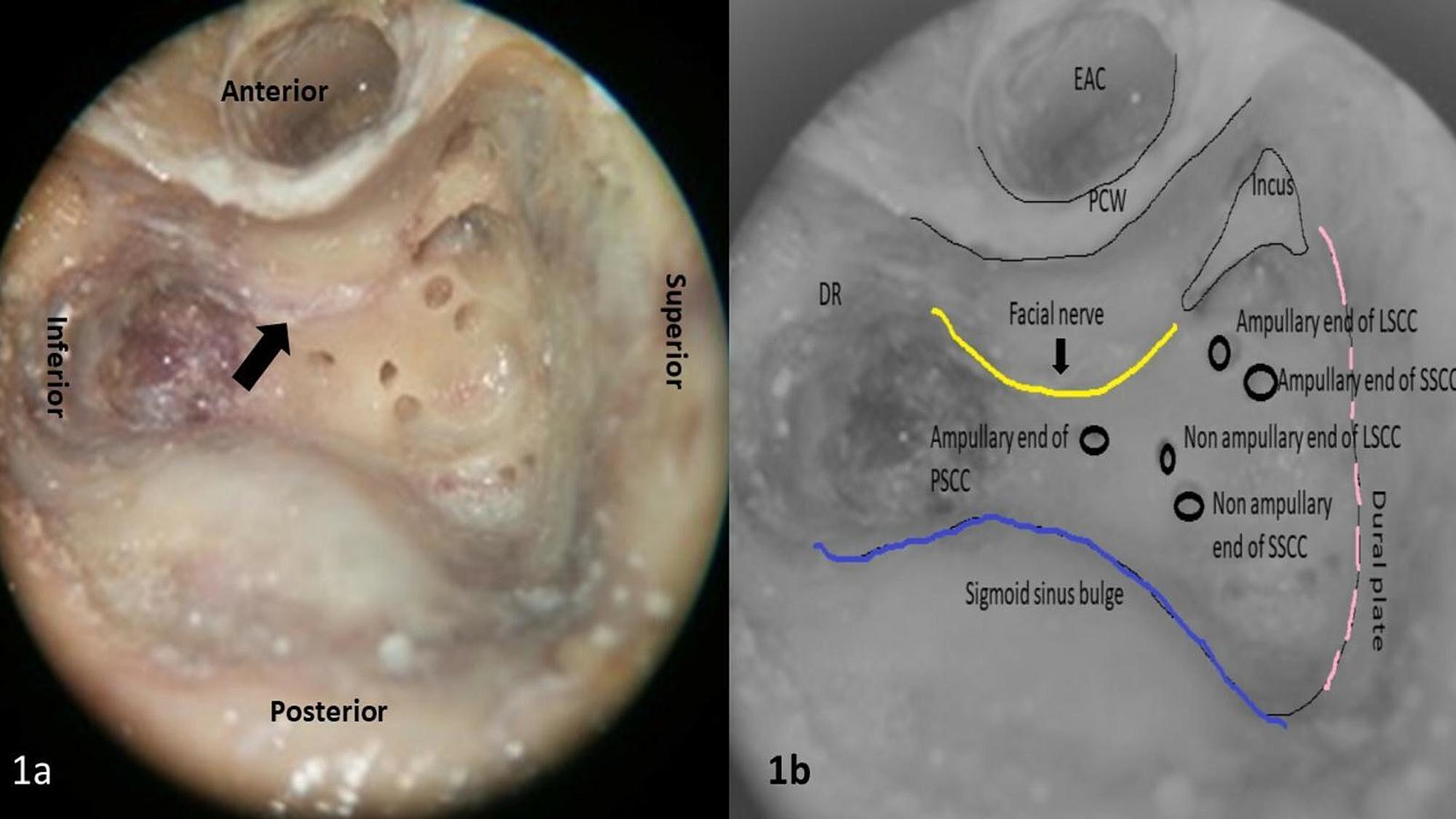 Cureus Anatomical Features Of Intratemporal Course Of
Cureus Anatomical Features Of Intratemporal Course Of
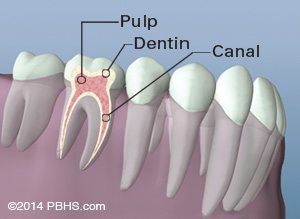 Root Canal Therapy Tooth Anatomy Diagram Raleigh
Root Canal Therapy Tooth Anatomy Diagram Raleigh
 Root Canal Procedure Who Performs It And What Does It Cost
Root Canal Procedure Who Performs It And What Does It Cost
 Internal Anal Sphincter Rectum Anal Canal Stock Vector
Internal Anal Sphincter Rectum Anal Canal Stock Vector
The Anatomy Of The Laboratory Mouse
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/8025/The_Hernia.png) Inguinal Canal Anatomy Contents And Hernias Kenhub
Inguinal Canal Anatomy Contents And Hernias Kenhub
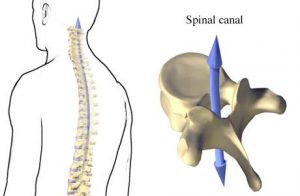 Vertebral Canal Anatomy And Contents Bone And Spine
Vertebral Canal Anatomy And Contents Bone And Spine
 Birth Canal Anatomy Britannica
Birth Canal Anatomy Britannica
Root Canal Anatomy Is Complex Elm Endodontics Broomfield
 Study Analyses Unique Root Canal Anatomy Patterns In Indian
Study Analyses Unique Root Canal Anatomy Patterns In Indian
 Anal Canal Anatomy Unlabeled Stock Illustration 229583629
Anal Canal Anatomy Unlabeled Stock Illustration 229583629
 Blue Summit Dental Group Root Canal Retreatment Davison Mi
Blue Summit Dental Group Root Canal Retreatment Davison Mi
 Anal Canal An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Anal Canal An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Complicated Root Canal Anatomy Portfolio Advanced
Complicated Root Canal Anatomy Portfolio Advanced
 Procedures Midwest Endodontics
Procedures Midwest Endodontics
 Introductory Chapter Some Important Aspects Of Root Canal
Introductory Chapter Some Important Aspects Of Root Canal
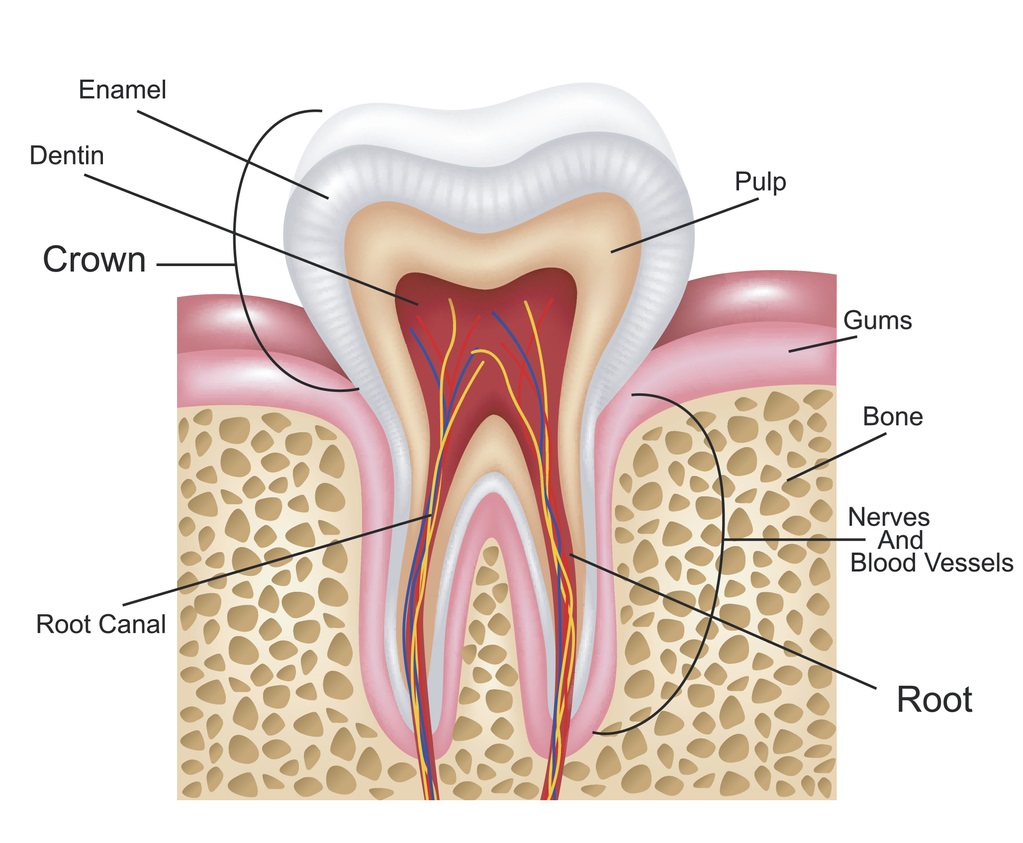 Root Canal Basics Root Canal Explained
Root Canal Basics Root Canal Explained

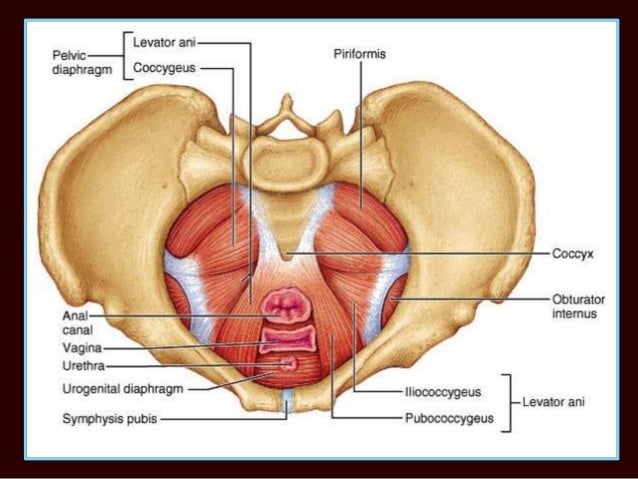
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar