In human nervous system. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe occupies the middle cranial fossa which is bounded anteriorly by the greater wing of the sphenoid bone inferiorly by the superior surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone and laterally by the squamous part of the temporal bone and the adjoining parietal bone.
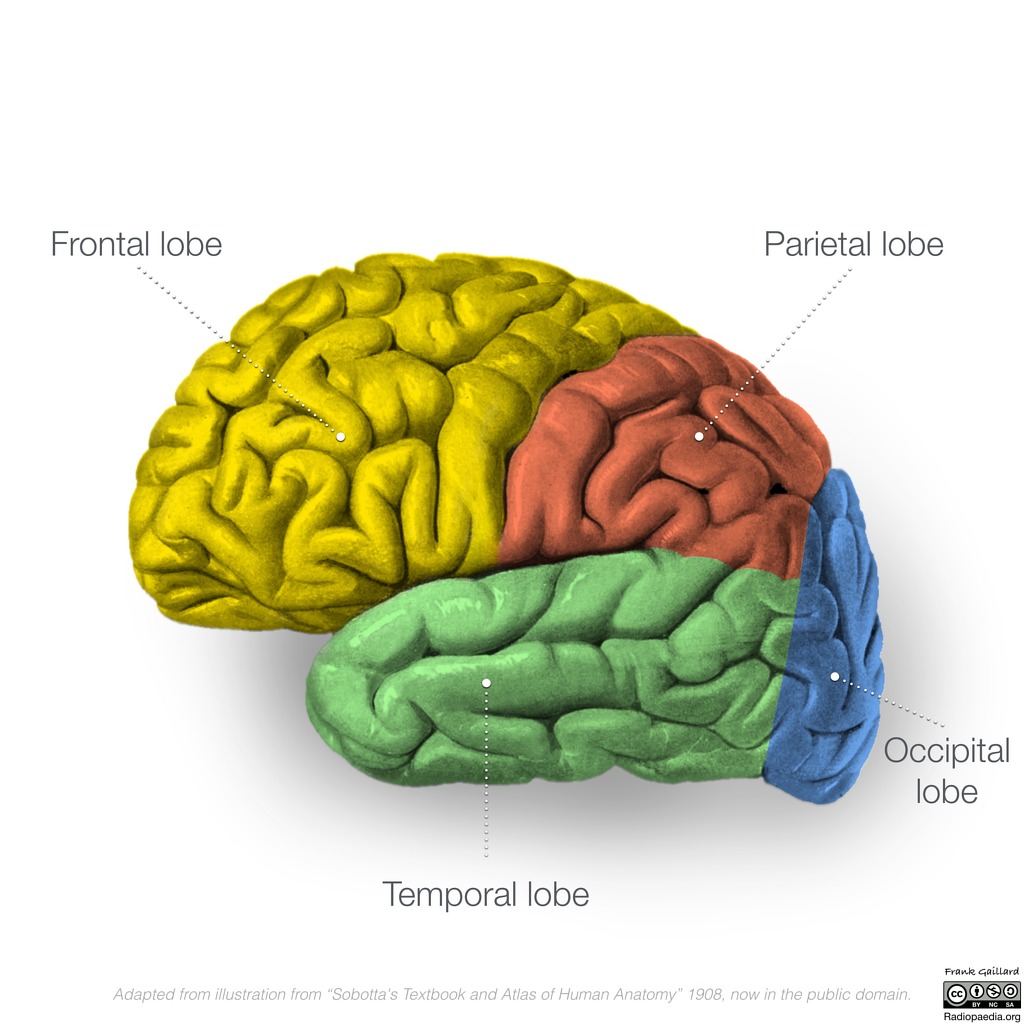
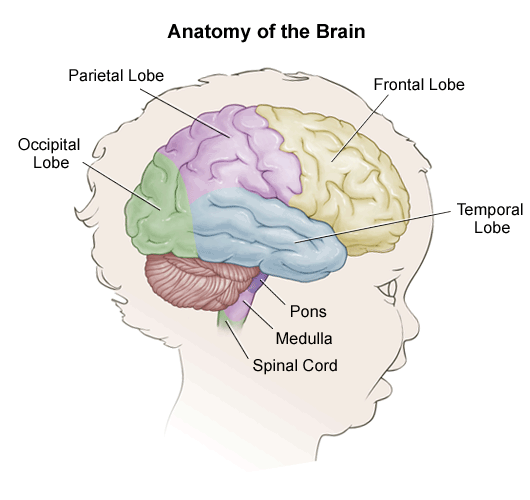
Anatomy of temporal lobe. The temporal lobe located just beneath the lateral fissure and crisscrossing both fissures of the brain. The temporal lobe is the second largest lobe after the larger frontal lobe accounting 22 of the total neocortical volume 6. The temporal lobes are located in the prosencephalon or forebrain between the occipital and parietal lobes.
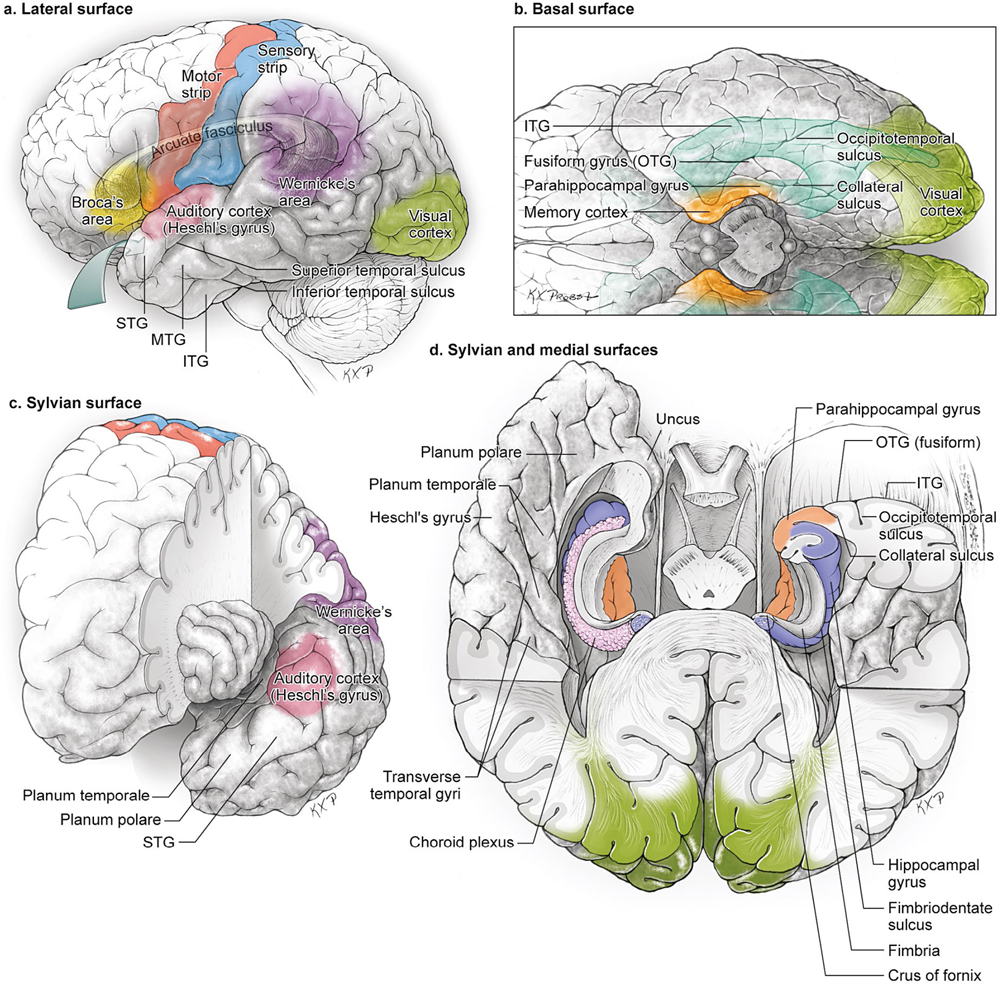
Hearing auditory cortex and association area. Anatomy of the temporal lobe. Structures of the cerebral cortex.
This vital structure of the temporal lobe supports process the sensory input including pain and the auditory stimuli. The temporal lobe is the second largest lobe after the larger frontal lobe accounting 22 of the total neocortical volume 6. The outer surface of the temporal lobe is an association area made up of the superior middle and inferior temporal gyri.
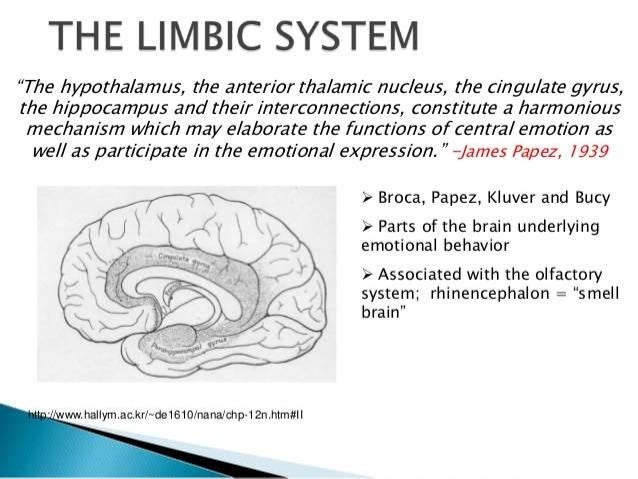
The hippocampal formation on the medial side of the lobe includes the parahippocampal gyrus subiculum hippocampus dentate gyrus and associated white matter notably the fimbria whose fibres continue into the fornix. The temporal lobe is involved in. The brains contain four lobes in the cortex including the occipital parietal temporal and frontal lobes.
The hippocampus is an inrolled gyrus that bulges into the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle. The temporal lobes are responsible for sensory processing auditory perception language and speech production and memory storage. Emotional response memory limbic association area.
Lobes of the cerebral cortex the temporal lobe inferior to the lateral sulcus fills the middle fossa or hollow area of the skull. The temporal lobe occupies the middle cranial fossa which is bounded anteriorly by the greater wing of the sphenoid bone inferiorly by the superior surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone and laterally by the squamous part of the temporal bone and the adjoining parietal bone. Temporal lobe gross anatomy.
Temporal lobe gross anatomy. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory language comprehension and emotion association. Object identification posterior association area.
 Temporal Lobe An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Temporal Lobe An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
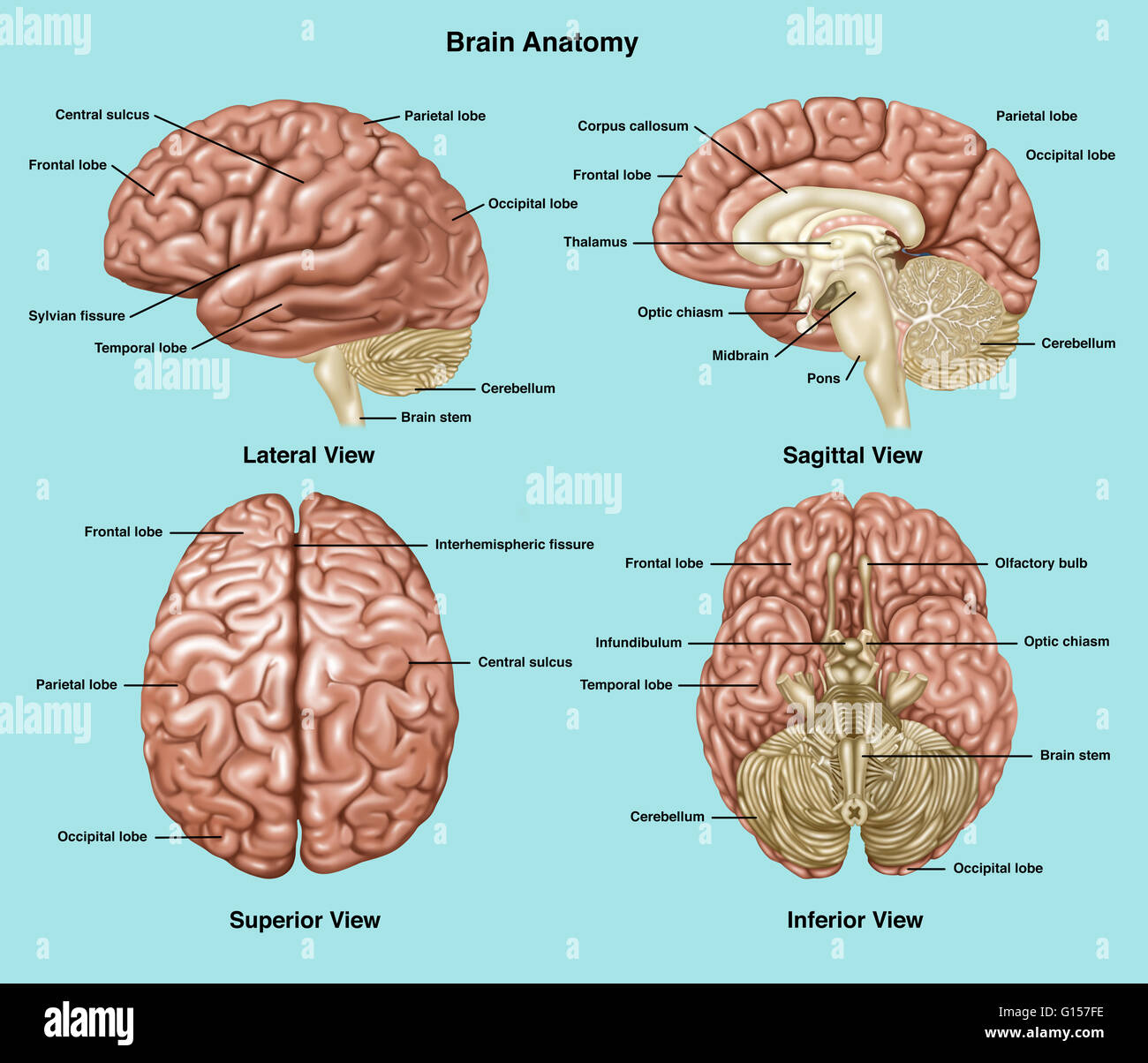 Illustration Showing Anatomy Of A Normal Brain In Lateral
Illustration Showing Anatomy Of A Normal Brain In Lateral
 Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Figure 7
Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Figure 7
 Vector Illustration Flat Temporal Lobe Of Human Brain Anatomy
Vector Illustration Flat Temporal Lobe Of Human Brain Anatomy
 Cerebral Cortex Neurology Medbullets Step 1
Cerebral Cortex Neurology Medbullets Step 1
 Neuroanatomy Lateral Cortex Diagrams Radiology Case
Neuroanatomy Lateral Cortex Diagrams Radiology Case
 Pdf Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Semantic Scholar
Pdf Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Semantic Scholar
 Temporal Lobe Brain Anatomy 3d Illustration
Temporal Lobe Brain Anatomy 3d Illustration
 Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Figure 8
Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Figure 8
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Temporal Lobe Normal
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Temporal Lobe Normal
 Temporal Arteriovenous Malformations Neupsy Key
Temporal Arteriovenous Malformations Neupsy Key
 Pdf Microsurgical Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe And Its
Pdf Microsurgical Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe And Its
 Approach To Temporal Lobe Anatomy Function Epilepsy Mri Finding
Approach To Temporal Lobe Anatomy Function Epilepsy Mri Finding
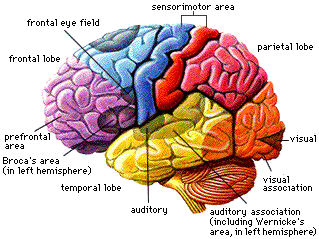 Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Changes In Personality Study Com
Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Changes In Personality Study Com
 Pdf Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Semantic Scholar
Pdf Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Semantic Scholar
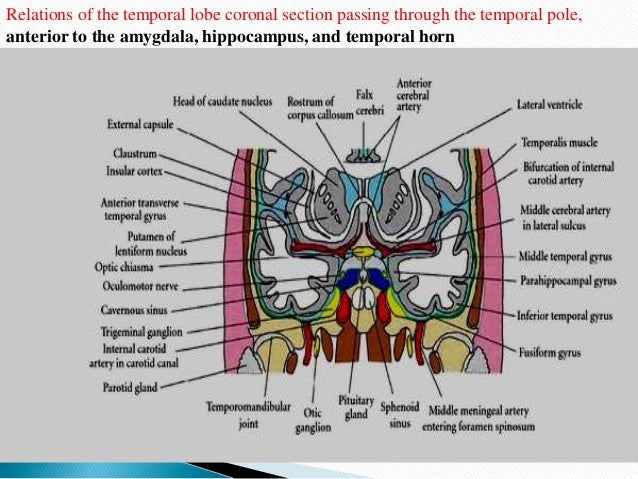 Approach To Temporal Lobe Anatomy Function Epilepsy Mri Finding
Approach To Temporal Lobe Anatomy Function Epilepsy Mri Finding
 Location Of The Temporal Lobes It Is On Both Sides Behind
Location Of The Temporal Lobes It Is On Both Sides Behind
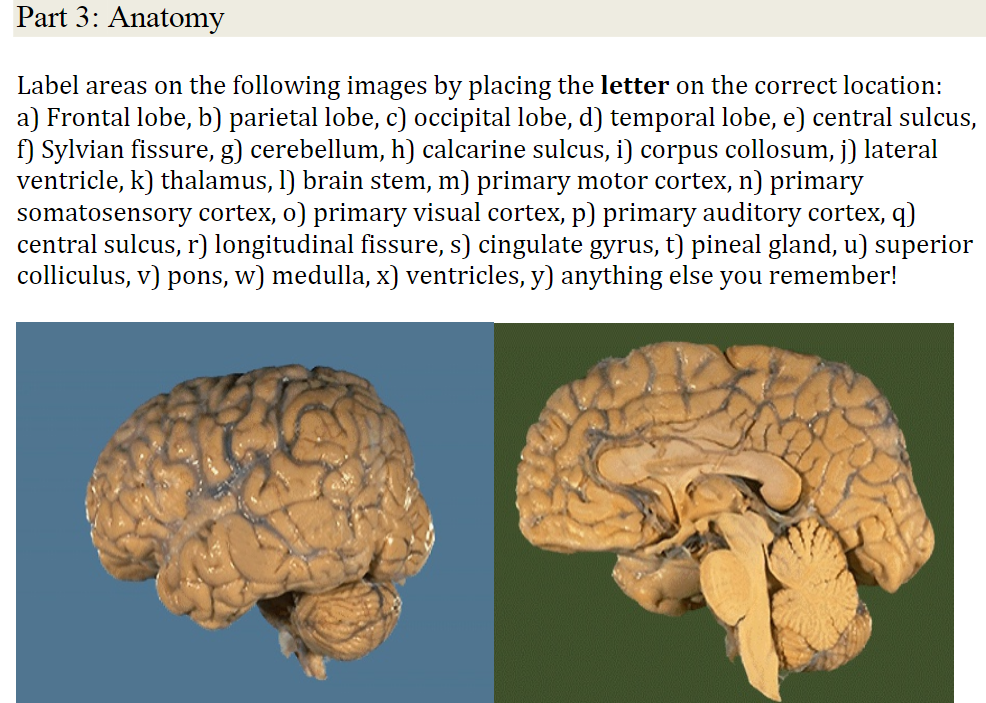 Solved Pari 3 Anatomy Label Areas On The Following Image
Solved Pari 3 Anatomy Label Areas On The Following Image
 Temporal Lobe Operative Neurosurgery
Temporal Lobe Operative Neurosurgery
 067 The Anatomy And Functions Of The Occipital And Temporal Lobes
067 The Anatomy And Functions Of The Occipital And Temporal Lobes
 Anatomical Relations Of The Temporal Lobe As Seen In A
Anatomical Relations Of The Temporal Lobe As Seen In A
 Temporal Brain Lobe Position Structure Function Role
Temporal Brain Lobe Position Structure Function Role
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Brain_lobes-571a4c0f5f9b58857db90d7e.jpg) Temporal Lobes In The Cerebral Cortex
Temporal Lobes In The Cerebral Cortex
 Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Figure 9
Anatomy Of The Temporal Lobe Figure 9
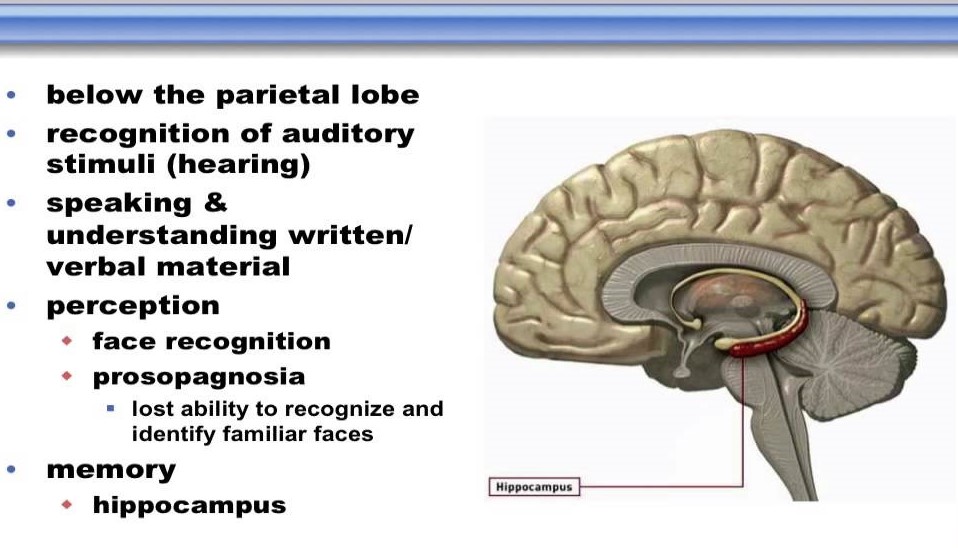 Temporal Lobe Anatomy Location Function Anatomy Info
Temporal Lobe Anatomy Location Function Anatomy Info
Memory Part 2 The Role Of The Medial Temporal Lobe



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar