Spinal cord anatomy in the neck internal anatomy of the spinal cord. It has a relatively simple anatomical course.
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Spinal
Spinal Cord Anatomy Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Spinal
It is composed of nerve fibres that mediate reflex actions and that transmit impulses to and from the brain.

Anatomy of spinal cord. Cross sectional anatomy of spinal cord. Protective layers of the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are grouped as cervical c1 c8 thoracic t1 t12 lumbar l1 l5.
Spinal cord major nerve tract of vertebrates extending from the base of the brain through the canal of the spinal column. Gray matter has a relatively dull color because it contains little myelin. Cervical enlargement corresponds roughly to the brachial plexus nerves.
The spinal cord is composed of neurons that send and receive signals along tracts towards and away from the brain. The spinal cord is a bundle of nerve fibers that extend from the brain stem down the spinal column to the lower back. It passes through the spinal canal or spinal cavity of the vertebral column ie the backbone or spine.
It contains the somas dendrites and proximal parts of the axons of neurons. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system cns. Spinal cord neural pathways are found within the spinal cord white matter.
It then travels inferiorly within the vertebral canal surrounded by the spinal meninges containing cerebrospinal fluid. There are two regions where the spinal cord enlarges. When viewed as a cross section from above.
Lumbar enlargement corresponds to the lumbosacral plexus nerves which innervate the lower limb. The spinal cord like the brain consists of two kinds of nervous tissue called gray and white matter. Signs and symptoms of spinal cord compression.
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system cns which extends caudally and is protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. The spinal cord arises cranially as a continuation of the medulla oblongata part of the brainstem. Cervical spinal cord injury.
Anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord. Basically spinal cord is a long and narrow bundle of nervous tissues and support cells which extends from the base of our brain to the upper lumbar region. It is covered by the three membranes of the cns ie the dura mater arachnoid and the innermost pia mater.
The spinal cord is a cylindrical structure greyish white in colour. The spinal meninges help prevent the spinal cord. A component of the central nervous system it sends and receives information between the brain and the rest of the body.
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Healthlink Bc
Spinal Cord Anatomy Healthlink Bc
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Scire Community
Spinal Cord Anatomy Scire Community
 Spinal Cord Anatomy And Innervation
Spinal Cord Anatomy And Innervation
 Ch 12 Gross Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord
Ch 12 Gross Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord
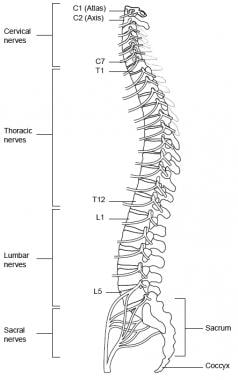 Topographic And Functional Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Gross
Topographic And Functional Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Gross
 Spinal Cord Lesions Neurology Medbullets Step 2 3
Spinal Cord Lesions Neurology Medbullets Step 2 3
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11475/anatomy-spinal-cord-cross-section_1.jpg) Spinal Cord Anatomy Structure Tracts And Function Kenhub
Spinal Cord Anatomy Structure Tracts And Function Kenhub
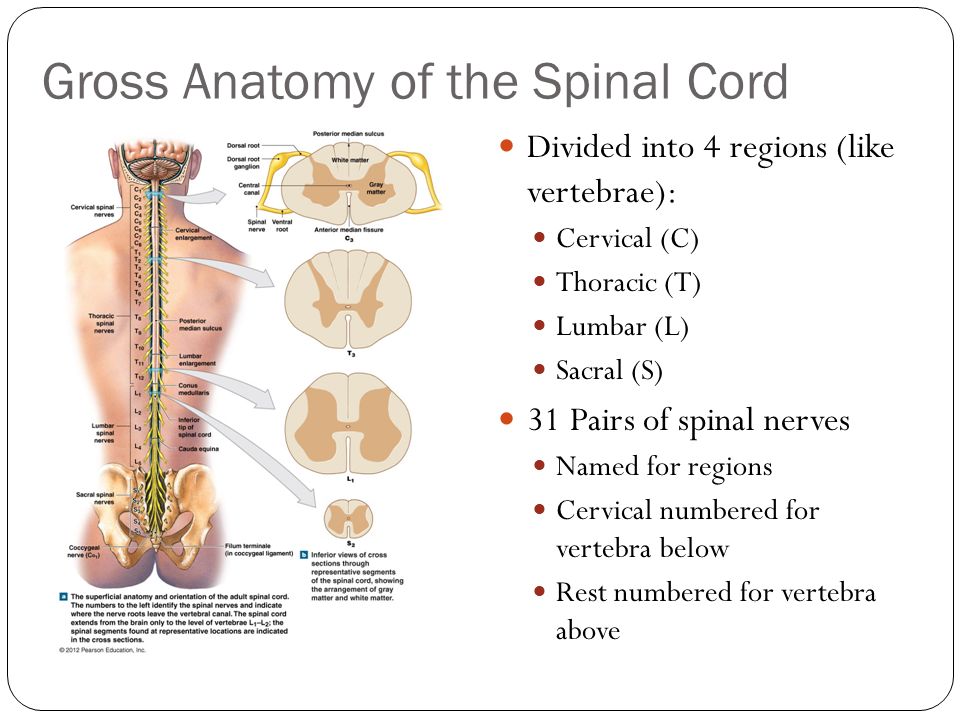 Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Ppt Video
Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Ppt Video
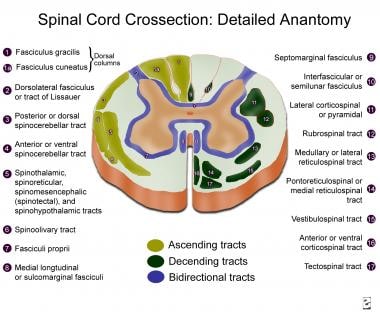 Topographic And Functional Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Gross
Topographic And Functional Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Gross
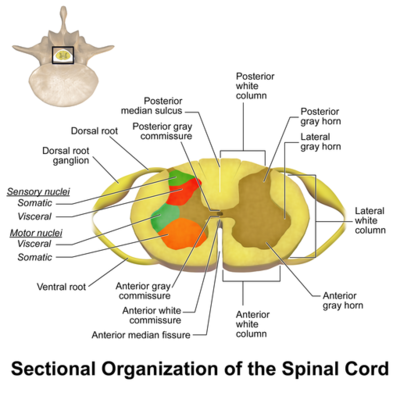 Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiopedia
Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiopedia
 Anatomy For First Aiders The Spinal Cord First Aid For Free
Anatomy For First Aiders The Spinal Cord First Aid For Free
 Schematic Representations Of The Spinal Cord Showing A The
Schematic Representations Of The Spinal Cord Showing A The
 Spinal Cord Anatomy In The Neck
Spinal Cord Anatomy In The Neck
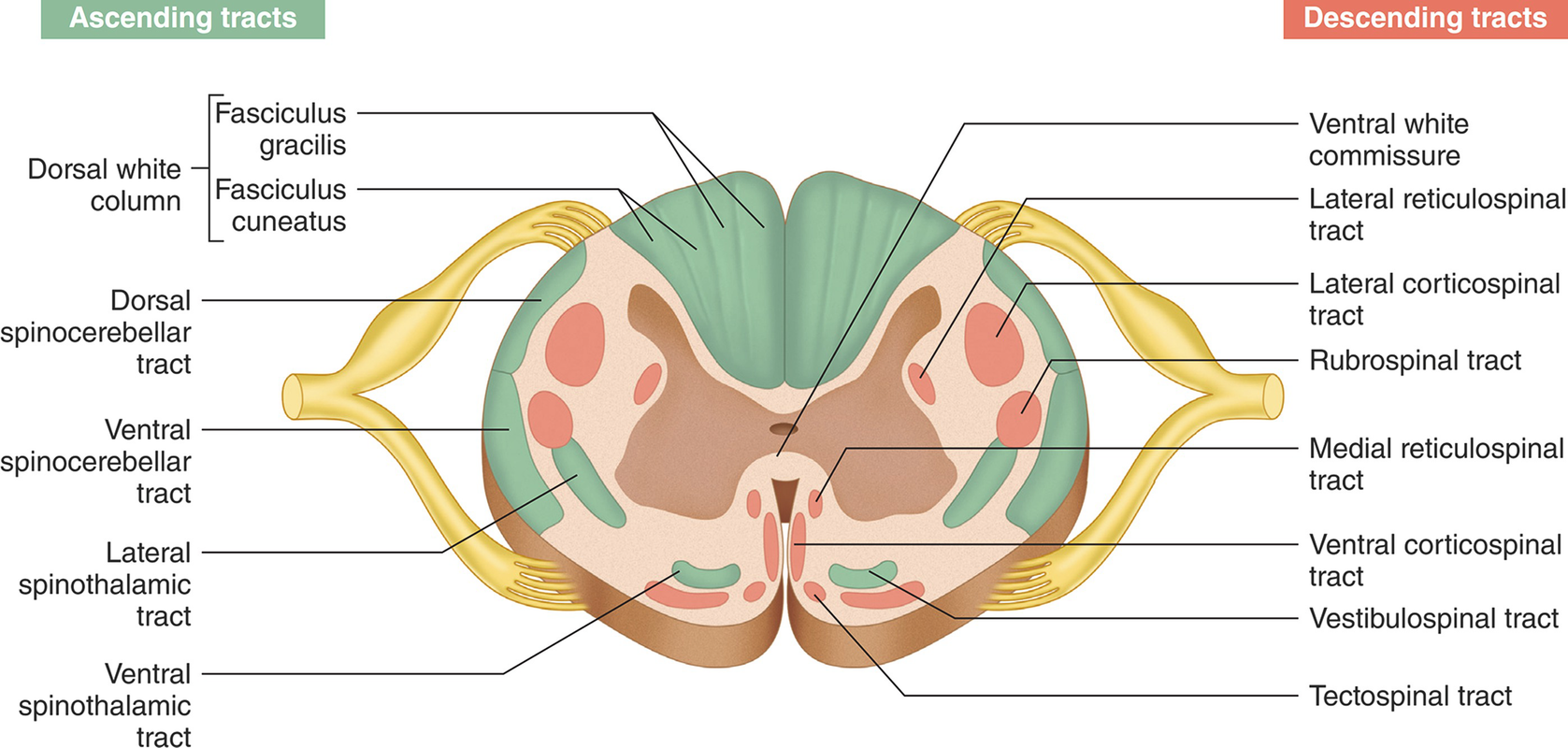 Functional Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Springerlink
Functional Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Springerlink
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/9264/anatomy-spinal-cord-cross-section_english.jpg) Spinal Cord Ascending And Descending Tracts Kenhub
Spinal Cord Ascending And Descending Tracts Kenhub
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Metro Health Hospital Metro Health
Spinal Cord Anatomy Metro Health Hospital Metro Health
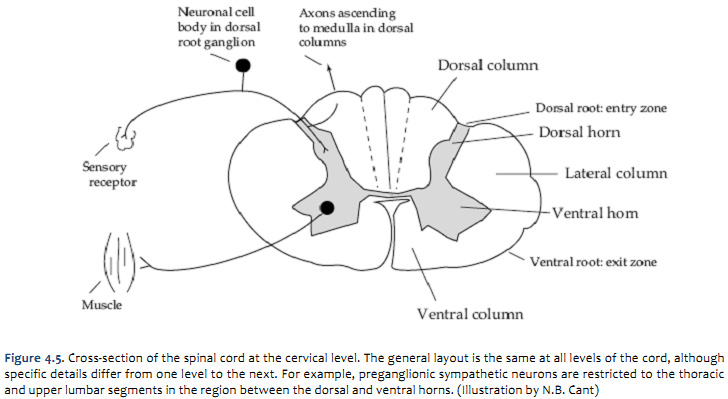 Duke Neurosciences Lab 2 Spinal Cord Brainstem Surface
Duke Neurosciences Lab 2 Spinal Cord Brainstem Surface
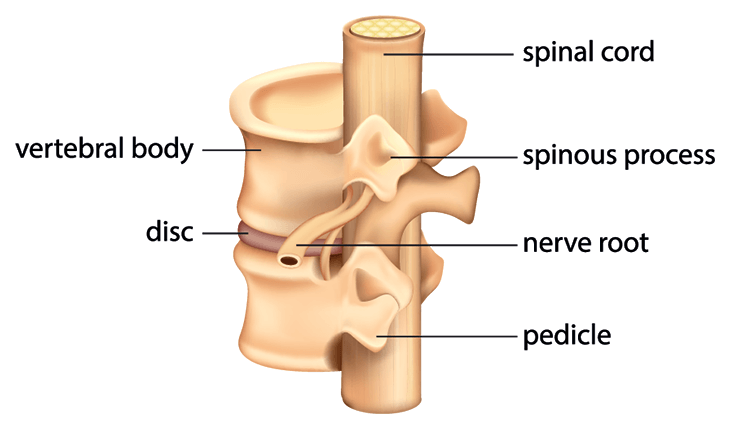 Spinal Cord Column Spinal Cord Injury Information Pages
Spinal Cord Column Spinal Cord Injury Information Pages
 Anatomy Of The Spine H N Radiation Oncology
Anatomy Of The Spine H N Radiation Oncology
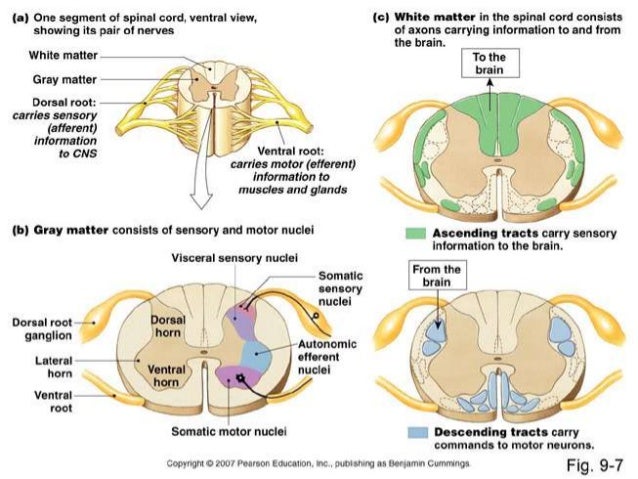 The Gross Anatomy Of Spinal Cord
The Gross Anatomy Of Spinal Cord
 Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord New Orleans
Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord New Orleans
 The Spinal Cord Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
The Spinal Cord Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
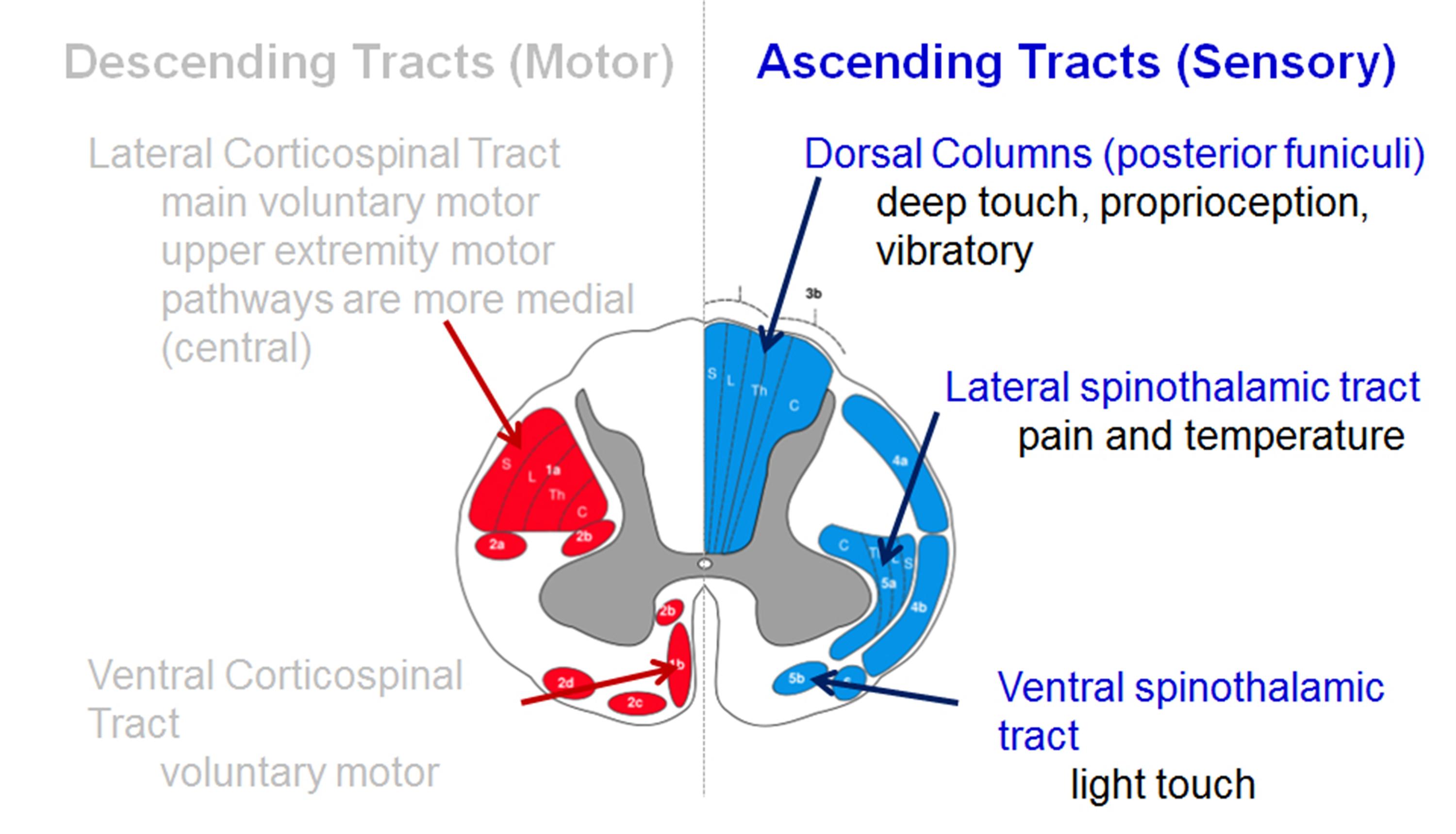 Spinal Cord Anatomy Spine Orthobullets
Spinal Cord Anatomy Spine Orthobullets
 What Is The Spinal Cord What Is Its Anatomy And Function
What Is The Spinal Cord What Is Its Anatomy And Function



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar