Posterior muscles such as the hamstrings and gluteus maximus produce the opposite motion extension of the thigh at the hip and flexion of the leg at the knee. The peroneal muscles peroneus longus and peroneus brevis on the outside edge.
 Abductor Hallucis Muscle Wikipedia
Abductor Hallucis Muscle Wikipedia
Foot ankle anatomy muscles tendons and ligaments.

Ankle anatomy muscles. Muscles of the ankle the muscles of the foot are classified as intrinsic and extrinsic. It is made up of three joints. Thus plantarflexion and dorsiflexion are the main movements that occur at the ankle joint.
There are also multiple muscles in the ankle that can be strained as follows. Its strength and joint function facilitate running jumping walking up stairs and raising the body onto the toes. Several intrinsic muscles also help support the arches of the foot.
It begins in the thigh area and extends to the head of the fibula near the knee. This long muscle flexes the knee. The intrinsic muscles are located within the foot and cause movement of the toes and are flexors plantar flexors extensors dorsiflexors abductors and adductors of the toes.
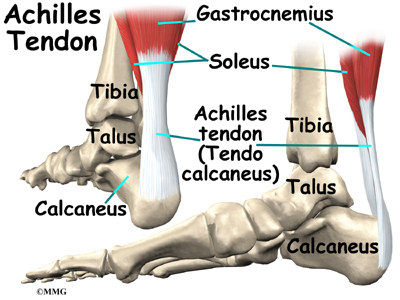
There are elastic tissues tendons in the foot that connect the muscles to the bones and joints. The largest and strongest tendon of the foot is the achilles tendon which extends from the calf muscle to the heel. Ankle anatomy the ankle joint also known as the talocrural joint allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot.
The anterior muscles such as the quadriceps femoris iliopsoas and sartorius work as a group to flex the thigh at the hip and extend the leg at the knee. It extends the thigh flexes the knee and helps rotate the tibia. The subtalar joint sits below the ankle joint and allows side to side motion of the foot.
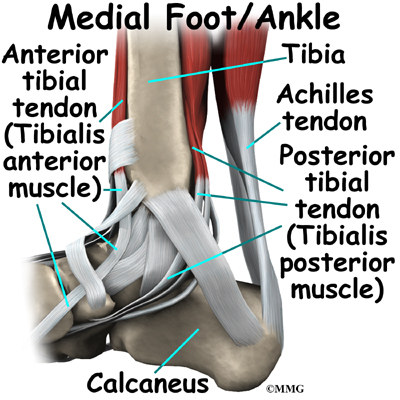
This long muscle extends from the pelvis to the tibia. The posterior tibialis muscle which supports. The foot consists of thirty three bones twenty six joints and over a hundred muscles ligaments and tendons.
The ankle joint allows up and down movement of the foot. Foot and ankle anatomy is quite complex. Upper ankle joint tibiotarsal talocalcaneonavicular and subtalar joints.
Movements and muscles involved the ankle joint is a hinge type joint with movement permitted in one plane. These all work together to bear weight allow movement and provide a stable base for us to stand and move on. The calf muscles gastrocnemius and soleus which are connected to the calcaneus via.
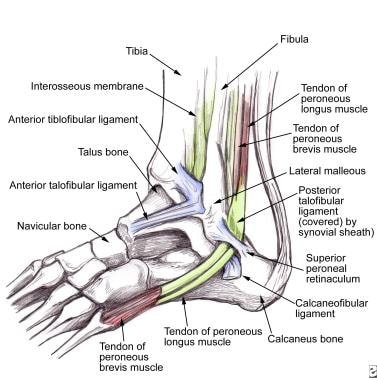 Peroneal Tendon Syndromes Practice Essentials Epidemiology
Peroneal Tendon Syndromes Practice Essentials Epidemiology
 Foot And Ankle Issues Northern Arizona Healthcare
Foot And Ankle Issues Northern Arizona Healthcare
 Snowboarding Stretches Ultimate Snowsports
Snowboarding Stretches Ultimate Snowsports
 Ankle Extensor And Flexor Muscles Acland S Video Atlas Of
Ankle Extensor And Flexor Muscles Acland S Video Atlas Of
 Arm Vertebrate Anatomy Britannica
Arm Vertebrate Anatomy Britannica
 Science Source Foot And Ankle Anatomy Medial
Science Source Foot And Ankle Anatomy Medial
 The Fasciae Around The Ankle Human Anatomy
The Fasciae Around The Ankle Human Anatomy
 Foot And Ankle Patient Education
Foot And Ankle Patient Education
 How To Work And Use Your Glute Muscles Correctly In Yoga
How To Work And Use Your Glute Muscles Correctly In Yoga
 Muscles Of The Foot Part 1 3d Anatomy Tutorial
Muscles Of The Foot Part 1 3d Anatomy Tutorial
 Foot And Leg Anatomy Essential Info For Yoga Teachers
Foot And Leg Anatomy Essential Info For Yoga Teachers
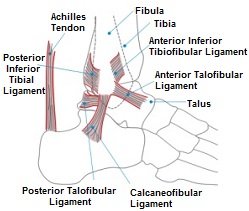 Foot And Ankle Anatomy Bones Muscles Ligaments Tendons
Foot And Ankle Anatomy Bones Muscles Ligaments Tendons
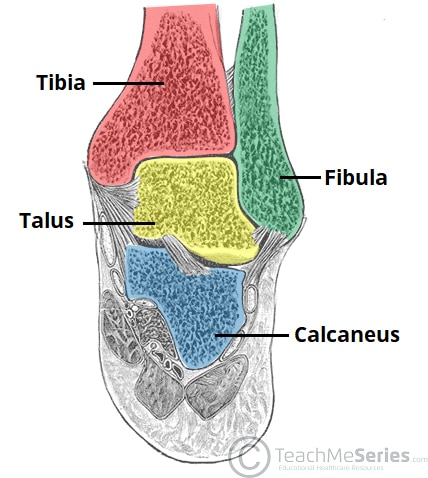 The Ankle Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The Ankle Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
 Muscular Function And Anatomy Of The Lower Leg And Foot
Muscular Function And Anatomy Of The Lower Leg And Foot
 Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
 Anatomy Of The Ankle Elliots World
Anatomy Of The Ankle Elliots World
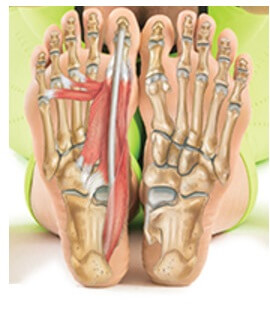 Foot And Ankle Anatomy Bones Muscles Ligaments Tendons
Foot And Ankle Anatomy Bones Muscles Ligaments Tendons
 Foot And Ankle Skeleton Model With Ligaments And Muscles
Foot And Ankle Skeleton Model With Ligaments And Muscles
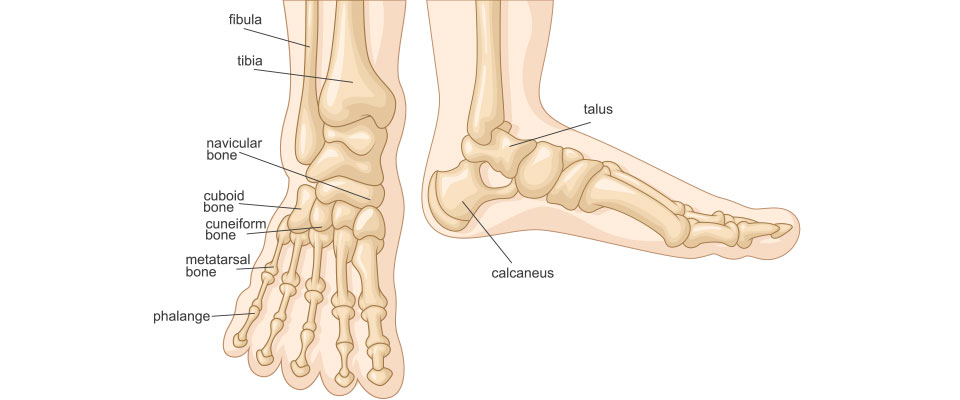 Stronger Ankles For Running Run And Become
Stronger Ankles For Running Run And Become
 Leg Muscles Anatomy Support Movement
Leg Muscles Anatomy Support Movement
 Muscle Anatomy Of The Gastrocnemius
Muscle Anatomy Of The Gastrocnemius
 Ligaments Of The Foot Muscles Tendons Ligaments Of The
Ligaments Of The Foot Muscles Tendons Ligaments Of The
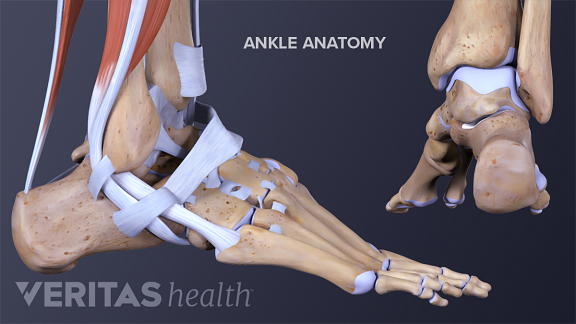 All About Ankle Sprains And Strains
All About Ankle Sprains And Strains
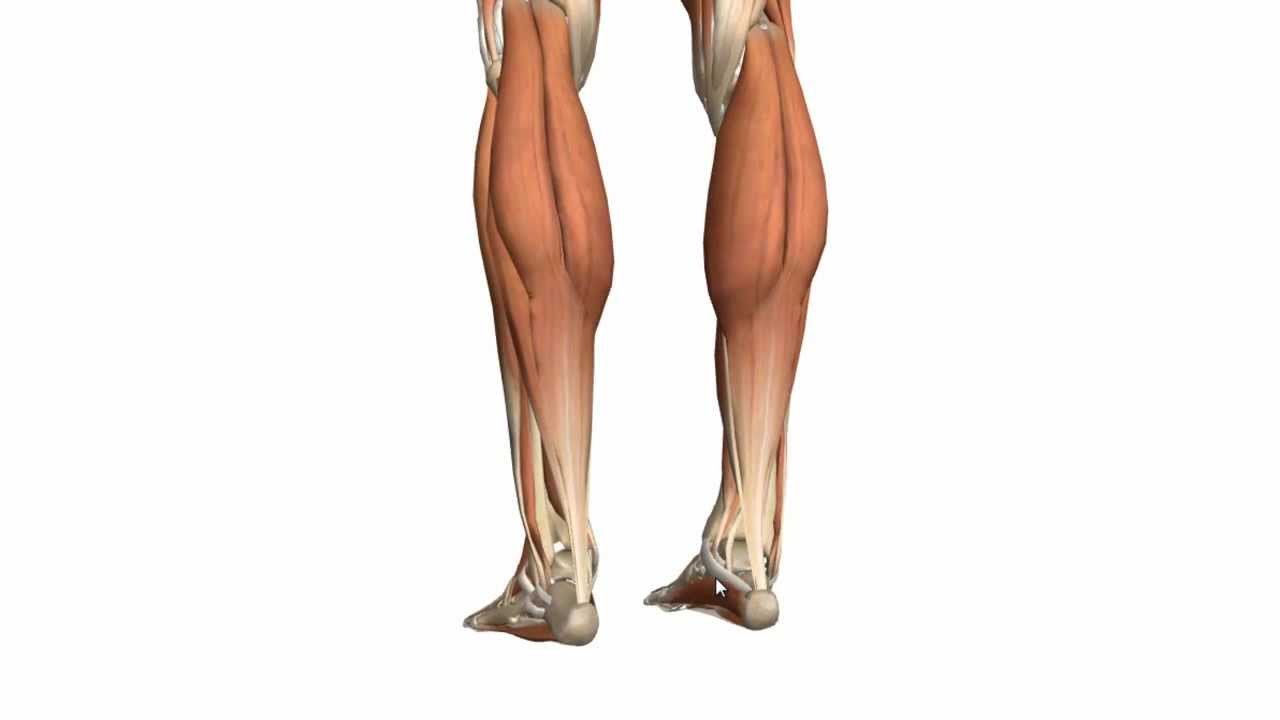 Muscles Of The Leg Part 1 Posterior Compartment Anatomy Tutorial
Muscles Of The Leg Part 1 Posterior Compartment Anatomy Tutorial
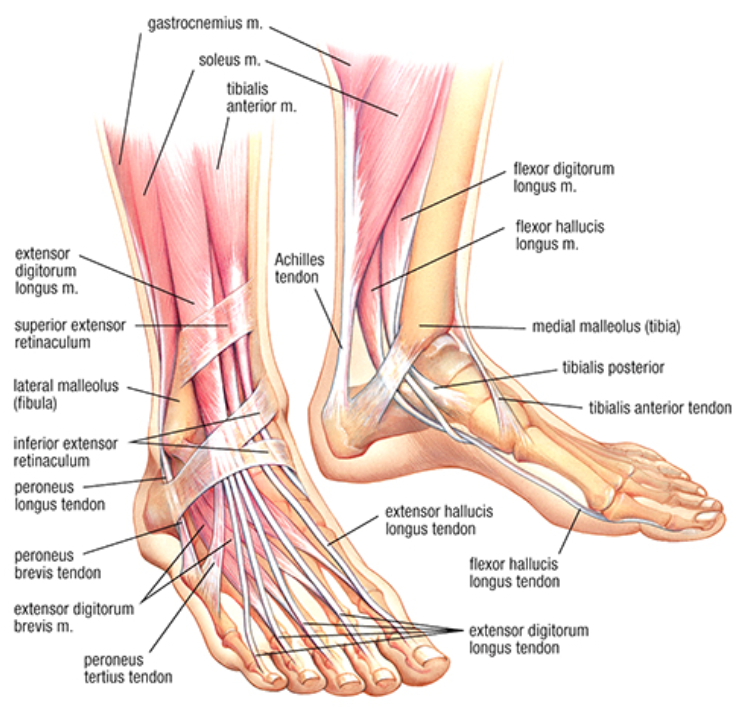 Developing Strength Stability In The Foot Ankle And
Developing Strength Stability In The Foot Ankle And
 Foot Ankle Anatomy Pictures Function Treatment Sprain Pain
Foot Ankle Anatomy Pictures Function Treatment Sprain Pain
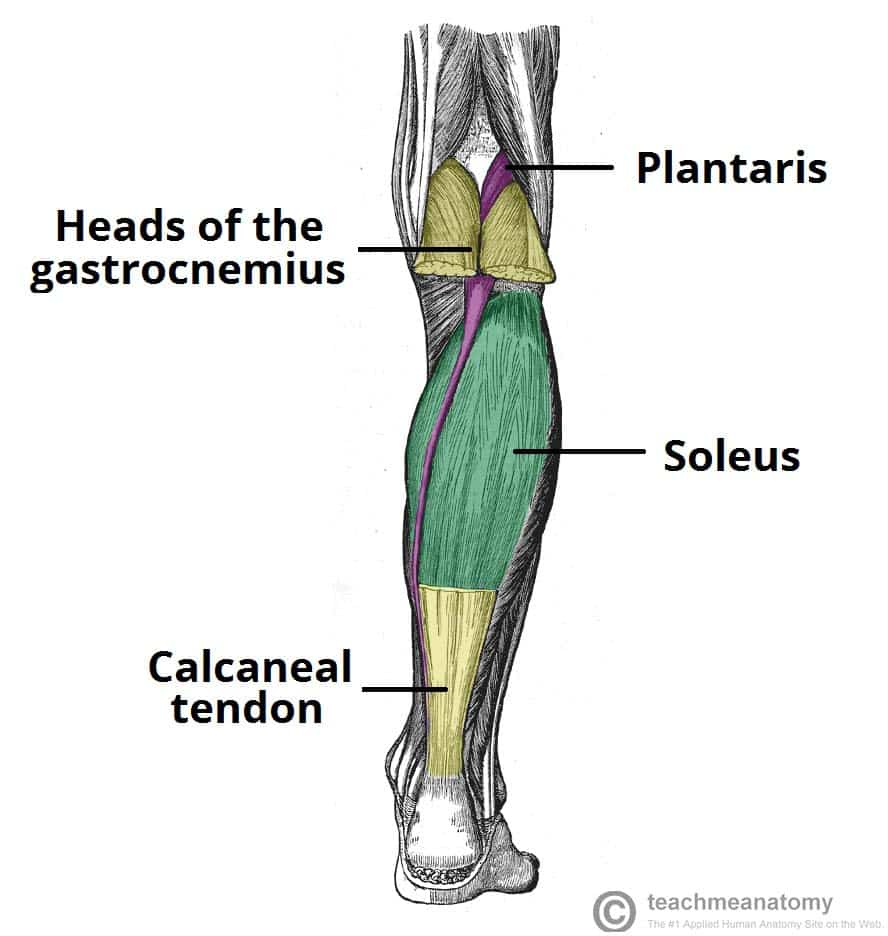 Muscles Of The Posterior Leg Attachments Actions
Muscles Of The Posterior Leg Attachments Actions


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar