The body and tail of the caudate nucleus follow the curve of the inferior horn of the lateral venetricle. In simple terms the basal ganglia provide a feedback mechanism to the cerebral cortex.
 Figure 1 From The Functional Anatomy Of Basal Ganglia
Figure 1 From The Functional Anatomy Of Basal Ganglia
Thalamus subthalamic nuclei red nucleus and substantia nigra liululliimportant in coordinating movement.
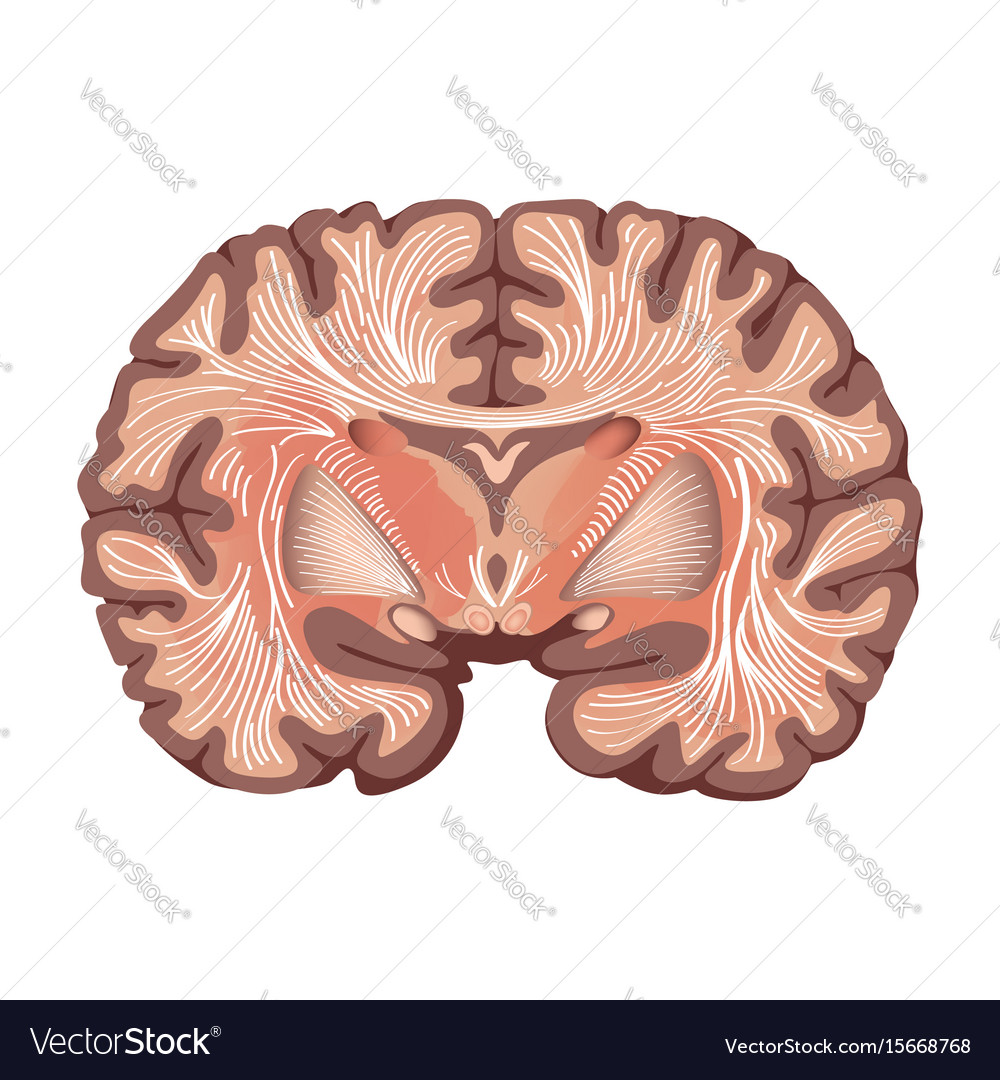
Anatomy of basal ganglia. The basal ganglia are a group of neurons also called nuclei located deep within the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. The basal ganglia consist of the corpus striatum a major group of basal ganglia nuclei and related nuclei. The term basal ganglia in the strictest sense refers to nuclei embedded deep in the brain hemispheres striatum or caudate putamen and globus pallidus whereas related nuclei consist of structures located in the diencephalon subthalamic nucleus mesencephalon substantia nigra and pons pedunculopontine nucleus.
They are called the caudate nucleus putamen globus pallidus subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra the last two are only functionally connected and related to this system. The basal ganglia nuclei of the basal ganglia. Anatomically the basal ganglia consist of parallel complementary pathways.
The basal ganglia is composed of the following grey nuclei. The anatomy of the basal ganglia is complex since it is spread throughout. Basal ganglia ullithe basal ganglia is a collection of gray matter in the cerebrum including the corpus striatum amygdala liululliand claustrum.
Liulullihas important connections with other regions of the brain particularly. Substantia nigra within the midbrain. Basal ganglia anatomy and connections.
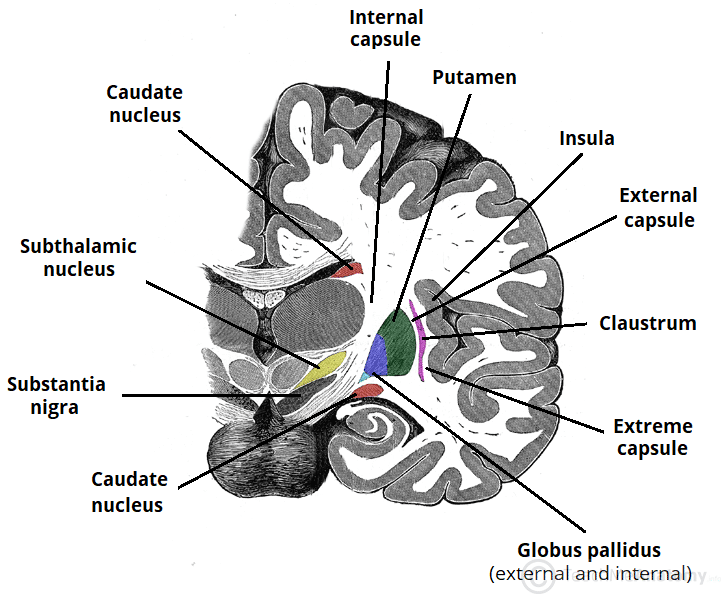
Basal ganglia anatomy as previously mentioned basal ganglia are fundamental brain structures that assemble different gray matter nuclei stored in the deepest regions of the brain. The caudate nucleus is largely separated from the lentiform nucleus by the internal capsule with the notable exception of prominent bridges through the anterior limb of the internal capsule. In order to execute purposeful movements a small number.
Anatomically speaking this brain structure has four parts or distinct nuclei. The majority of basal ganglia nuclei have projection neurons. Amygdaloid nuclear complex or amygdala.
The basal ganglia are a collection of subcortical structures consisting of several connected nuclei located in the brain.
 Basal Ganglia Clinical Anatomy Physiology
Basal Ganglia Clinical Anatomy Physiology
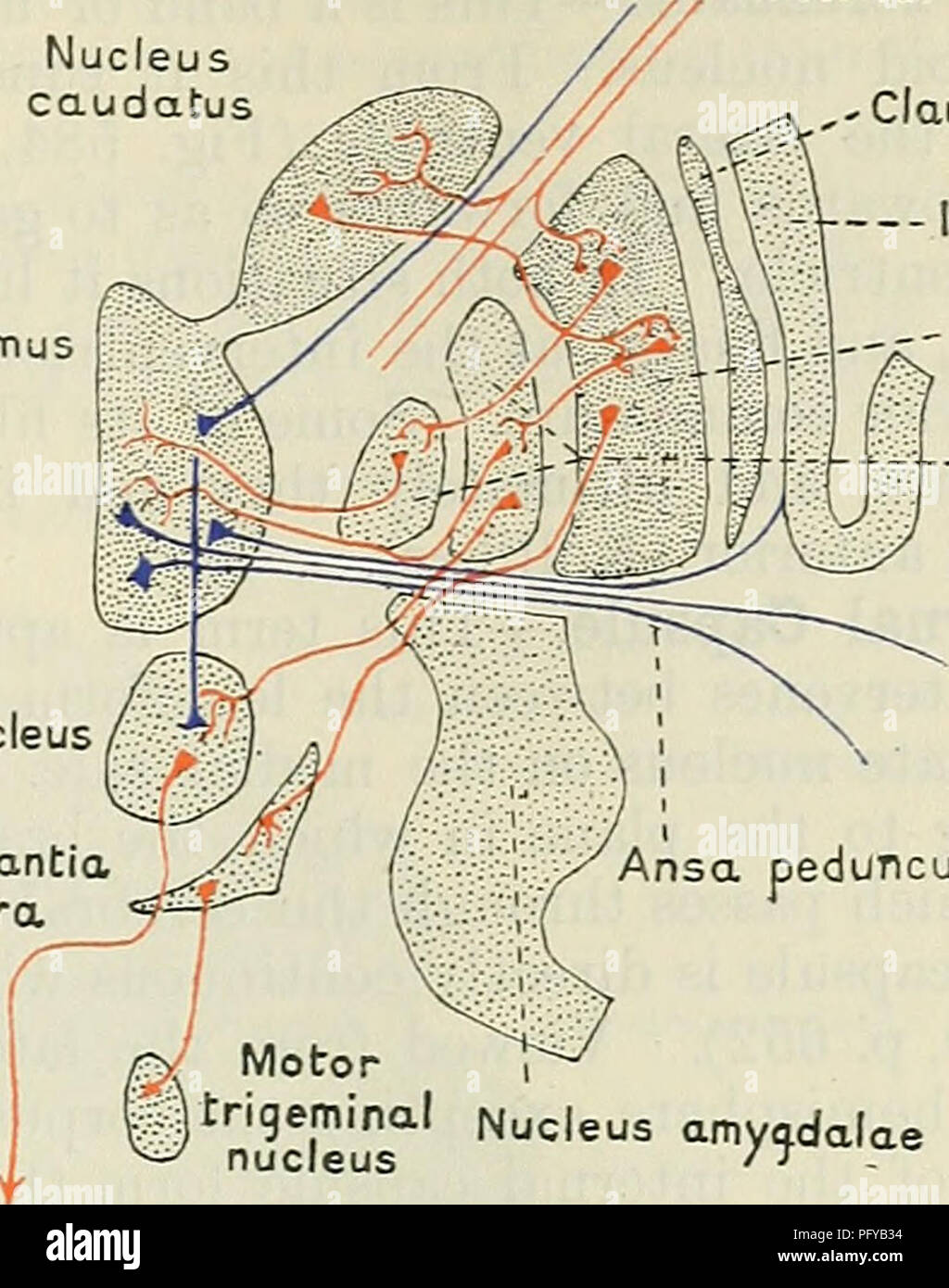 Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Basal Ganglia Of
Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Basal Ganglia Of
 Basal Ganglia Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
Basal Ganglia Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
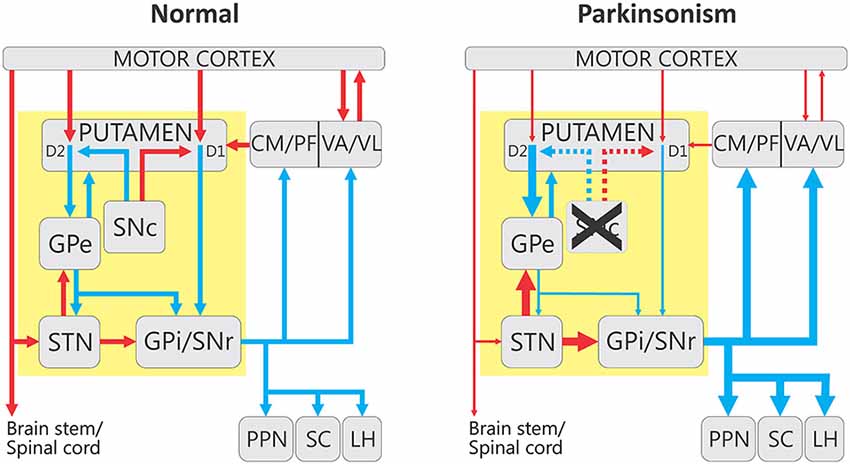 Frontiers Alterations In Neuronal Activity In Basal
Frontiers Alterations In Neuronal Activity In Basal
Basal Ganglia Anatomy Pharmacology 2 15 Bb Flashcards
 Simplified Anatomy Of The Basal Ganglia
Simplified Anatomy Of The Basal Ganglia
 The Basal Ganglia Direct Indirect Nuclei Teachmeanatomy
The Basal Ganglia Direct Indirect Nuclei Teachmeanatomy
 Functional Anatomy Of The Basal Ganglia Download
Functional Anatomy Of The Basal Ganglia Download
 An Introduction To The Basal Ganglia Fewer Lacunae
An Introduction To The Basal Ganglia Fewer Lacunae
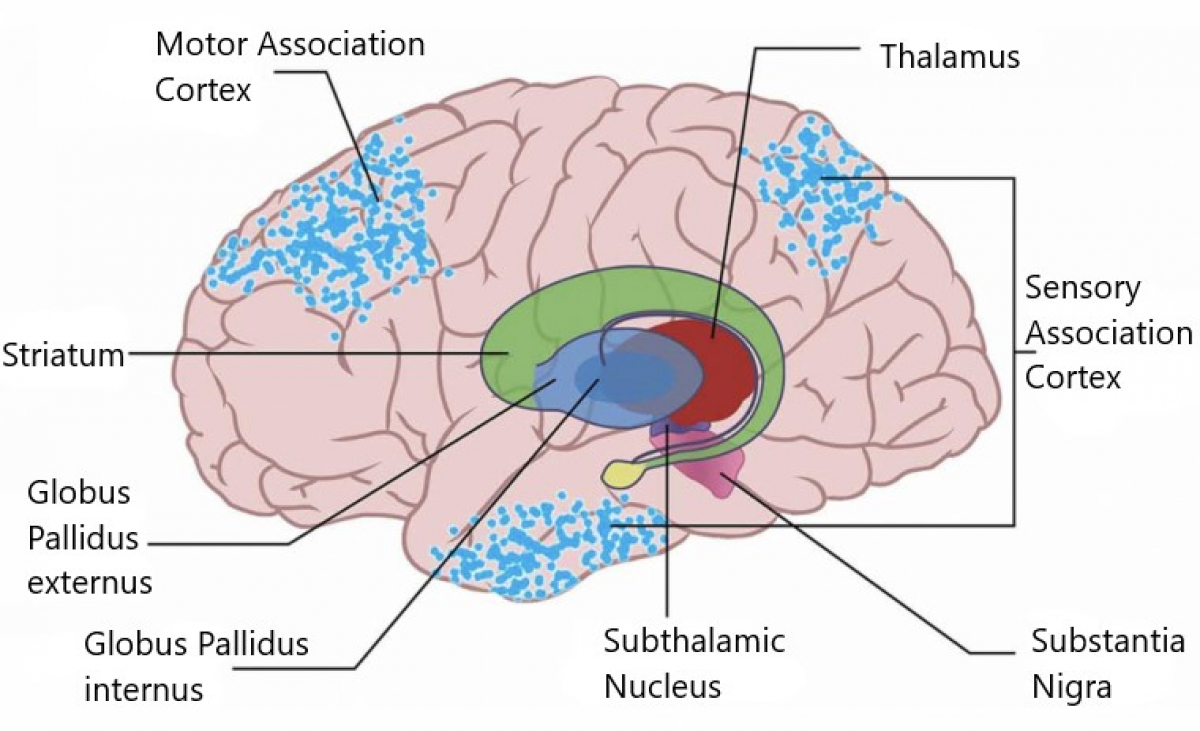 Basal Ganglia A Definition Anatomy And Function
Basal Ganglia A Definition Anatomy And Function
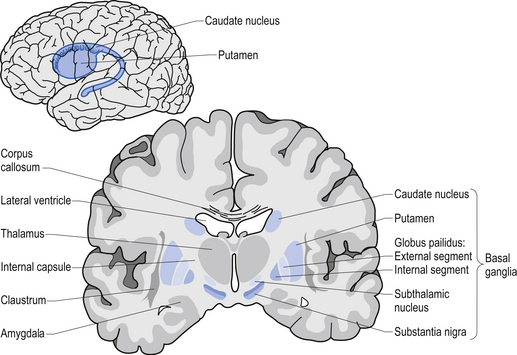 The Basal Ganglia Clinical Gate
The Basal Ganglia Clinical Gate
 Anatomy Of The Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia Is Located
Anatomy Of The Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia Is Located
 An Introduction To The Basal Ganglia Fewer Lacunae
An Introduction To The Basal Ganglia Fewer Lacunae
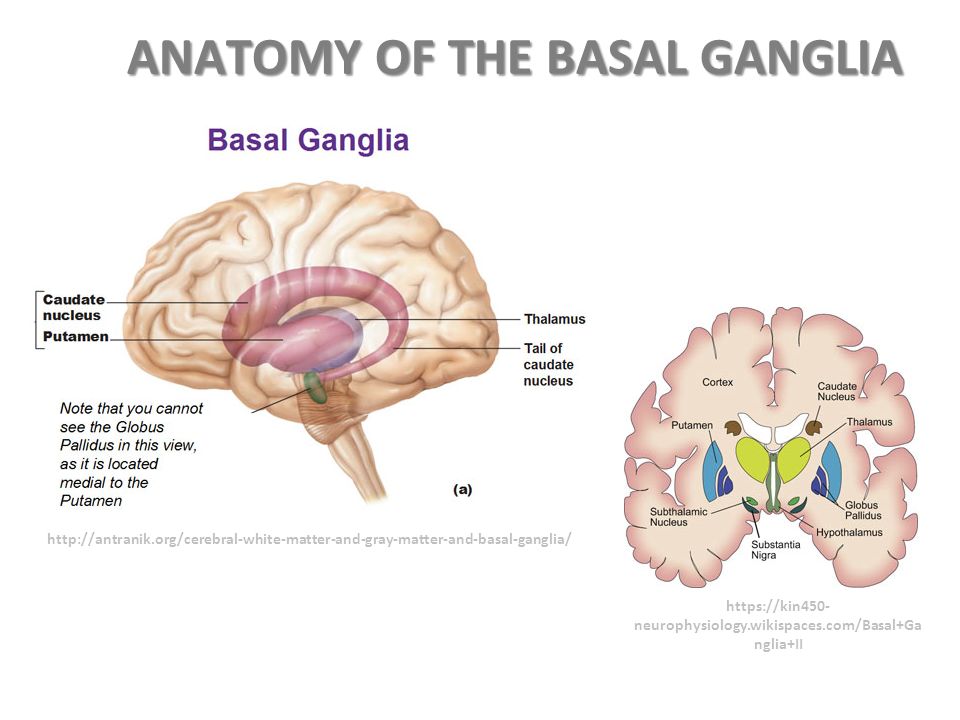 Control Circuits Integrate And Control The Activities Of The
Control Circuits Integrate And Control The Activities Of The
 The Basal Ganglia Purposegames
The Basal Ganglia Purposegames
The Basal Ganglia Motor Systems Part 1
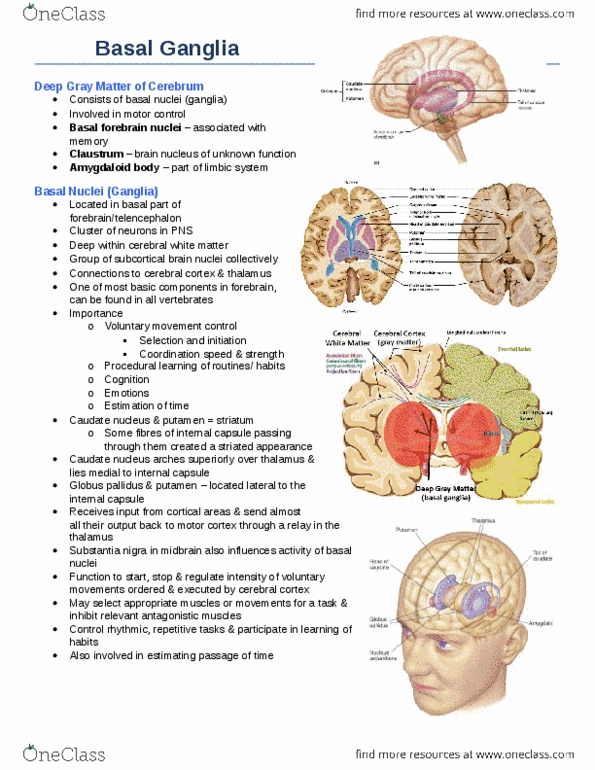 Anatomy And Cell Biology 3319 Chapter Notes Hard Palate Inferior Nasal Concha Alveolar Process
Anatomy And Cell Biology 3319 Chapter Notes Hard Palate Inferior Nasal Concha Alveolar Process
 Chapter 4 Abnormalities Of Movement And Posture Caused By
Chapter 4 Abnormalities Of Movement And Posture Caused By
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/basal_ganglia-57d71c383df78c5833761812.jpg) Basal Ganglia Function And Location
Basal Ganglia Function And Location
Components Of The Basal Ganglia
 Royalty Free Basal Ganglia Stock Images Photos Vectors
Royalty Free Basal Ganglia Stock Images Photos Vectors
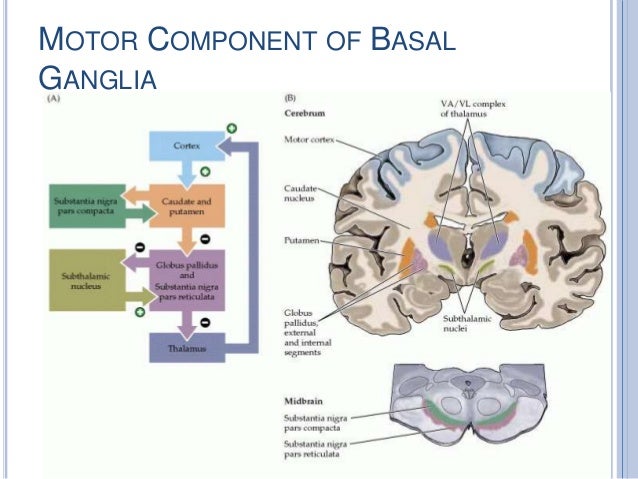 Basal Ganglia Clinical Anatomy Physiology
Basal Ganglia Clinical Anatomy Physiology
 Anatomy Basal Ganglia At Harvard University Studyblue
Anatomy Basal Ganglia At Harvard University Studyblue
 Basal Ganglia Nuclei Anatomy Qa
Basal Ganglia Nuclei Anatomy Qa
 File Anatomy Of The Basal Ganglia Jpg Wikimedia Commons
File Anatomy Of The Basal Ganglia Jpg Wikimedia Commons
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5201/GnV8DvekwRAaBUxqsV1tQ_Putamen_01.png.jpeg) Connections Of Basal Ganglia Anatomy Kenhub
Connections Of Basal Ganglia Anatomy Kenhub
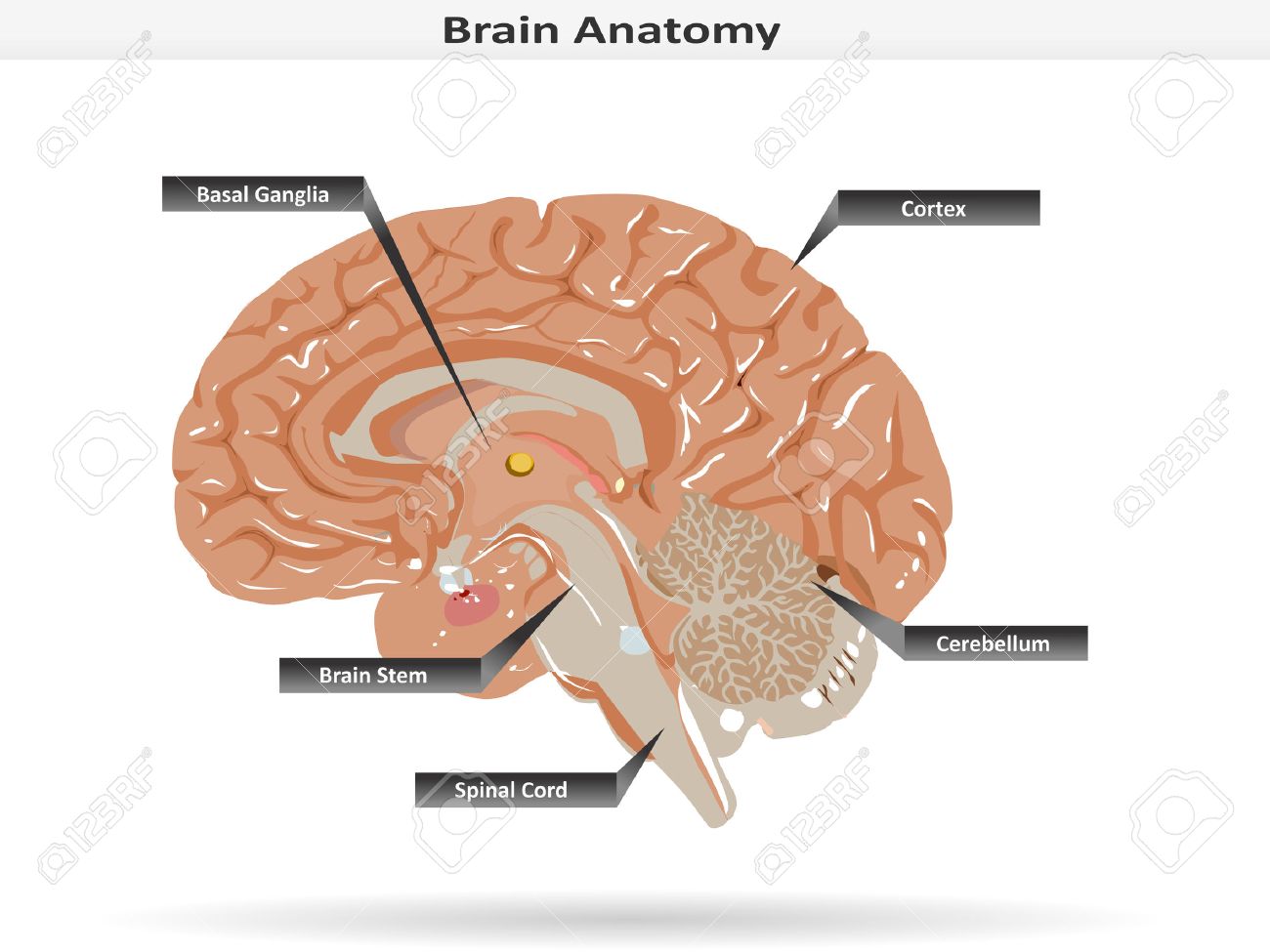 Brain Anatomy With Basal Ganglia Cortex Brain Stem Cerebellum
Brain Anatomy With Basal Ganglia Cortex Brain Stem Cerebellum
 Brain Anatomy Showing Basal Ganglia And Thalamic
Brain Anatomy Showing Basal Ganglia And Thalamic
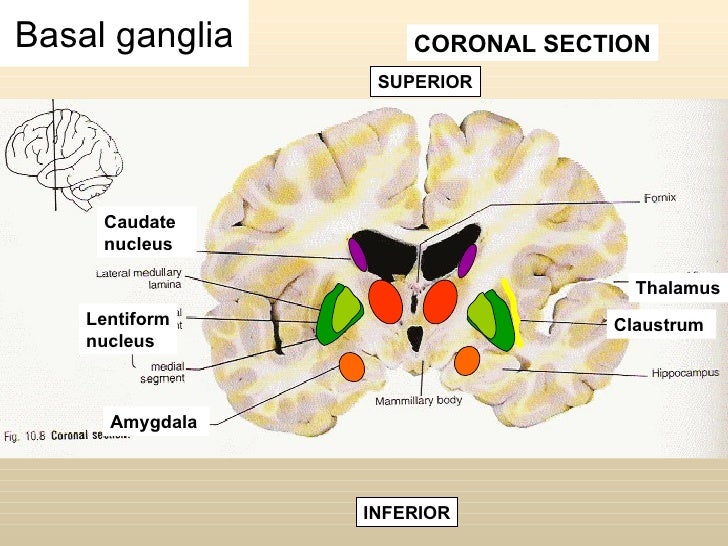

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar