From anatomy mouth pharynx esophagus sotmach small intestine large intestine and some not in the gi tracts. The large intestine completes absorption and compacts waste.
 Large Intestine Anatomy And Physiology
Large Intestine Anatomy And Physiology
Mediastinum definition separates the thorax into two compartments containing the right and left lungs the other thoracic organs heart esophagus etc are within it parietal.

Absorption definition anatomy. Absorption is the process by which digested molecules and compounds pass through the epithelial layer the skin cells that line the inside of the digestive tract as well as many other parts of. Describe the anatomy of the digestive system and the gastrointestinal gi tract. Absorption in general sense is the act or process of absorbing or assimilating.
Food moves through the mucous membrane lining of the small intestine into the blood. Chyme passes from the small intestine through the ileocecal valve and into the cecum of the large intestine. When enzymes speed up reactions that add water hydro to chemically break up or split lysis large molecules into small molecules.
Jejunum definition the jejunum is one of three sections that make up the small intestine. Anatomy and physiology chapter 1. Salivary glands liver gallbladder exocrine pancreas.
Protects the body keeps harmful material out regulates body temperature senses and responds to the environment and creates important chemicals. Digestive absorption the passage of the end products of digestion from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood and lymphatic vessels and the cells of tissues. Chemical absorption any process by which one substance in liquid or solid form penetrates the surface of another substance.
The small intestine is part of the digestive system and is vital for breaking down and absorbing nutrients. In biology absorption pertains particularly to the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into the cell or across the tissues and organs. Absorption of monosaccharides amino acids dipeptides tripeptides lipids electrolytes vitamins and water glucose amino acids fats and vitamins are absorbed in the small intestine via the action of hormones and electrolytes.
Any remaining nutrients and some water are absorbed as peristaltic waves move the chyme into the ascending and transverse colons.
 Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption
Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption
Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Human Nutrition
 Small Intestine Nutrient Absorption And Role In Digestion
Small Intestine Nutrient Absorption And Role In Digestion
 Absorption Of Micronutrients And Water Into The Bloodstream
Absorption Of Micronutrients And Water Into The Bloodstream
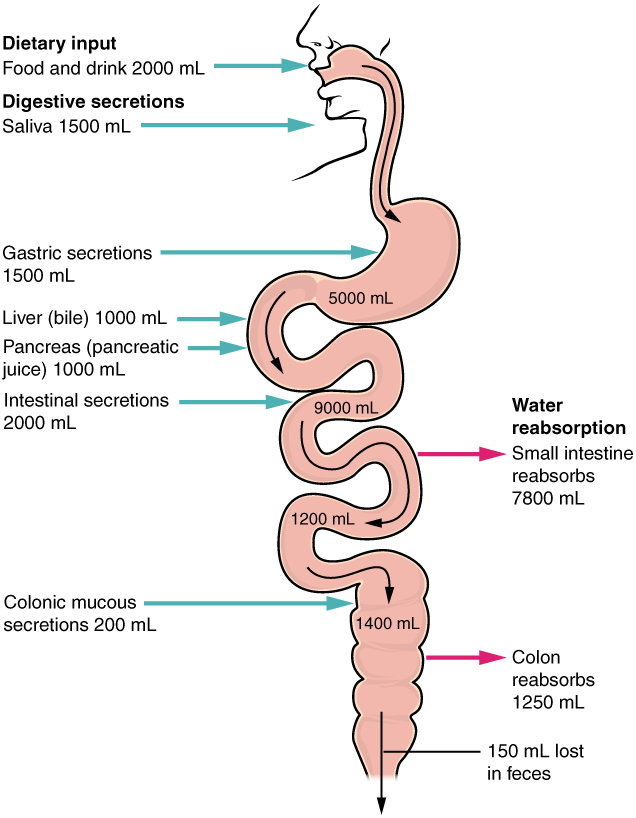 23 7 Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look
23 7 Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stomach_intestines-57ffd6795f9b5805c2ac495f.jpg) Nutrient Absorption In The Digestive System
Nutrient Absorption In The Digestive System
 23 1 Overview Of The Digestive System Anatomy Physiology
23 1 Overview Of The Digestive System Anatomy Physiology
 Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals The Gut And Digestion
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals The Gut And Digestion
 Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look Anatomy
Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look Anatomy
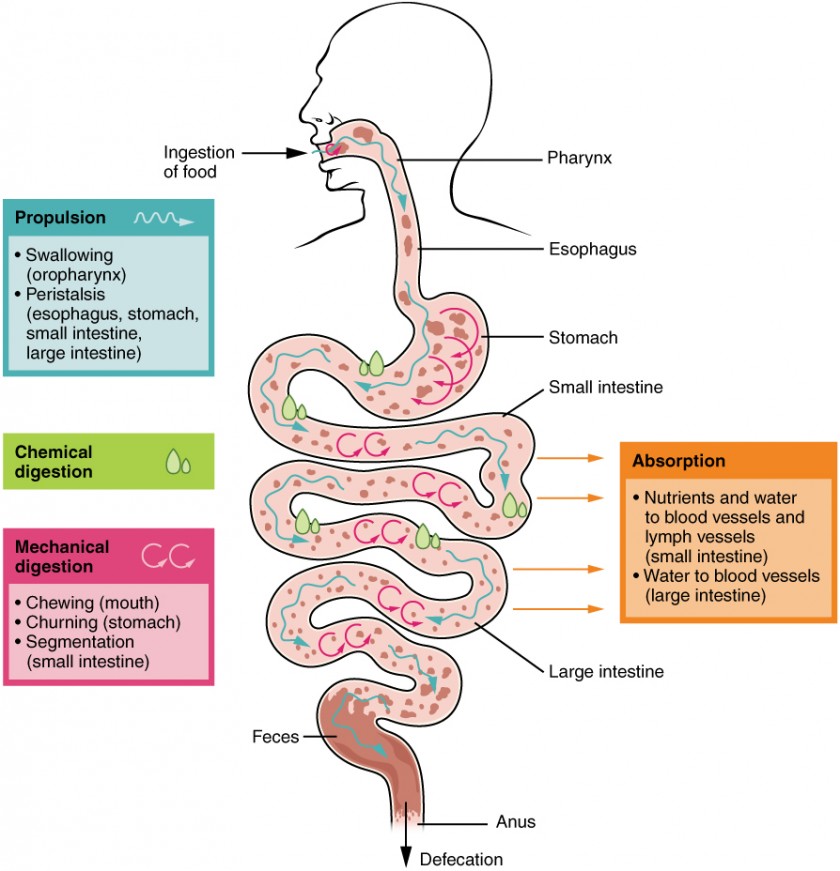 Digestive System Processes And Regulation Anatomy And
Digestive System Processes And Regulation Anatomy And
 Absorption Of Lipids Physiology Anatomy Medical
Absorption Of Lipids Physiology Anatomy Medical
 Pharmacokinetics The Dynamics Of Drug Absorption
Pharmacokinetics The Dynamics Of Drug Absorption
 Toxtutor Gastrointestinal Tract
Toxtutor Gastrointestinal Tract
 Small Intestine Parts Function Quiz Biology Dictionary
Small Intestine Parts Function Quiz Biology Dictionary
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ph-of-the-stomach-608195_final-da87214880ac4716bd5e570b31601029.png) Nutrient Absorption In The Digestive System
Nutrient Absorption In The Digestive System
 Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look Anatomy
Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look Anatomy
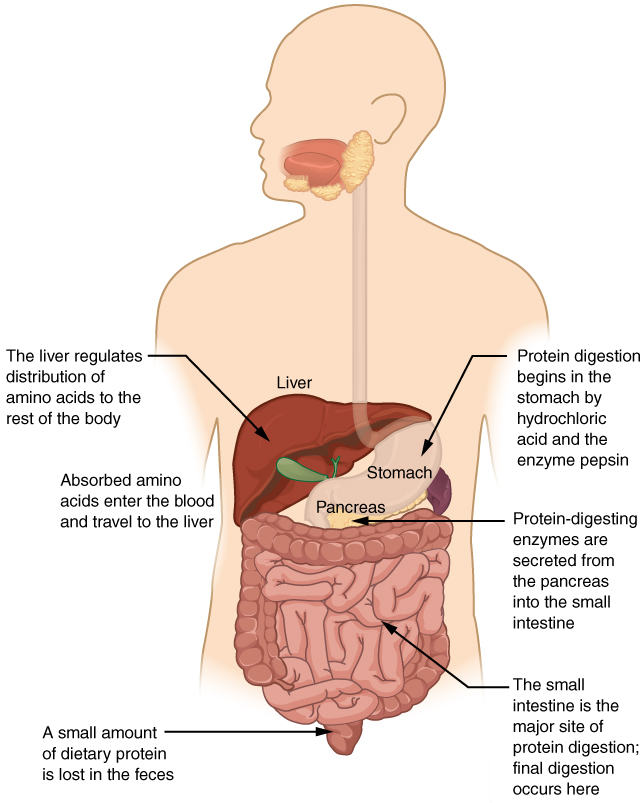 23 7 Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look
23 7 Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look







Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar