Acl anterior cruciate ligament strain or tear. Ligaments in the knee.
 Monmed Life Size Human Knee Joint Model With Knee Ligament Knee Anatomy Model Anatomy Of The Knee Model With Ligaments
Monmed Life Size Human Knee Joint Model With Knee Ligament Knee Anatomy Model Anatomy Of The Knee Model With Ligaments
The kneecap slides along a groove in the femur as the knee bends.
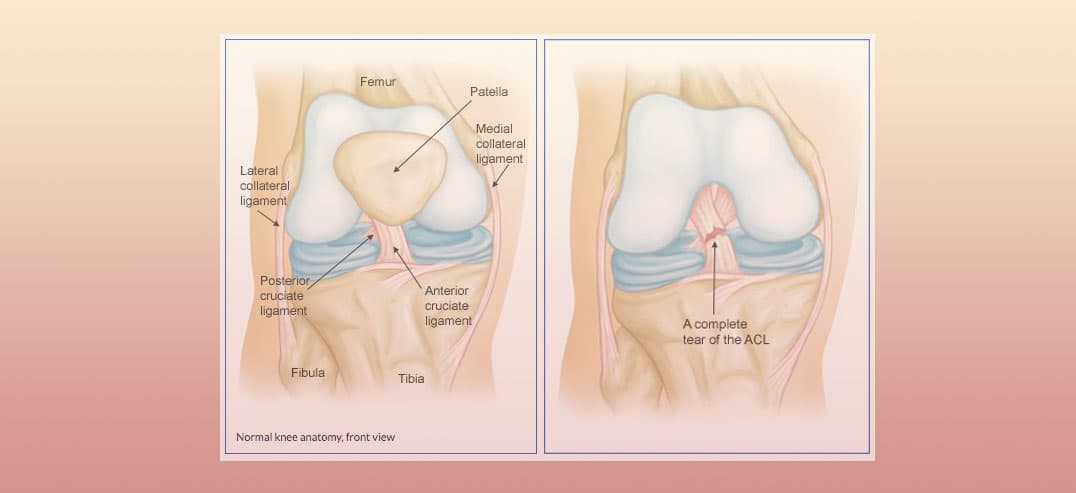
Knee anatomy ligament. Sometimes due to numerous complications the kneecap comes out of its groove and becomes dislocated. The knee includes four important ligaments all of which connect the femur to the tibia. Two groups of muscles support the knee.
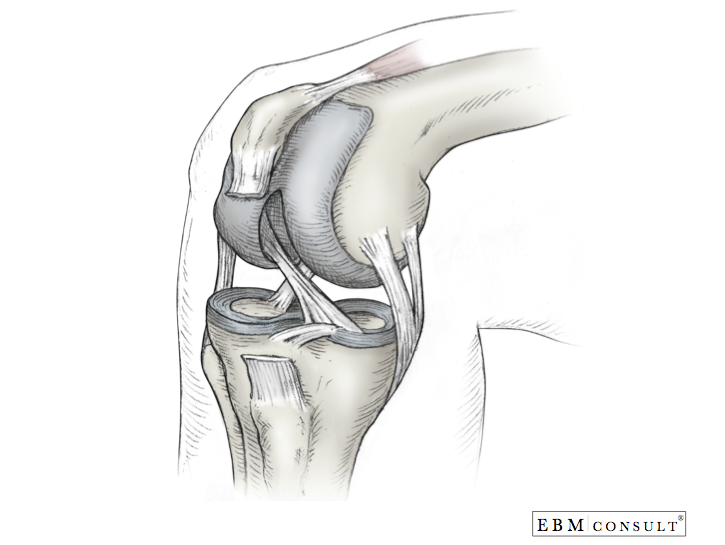
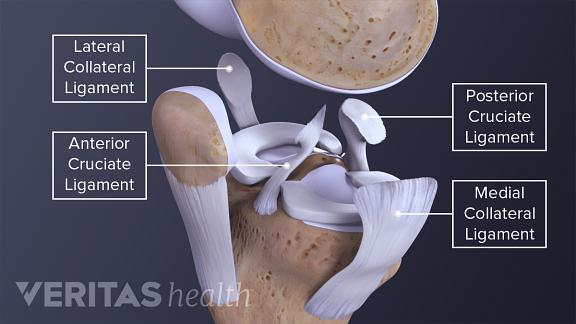
There are four knee ligaments thick bands of tough tissue that serve to maintain the stability of the knee joint. Anterior cruciate ligament acl which is located in the center of the knee and prevents excessive forward movement of the tibia. These two prevent sideways sliding of the knee joint ad also brace it against unusual movement.
Ligaments of the knee ligaments are structures that connect two bones together. Magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound have identified the ligament and linked it with the classically described segond fracture. The acl is responsible for a large part of the knees stability.
In knee joint anatomy knee ligaments are the main stabilising structures of the knee preventing excessive movements and instability. Those connect to the femur and tibia. It is held in place by a ligament at the bottom and a tendon on top.
Ligaments are strong tough bands that are not particularly flexible. It consists of bones meniscus ligaments and tendons. Once stretched they tend to stay stretched and if stretched too far they snap.
The anterior cruciate ligament and posterior cruciate ligament provide front and back anterior and. On the sides of the knee are the medial collateral ligament mcl and the lateral collateral ligament lcl. There are four major ligaments that surround the knee joint.
Pcl tears can cause pain swelling and knee instability. An acl tear often leads to the knee giving out and may require surgical repair. Two of these ligaments are in the center of the joint and they cross each other.
Knee ligament impose limitations on the movement of the knee allowing it to concentrate forces of the muscles on extension and flexion. The knee is a hinge joint that is responsible for weight bearing and movement. Ligaments are tough fibrous connective tissues which link bone to bone made of collagen.
The function of ligaments is to attach bones to bones and give strength and stability to the knee as the knee has very little stability. The proper term for this condition is patellar subluxation. While the all likely plays a role in rotational stability of the knee further studies investigating the significance of all injuries and the role of all reconstruction in combination with acl reconstruction are warranted.
Pcl posterior cruciate ligament strain or tear. Posterior cruciate ligament pcl which is located in the center of the knee and prevents excessive backward shifting of the knee. The knee is designed to fulfill a number of functions.
Adolescent Sports Injuries Of The Knee Cleveland Clinic
Anatomy Of The Knee Knee Specialist Fairfield Shelton
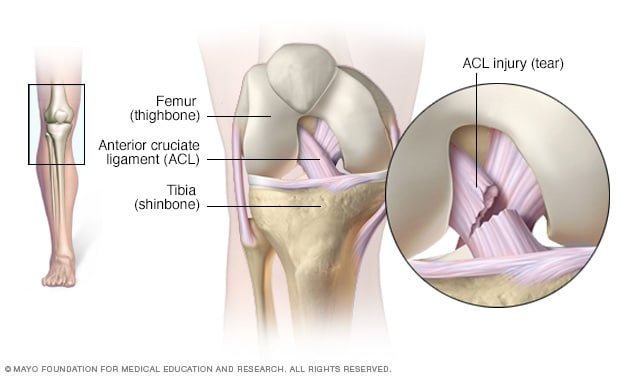 Acl Injury Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Acl Injury Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
 The Knee And Related Structures Essentials Of Athletic
The Knee And Related Structures Essentials Of Athletic
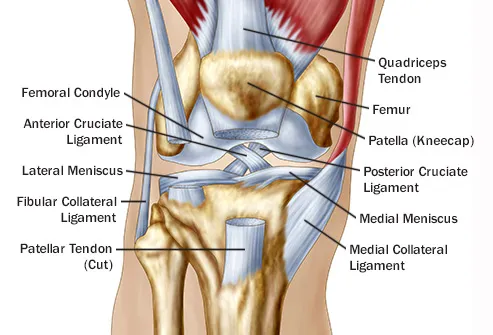 Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
 Knee Ligament Injury Anatomy Ligament Injury Knee
Knee Ligament Injury Anatomy Ligament Injury Knee
 Knee Injuries For Parents Nemours Kidshealth
Knee Injuries For Parents Nemours Kidshealth
 Figure Anatomy Of The Right Knee Download Scientific Diagram
Figure Anatomy Of The Right Knee Download Scientific Diagram
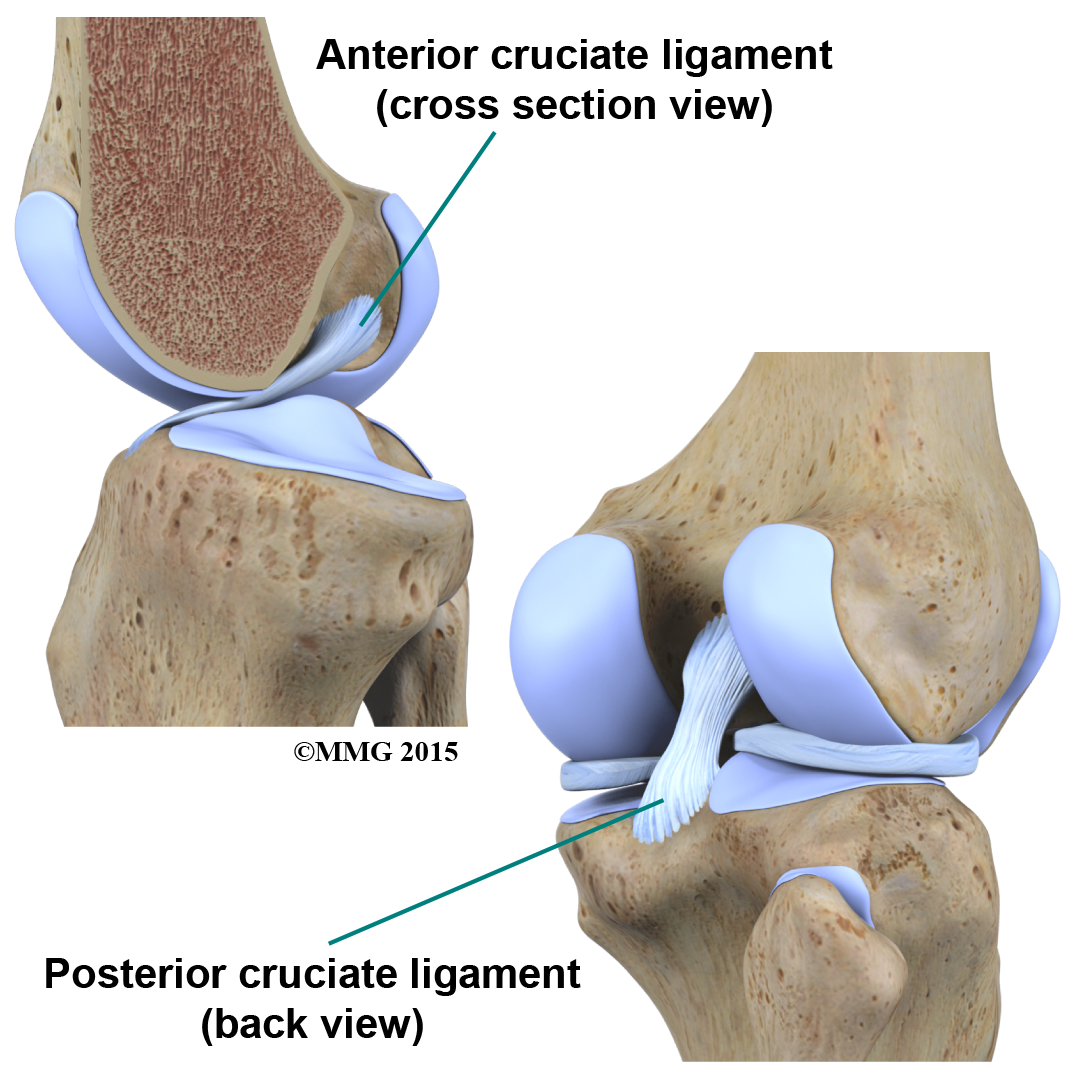 Physical Therapy In Buffalo For Knee Anatomy
Physical Therapy In Buffalo For Knee Anatomy
 14102 04b Tendons And Ligaments Of The Right Knee Anatomy
14102 04b Tendons And Ligaments Of The Right Knee Anatomy
 Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Common Knee Injuries Orthoinfo Aaos
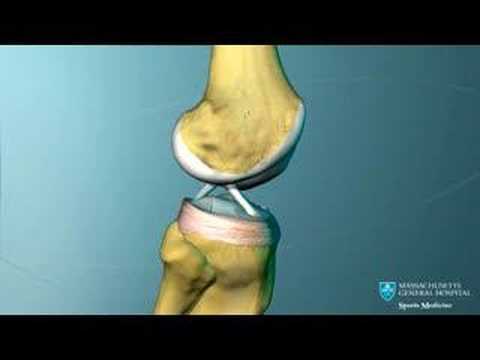 Knee Ligament Anatomy Animation
Knee Ligament Anatomy Animation
 Knee Sprain Aka Anterior Cruciate Ligament Sprain
Knee Sprain Aka Anterior Cruciate Ligament Sprain
 Popliteal Ligament An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Popliteal Ligament An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
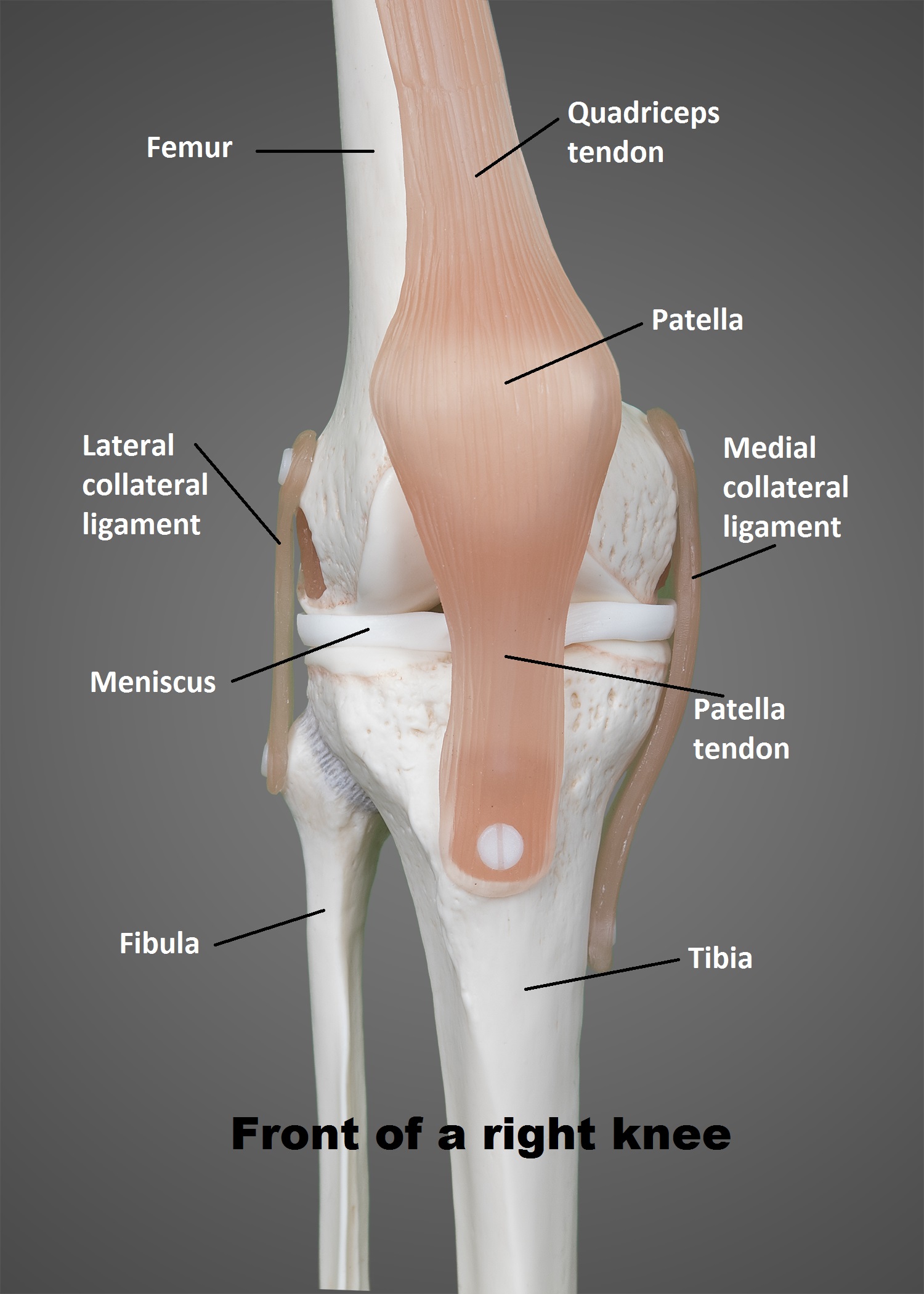 The Knee Ut Health San Antonio
The Knee Ut Health San Antonio
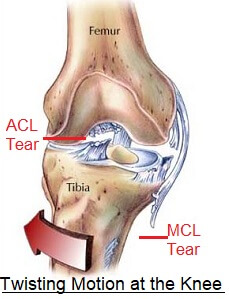 Twisted Knee Common Injuries Treatment Knee Pain Explained
Twisted Knee Common Injuries Treatment Knee Pain Explained
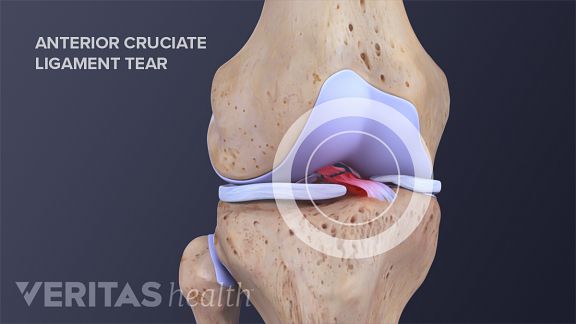 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl Tears
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl Tears
Collateral Ligament Injuries Orthoinfo Aaos
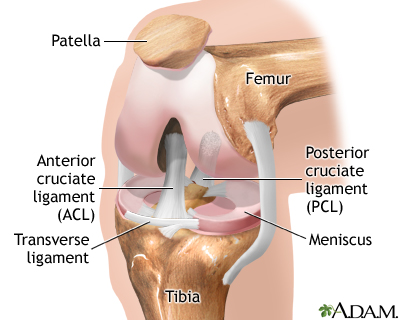 Knee Arthroscopy Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
Knee Arthroscopy Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
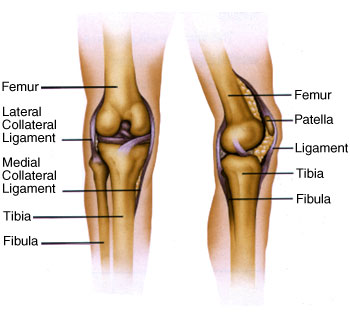 Knee Anatomy Wilmington Health
Knee Anatomy Wilmington Health
 Knee Pain On The Inside Of Your Joint Causes Solutions
Knee Pain On The Inside Of Your Joint Causes Solutions
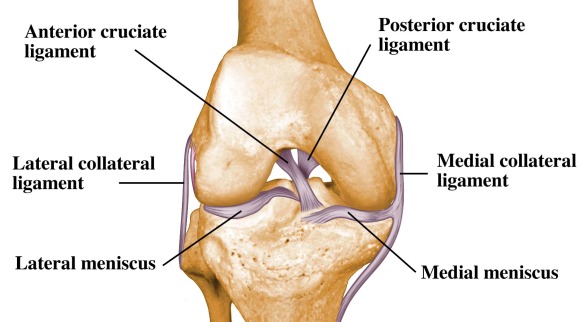
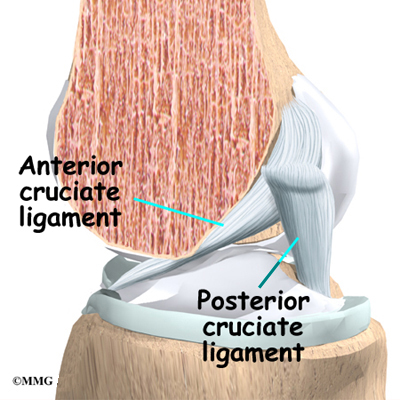
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar