A generic connective tissue cell that produces fibers. The progenitor of all other connective tissue cell types.
 Tunica Adventitia Anatomy Britannica
Tunica Adventitia Anatomy Britannica
Unstructured semifluid substance that fills the space between cells in connective tissues or inside organelles.

Collagen fibers definition anatomy. Collagen is converted into gelatin when boiled in water. Tough bundles of collagen called collagen fibers are a major component of the extracellular matrix that supports most tissues and gives cells structure from the outside but collagen is also found inside certain cells. Collagen is a type of protein fiber found abundantly throughout our body.
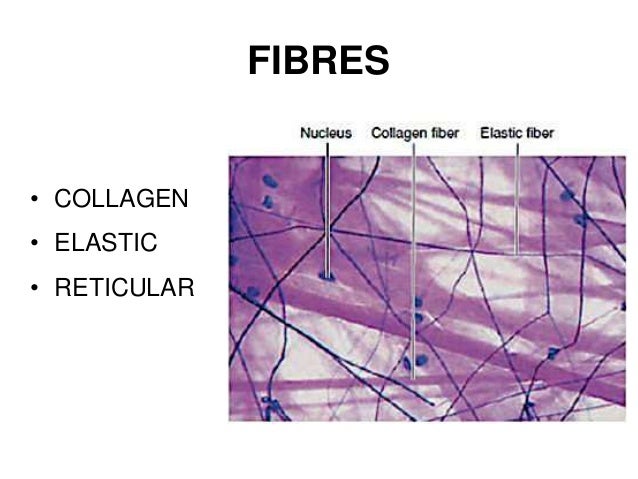
Material composed principally of collagen proteins. The reticular fibres are composed of randomly oriented collagenous fibrils lying in an amorphous matrix substance. Forms structures such as tendons and ligaments.
Material composed principally of collagen proteins. Botany one of the elongated thick walled cells that give strength and support to plant. Collagen fibers are known for their great tensile strength and are a major component of the bodys connective tissues.
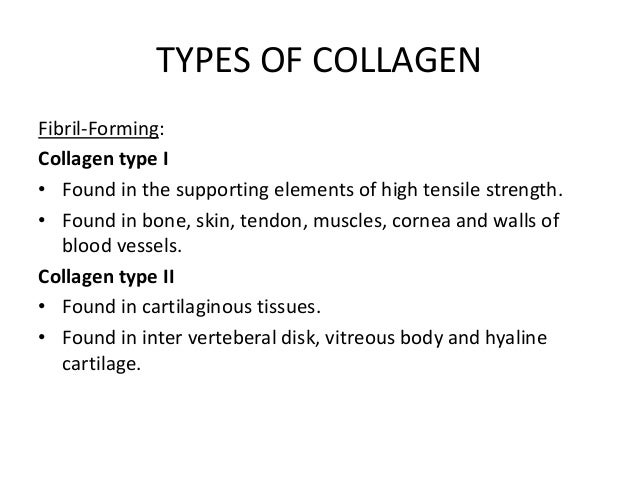
Collagen fibers are made up collagen fibrils which consist of collagen molecules arranged side by side which in turn consist of three alpha chains arranged in a triple helix. Dense regular connective tissue that contains abundant collagen fibers giving it a white appearance. More specifically collagen is found in our various types of connective tissues such as cartilage tendons bones and ligaments.
Any of a class of extracellular proteins that are composed of three coiled polypeptide chains form strong fibers and are the main constituents of cartilage bone and other connective tissues in animals. A slender elongated threadlike object or structure. Collagen is converted into gelatin when boiled in water.
It provides strength and cushioning to many different areas of the body including the skin. Collagen fibers synonyms collagen fibers pronunciation collagen fibers translation english dictionary definition of collagen fibers. Anatomy and physiology chapter 4.
One of three types of fiber embedded in the matrix between cells of connective tissue. An individual scleroprotein fiber composed of fibrils and usually arranged in branching bundles of indefinite length. Fibers give the tissue considerable strength and resistance to stretching.
Any of a class of extracellular proteins that are composed of three coiled polypeptide chains form strong fibers and are the main constituents of cartilage bone and other connective tissues in animals. Reticular fibre reticular fibre in anatomy fine fibrous connective tissue occurring in networks to make up the supporting tissue of many organs.
 Connective Tissue Fatima Al Sayed
Connective Tissue Fatima Al Sayed
 The Mechanical Role Of Collagen Fibers In The Intervertebral
The Mechanical Role Of Collagen Fibers In The Intervertebral
 Areolar Tissue Human Anatomy Physiology Anatomy
Areolar Tissue Human Anatomy Physiology Anatomy
Connective Tissue Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body
4 The Microstructure Of The Femur Includes Hydroxyapatite
 Connective Tissue Lecture Bio264 Byu Idaho Studocu
Connective Tissue Lecture Bio264 Byu Idaho Studocu
 Structured Polarized Light Microscopy For Collagen Fiber
Structured Polarized Light Microscopy For Collagen Fiber
 Collagen Fiber An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Collagen Fiber An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric Diagram Quizlet
Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric Diagram Quizlet
 Structured Polarized Light Microscopy For Collagen Fiber
Structured Polarized Light Microscopy For Collagen Fiber
 Types Of Connective Tissue What Is Connective Tissue Functions Of Connective Tissue
Types Of Connective Tissue What Is Connective Tissue Functions Of Connective Tissue
 What Is Collagen Definition Types And Diseases Video
What Is Collagen Definition Types And Diseases Video
Difference Between Collagen And Elastin Definition
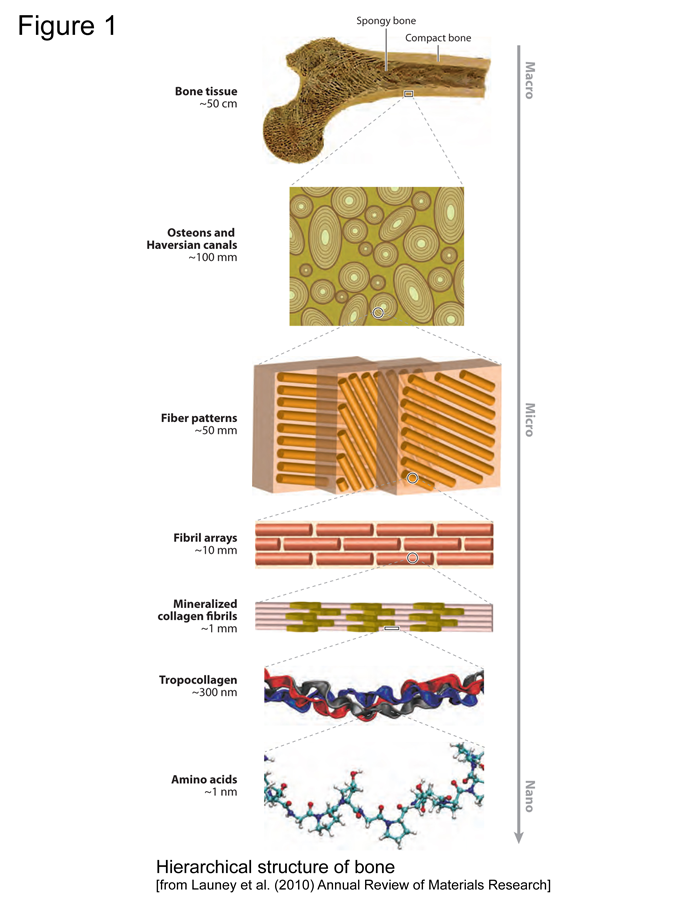 Basic Biology Of Bone Team Bone
Basic Biology Of Bone Team Bone
 Difference Between Loose And Dense Connective Tissue
Difference Between Loose And Dense Connective Tissue
 Fibrous Joints Are Where Two Adjacent Bones Are Bound By
Fibrous Joints Are Where Two Adjacent Bones Are Bound By
Demonstration Of Connective Tissue Sheaths Surrounding
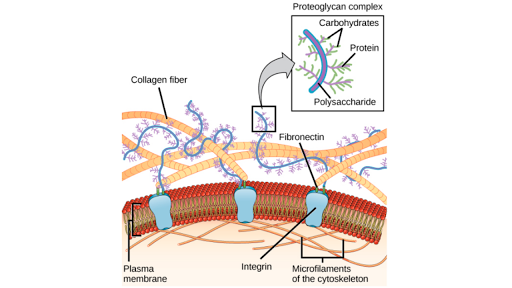
 Connective Tissues Test One Human Anatomy 110 With Rem At
Connective Tissues Test One Human Anatomy 110 With Rem At
 Strong Triaxial Coupling And Anomalous Poisson Effect In
Strong Triaxial Coupling And Anomalous Poisson Effect In
Connective Tissue Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body
 Extracellular Matrix Video Anatomy Definition Osmosis
Extracellular Matrix Video Anatomy Definition Osmosis



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar