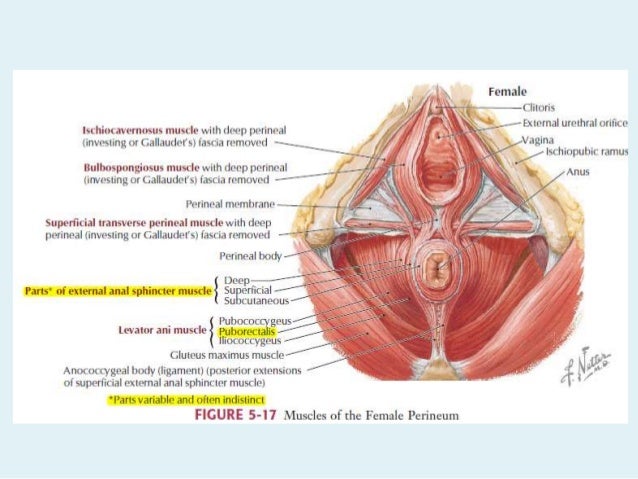
Beyond the verge traveling outwards for 2 inches is the perianal skin. Structure the upper 23 has longitudinal folds or elevations of tunica mucosa.
This is followed by the anal canal which leads to the anal verge which is the junction on the outside of the anus of hair bearing and non hair bearing skin similar to the junction of the lip of the mouth with the skin of the face.
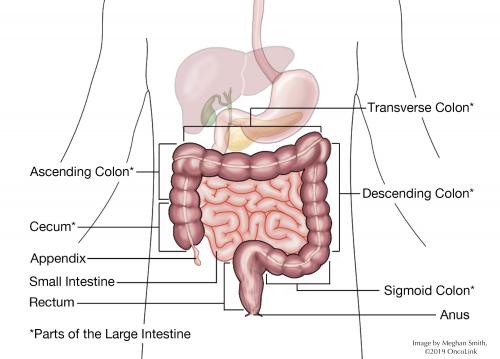
Anal anatomy. It has an important role in defecation and maintaining faecal continence. In surgical usage however the anal canal is frequently limited to that part of the intestine below the pectinate line. The description in this topic is from below upwards as that is how this region is usually examined in clinical practice.
Anus tests physical examination. Its diameter is narrower than that of the rectum to which it connects. An endoscope is inserted into the anus and the entire colon is viewed to look.
The rectum is a part of the lower gastrointestinal tract. The lower third of the anal canal is supplied by. This part differs from the part above the pectinate line in several respects including innervation.
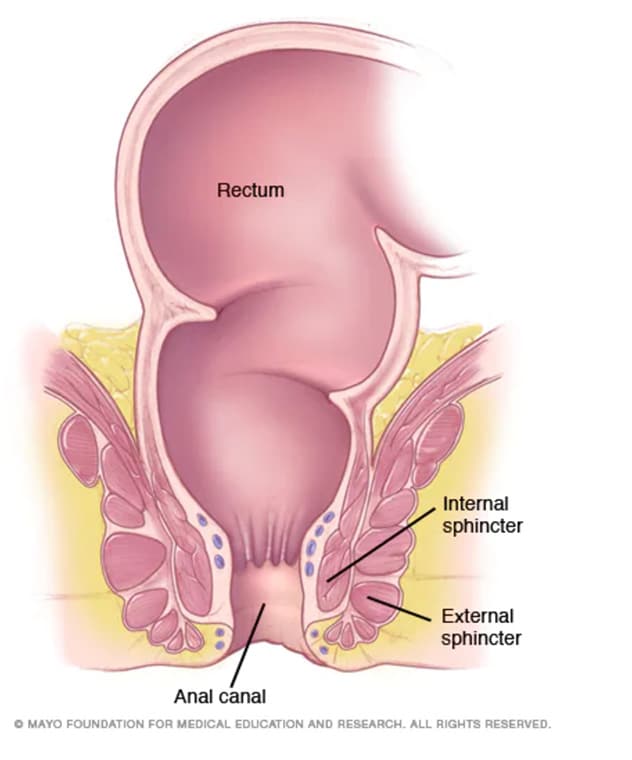
The lower 13 of the anal canal is lined by stratified squamous epithelium that blends with the skin. The anal canal is the final segment of the gastrointestinal tract. A doctor may inspect the outside of the anus.
Anal canal the terminal portion of the digestive tract distinguished from the rectum because of the transition of its internal surface from a mucous membrane layer endodermal to one of skinlike tissue ectodermal. An endoscope flexible tube with a lighted camera on its tip is inserted into. The anal canal is the most terminal part of the lower gi tractlarge intestine which lies between the anal verge anal orifice anus in the perineum below and the rectum above.
The rectum follows the shape of the sacrum and ends in an expanded section called the rectal ampulla where feces are stored before their release via the anal canal. Anatomy of the anus. The anal canal is 25 to 4 cm 1 to 15 inches in length.
Anatomically the anal canal extends from the level of the upper aspect of the pelvic diaphragm to the anus. In this article we shall look at the anatomy of the anal canal its position structure relations and neurovascular supply. Its mucosa is lined by simple columnar epithelium.
The rectum is a continuation of the sigmoid colon and connects to the anus.
 Common Anorectal Conditions Part I Symptoms And Complaints
Common Anorectal Conditions Part I Symptoms And Complaints
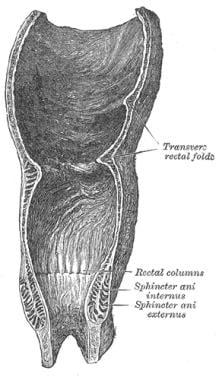 Anal Canal Anatomy Gross Anatomy Tissue Nerves And
Anal Canal Anatomy Gross Anatomy Tissue Nerves And
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/262/wqpUdLqhtEXC6xRG0BfAZg_male-pelvic-viscera-and-perineum_english.jpg) Anal Canal Anatomy Histology And Function Kenhub
Anal Canal Anatomy Histology And Function Kenhub
 Anatomy Of The Anus Anal Cancer Information
Anatomy Of The Anus Anal Cancer Information
 Anatomy Of The Rectum And Anal Canal Sciencedirect
Anatomy Of The Rectum And Anal Canal Sciencedirect
 Anus Definition Parts Diseases And Functions In Human
Anus Definition Parts Diseases And Functions In Human
Digestive Diseases Rectal Colon Diseases Cleveland Clinic
 All About Anal Cancer Oncolink
All About Anal Cancer Oncolink
 Surgical Anatomy Of The Colon Rectum And Anus Abdominal Key
Surgical Anatomy Of The Colon Rectum And Anus Abdominal Key
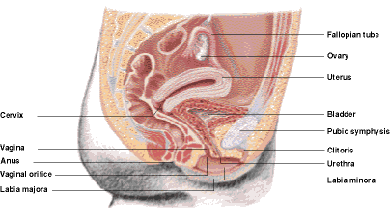 Anatomy Of The Anus Saint Luke S Health System
Anatomy Of The Anus Saint Luke S Health System
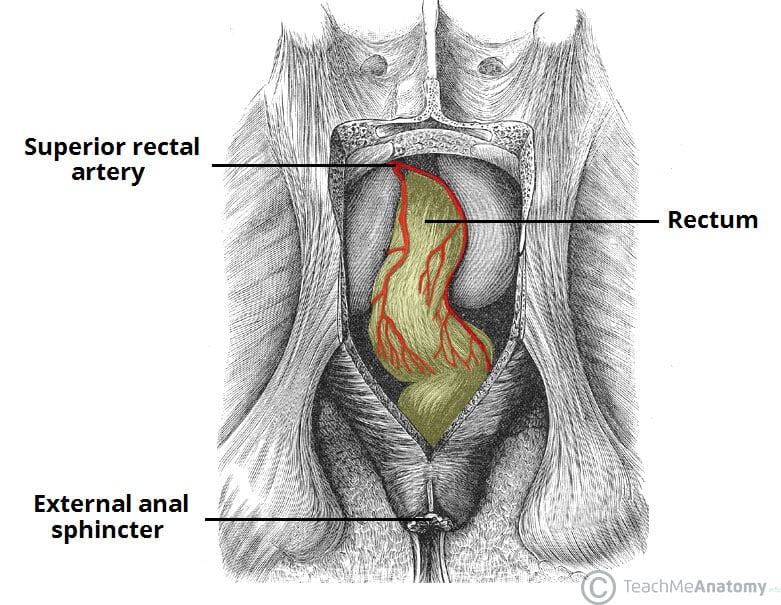 The Rectum Position Neurovascular Supply Teachmeanatomy
The Rectum Position Neurovascular Supply Teachmeanatomy
 3 Venous Drainage Of The Rectum And Anal Canal Note The
3 Venous Drainage Of The Rectum And Anal Canal Note The
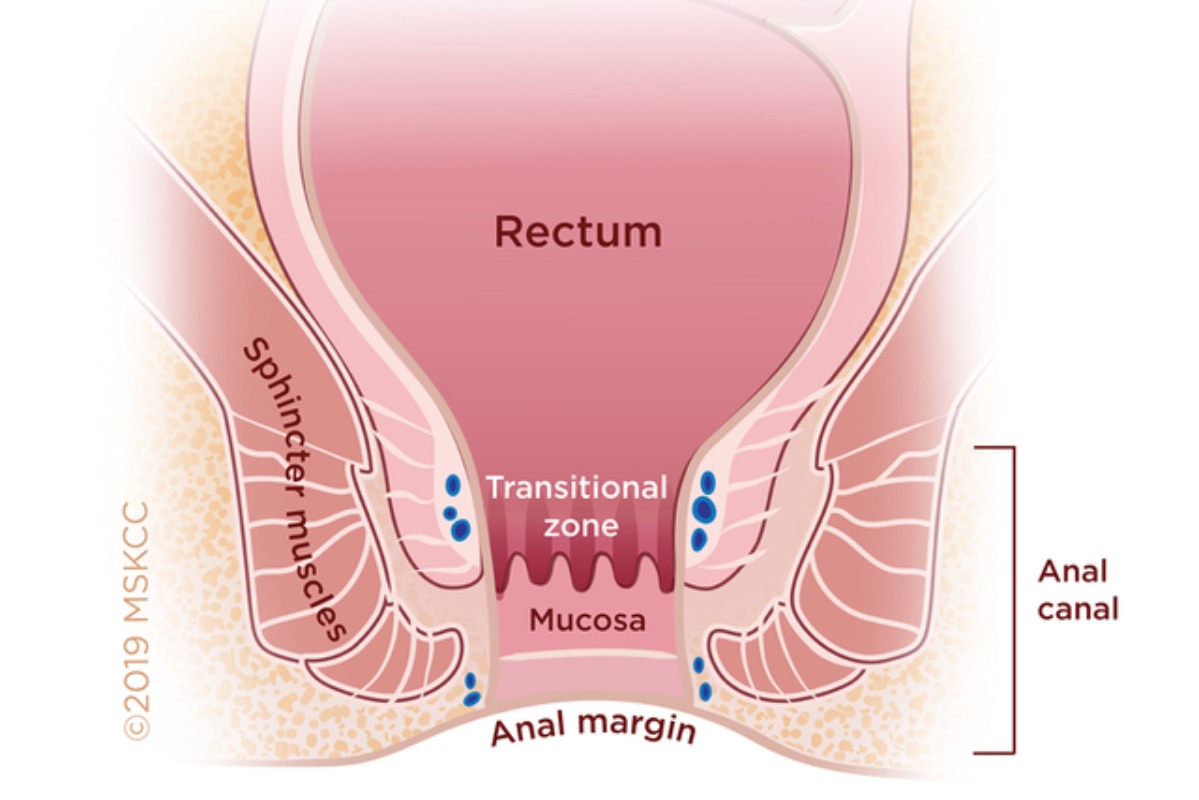 Anal Cancer Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Anal Cancer Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
 Cross Section Rectum Anal Canal Anatomy Stock Vector
Cross Section Rectum Anal Canal Anatomy Stock Vector
 What Is Anal Cancer Cancer Research Uk
What Is Anal Cancer Cancer Research Uk

Anal Dysplasia And Anal Cancer Cleveland Clinic
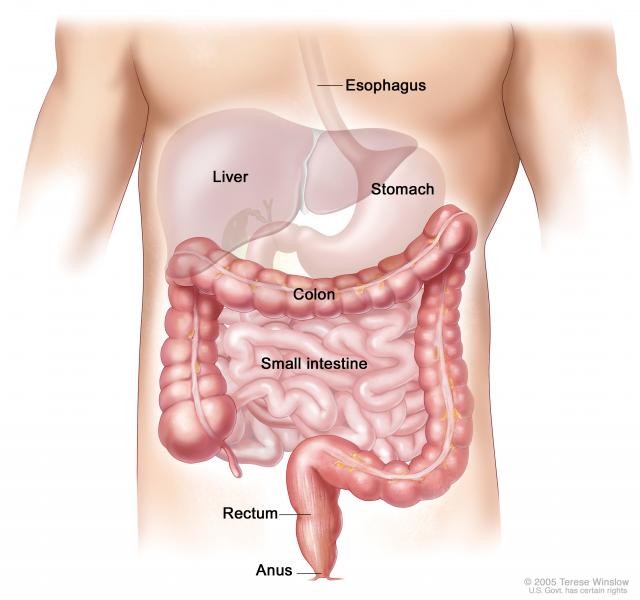 What Is The Difference Between Anal Cancer And Colon Cancer
What Is The Difference Between Anal Cancer And Colon Cancer
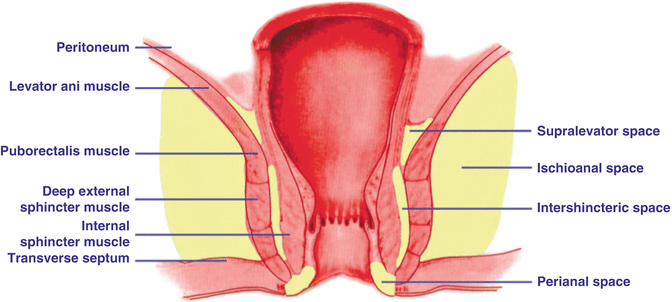 Surgical Anatomy Of Anal Canal And Rectum Springerlink
Surgical Anatomy Of Anal Canal And Rectum Springerlink
 Rectum And Anal Canal Anatomy And Function Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
Rectum And Anal Canal Anatomy And Function Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
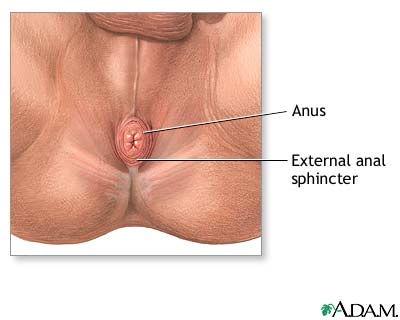 Anal Fissure Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus Medical
Anal Fissure Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus Medical

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar