The trachea transport air in and out of the lungs. Published on nov 25 2007 this video illustrates the anatomical differences between the esophagus which has no defined posterior structures and the trachea which has recognizable defined.
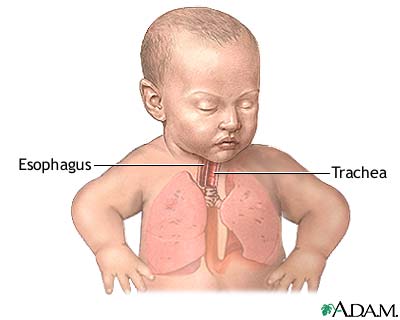 Tracheoesophageal Fistula Repair Series Normal Anatomy
Tracheoesophageal Fistula Repair Series Normal Anatomy
The trachea descends anterior to the esophagus enters the superior mediastinum and divides into right and left main bronchi.
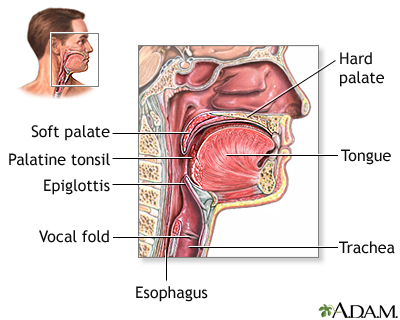
Trachea and esophagus anatomy. The trachea begins just under the larynx voice box and runs down. The esophagus is about 8 inches long and is lined by moist pink tissue called mucosa. The trachea is a median structure but near its lower end deviates slightly to the right resulting in the left main bronchus crossing anterior to the esophagus.
The esophagus runs behind. The trachea belongs to the respiratory system whereas the esophagus belongs to the digestive system. Its located just behind the trachea.
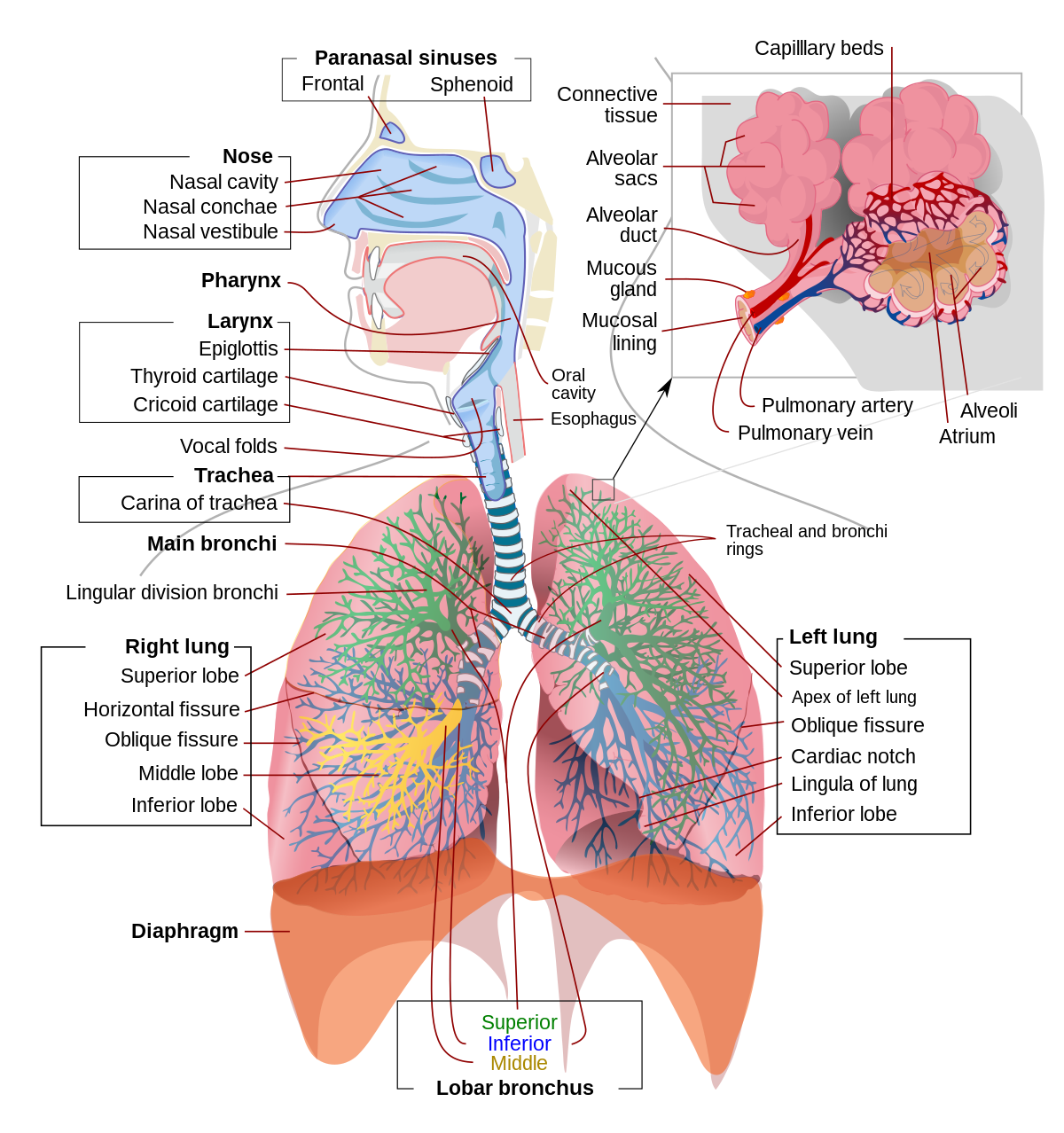
The trachea commonly known as the windpipe is a tube about 4 inches long and less than an inch in diameter in most people. The connective tissue beneath the tracheal epithelium contains lymphatic nodules mucous and serous glands and the tracheal cartilages. The trachea transports air while the esophagus transports food.
Trachea also known as the windpipe is a part of the respiratory system and it leads to lungs whereas esophagus also known as foodpipe is a part of the digestive system. The trachea lies behind the sternum breastbone and in front of the esophagus in the area of the chest between the lungs known as the mediastinum. The trachea is a part of the respiratory system while the esophagus is a part of the digestive system.
The outermost layer of the trachea called the adventitia is fibrous connective tissue that blends into the adventitia of other organs of the mediastinum especially the esophagus. The trachea is the longer tube but the esophagus is more flexible. The esophagus is a muscular tube connecting the throat pharynx with the stomach.
The main difference between trachea and esophagus is that trachea is the major bronchi or the windpipe of humans whereas esophagus is the food pipe which connects the pharynx to the stomach. The firmness of the cartilages helps to keep the trachea from collapsing 8 while their flexibility allows it to move freely during breathing. Each tracheal ring is around 1 2 mm thick and 4 5 mm deep being open at the posterior side of the trachea where it is closest to the esophagus the passage between the throat and stomach 4.
The beginning of the trachea lies beneath the thyroid gland with the inferior end connecting with the carinathe area in which the main bronchus separates into two bronchi one of which enters each lung.
 General Surgery Thyroid Cancer
General Surgery Thyroid Cancer
 Throat Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Throat Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Difference Between Trachea And Esophagus Definition
 Trachea Windpipe Definition Anatomy Function Diagram
Trachea Windpipe Definition Anatomy Function Diagram
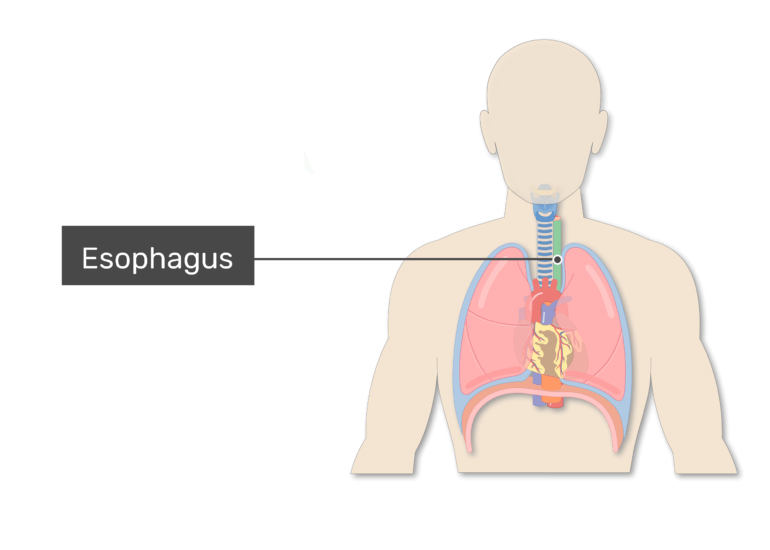 Trachea Or Windpipe Location Anatomy And Physiology
Trachea Or Windpipe Location Anatomy And Physiology
 Diagram Of The Esophagus Diagram Of The Esophagus
Diagram Of The Esophagus Diagram Of The Esophagus
Stock Image Illustration Of The Upper Digestive System
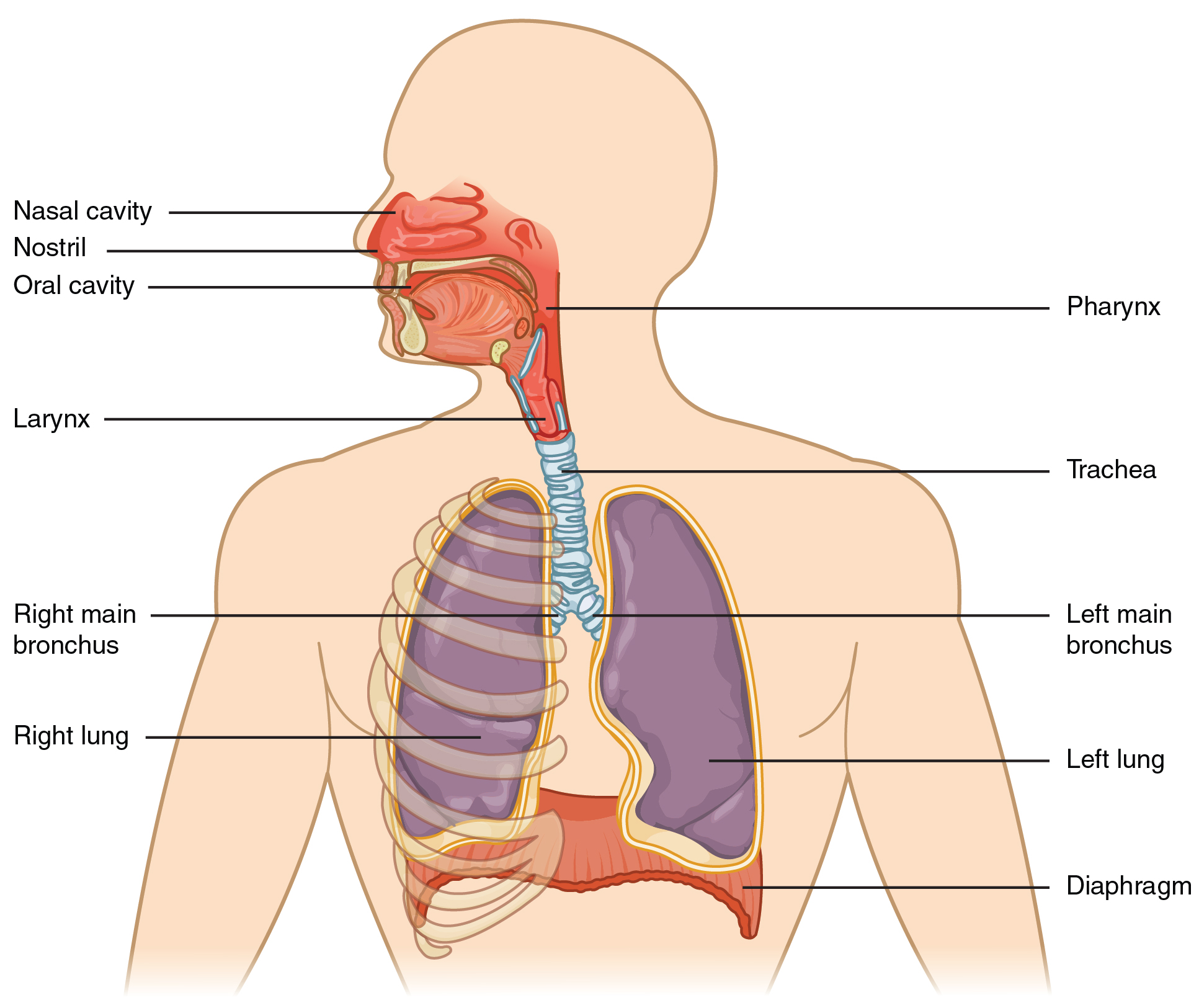 22 1 Organs And Structures Of The Respiratory System
22 1 Organs And Structures Of The Respiratory System
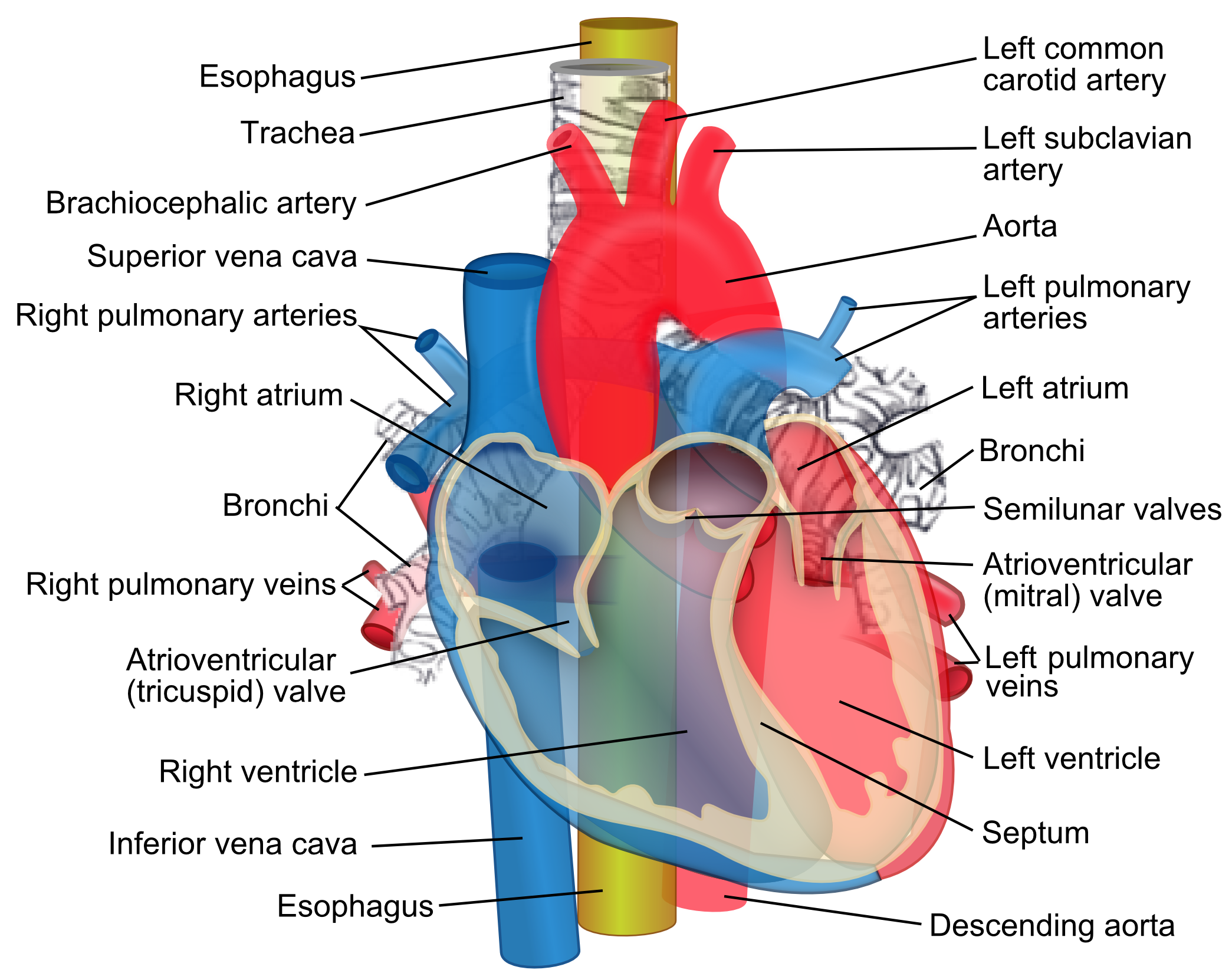 File Relations Of The Aorta Trachea Esophagus And Other
File Relations Of The Aorta Trachea Esophagus And Other
Is The Esophagus Posterior To The Trachea Quora
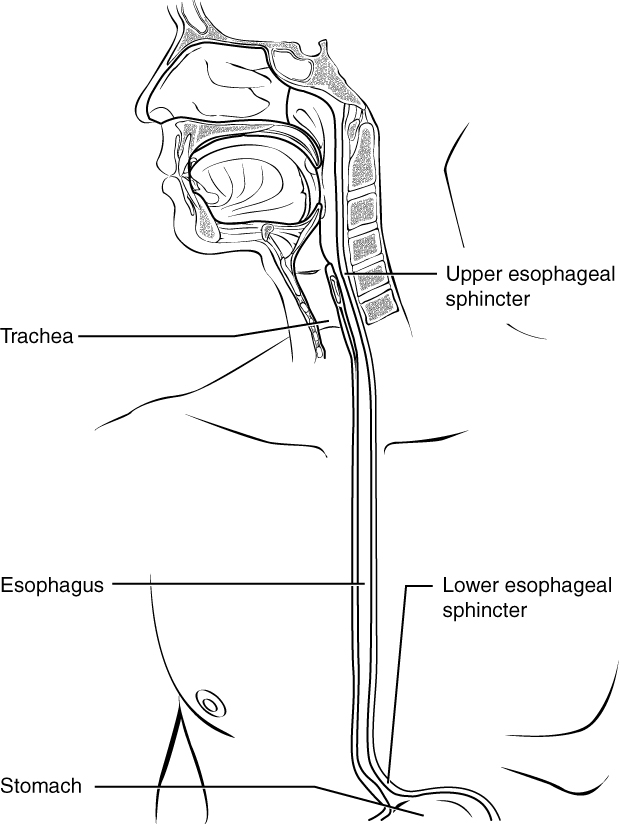 23 3 The Mouth Pharynx And Esophagus Anatomy And Physiology
23 3 The Mouth Pharynx And Esophagus Anatomy And Physiology
 Throat Esophagus Anatomy Album On Imgur
Throat Esophagus Anatomy Album On Imgur
 Anatomy 3 02 Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy 3 02 Flashcards Quizlet
Histology Website Resource Ha8 Trachea And Esophagus Monkey
 Oesophagus Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
Oesophagus Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
 Larynx Voice Box Definition Function Anatomy And Diagram
Larynx Voice Box Definition Function Anatomy And Diagram
 Trachea Esophagus Anatomy Stock Vector Royalty Free 1073886308
Trachea Esophagus Anatomy Stock Vector Royalty Free 1073886308
 Heart Anatomy Model 7 Part Model Esophagus Trachea Svc Aorta Front Heart Wall Upper Half Of Heart
Heart Anatomy Model 7 Part Model Esophagus Trachea Svc Aorta Front Heart Wall Upper Half Of Heart
 Double Aortic Arch An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Double Aortic Arch An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
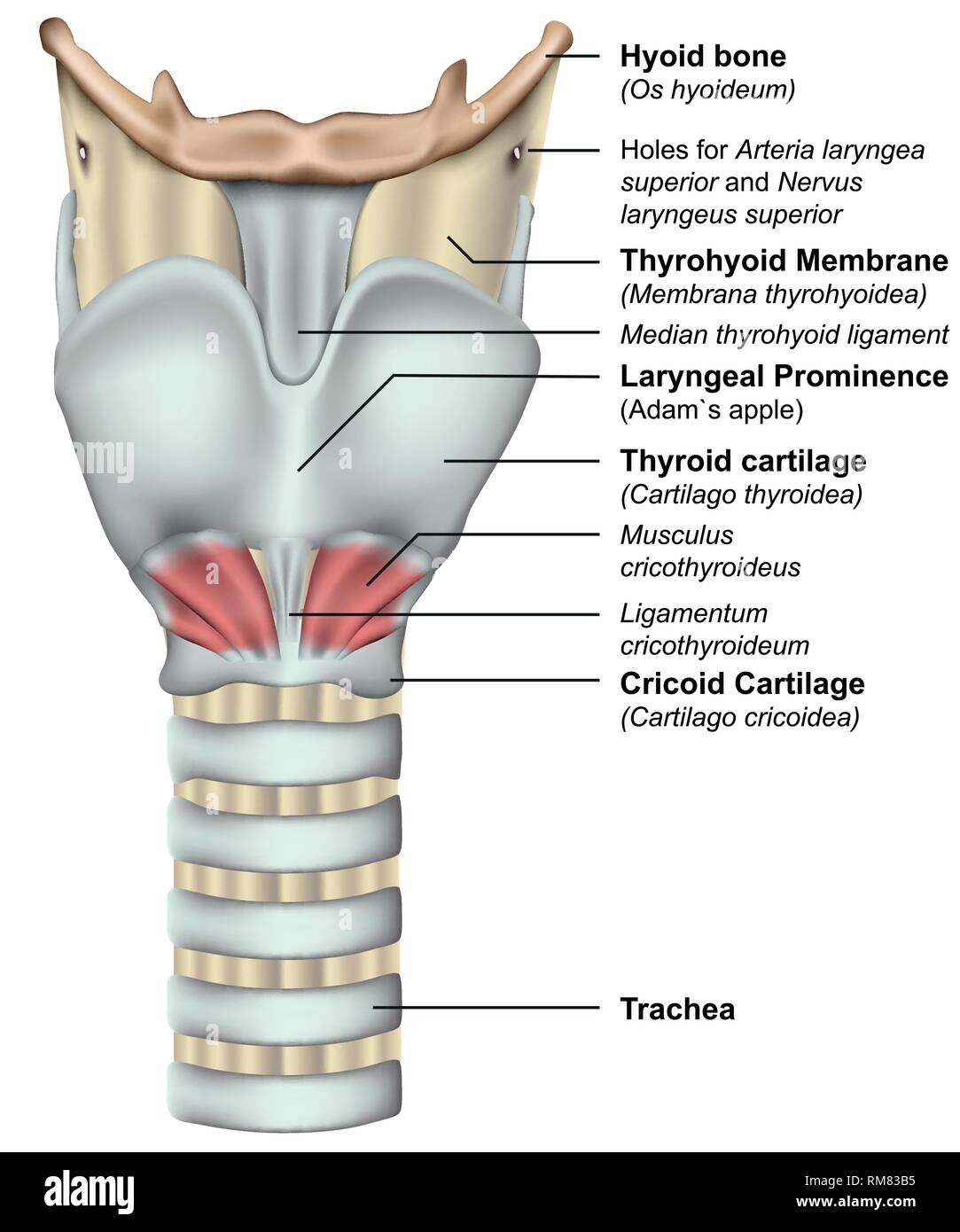 Trachea And Esophagus Stock Photos Trachea And Esophagus
Trachea And Esophagus Stock Photos Trachea And Esophagus
 Ea Tef Genetics Home Reference Nih
Ea Tef Genetics Home Reference Nih
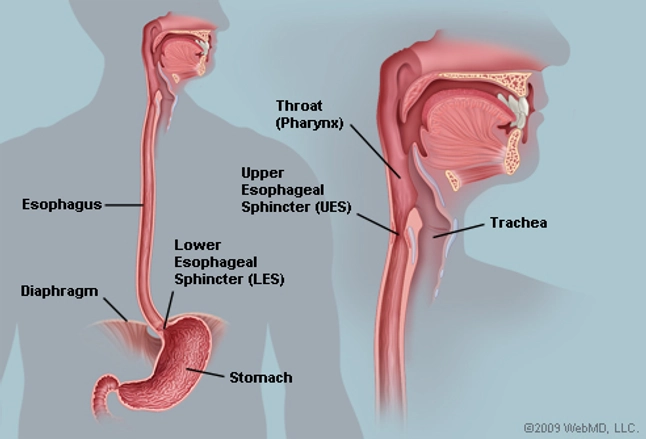 The Esophagus Human Anatomy Picture Function Conditions
The Esophagus Human Anatomy Picture Function Conditions


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar