Tube leading to the lungs esophagus. Start a free trial of quizlet plus by thanksgiving lock in 50 off all year try it free ends in 03d 09h 29m 56s.
Lecture On Frog Anatomy Bucal Cavity External Biology
They can detect high pitched sounds with their ears and low pitched sounds through their skin.

External anatomy of a frog. Many frogs have patterned skin on their dorsal side and a white or yellow ventral side to camouflage them in their aquatic habitat. Front attached aids in grabbing prey tympanic membrane. Tail is absent fig.
A diagram showing the external anatomy of a frog. Choose from 500 different sets of frog external anatomy flashcards on quizlet. Functions of the external anatomy of the frog.
Internal nares nostrils breathing connect to lungs eustachian tubes. Equalize pressure in inner ear glottis. Frogs can detect predators and prey using their large eyes that protrude from their head.
In this article we will discuss about the external anatomy of a frog explained with the help of suitable diagrams. The frog breathes and vocalizes with the glottis. Clear eyelid protects the eye.
Use your probe to open the glottis and compare that opening to the esophagus. Frog internal and external anatomy. They also have a highly developed sense of sight and smell.
Cloacal opening opening of cloaca through which undigested food urine eggs and sperm are passed. Nictitating membrane a transparent part of a frogs lower eyelid that moves over the eye to clean it and protect it. Tube leading to the stomach tongue.
The body is divisible into two partsthe posterior short and stout trunk and the anterior broad depressed head. The vomerine teeth are found on the roof of the mouth. Look at how each limb of the frog contributes to its everyday movement in life.
Nictitating membrane a transparent part of a frogs lower eyelid that moves over the eye to clean it and protect it. Anatomy of the frogs mouth. Frog anatomy and dissection.
The frog has two sets of teeth. Our frog can be divided into the dorsal or top side and the ventral or bottom side. There is no neck between the head and the trunk.
Frogs have two forelimbs in the front or anterior end and two powerful hind limbs in the rear. Cloacal opening opening of cloaca through which undigested food urine eggs and sperm are passed. Dorsalthe back or upper surface of an organism ventralthe stomach or lower surface of an organism anteriorhead end of an organism posteriortail end of an organism.
Eardrum located behind eyes nictitating membrane. External anatomy of a frog 1. Frogs have a highly developed sense of hearing.
This slit is the glottis and it is the opening to the lungs.
 Parts Of The External Anatomy Of A Frog Brainly In
Parts Of The External Anatomy Of A Frog Brainly In
Dissections Serra Kimsey S Digital Portfolio
 Circulation Anatomy Of The Frog Diagram
Circulation Anatomy Of The Frog Diagram
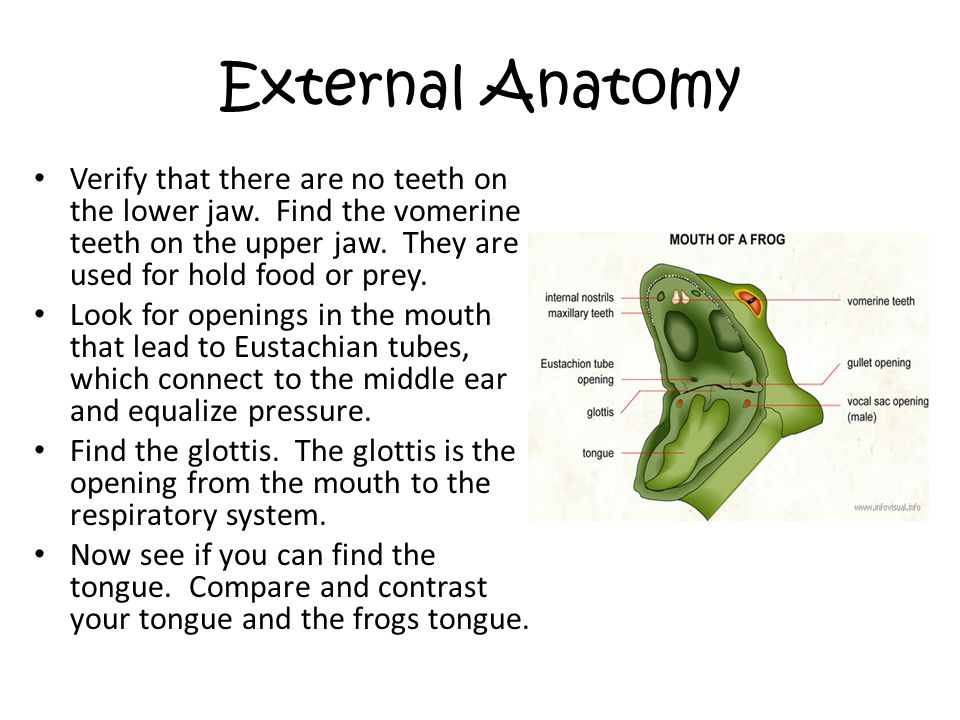 Frog Dissection Northridge Middle School Ppt Video Online
Frog Dissection Northridge Middle School Ppt Video Online
 Chapter 4 7 Frog Anatomy Lab Activity
Chapter 4 7 Frog Anatomy Lab Activity
 The Anatomy Of The Frog Frogs Anatomy Amphibians
The Anatomy Of The Frog Frogs Anatomy Amphibians
 Vertebrates External Anatomy Book Set 5 Book Set Including
Vertebrates External Anatomy Book Set 5 Book Set Including
 Frog Morphology Anatomy Body Systems With Questions And
Frog Morphology Anatomy Body Systems With Questions And
Toad Habitat Structure And Life History Amphibians
Lab 19h Frog Dissection Safety
 Frog Morphology Anatomy Body Systems With Questions And
Frog Morphology Anatomy Body Systems With Questions And
 Frog External Anatomy Handouts Reference For 9th 12th
Frog External Anatomy Handouts Reference For 9th 12th
 Frog Anatomy Labeling External Anatomy 1 Diagram Quizlet
Frog Anatomy Labeling External Anatomy 1 Diagram Quizlet
 Frog Dissection Biology Junction
Frog Dissection Biology Junction
 Science Source Frog Anatomy Illustration
Science Source Frog Anatomy Illustration
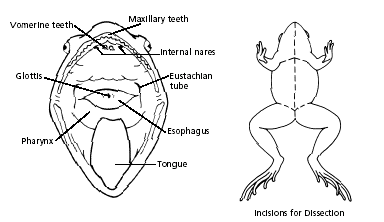 Frog Dissection Biology Junction
Frog Dissection Biology Junction
 Frog Dissections Starkville Science Club
Frog Dissections Starkville Science Club





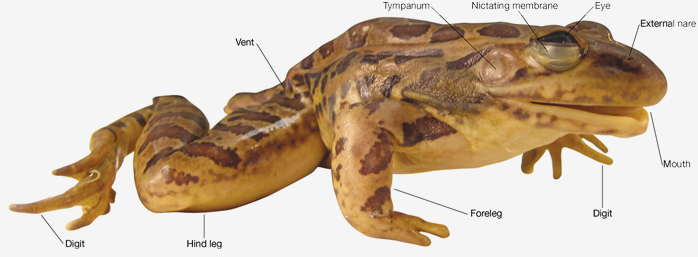



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar