The thumb has two. Distal interphalangeal dip proximal interphalangeal pip and metacarpophalangeal mcp.
The thumb has a distal and proximal phalanx as well as an interphalangeal and mcp joint.

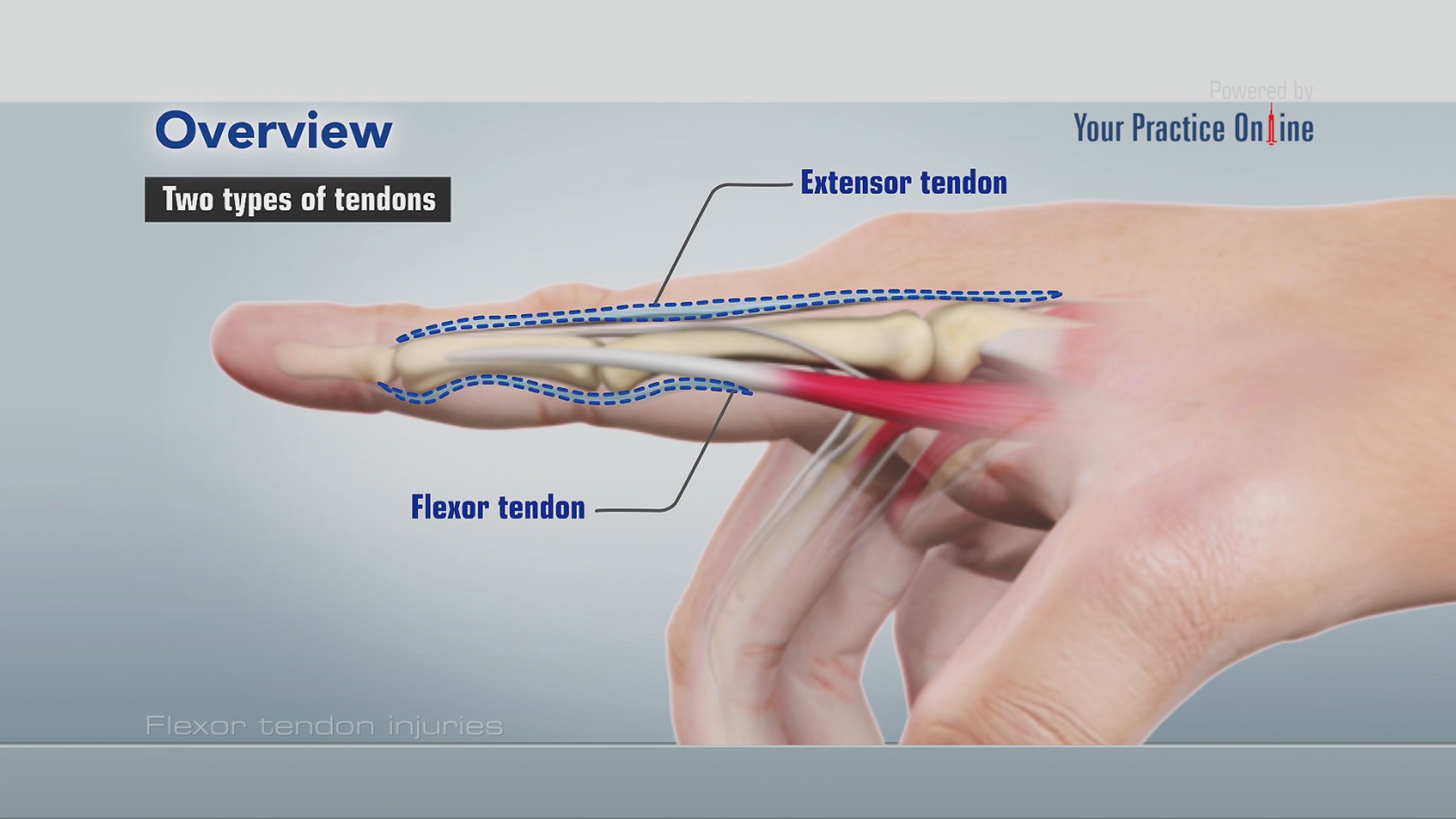
Anatomy of the index finger. Each finger has three phalanges the distal middle and proximal. The index finger is composed of three bones. And fingers move by the pull of forearm muscles on the tendons.
There are no muscles in the fingers. The distal phalanx intermediate phalanx and proximal phalanx. It is also called the index finger or the forefinger.
The index middle ring and fifth digits have proximal middle and distal phalanges and three hinged joints. Tendons connect muscles to bones. The thumb has two.
The index finger has three phalanges. The median nerve innervates the fingers skin. The index finger does not contain any muscles but is controlled by muscles in the hand by attachments of tendons to the bones.
The phalanges singular phalanx the 14 narrow bones that make up the fingers of each hand. Ligaments connect finger bones and help keep them in place. The extensor indicis extends the index finger while the palmar interosseus adducts it.
Fingers are constructed of ligaments strong supportive tissue connecting bone to bone tendons attachment tissue from muscle to bone and three phalanges bones. Picture of finger anatomy. Oxygenated blood arrives at the finger through the common palmar artery which extends off of the palmar arch connecting the ulnar and radial arteries.
The thumb has two of each. This finger often possesses the largest amount of sensitivity and greatest dexterity of any of the fingers. The little finger and index finger both have an extra muscle.
Each finger has 3 phalanges bones and 3 hinged joints. Finger movement is controlled by muscles in the forearms that pull on finger tendons. Basic anatomy of the finger.
Fingers have a complex anatomy. Each finger has three phalanges the distal middle and proximal. Anatomy of the fingers the human finger is mainly a bony structure with multiple joints giving it strength and flexibility.
A digit includes the hand bones but these bones are not separated into individual appendages like a finger.
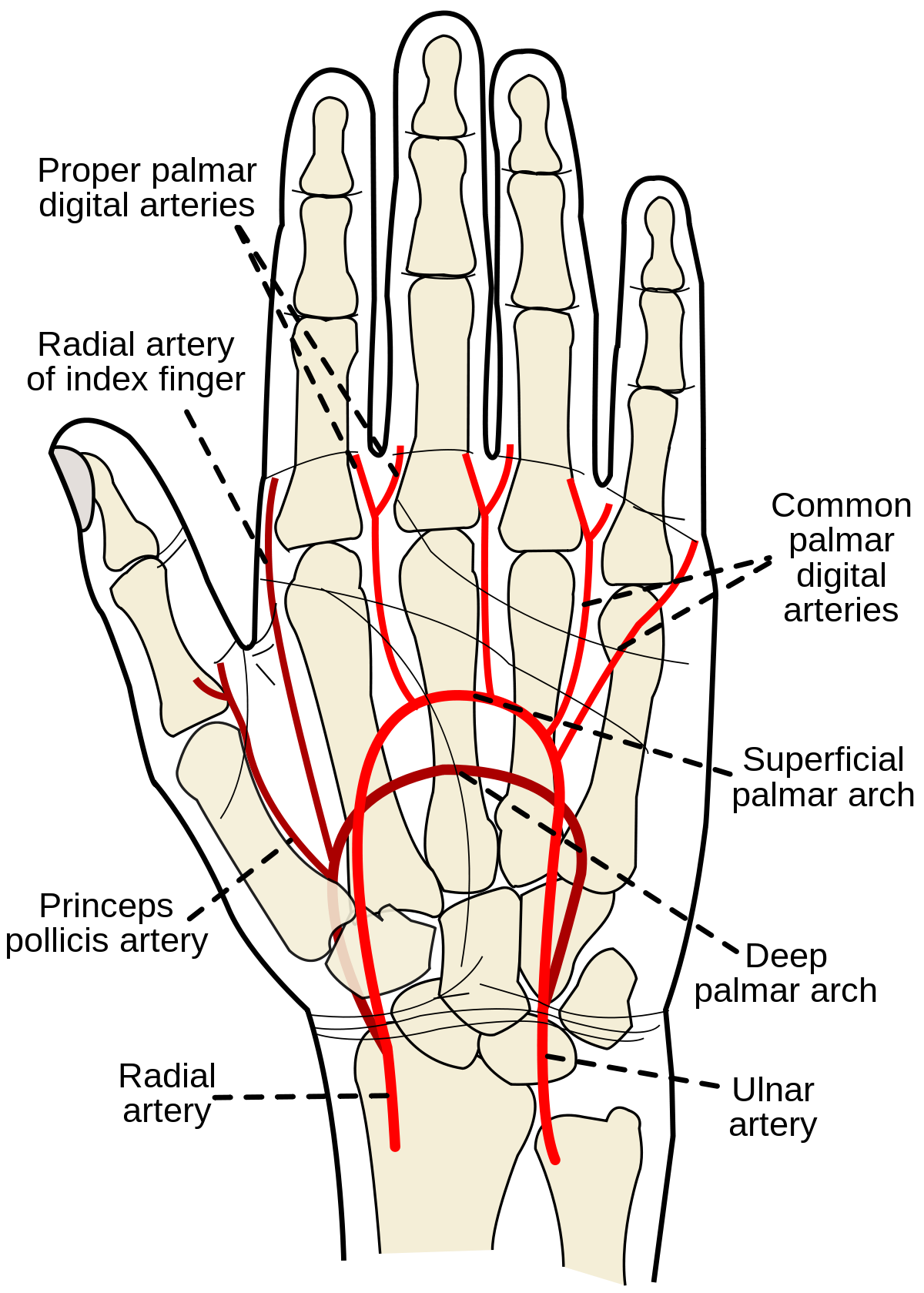 Radial Artery Of Index Finger Wikipedia
Radial Artery Of Index Finger Wikipedia
 Jpma Journal Of Pakistan Medical Association
Jpma Journal Of Pakistan Medical Association
 Modern Human Thumb And Index Finger Right Hand During Pad
Modern Human Thumb And Index Finger Right Hand During Pad
 A Arterial Anatomy At The Fingertip B Dorsal Venous
A Arterial Anatomy At The Fingertip B Dorsal Venous
 Related Image Hand Anatomy Anatomy Illustration
Related Image Hand Anatomy Anatomy Illustration
 The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Human Anatomy
The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Human Anatomy
 How The 5 Fingers Got Their Names Mental Floss
How The 5 Fingers Got Their Names Mental Floss
 Illustration Picture Of Hand Structures Finger Anatomy
Illustration Picture Of Hand Structures Finger Anatomy
Trigger Finger Trigger Thumb Orthoinfo Aaos
Hand Surface Anatomy Language Of Hand And Arm Surgery Series
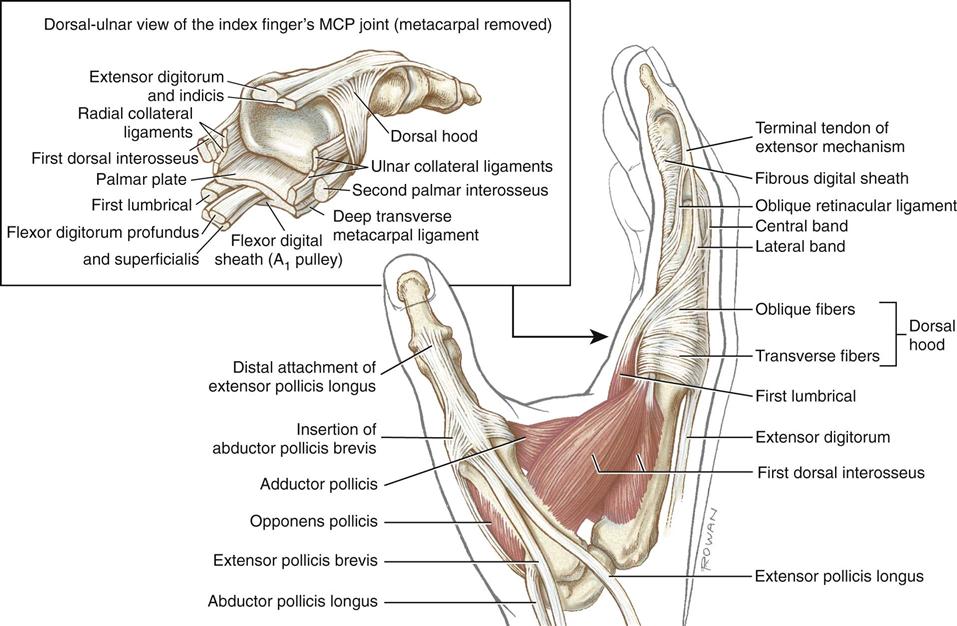 Forearm Wrist And Hand Clinical Gate
Forearm Wrist And Hand Clinical Gate
Hand Anatomy Midwest Bone Joint Institute Elgin Illinois
 Index Finger Anatomy Chiropractic Warwick Synovial Fluid
Index Finger Anatomy Chiropractic Warwick Synovial Fluid
 Ucsd S Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine
Ucsd S Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine
 Surface Anatomy Hand Surgery Source
Surface Anatomy Hand Surgery Source
 Proper Palmar Digital Nerves Of Median Nerve Wikipedia
Proper Palmar Digital Nerves Of Median Nerve Wikipedia
 Tactilus Compression Force Sensing Resistor Fsr Force
Tactilus Compression Force Sensing Resistor Fsr Force
 How To Avoid Sore Hands From Mountain Biking Total
How To Avoid Sore Hands From Mountain Biking Total
 Outstretched Index Finger Pointing To Something Illustration
Outstretched Index Finger Pointing To Something Illustration
 Gifts Delight Laminated 36x24 Inches Poster Hand Middle Finger X Ray Radiation Finger Gesture Anatomy Bone Finger Thumb Index Finger Pinkie Finger
Gifts Delight Laminated 36x24 Inches Poster Hand Middle Finger X Ray Radiation Finger Gesture Anatomy Bone Finger Thumb Index Finger Pinkie Finger
Muscles Of Hands Human Anatomy
 The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy
The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy
 How To Avoid Sore Hands From Mountain Biking Total
How To Avoid Sore Hands From Mountain Biking Total
 Injuries Of The Left Index Finger With Surgical Repairs
Injuries Of The Left Index Finger With Surgical Repairs
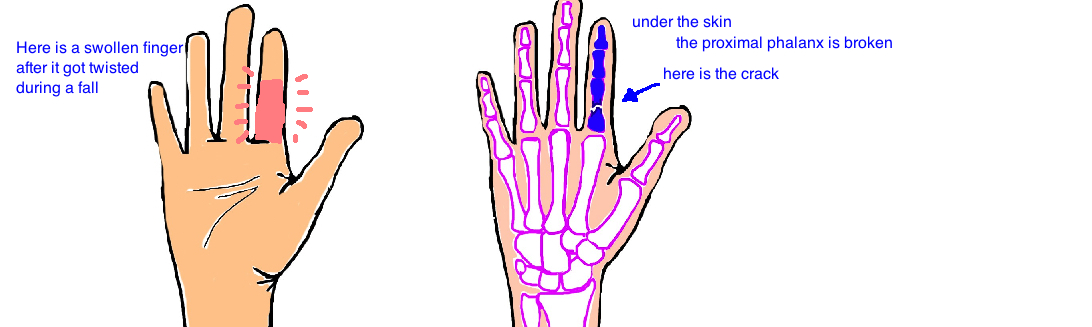
 Right Index Finger Fractures Medical Illustration Human
Right Index Finger Fractures Medical Illustration Human
 What Peculiarities Of The Anatomy Of Hands Should Be Taken
What Peculiarities Of The Anatomy Of Hands Should Be Taken

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar