When the biceps contracts it pulls the forearm up and rotates it outward. In general muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm perform flexion at the wrist and fingers and pronation.
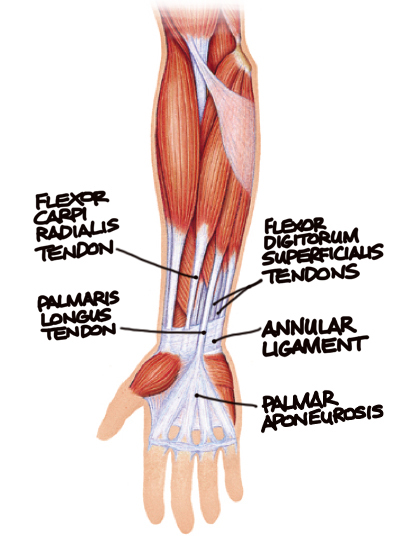 Human Anatomy For The Artist The Ventral Forearm What Are
Human Anatomy For The Artist The Ventral Forearm What Are
Lesson on the anatomy of the forearm.
Forearm anatomy tendons. The tear creates swelling and pressure on the tendon which leads to inflammation and tendonitis. Superficial compartment the superficial muscles in the anterior compartment are the flexor carpi ulnaris palmaris longus flexor carpi radialis and pronator teres. It then travels around a prominent part of the radius bone that acts like a pulley.
Damage to these tendons called tendinitis or tendinopathy often occurs with overuse of your forearm muscles. Its muscle belly is in the forearm and the tendon travels along the wrist and enters the third compartment of the band that holds the tendons in position at the wrist. The third main cause is age.
This is lesson 1 on the anatomy of the forearm. The radial artery in the lower part of the forearm lies between the tendon of this muscle and the brachioradialis. The tendon is inserted into the base of the second metacarpal bone and sends a slip to the base of the third metacarpal bone.
In this lesson we look at the muscles and tendons of both the anterior and. The tendons that connect the biceps muscle to the shoulder joint in two places are called the proximal biceps tendons. It is a strong but flexible ligament that connects the radius and the ulnathe two bones that make up the lower arm.
The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb but which in anatomy technically means only the region of the upper arm. The tendon that attaches the biceps muscle to the forearm bones radius and ulna is called the distal biceps tendon. Forearm tendonitis often occurs when the forum tendon or muscle is torn.
Forearm tendonitis is inflammation of the tendons of the forearm. The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The forearm is the part of your arm between the wrist and elbow.
Tendons connect muscles in your forearm to the bones in your wrist and elbow. Tendons are soft bands of connective tissue that attach muscles. The interosseous membrane increases stability between the two bones but also allows for pronationtwisting of the lower arm.
As the human body ages the tendons lose their elasticity and become brittle. The ligament of the forearm is called an interosseous membrane.
 Forearm Pain Relief Cause And Treatment Deep Recovery
Forearm Pain Relief Cause And Treatment Deep Recovery
Anatomy Stock Images Forearm Musculus Extensor Carpi
 Anatomy Hands Forearm Tendon Print Sra3 12x18 Conqueror Laid Paper
Anatomy Hands Forearm Tendon Print Sra3 12x18 Conqueror Laid Paper
 Anatomy Muscular System Hand Forearm Palm Stock Vector
Anatomy Muscular System Hand Forearm Palm Stock Vector
 The Muscles Of The Arm And Hand Anatomy Medicine Com
The Muscles Of The Arm And Hand Anatomy Medicine Com
 1867 Masse Human Anatomy Print Forearm Hand Fingers
1867 Masse Human Anatomy Print Forearm Hand Fingers
 Video Forearm Anatomy And Flexor Muscle Myofascial Release
Video Forearm Anatomy And Flexor Muscle Myofascial Release
 Forearm Pain Relief Cause And Treatment Deep Recovery
Forearm Pain Relief Cause And Treatment Deep Recovery
Anatomy 101 Elbow Tendons The Handcare Blog
 Bicep Tendon Tears Injuries Glenelg Orthopaedics
Bicep Tendon Tears Injuries Glenelg Orthopaedics
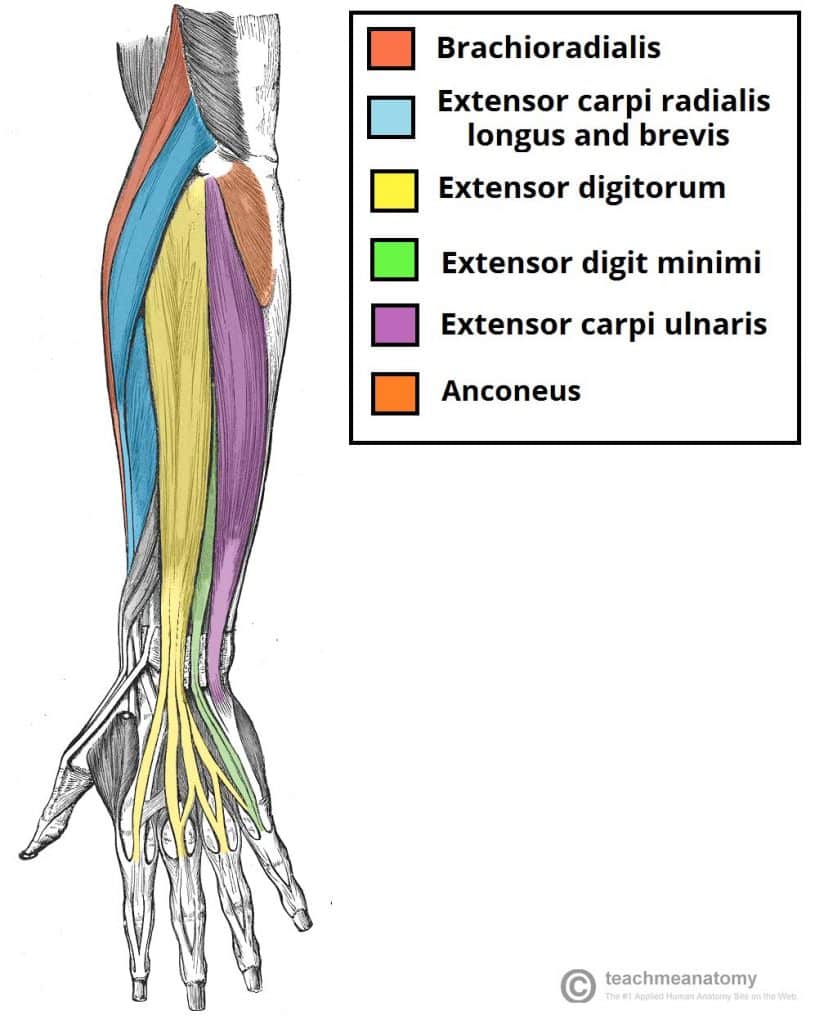
 Anatomy Of Muscular System Hand Forearm Palm Muscle
Anatomy Of Muscular System Hand Forearm Palm Muscle
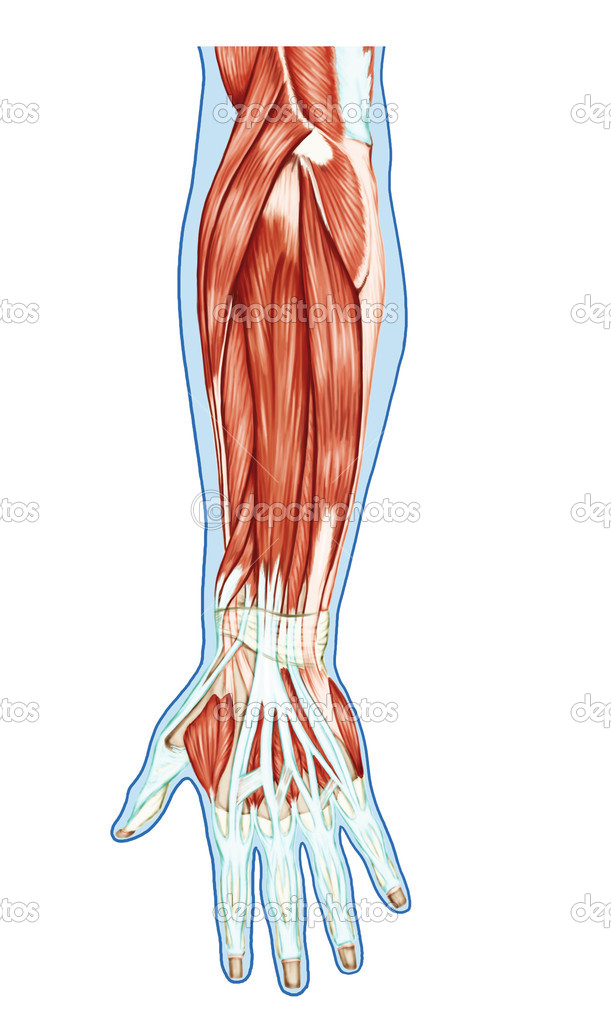
 Muscles Of The Posterior Forearm Superficial Deep
Muscles Of The Posterior Forearm Superficial Deep
 Forearm Pain A New Treatment For An Old Problem Drum
Forearm Pain A New Treatment For An Old Problem Drum
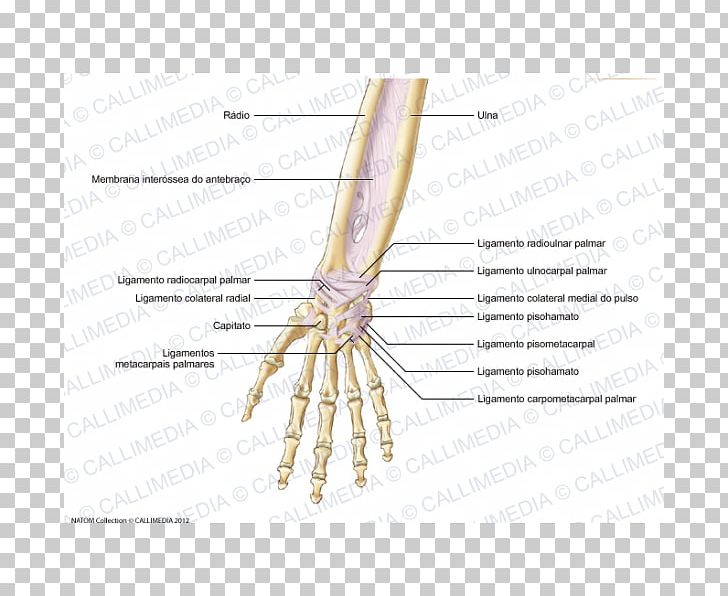 Finger Ligament Forearm Anatomy Tendon Png Clipart Anatomy
Finger Ligament Forearm Anatomy Tendon Png Clipart Anatomy
 Elbow Forearm Tendon Ligament Tear Health Life Media
Elbow Forearm Tendon Ligament Tear Health Life Media
 Arm Muscle Anatomy 3d Medical Vector Illustration Forearm
Arm Muscle Anatomy 3d Medical Vector Illustration Forearm
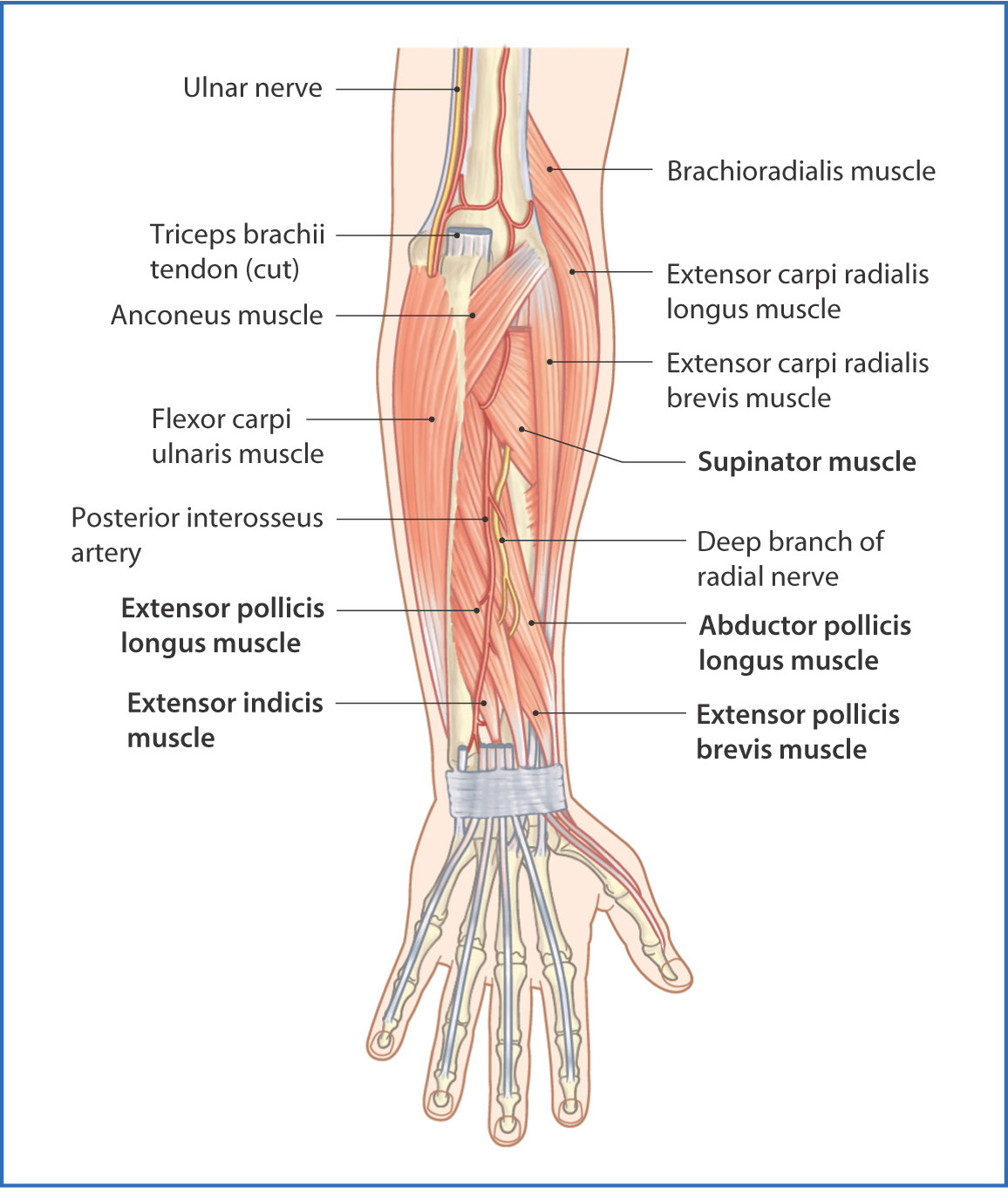 Posterior Forearm Basicmedical Key
Posterior Forearm Basicmedical Key
 Arm Vertebrate Anatomy Britannica
Arm Vertebrate Anatomy Britannica
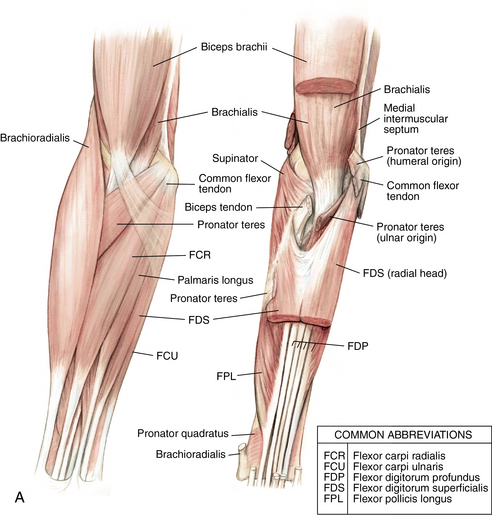 Elbow And Forearm Musculoskeletal Key
Elbow And Forearm Musculoskeletal Key
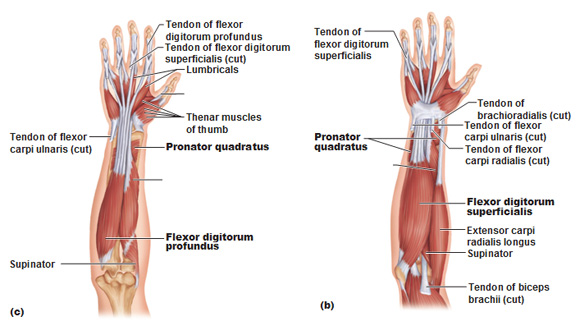
 Human Anatomy For The Artist The Dorsal Forearm Part 2
Human Anatomy For The Artist The Dorsal Forearm Part 2

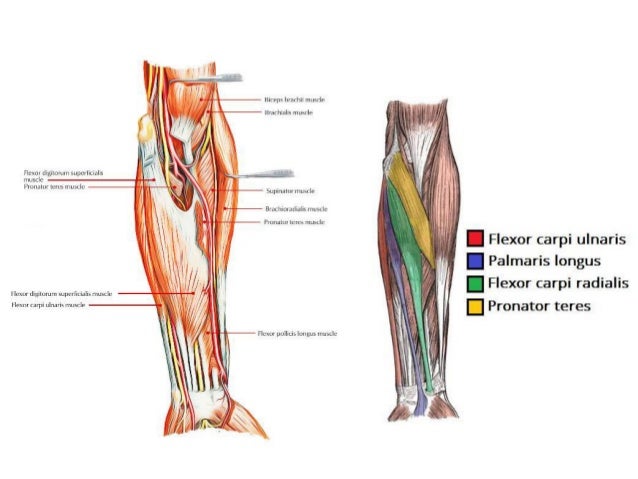
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar