Fractures of the neck of femur are very common injuries which mainly occur in elderly females with osteoporotic bones. Obq11233 a 48 year old active female runner underwent percutaneous screw fixation of a minimally displaced femoral neck fracture six months ago.
 Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis Orthoinfo Aaos
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis Orthoinfo Aaos
This structure supports the head of the femur bone and its insertion into the hip.
Femoral neck anatomy. Femoral neck fractures are a subset of proximal femoral fractures. Abstract paediatric femoral neck fractures are uncommon injuries and are usually caused by high energy trauma. Surgical options can vary based on age delbet classification and displacement of the fracture.
At the ends of the femur are areas of compact bone which is solid and does not contain marrow. Inside the body of the femur is the medullary cavity which contains bone marrow. The femoral aspect of the hip is made up of the femoral head with its articular cartilage and the femoral neck which connects the head to the shaft in the region of the lesser and greater.
Surrounding the compact bone is spongy bone which has lots of small cavities dispersed throughout it. A fractured neck of femur is classified as either intracapsular or extracapsular. The femoral neck is the weakest part of the femur.
Since disruption of blood supply to the femoral head is dependent on the type of fracture and causes significant morbidity diagnosis and classification of these fractures is important. The neck and head of the femur contain spongy bone. The classical clinical finding is that of an externally rotated shortened leg.
The hip joint capsule inserts along the intertrochanteric line. The femur neck femoral neck or neck of the femur is a flattened pyramidal process of bone connecting the femoral head with the femoral shaft and forming with the latter a wide angle opening medialward. Low energy trauma can result in pathologic neck fractures and stress fractures of the neck due to repetitive activity.
There were no immediate post operative complications and she was progressed to full weight bearing three months after surgical fixation. A fracture distal to this line is therefore extracapsular whereas a fracture proximal to this is intracapsular. The femoral neck the femoral neck usually sits at a 120 135 degree angle with some variation.
A fracture of this area is known as a hip fracture and happens during aging.
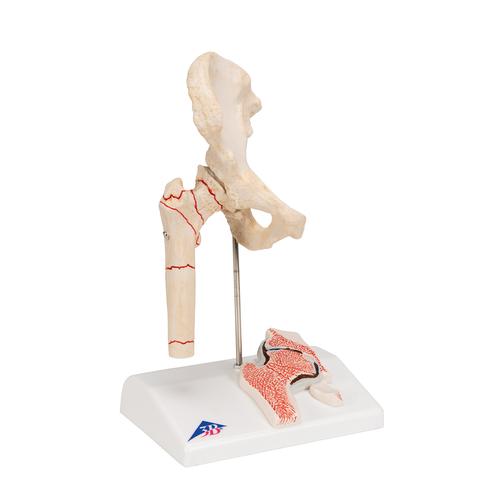 Human Femoral Fracture Hip Osteoarthritis Model 3b Smart Anatomy
Human Femoral Fracture Hip Osteoarthritis Model 3b Smart Anatomy
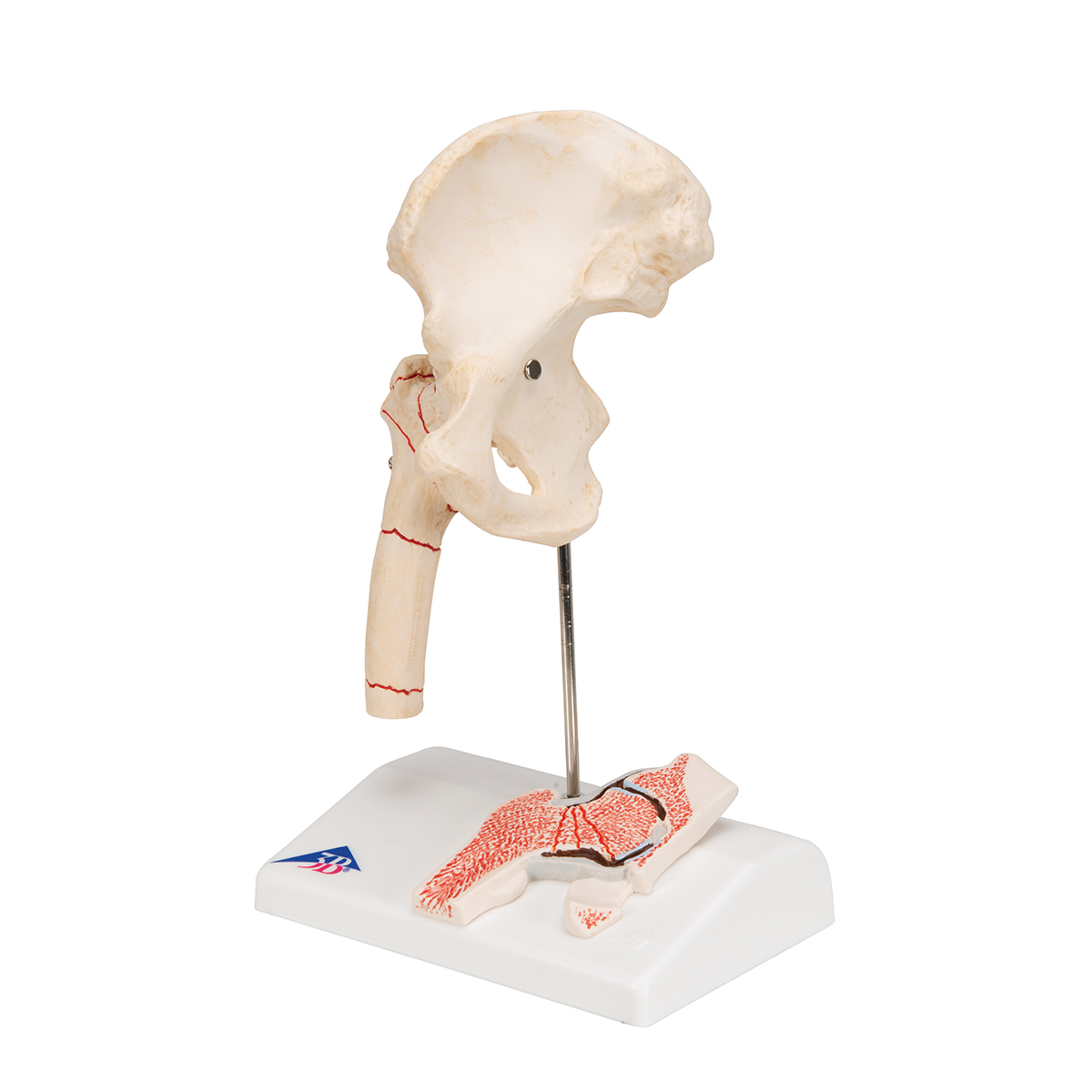
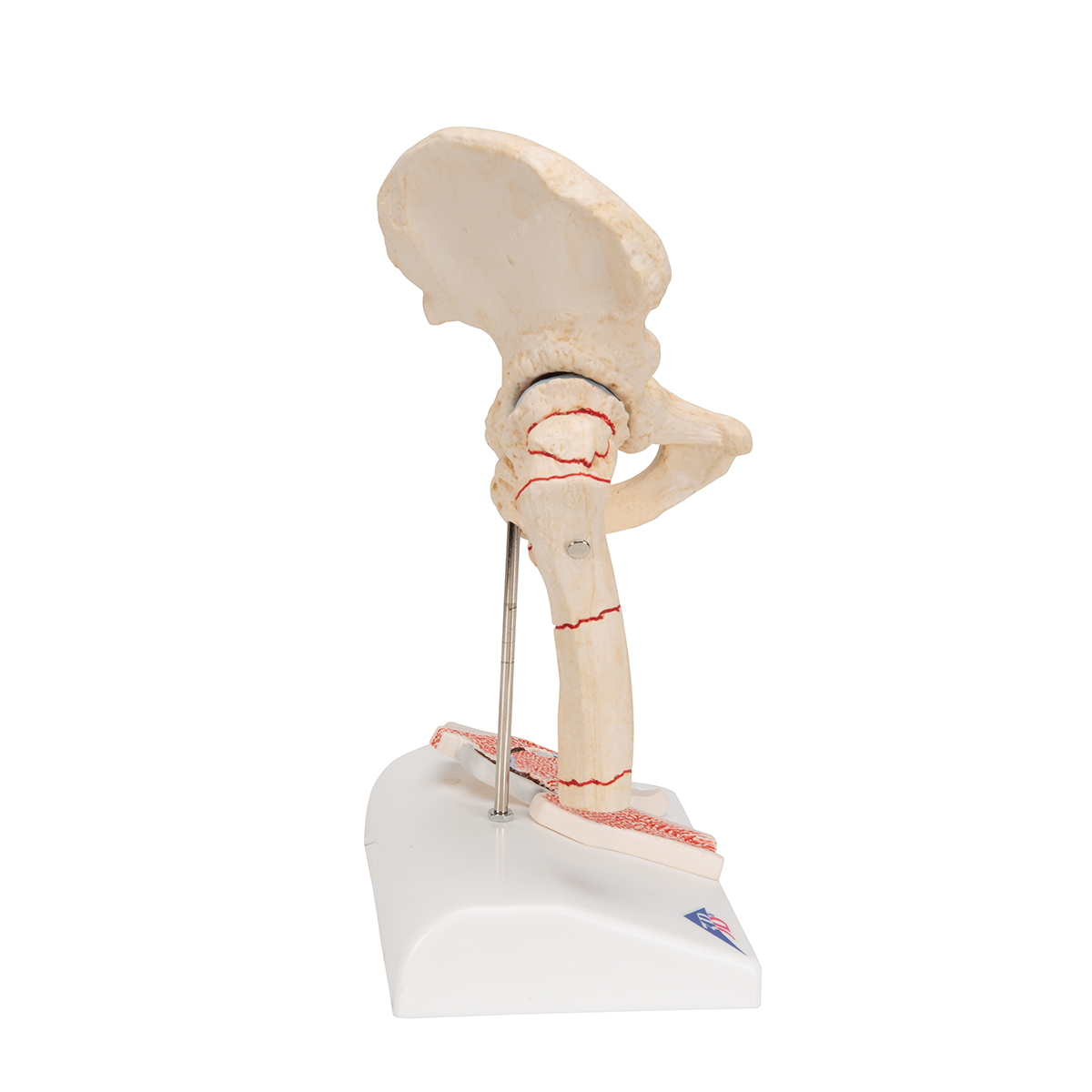 Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
 Two Little Runners A Diagnosis Femoral Neck Stress Reaction
Two Little Runners A Diagnosis Femoral Neck Stress Reaction
Transient Osteoporosis Of The Hip Orthoinfo Aaos
 Hip Fracture Anatomy Causes And Consequences Intechopen
Hip Fracture Anatomy Causes And Consequences Intechopen
 Femoral Neck Axis And Hip Joint Axis A Schematic
Femoral Neck Axis And Hip Joint Axis A Schematic
 Obturator Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator
Obturator Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator
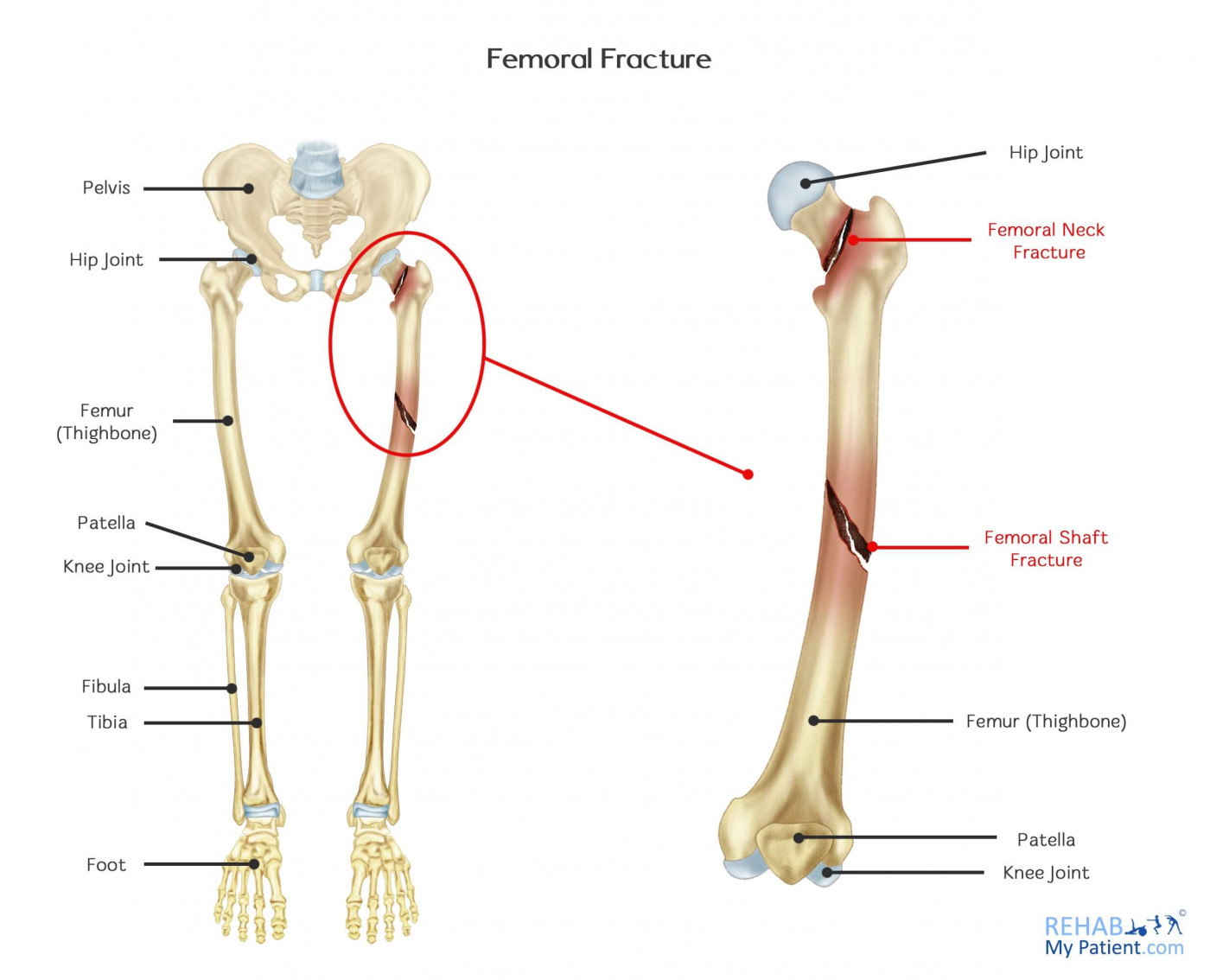 Femoral Fracture Rehab My Patient
Femoral Fracture Rehab My Patient
 Femur Neck Fractures Classification Hip Fracture Medical
Femur Neck Fractures Classification Hip Fracture Medical
Anatomical Context Of Focal Thinning In Women With Femoral
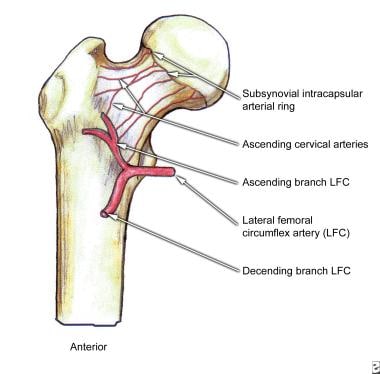 Femoral Neck Fracture Background Epidemiology Functional
Femoral Neck Fracture Background Epidemiology Functional
 The Hip Practical Office Orthopedics Accessmedicine
The Hip Practical Office Orthopedics Accessmedicine
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11238/anatomy-hip-joint_english.jpg) Femur Bone Anatomy Proximal Distal And Shaft Kenhub
Femur Bone Anatomy Proximal Distal And Shaft Kenhub
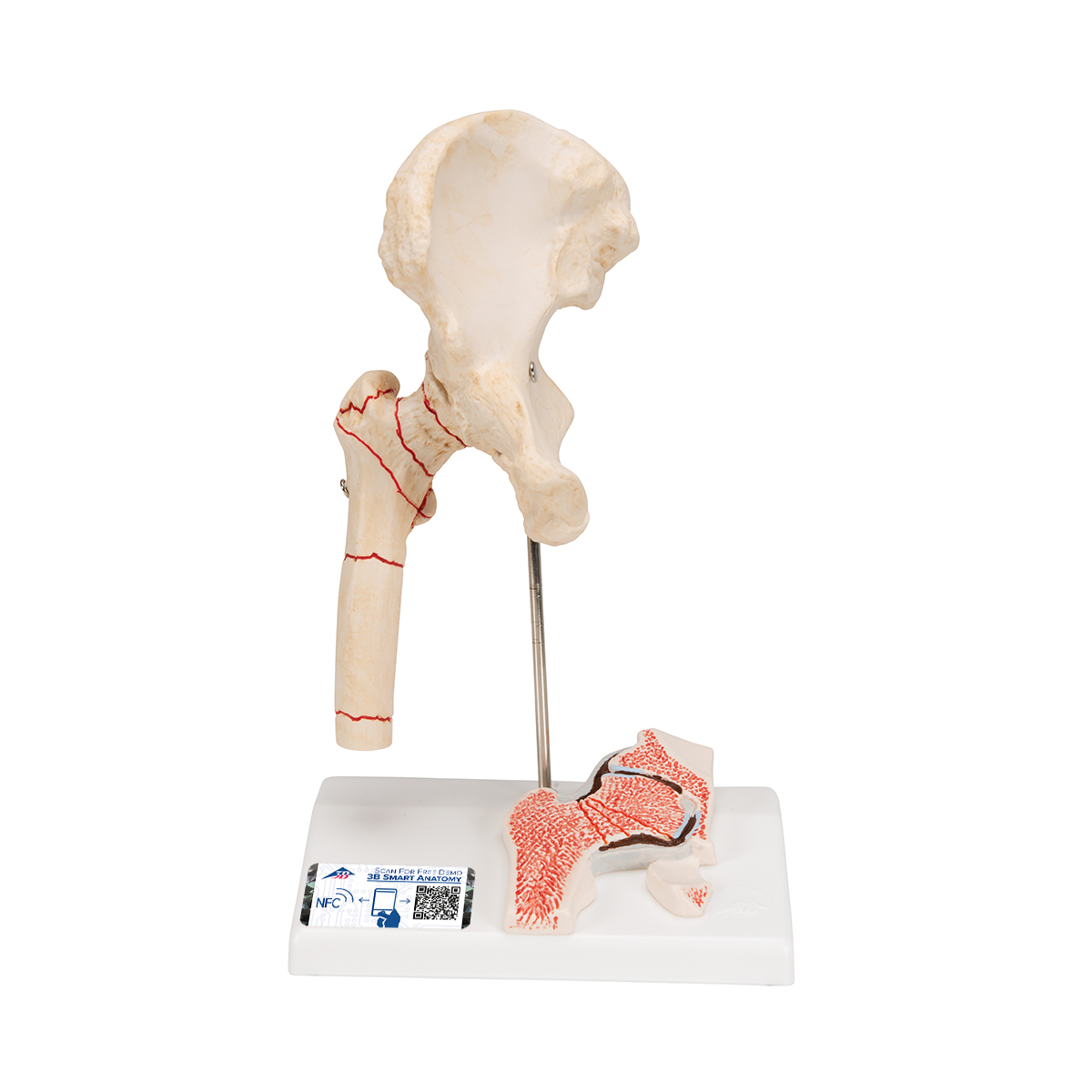 Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
 Femoral Neck Fracture Hip Fracture Physioadvisor
Femoral Neck Fracture Hip Fracture Physioadvisor

 Blood Supply Of Femoral Head Made Easy Neet Pg Femur Anatomy The Young Orthopod
Blood Supply Of Femoral Head Made Easy Neet Pg Femur Anatomy The Young Orthopod
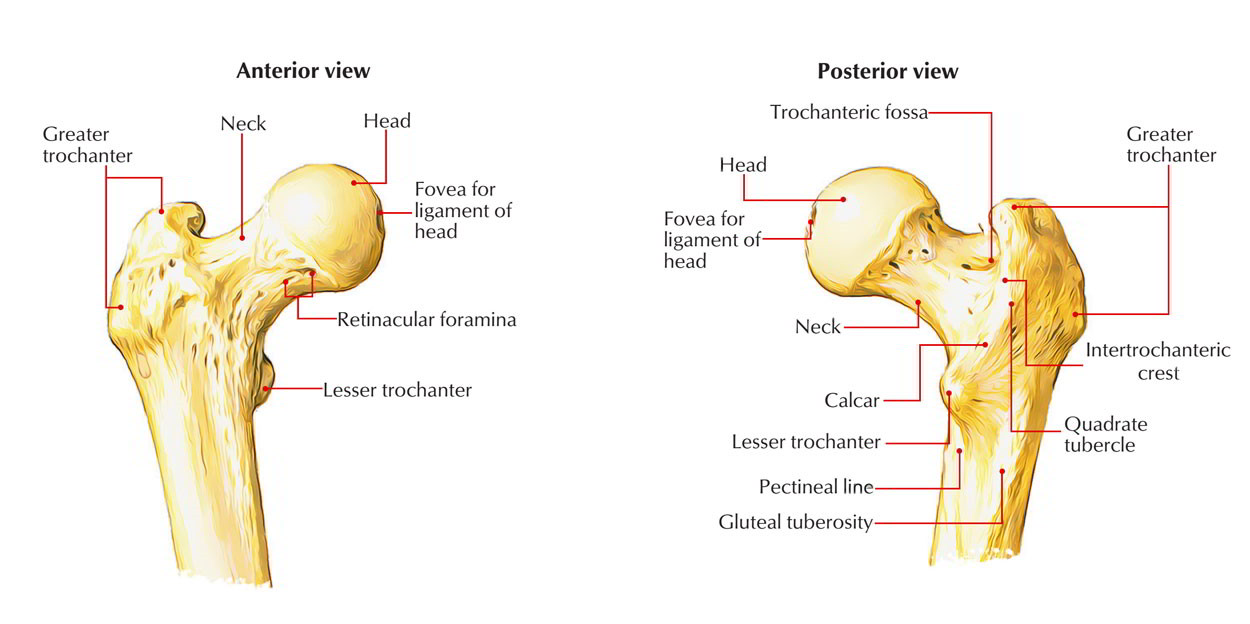 Easy Notes On Femur Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
Easy Notes On Femur Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
 Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
 Proximal Femur Approach Lateral Approach Femoral Neck
Proximal Femur Approach Lateral Approach Femoral Neck
 Legg Calve Perthes Disease Vca Animal Hospital
Legg Calve Perthes Disease Vca Animal Hospital
 Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
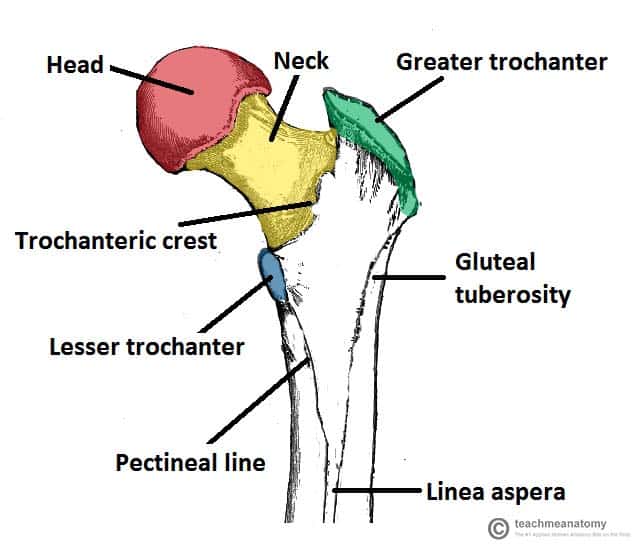 The Femur Proximal Distal Shaft Teachmeanatomy
The Femur Proximal Distal Shaft Teachmeanatomy
Hip Resurfacing Orthoinfo Aaos








Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar