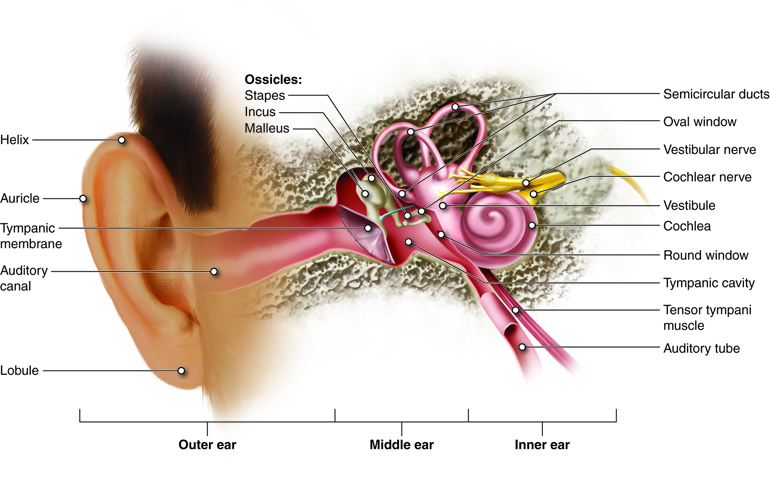
Extends from auricle to ear drum. Sound waves received amplified and transduced to action pote three parts.
Special Senses Anatomy Of The Ear Oer Commons
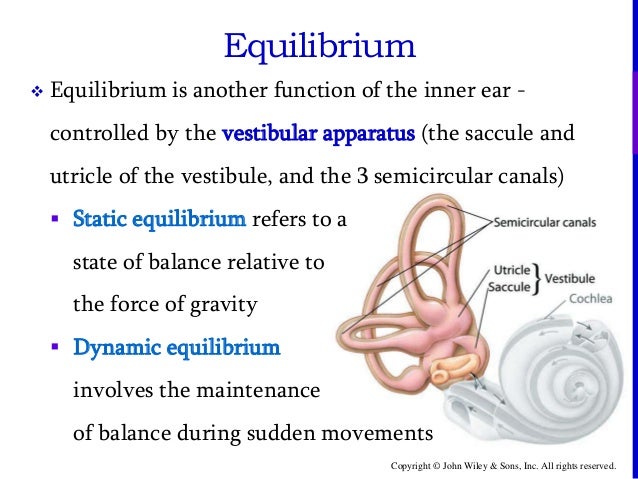
It is integrated with the equilibrium of movement or dynamic equilibrium.

Static equilibrium anatomy. Static equilibrium also known as mechanical equilibrium means the reaction has stopped. The role of the saccule is less completely understood. The organs can respond to changes in position and acceleration because the tips of their stereocilia project into a dense otolithic membrane made up of a mixture containing granules of calcium and protein called otoliths translated in medical terminology ear stones.
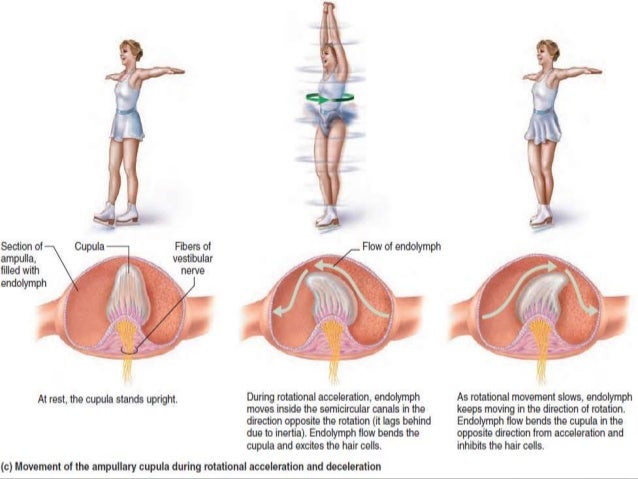
Dynamic equilibrium maintains the position of the head in response to rotational motion of the body such as rocking as in a boat or turning. Consists of the auricle external acoustic meatus and tympan elastic cartilage covered in thick skin. In other words the system is at rest.
2 functions of the vestibular apparatus. Static and dynamic equilibrium. Anatomy anatomy and physiology.
The movement at the oval window sets the fluids of the inner ear into motion exciting the receptors. The functional components of the membranous labyrinth involved in the sensations of static and dynamic equilibrium are a system of thin walled intercommunicating tubes and ducts situated within the petrous part of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. The ability of an individual to adjust to displacements of his or her center of gravity while maintaining a constant base of support.
The helix and lob short curved tube. The ability to maintain a steady position of the head and body in relation to gravity. There are five vestibular structures.
These sensory organs particularly the utricle have an important role in the righting reflexes and in reflex control of the muscles of the legs trunk and neck that keep the body in an upright position. When the head moves. Inner ear hearing and equilibrium.
15 inner ear static dynamic equilibrium. Detection of linear acceleration. Step 9 in the physiology of hearing.
Additional anatomy flashcards. How do the bones of the middle ear affect the inner ear. Nerve impulses are carried via the vestibulocochlear nerve to the medulla to the thalamus and finally to the primary auditory area in the temporal love of the cerebral cortex.
The anvil on turn passes on to the stirrup which presses on the oval window of the inner ear. Static equilibrium maintains the position of the head in response to linear movements of the body such as starting to walk or stopping. Cards return to set details.
Equilibrium receptors in the inner ear are called the what. When the eardrum moves the hammer moves with it and transfers the vibration to the anvil. In biology the equilibrium of a system is called homeostasis.
 Difference Between Static And Dynamic Equilibrium Biology
Difference Between Static And Dynamic Equilibrium Biology
 Special Senses Equilibrium And Hearing
Special Senses Equilibrium And Hearing
 Somatic And Special Senses Physiology And Anatomy Quiz
Somatic And Special Senses Physiology And Anatomy Quiz
 Anatomy And Physiology Of Ageing 6 The Eyes And Ears
Anatomy And Physiology Of Ageing 6 The Eyes And Ears
 Anatomy Of The Ear Human Body Anatomy Lecture Notes
Anatomy Of The Ear Human Body Anatomy Lecture Notes
Anatomy Of The Ear Lecture Notes 23 Bio N212 Iupui
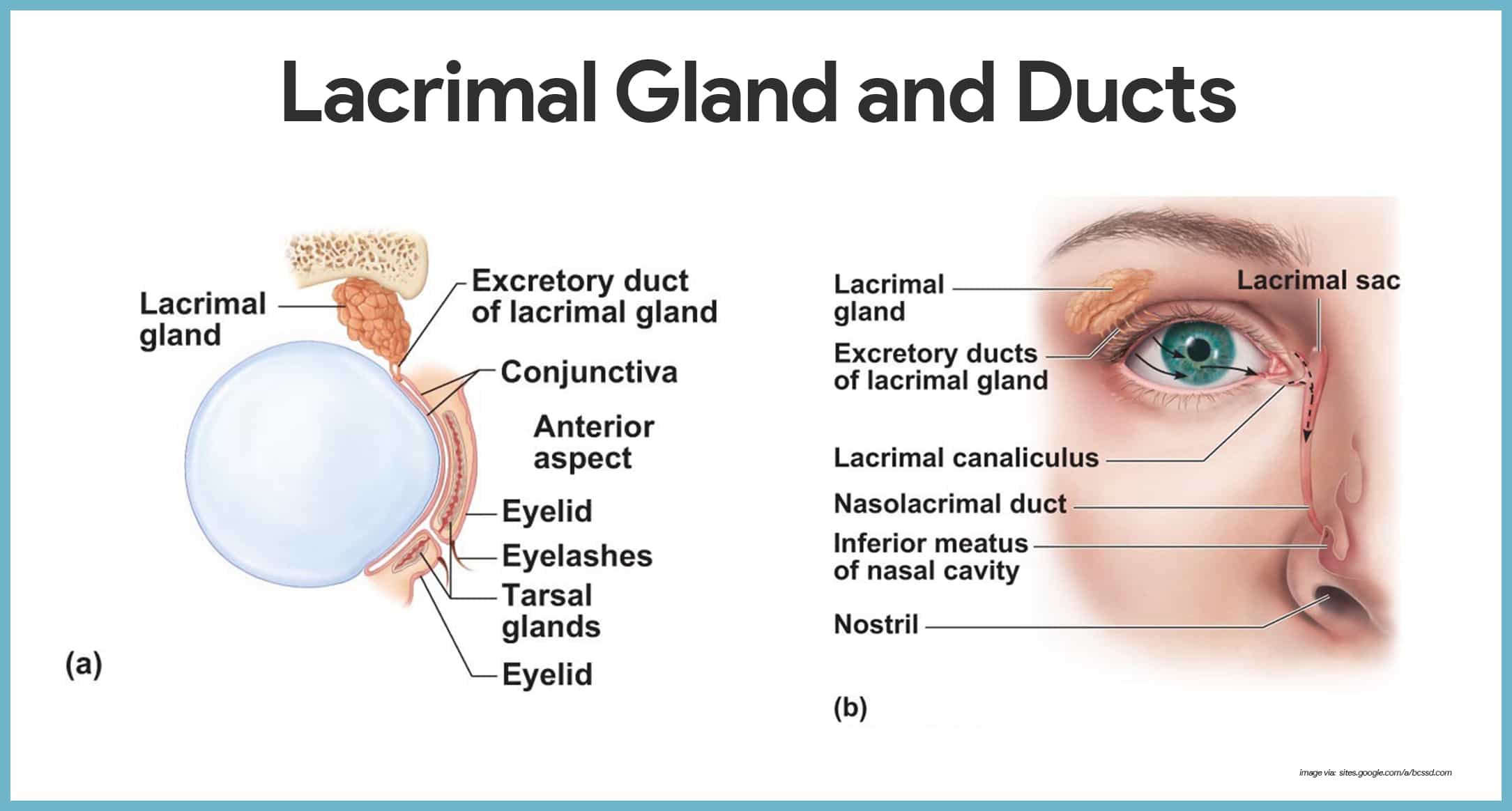 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Special Senses Hearing Equilibrium At Piedmont Technical
Special Senses Hearing Equilibrium At Piedmont Technical
 Special Senses Ppt Video Online Download
Special Senses Ppt Video Online Download
 Two Kinds Of Equilibrium 1 Static Equilibrium Refers To The
Two Kinds Of Equilibrium 1 Static Equilibrium Refers To The
 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Electronystagmography Eng Otolaryngology Specialists Of
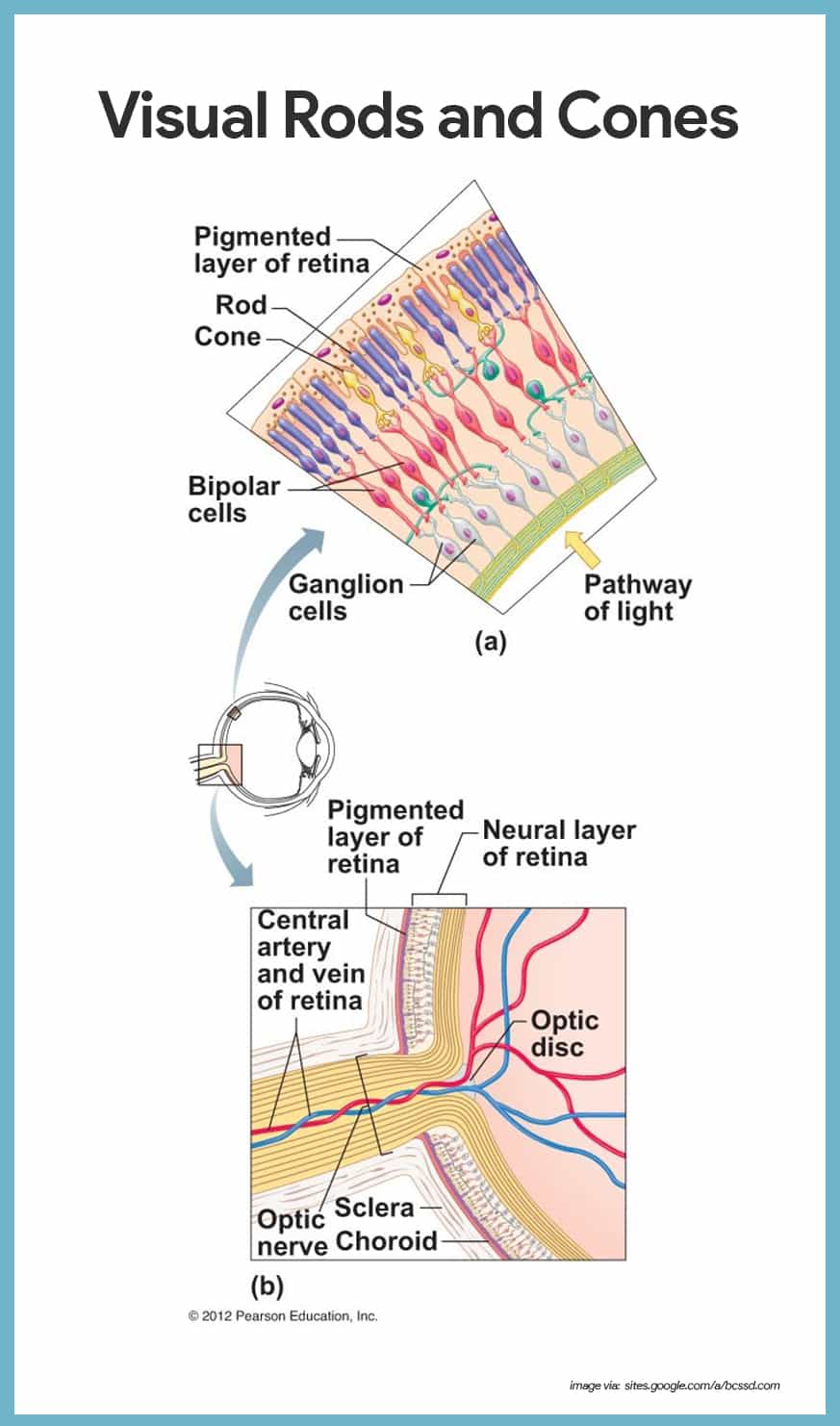 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 If A Tree Falls If A Tree Falls In The Forest And There Is
If A Tree Falls If A Tree Falls In The Forest And There Is
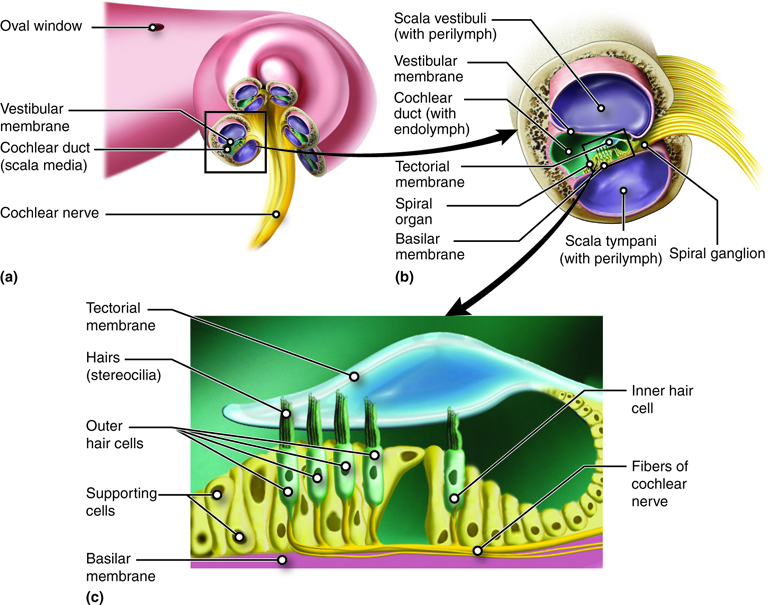 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
 Physics 200 Lab 10 Torque And Static Equilibrium Objectives
Physics 200 Lab 10 Torque And Static Equilibrium Objectives
 Sense Of Hearing Anatomy And Physiology 1 2 With Mrs
Sense Of Hearing Anatomy And Physiology 1 2 With Mrs
Ch 15 Inner Ear Static Dynamic Equilibrium
 Solved Anatomy And Ph General Proced For Hand Mouthps Ith
Solved Anatomy And Ph General Proced For Hand Mouthps Ith
 Physiology Of Equilibrium Balance
Physiology Of Equilibrium Balance
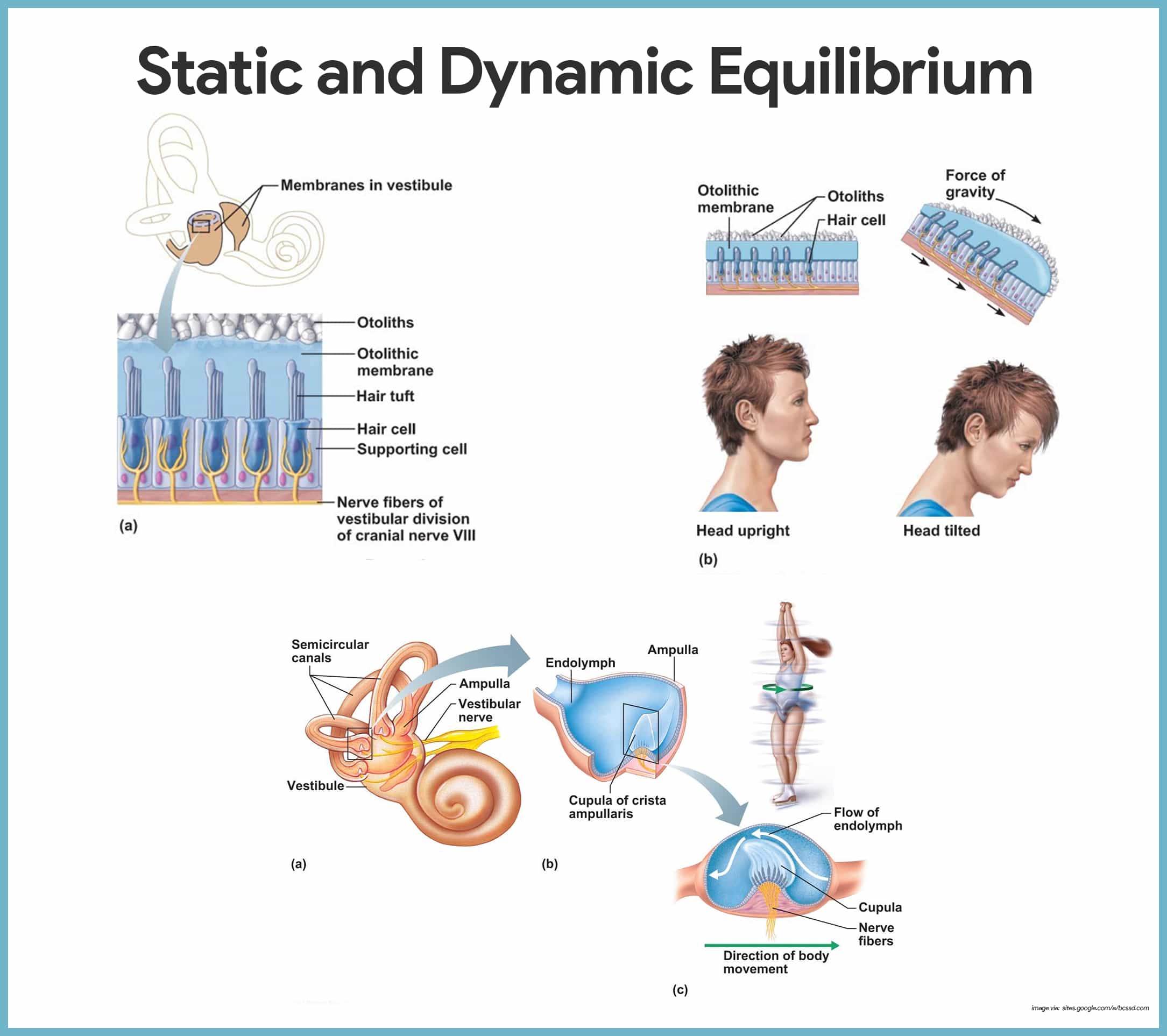 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Vestibular System Functions Anatomy Structure Nervous
Vestibular System Functions Anatomy Structure Nervous
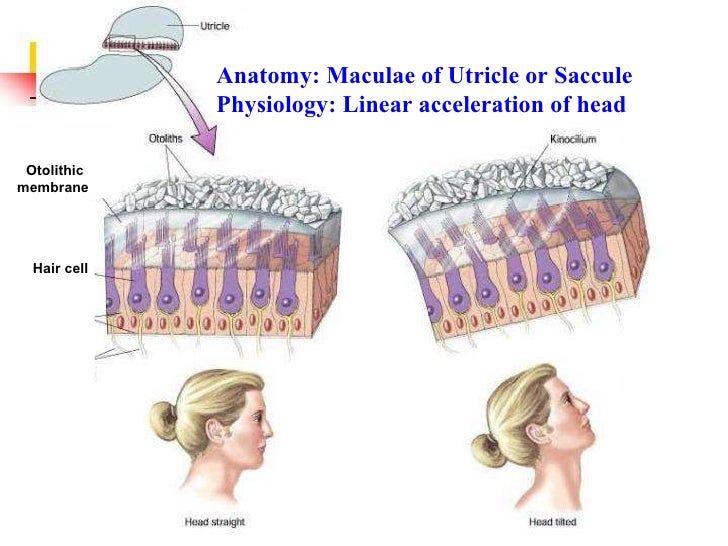 Physiology Of Equilibrium Balance
Physiology Of Equilibrium Balance
 Anatomy Of Ear Region Physiology And Anatomy Lecture
Anatomy Of Ear Region Physiology And Anatomy Lecture
Anatomy Special Sensory Global Indian Nurses Organization
 Tortora Grabowski 9e 2000 Vestibular Apparatus Static
Tortora Grabowski 9e 2000 Vestibular Apparatus Static
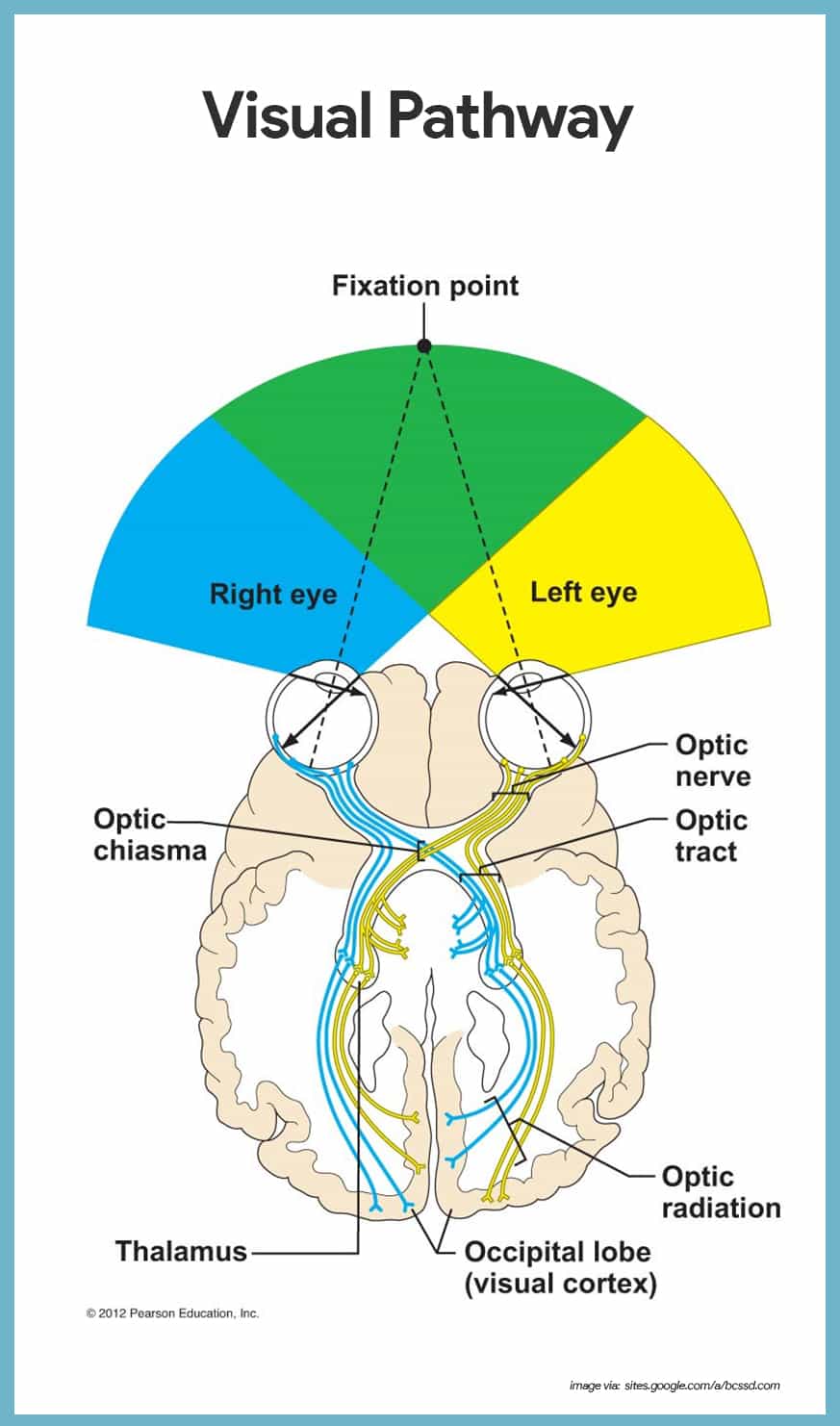 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar