A bronchus is a passage or airway in the respiratory system that conducts air into the lungs. The primary bronchi have cartilage and a mucous membrane that are similar.
 Anatomy Lectures Thorax Bronchial Tree And Trachea
Anatomy Lectures Thorax Bronchial Tree And Trachea
Think of them as highways for gas exchange with oxygen going to the lungs and carbon dioxide leaving the lungs through them.

Anatomy of the bronchi. It enters the root of the left lung opposite the sixth thoracic vertebra. The left bronchus bronchus sinister is smaller in caliber but longer than the right being nearly 5 cm. This initial division is into secondary or lobar bronchi but subsequent divisions give rise to smaller and smaller bronchi and bronchioles until the smallest bronchioles connect to the innumerable alveoli.
Location structure and anatomy. A bronchus which is also known as a main or primary bronchus. The bronchi function as a passageway for air to travel from the mouth and trachea.
They are part of the conducting zone of the respiratory system. The bronchi are made up of smooth muscles with walls of cartilage giving them stability. The mucus is an important air purifier.
The bronchi become smaller the closer they get to the lung tissue and are then considered bronchioles. The bronchi are located in the thoracic cavity 3 along with the trachea and lungs. The alveoli are responsible for the primary function of the lungs which is exchanging carbon dioxide and oxygen.
The first bronchi to branch from the trachea are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus also known as the primary bronchi. Nerve supply is autonomic from the pulmonary plexus at the hilum. Several medical conditions can involve the bronchi.
The bronchi are supplied by the bronchial arteries from the aorta and drained by the azygos vein on the right and the hemiazygos vein on the left. These passageways then evolve into tiny air sacs called alveoli which is the site of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange in the respiratory system. The bronchi singularly known as a bronchus are extensions of the windpipe that shuttle air to and from the lungs.
A layer of protective mucus called a mucus blanket covers a large portion of the membrane lining the bronchial tree. The next step is through the trachea which carries the air to the left and right bronchus. Each segment has its own pulmonary arterial branch and thus the bronchopulmonary segment is a portion.
No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi. It divides into two branches for the middle and lower lobes. What are the bronchi.
It originates from the lower end of the trachea or windpipe where it divides or bifurcates at the point of carina into the left and right bronchus 4. The bronchus now passes below the artery and is known as the hyparterial branch. There is also some drainage via the bronchial and pulmonary veins which contributes to physiological shunt.
Lung Anatomy And Structure Infographic Lifemap Discovery
 Respiratory System Bronchiole And Bronchi Diaphragm Trachea
Respiratory System Bronchiole And Bronchi Diaphragm Trachea
 Terminal Bronchi And Alveoli Anatomy Pictures And Information
Terminal Bronchi And Alveoli Anatomy Pictures And Information
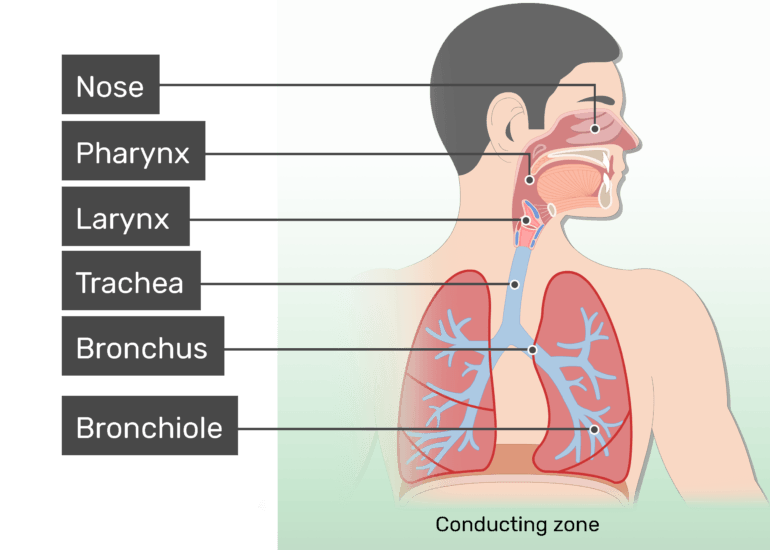 Respiratory System Anatomy Major Zones Divisions
Respiratory System Anatomy Major Zones Divisions
 Respiratory System Medical Biology Illustrated Notes
Respiratory System Medical Biology Illustrated Notes
 Development And Functional Anatomy Of The Lungs And Airways
Development And Functional Anatomy Of The Lungs And Airways
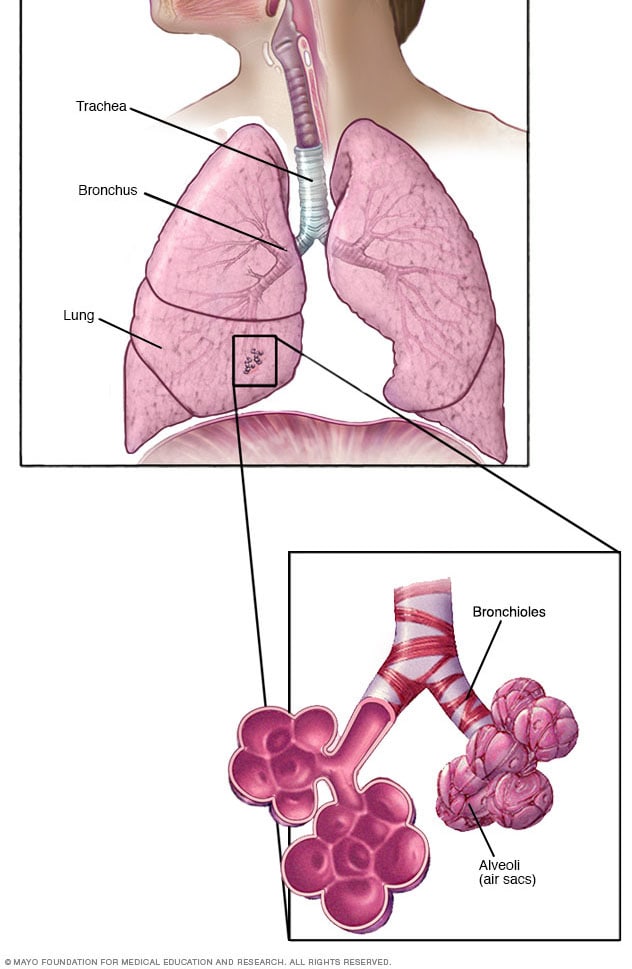 Bronchioles And Alveoli In The Lungs Mayo Clinic
Bronchioles And Alveoli In The Lungs Mayo Clinic

:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/546/zWA0X5wEg7ZQlmH0j4Xzgg_the-trachea_english.jpg) Bronchi Anatomy Function And Histology Kenhub
Bronchi Anatomy Function And Histology Kenhub
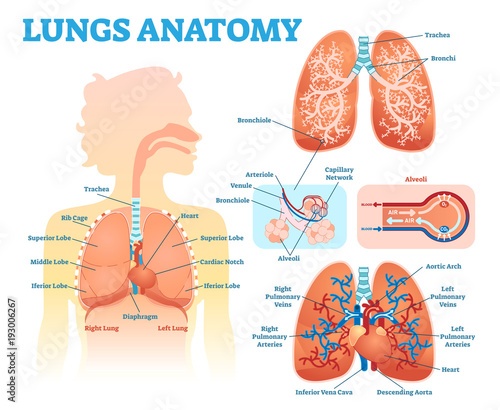 Lungs Anatomy Medical Vector Illustration Diagram Set With
Lungs Anatomy Medical Vector Illustration Diagram Set With
 Figure 3 Anatomy Development And Physiology Of The Lungs
Figure 3 Anatomy Development And Physiology Of The Lungs
 Normal Anatomy Of The Chest Chest Radiology The
Normal Anatomy Of The Chest Chest Radiology The
 Anatomy And Physiology Lungs Bronchi Trachea Nose
Anatomy And Physiology Lungs Bronchi Trachea Nose
 Anatomy Of The Trachea Carina And Bronchi Sciencedirect
Anatomy Of The Trachea Carina And Bronchi Sciencedirect
 Anatomy Of The Trachea Primary Bronchi Diagram Quizlet
Anatomy Of The Trachea Primary Bronchi Diagram Quizlet
 The Respiratory System Diagram Structure Function
The Respiratory System Diagram Structure Function

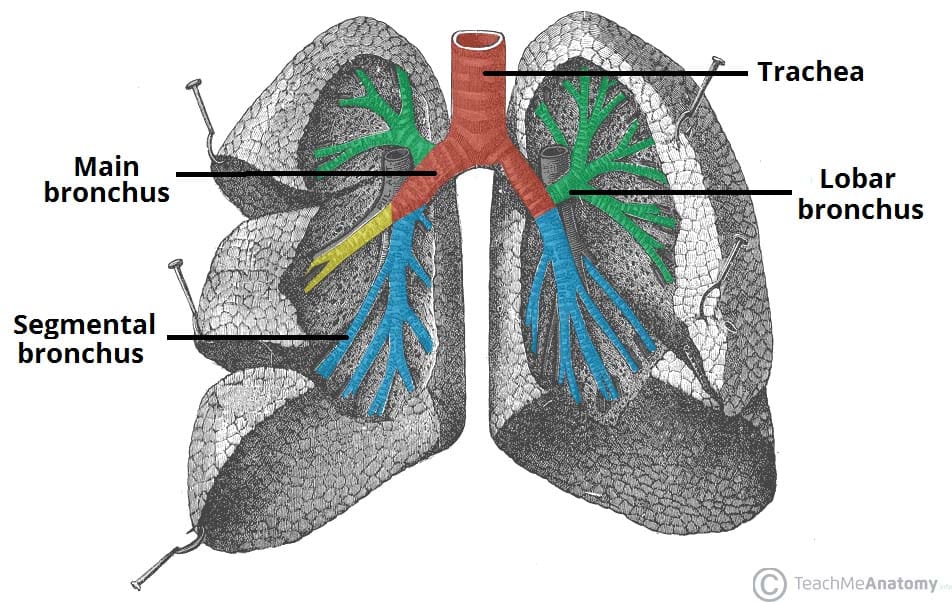 The Tracheobronchial Tree Trachea Bronchi Teachmeanatomy
The Tracheobronchial Tree Trachea Bronchi Teachmeanatomy
 Bronchial Tree Left Main Bronchus Human Anatomy Stock
Bronchial Tree Left Main Bronchus Human Anatomy Stock
 Bronchi Anatomy Respiratory System Anatomy Respiratory
Bronchi Anatomy Respiratory System Anatomy Respiratory
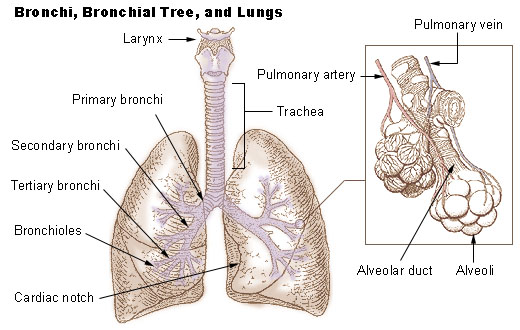 Seer Training Bronchi Bronchial Tree Lungs
Seer Training Bronchi Bronchial Tree Lungs
 Anatomy Of Trachea Bronchi Pleura And Lungs
Anatomy Of Trachea Bronchi Pleura And Lungs




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar