If the place is on the bone that moves during the action. Max contraction of muscle tissue necessary to lift a given resistance or weight.
Basic Biomechanics Moment Arm Torque
Hip flexion keeps the upper body from falling backwards when standing erect.
Muscle action definition anatomy. Thus in russia it is referred to as yielding or succumbing contraction. Mainly skeletal muscle composed of parallel bundles of striated multinucleate fibers. A skeletal muscle attaches to bone or sometimes other muscles or tissues at two or more places.
Name the action origin insertion and innervation of the pectineus muscle. Muscle whose action is normally controlled by an individuals will. If the place is a bone that remains immobile for an action the attachment is called an origin.
Groups of muscles are involved in most movements and names are used to describe the. The action or particular movement of a muscle can be described relative to the joint or the body part moved. Skeletal muscle actions knowing the muscular organization of each region of the body is crucial in anatomy.
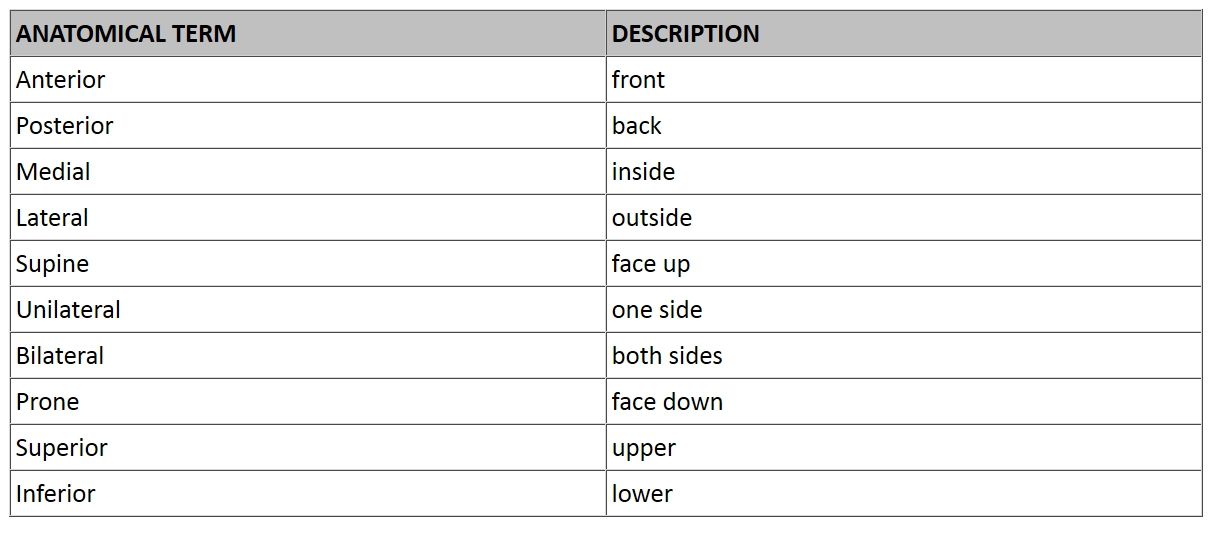
As for anatomical terms of location the terms used assume that the body starts in the anatomical position. The work done during eccentric contraction is often called negative. A muscle that fixes or holds a bone so that the agonist can carry out the intended movement is said to have a neutralising action.
Eccentric contraction refers to muscle action in which the muscle force yields to the imposed load. A muscle such as any of the striated muscles except the heart whose action is normally controlled by individual volition. Muscles contract to produce movement at joints and the subsequent movements can be precisely described using the terminology below.
Muscles attach to bones at locations called origins and insertions. Origin of voluntary muscle. Muscular strength is increased as resistance to the action is progressively increased.
With an understanding of where a muscle originates and inserts you can calculate the movements that will occur at a joint when these two points are brought together following an isotonic muscular contraction.
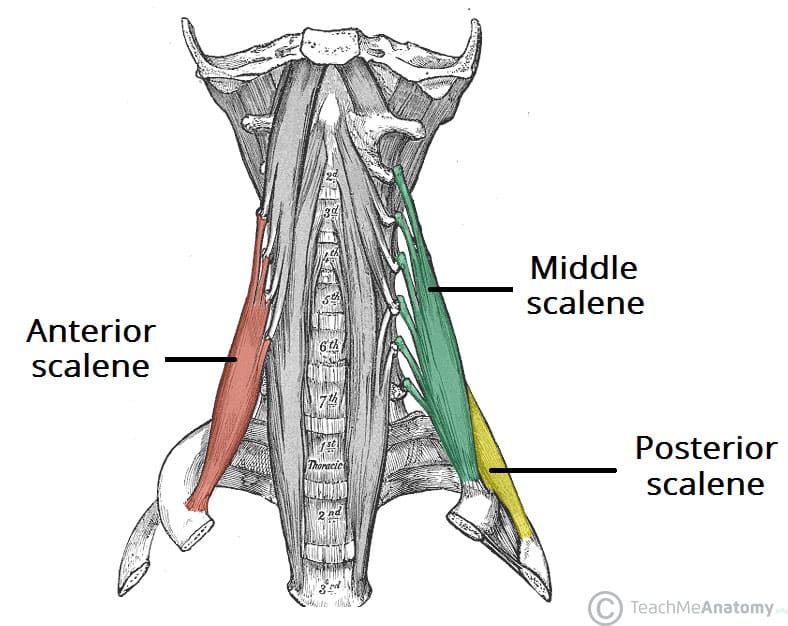
 The Scalene Muscles Attachments Action Innervation
The Scalene Muscles Attachments Action Innervation
 Interactions Of Skeletal Muscles Anatomy And Physiology I
Interactions Of Skeletal Muscles Anatomy And Physiology I
 Posterior Superior Serratus Muscle Human Anatomy Kenhub
Posterior Superior Serratus Muscle Human Anatomy Kenhub
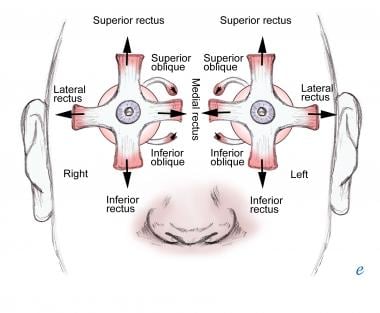 Extraocular Muscle Actions Eye Movements Rectus Muscles
Extraocular Muscle Actions Eye Movements Rectus Muscles
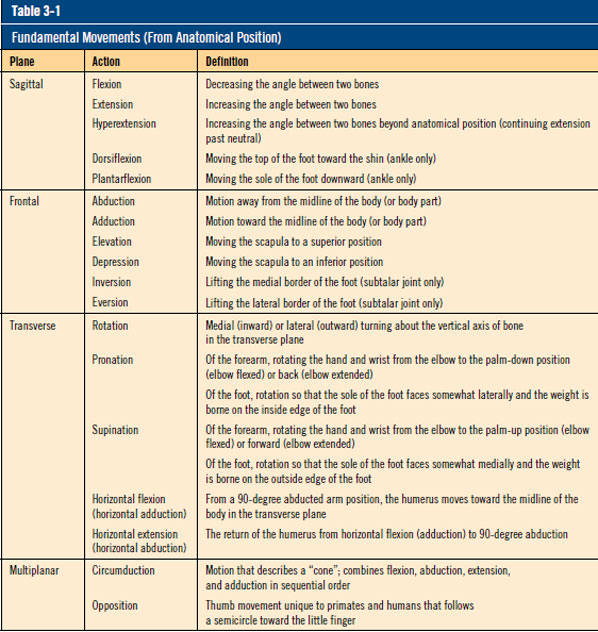 Ace S Essentials Of Exercise Science Helper
Ace S Essentials Of Exercise Science Helper
 Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
 Adductors What Are The Adductor Muscles Attachments And
Adductors What Are The Adductor Muscles Attachments And
Hyoglossus Muscle Muscular Musculoskeletal Anatomyzone
 Muscle Biochemistry Structure And Function
Muscle Biochemistry Structure And Function
 Muscle Origin And Insertion Definition And Actions Video
Muscle Origin And Insertion Definition And Actions Video
 Anatomy Of Your Leg Muscles Plus How Genetics And Exercise
Anatomy Of Your Leg Muscles Plus How Genetics And Exercise
 The Nasm Cpt Podcast How To Remember The Names Of The
The Nasm Cpt Podcast How To Remember The Names Of The
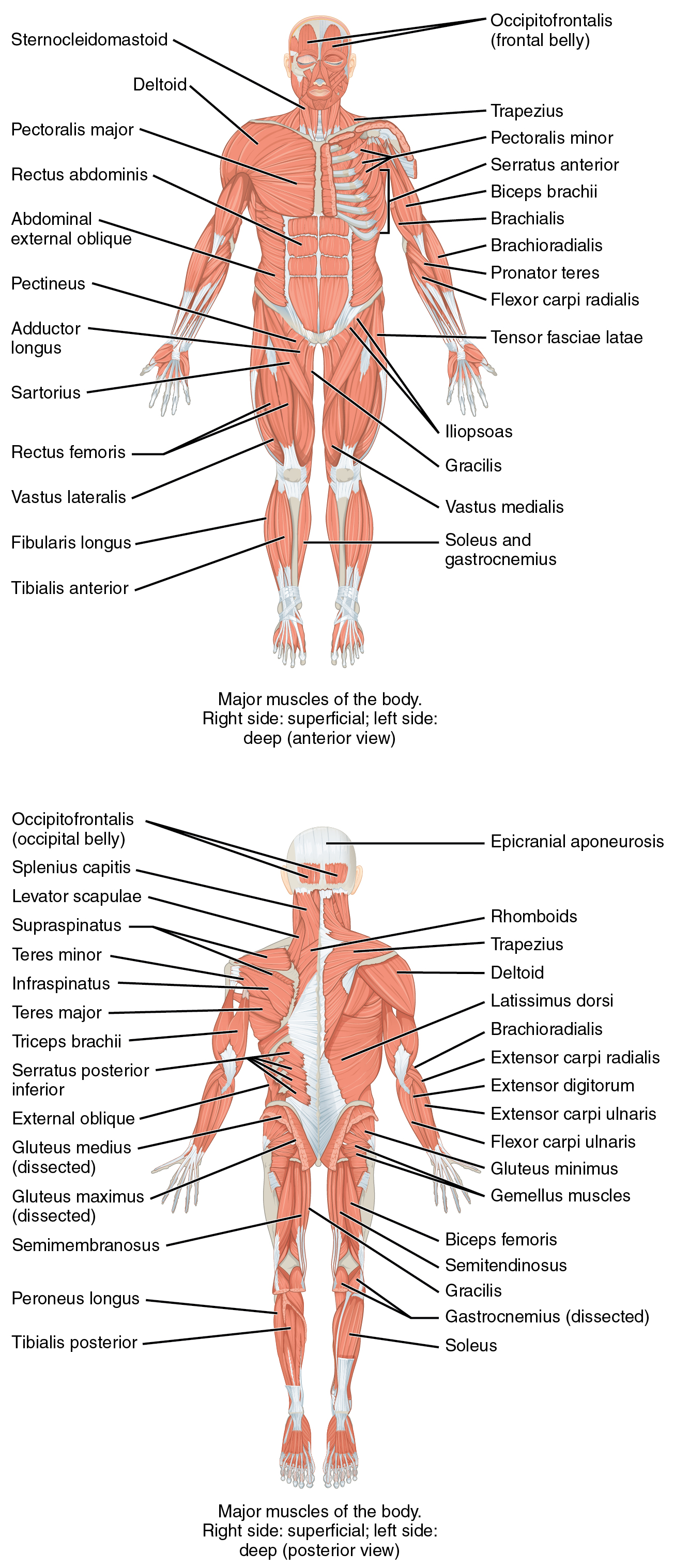 11 2 Naming Skeletal Muscles Anatomy And Physiology
11 2 Naming Skeletal Muscles Anatomy And Physiology
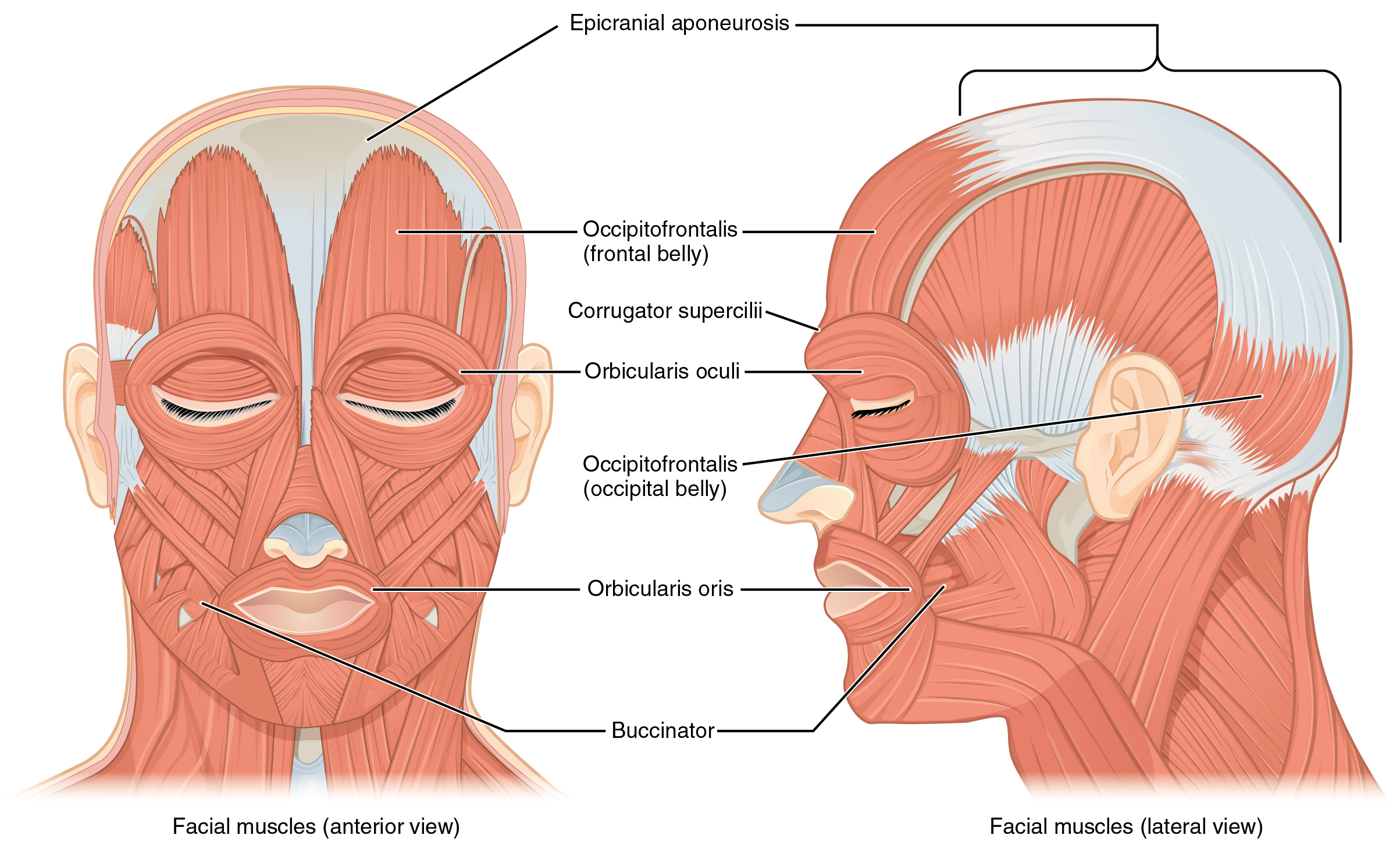 11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/musculus-coracobrachialis/5GwxiArugHqENyG0mwhknQ_xg4SJz1udc_M._coracobrachialis_1.png) Coracobrachialis Muscle Anatomy Innervation Function Kenhub
Coracobrachialis Muscle Anatomy Innervation Function Kenhub
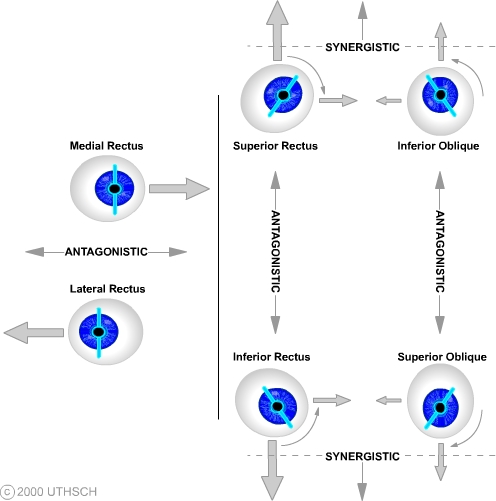 Ocular Motor Control Section 3 Chapter 8 Neuroscience
Ocular Motor Control Section 3 Chapter 8 Neuroscience
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-87308179-56a05f563df78cafdaa14cd4.jpg) Anatomy Of The Hamstring Muscles
Anatomy Of The Hamstring Muscles
 Muscle Origin Action Insertion Human Anatomy 35 With
Muscle Origin Action Insertion Human Anatomy 35 With
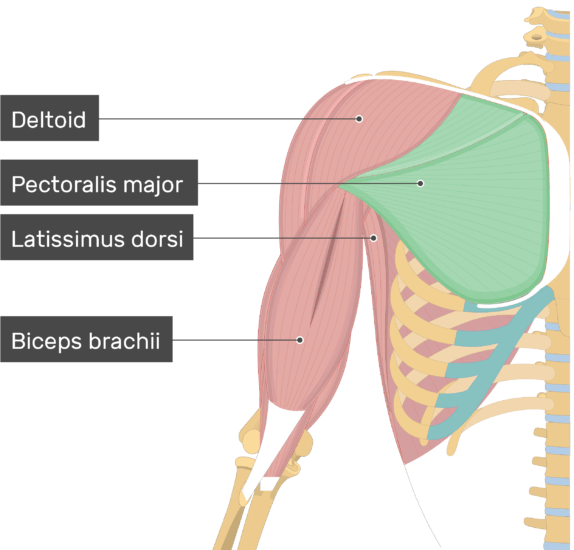 Pectoralis Major Muscle Attachment Action Innervation
Pectoralis Major Muscle Attachment Action Innervation
 Experiment Emgs During Muscle Fatigue
Experiment Emgs During Muscle Fatigue
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-muscles-of-the-thigh-87394652-5becaa51c9e77c00263c91d3.jpg) Function Of The Rectus Femoris Muscle
Function Of The Rectus Femoris Muscle
 Naming Muscles Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141
Naming Muscles Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141
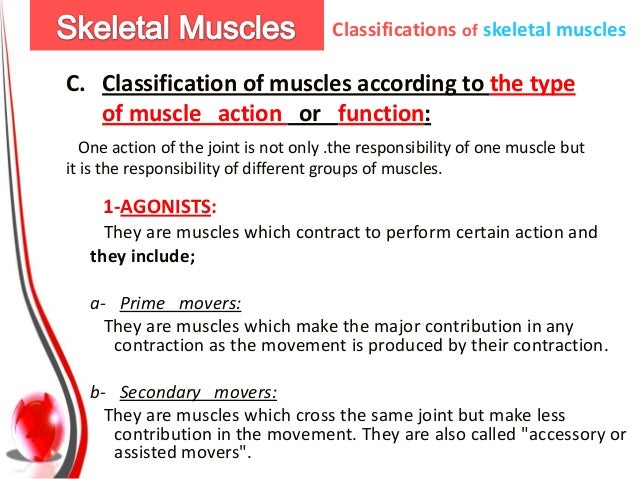
Retraction Muscle Actions Joint Movements
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar