When sounds enter the middle ear they are transmitted to tiny bones called the ossicles. The ear canal contains protective hairs and ear wax cerumen.
 Human Ear Anatomy Ears Inner Structure Organ Of
Human Ear Anatomy Ears Inner Structure Organ Of
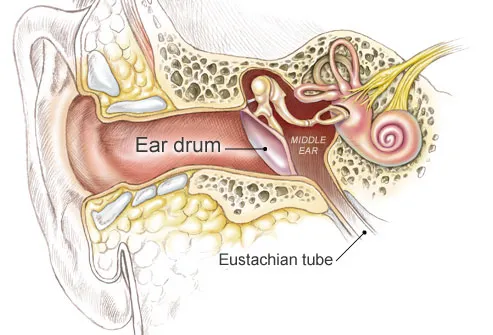
The middle ear tympanic cavity lies behind the eardrum.
Anatomy of the ear canal. External auditory canal or tube. External or outer ear consisting of. The outer ear includes an ear canal that is is lined with hairs and glands that secrete wax.
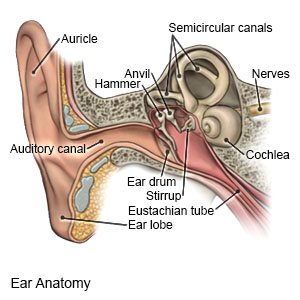
Auricle cartilage covered by skin placed on opposite sides of the head auditory canal also called the ear canal eardrum outer layer also called the tympanic membrane the outer part of the ear collects sound. Sound causes the eardrum and its tiny attached bones in the middle portion of the ear to vibrate. This is the outside part of the ear.
The parts of the ear include. In its outer third the wall of the canal consists of cartilage. The three bones are called the malleus the incus and the stapes.
Picture of the ear. The ear canal functions as an entryway for sound waves which get propelled toward the tympanic membrane known as the eardrum. Anatomy and physiology of the ear what is the ear.
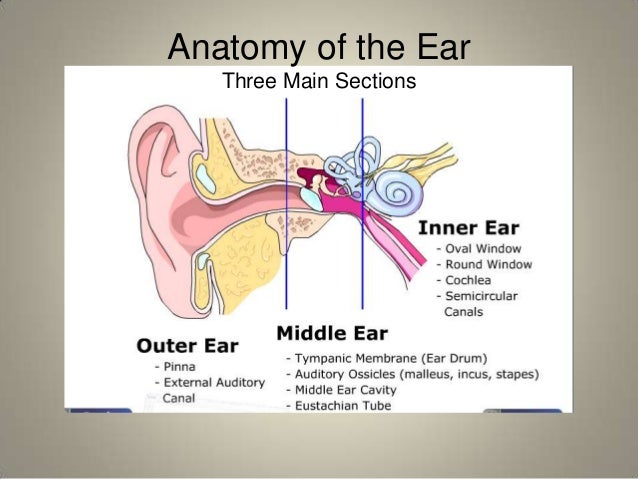
The ear is comprised of the ear canal also known as the outer ear the middle ear and the inner ear. Sound travels through the auricle and the auditory canal a short tube that ends at the eardrum. The outer ear gathers sound and allows it to pass through the ear canal to the eardrum.
Three tiny bones the malleus incus and stapes within the middle ear transfer sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. In its inner two thirds of bone. A canal that links the middle ear with the back of the nose.
Sound funnels through the pinna into the external auditory canal a short tube that ends at the eardrum tympanic membrane. The middle ear contains three bones the malleus incus and stapes that amplify the sound. The outer ear includes.
The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 25 centimetres 1 in in length and 07 centimetres 03 in in diameter. Fine hairs directed outward and modified sweat glands that produce earwax or cerumen. This part of the ear provides protection and channels sound.
The middle ear contains three small bones ossicles that transmit sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear. This is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear. The eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure in the middle ear.
The outer ear is called the pinna and is made of ridged cartilage covered by skin. Equalized pressure is needed for the proper transfer of sound waves. The fluid filled inner ear contains the cochleaits job is to translate sound vibrations into electrical signals which are then sent by nerves to the brain.
The ear canal external acoustic meatus external auditory meatus eam is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. The entire length of the passage 24 mm or almost 1 inch is lined with skin which also covers the outer surface of the tympanic membrane.
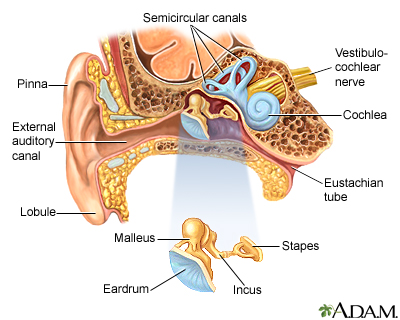 Earache Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia
Earache Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia
How Our Hearing Works Take The Journey Through The Ear
Ear Anatomy Causes Of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
Ear Infections Fluid And Hearing Loss Michael Rothschild Md
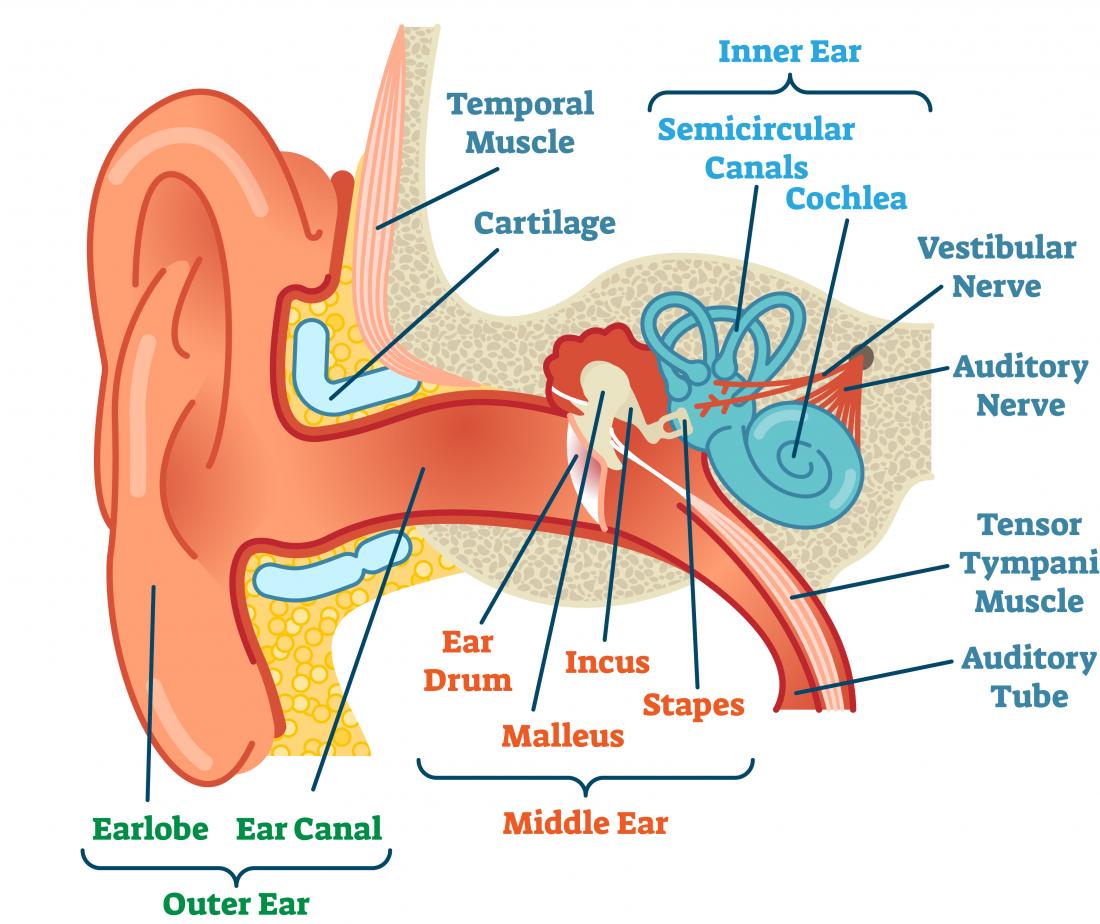 Ears And Hearing How Do They Work
Ears And Hearing How Do They Work
How Hearing Works How We Hear Hearnet Online
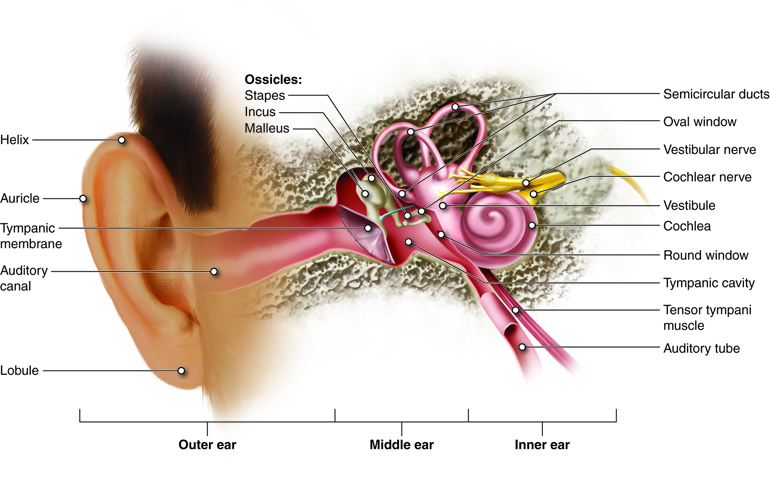 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
 Microtia Congenital Ear Deformity Institute Hearing
Microtia Congenital Ear Deformity Institute Hearing
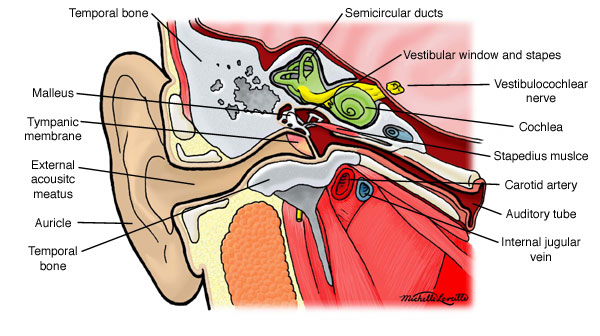 Anatomy Atlases Anatomy Of First Aid A Case Study Approach
Anatomy Atlases Anatomy Of First Aid A Case Study Approach
 Ear Wax Anatomy Revealing Medical Anatomy For The Inner
Ear Wax Anatomy Revealing Medical Anatomy For The Inner
Hearing Loss Annapolis Sensorineural Conductive Hearing Loss
 Anatomy And Physiology Of Ageing 6 The Eyes And Ears
Anatomy And Physiology Of Ageing 6 The Eyes And Ears
Medical Illustrations Laura Maaske Medical Illustrator
 Tympanoplasty Precare What You Need To Know
Tympanoplasty Precare What You Need To Know
Ear Infections Fluid And Hearing Loss Michael Rothschild Md





Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar