Pivot joints are formed by a central bony pivot surrounded by an osteo ligamentous. Synovial joints have a rich supply from articular nerves.
The articular surface of the movable joint and has a smooth lining called cartilage.

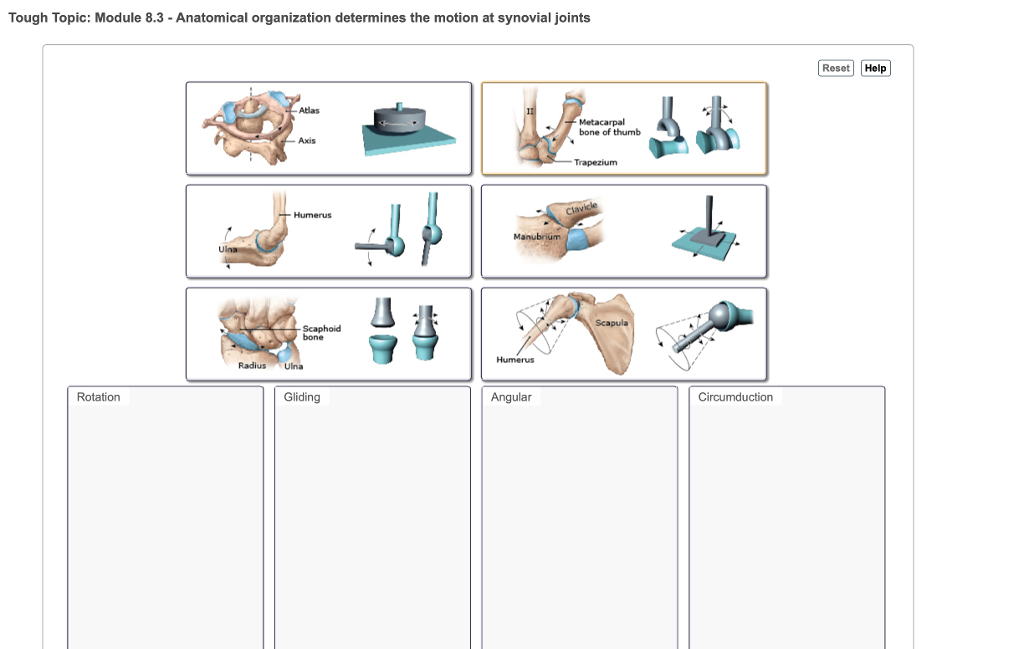
Anatomy of synovial joint. The six types of synovial joints are pivot hinge condyloid saddle plane and ball and socket joints figure 943. Smooth cartilage allows friction less movement and this smoothness is further enhanced by body lubricants. Accessory structures of a synovial joint.
Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body figure 1. Synovial joints are subdivided based on the shapes of the articulating surfaces of the bones that form each joint. The six types of synovial joints are pivot hinge condyloid saddle plane and ball and socket joints.
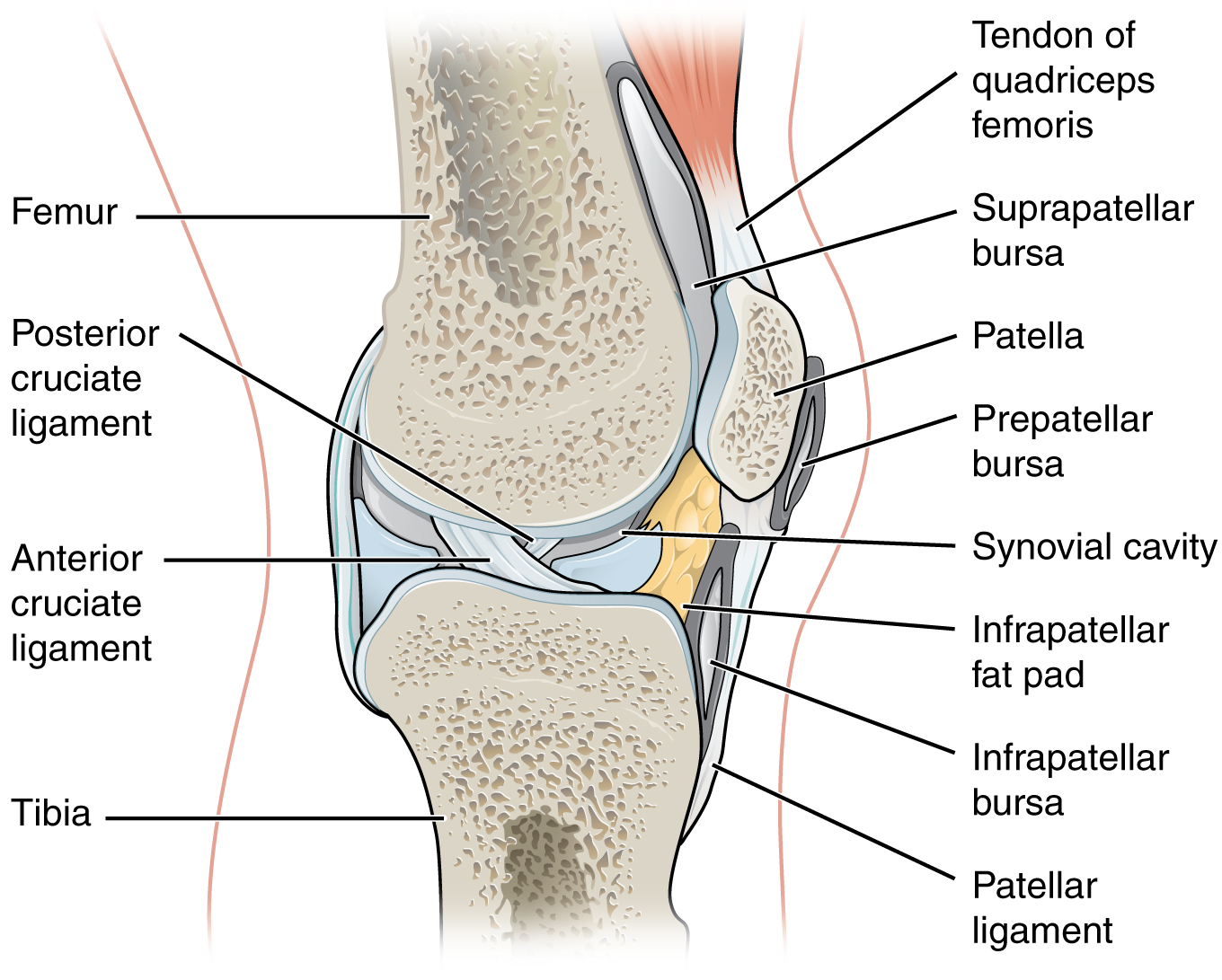
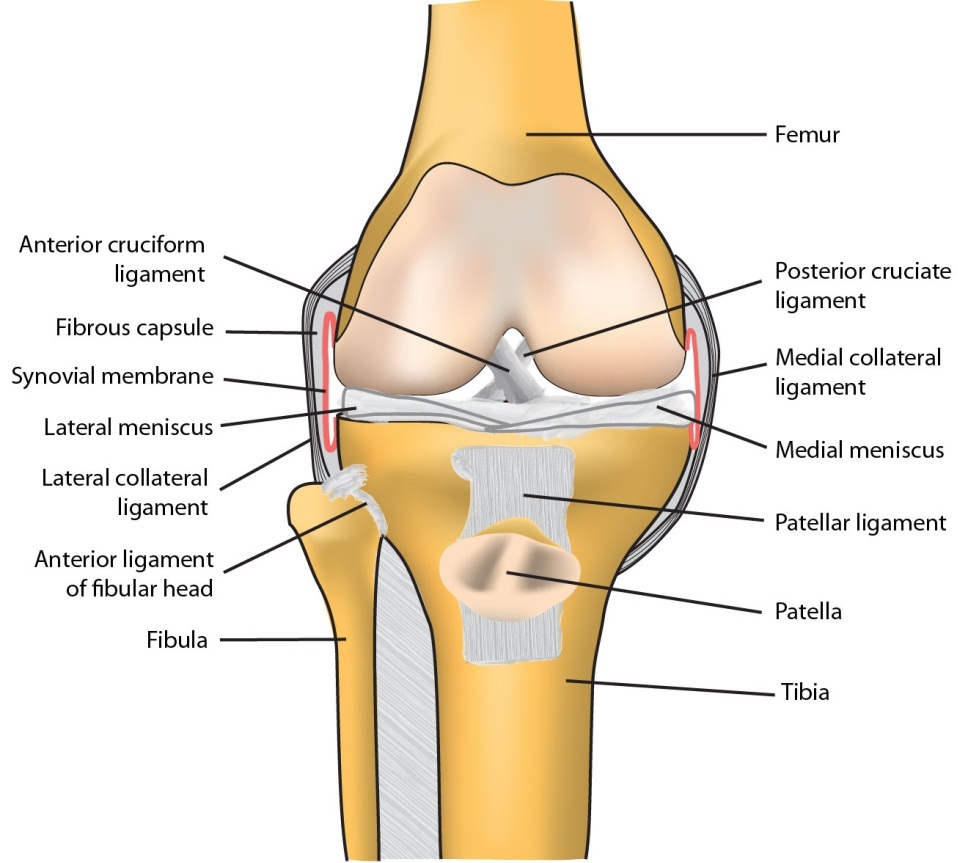
Synovial joint not directly joined the bones have a synovial cavity and are united by. Structures of a synovial joint key structures of a synovial joint. There are four structural classifications of joints.
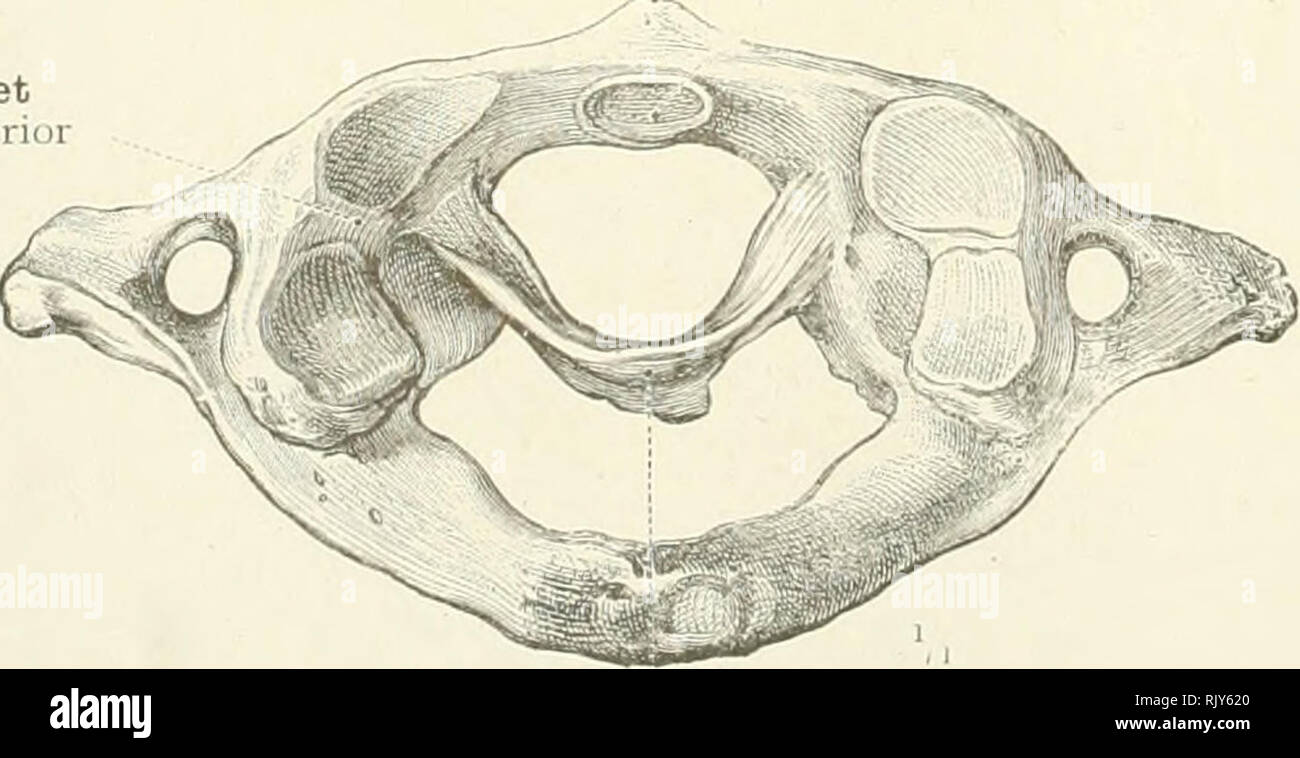
In these joints the articular surfaces are pulley shaped. A pivot joints allow for rotation around an axis such as between the first and second cervical vertebrae which allows for side to side rotation of the head. In addition to being held together by the intervertebral discs adjacent vertebrae also articulate with each other at synovial joints formed between the superior and inferior articular processes called zygapophysial joints facet joints see figure 93.
The six types of synovial joints allow the body to move in a variety of ways. Facet joint. Types of synovial joints.
The accessory ligaments are separate ligaments or parts. Bursas are found between structures that glide upon each other and all motion at diarthroses entails some gliding the amount varying from one joint to another. Fibrous joint joined by dense regular connective tissue that is rich in collagen fibers.
These are plane joints that provide for only limited motions between the vertebrae. The articular surfaces of plane synovial joints are more or less plane. Cartilaginous joint joined by cartilage.
Synovial joints are subdivided based on the shapes of the articulating surfaces of the bones that form each joint. A key structural characteristic for a synovial joint that is not seen at fibrous or cartilaginous joints is the presence of a joint cavity. The bursal fluid exuded by the.
Our movable joints are also lubricated and filled with fluid known as synovial fluid and this is why we call this joint as synovial joint. This fluid filled space is the site at which the articulating surfaces of the bones contact each other. The three main features of a synovial joint are.
Types of synovial joints. Structure and elements of synovial joints the synovial bursas are closed thin walled sacs lined with synovial membrane. B the hinge joint of the elbow works like a door hinge.

 Synovial Joint Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Synovial Joint Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Anatomy Synovial Joint Diagram Diagram Quizlet
Anatomy Synovial Joint Diagram Diagram Quizlet
 Solved Tough Topic Module 8 3 Anatomical Organization D
Solved Tough Topic Module 8 3 Anatomical Organization D
 9 4 Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology
9 4 Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology
Anatomy Of Selected Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology
 Finger Joint Anatomy Google Search Synovial Joint Body
Finger Joint Anatomy Google Search Synovial Joint Body
Synovial Trevor S Anatomy Page
 An Atlas Of Human Anatomy For Students And Physicians
An Atlas Of Human Anatomy For Students And Physicians
 The Six Types Of Synovial Joints Examples Definition
The Six Types Of Synovial Joints Examples Definition
 Anatomy Review Synovial Joints Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy Review Synovial Joints Flashcards Quizlet
Human Being Anatomy Skeleton Types Of Synovial Joints
 Articulations 4 Synovial Joint Anatomy
Articulations 4 Synovial Joint Anatomy
 General Anatomy 11 Types Of Synovial Joints By Dr Sameh Ghazy
General Anatomy 11 Types Of Synovial Joints By Dr Sameh Ghazy
 Structural And Functional Features Of Major Synovial Joints
Structural And Functional Features Of Major Synovial Joints
 The Six Types Of Synovial Joints Examples Definition
The Six Types Of Synovial Joints Examples Definition
 Anatomy Of Selected Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology
Anatomy Of Selected Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology
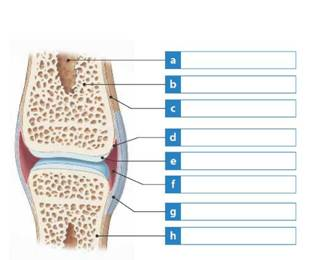 Solved Label The Structures In The Synovial Joint Figure At
Solved Label The Structures In The Synovial Joint Figure At
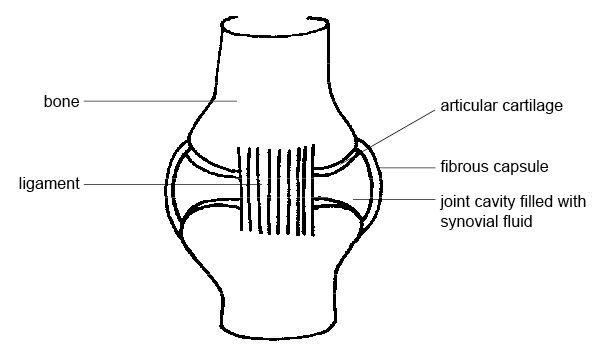 File Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Synovial Joint Jpg
File Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Synovial Joint Jpg
Equine Joint Anatomy Luitpold Animal Health
 Synovial Fluid Anatomy Britannica
Synovial Fluid Anatomy Britannica
 Anatomy Joint Children S Wisconsin
Anatomy Joint Children S Wisconsin


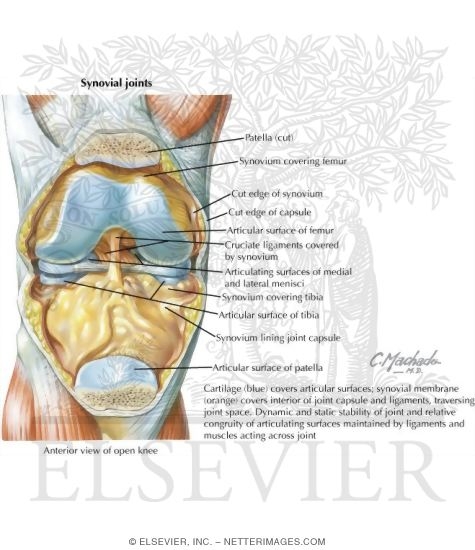
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar