Process by which the resting potential is decreased as sodium ions move into the axon. This is called the resting potential.
This set is often in folders with.
Depolarization anatomy definition. The cell membrane of the cardiac muscle cell separates different concentrations of ions such as sodium potassium and calcium. Monomer for proteins monomer nucleic acids monomer unit for carbohydrates. Corresponds to the period of repolarization of the neuron.
Polar and nonpolar cov. Depolarization and hyperpolarization occur when ion channels in the membrane open or close. Sf nervous sysment h exam review richards9202011 80 terms.
Cardiac cells at rest are considered polarized meaning no electrical activity takes place. In depolarization the inside of the membrane which is normally negatively charged becomes positive and the outside negative. Depolarization occurs when the nerve cell reverses these charges.
Inside the cell there is a greater concentration of k. Hyperpolarization is when the membrane potential becomes more negative at a particular spot on the neurons membrane while depolarization is when the membrane potential becomes less negative more positive. To change them back to an at rest state the neuron sends another electrical signal.
A voltage change that rings a neuron closer to its threshold for firing. Loss of the difference in charge between the inside and outside of the plasma membrane of a muscle or nerve cell due to a change in permeability and migration of sodium ions to the interior. This is brought about by positive sodium ions rapidly passing into the axon.
Action potential occurs na channels rapidly open resulting in depolarization. In biology depolarization is a change within a cell during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution resulting in less negative charge inside the cell. Anatomy final chapter 19 26 terms.
The entire process occurs when the cell allows specific ions to flow into and out of the cell. The membrane potential becomes less negative and moves to zero. The process of depolarizing something or the state of being depolarized.
What does the action potential represents in terms of the nerve impulse of the atom. Almost as soon as the depolarization wave begins a repolariza outside the cell there is a greater concentration of na. Monomer of proteins a molecule.
Depolarization the process of reversing the charge across a cell membrane usually a neuron so causing an action potential. Depolarization is essential to the function of many cells communication between cells and the overall physiology of an organism.
Difference Between Depolarization And Repolarization

 Depolarization Physiology Process Summary Facts
Depolarization Physiology Process Summary Facts
 Diastolic Depolarization Physiology Britannica
Diastolic Depolarization Physiology Britannica
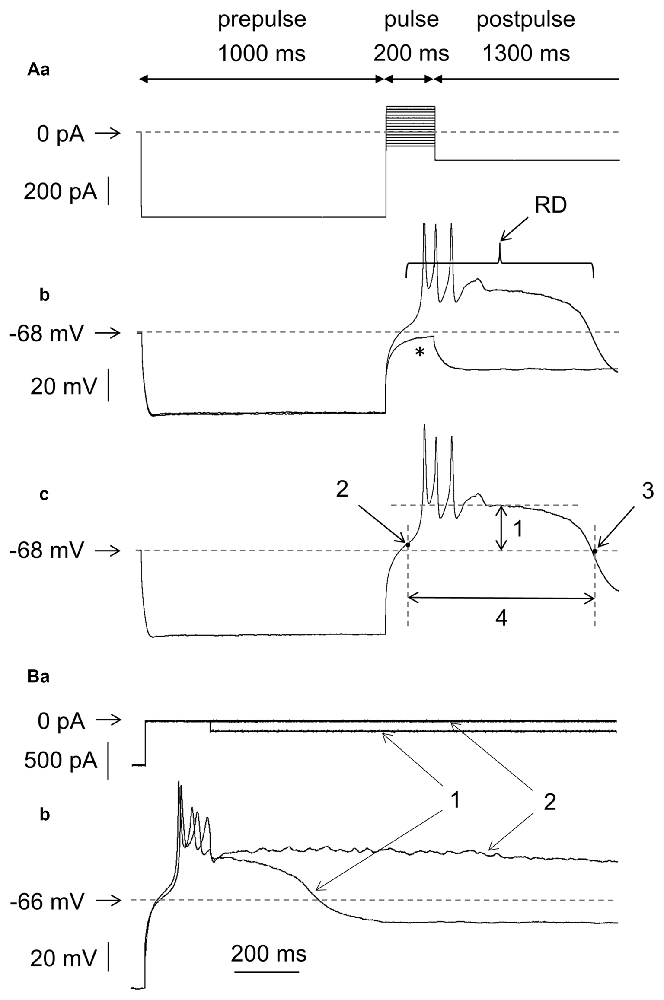 Frontiers Ionic Mechanism Underlying Rebound
Frontiers Ionic Mechanism Underlying Rebound
 Depolarization Physiology Process Summary Facts
Depolarization Physiology Process Summary Facts
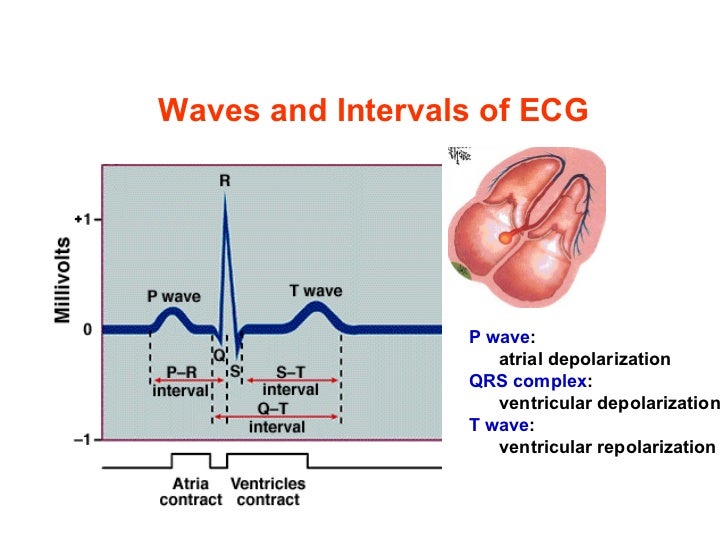
 Cv Physiology Electrocardiogram Ekg Ecg
Cv Physiology Electrocardiogram Ekg Ecg
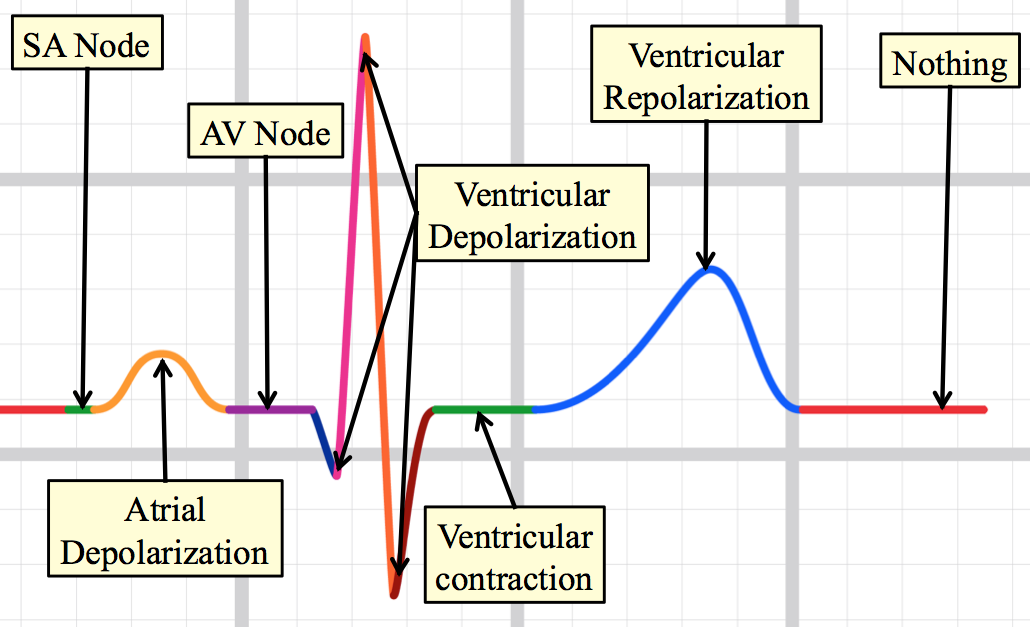
Introduction To Cardiac Physiology Electrophysiology Tusom
 Cardiac Action Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cardiac Action Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Understanding The Transmission Of Nerve Impulses Dummies
Understanding The Transmission Of Nerve Impulses Dummies
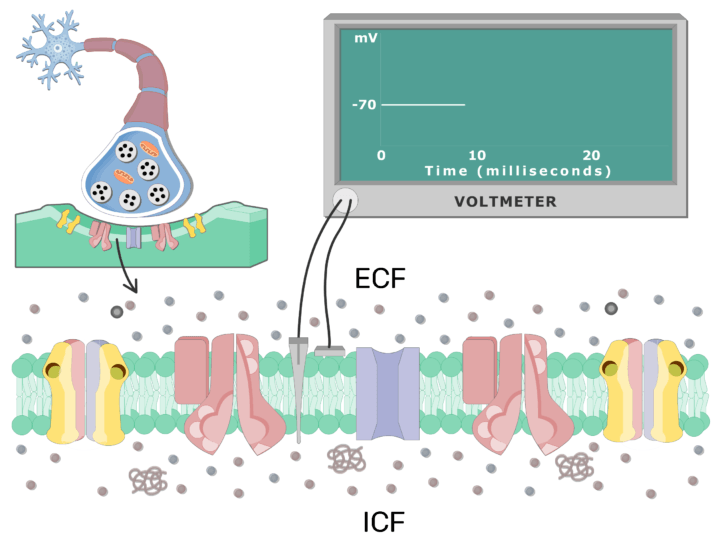 Depolarization Of The Postsynaptic Neuron Membrane
Depolarization Of The Postsynaptic Neuron Membrane
Cardiac Action Potential Cellular Basis Pathway Medicine
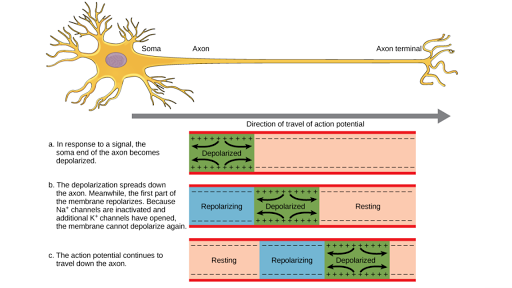
 Neuron Action Potential Part 2 Depolarization Repolarization Hyperpolarization
Neuron Action Potential Part 2 Depolarization Repolarization Hyperpolarization
 Depolarization Repolarization And Hyper Polarization
Depolarization Repolarization And Hyper Polarization
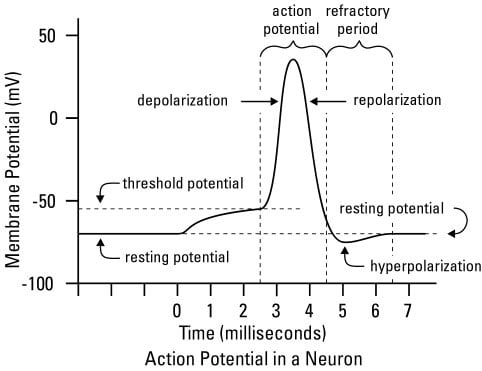
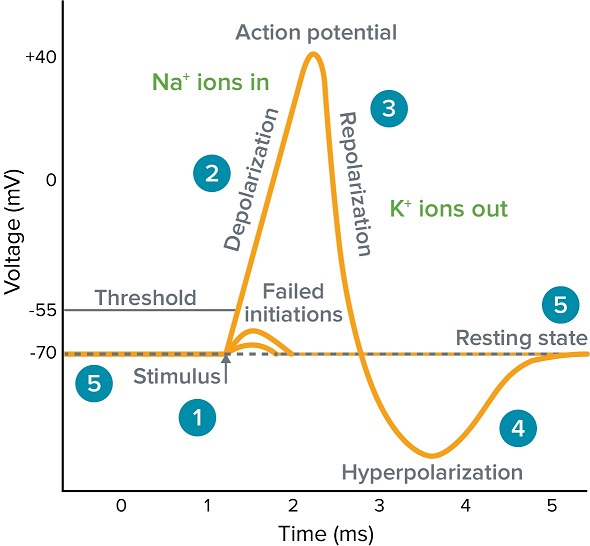 What Is An Action Potential Action Potential Chart
What Is An Action Potential Action Potential Chart
Introduction To Cardiac Physiology Electrophysiology Tusom




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar