Inflammation of the bursa the small sac of fluid that rests over the rotator cuff tendons. Ligaments found in the shoulder include.
The deepest layer includes the bones and the joints of the shoulder.
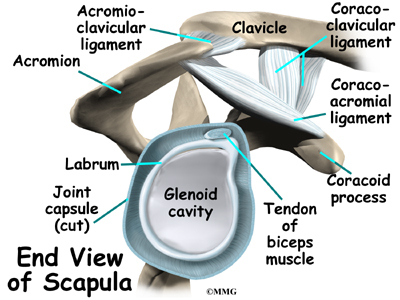
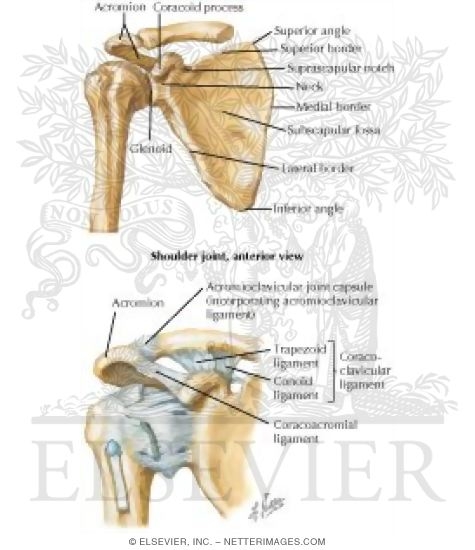
Anatomy of shoulder ligaments. In the shoulder joint the ligaments play a key role in stabilising the bony structures. Another ligament links the coracoid to the acromion coracoacromial ligament cal. The scapule the clavicle and the humerus.
For completeness the other joints are the sternoclavicular acromioclavicular and scapulothoracic joints. The shoulder joint ligaments shown are the acromioclavicular ligament coracoclavicular ligament the superior transverse scapular ligament and the joint capsule or glenohumeral ligaments. Boney structures shown are the acromion of the scapula the clavicle and the humerus.
The nerves supply all the structures above and make them work. Choose from 500 different sets of week 5 quiz anatomy shoulder ligaments flashcards on quizlet. Nerves carry signals from the brain to the muscles to move the shoulder and carries signals from the muscles back to the brain about pain pressure and temperature.
Learn week 5 quiz anatomy shoulder ligaments with free interactive flashcards. Shoulder glenohumeral joint the glenohumeral joint is one of the joints associated with the shoulder girdle that allow a full range of movement of the upper limb. The superior middle and inferior glenohumeral ligaments.
The next layer is made up of the ligaments of the joints. They are the superior middle and inferior glenohumeral ligaments. Bones of the shoulder.
This ligament can thicken and cause impingement syndrome. Glenohumeral ligaments superior middle and inferior the joint capsule is formed by this group of ligaments connecting the humerus to the glenoid fossa. The coracohumeral ligament the transverse humeral ligament the coraco clavicular ligament.
They are the main source of stability for the shoulder holding it in place and preventing it from dislocating anteriorly. Nerves and blood vessels supply the muscles and bones of the shoulder. They help hold the shoulder in place and keep it from dislocating.
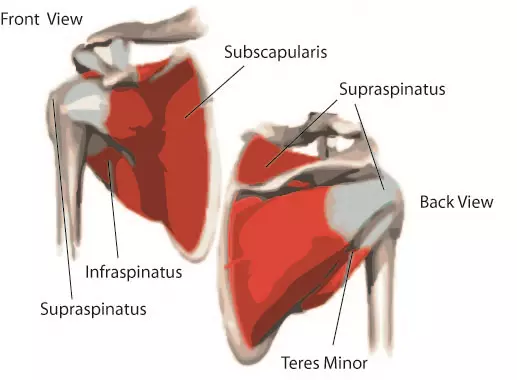
Inflammation of one of the tendons in the shoulders rotator cuff. The tendons and the muscles come next. Pain with overhead activities or pressure on the upper outer arm are symptoms.
These ligaments are the main source of stability for the shoulder.
 Shoulder Joint Human Body Anatomy Infographic Stock Vector
Shoulder Joint Human Body Anatomy Infographic Stock Vector
 Anatomy Of The Shoulder Shoulder Anatomy
Anatomy Of The Shoulder Shoulder Anatomy
 Front View Of Shoulder Anatomy Showing Bones Muscles
Front View Of Shoulder Anatomy Showing Bones Muscles
Anatomy Stock Images Shoulder Ac Joint Ligaments
Ligaments The Shoulder Complex
Shoulder Range Of Motion Manchester Bedford Myoskeletal Llc
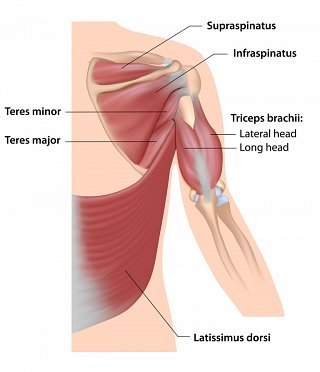 Understanding Shoulder Anatomy
Understanding Shoulder Anatomy
Understanding Shoulder Locks Doctor Kickass
 Understanding The Anatomy Of The Shoulder Bodyheal
Understanding The Anatomy Of The Shoulder Bodyheal
 Yoga And Shoulders It S A Scapular Matter Part 2
Yoga And Shoulders It S A Scapular Matter Part 2
Shoulder Joint Impingement Type Syndromes Morphopedics

 The Shoulder Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
The Shoulder Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
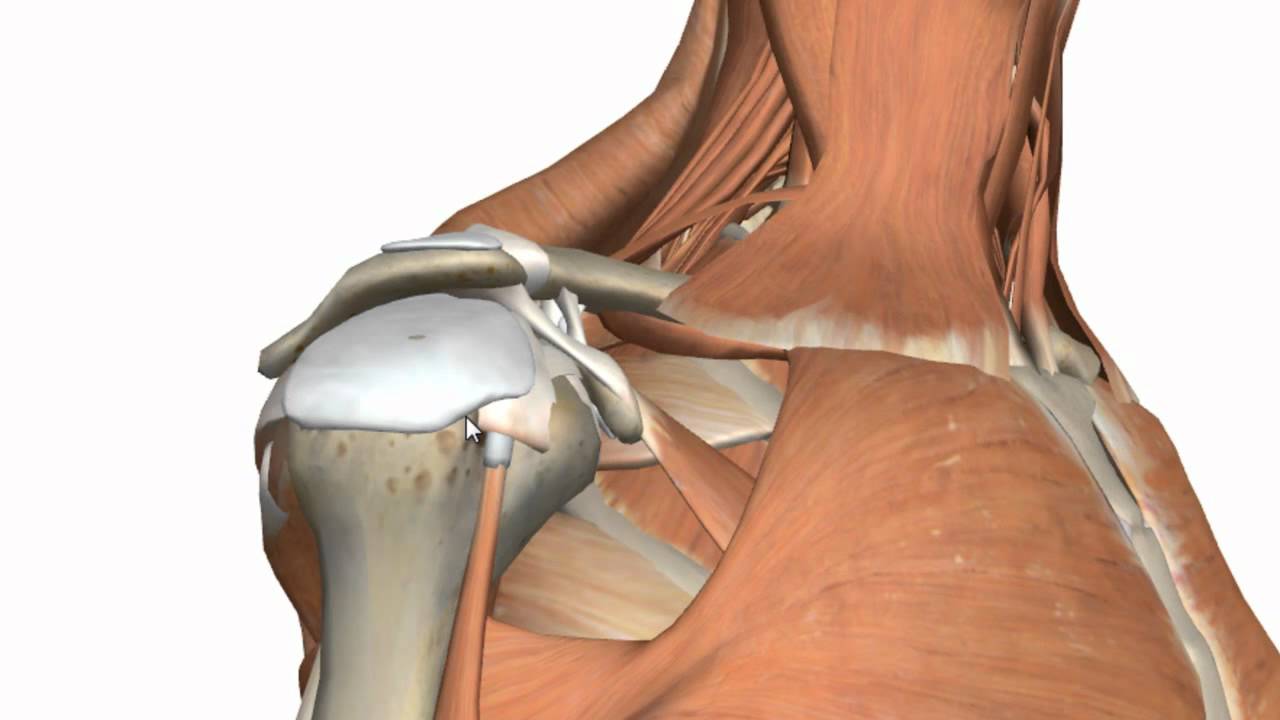 Shoulder Joint Glenohumeral Joint 3d Anatomy Tutorial
Shoulder Joint Glenohumeral Joint 3d Anatomy Tutorial
 Ligaments Of The Joints Anatomical Chart
Ligaments Of The Joints Anatomical Chart
 Shoulder Anatomy Eorthopod Com
Shoulder Anatomy Eorthopod Com
Chronic Shoulder Instability And Dislocation Orthoinfo Aaos
 Pix For Ligaments And Tendons Of The Arm Bicep
Pix For Ligaments And Tendons Of The Arm Bicep
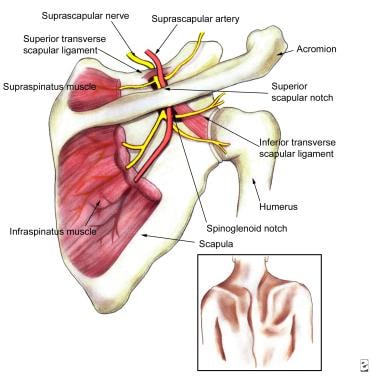
 Suprascapular Neuropathy Background Epidemiology
Suprascapular Neuropathy Background Epidemiology
 Shoulder Joint Anatomy Tutorial Ligaments
Shoulder Joint Anatomy Tutorial Ligaments
 Shoulder Joint Capsule Tissue Picture Anterior Dislocation
Shoulder Joint Capsule Tissue Picture Anterior Dislocation
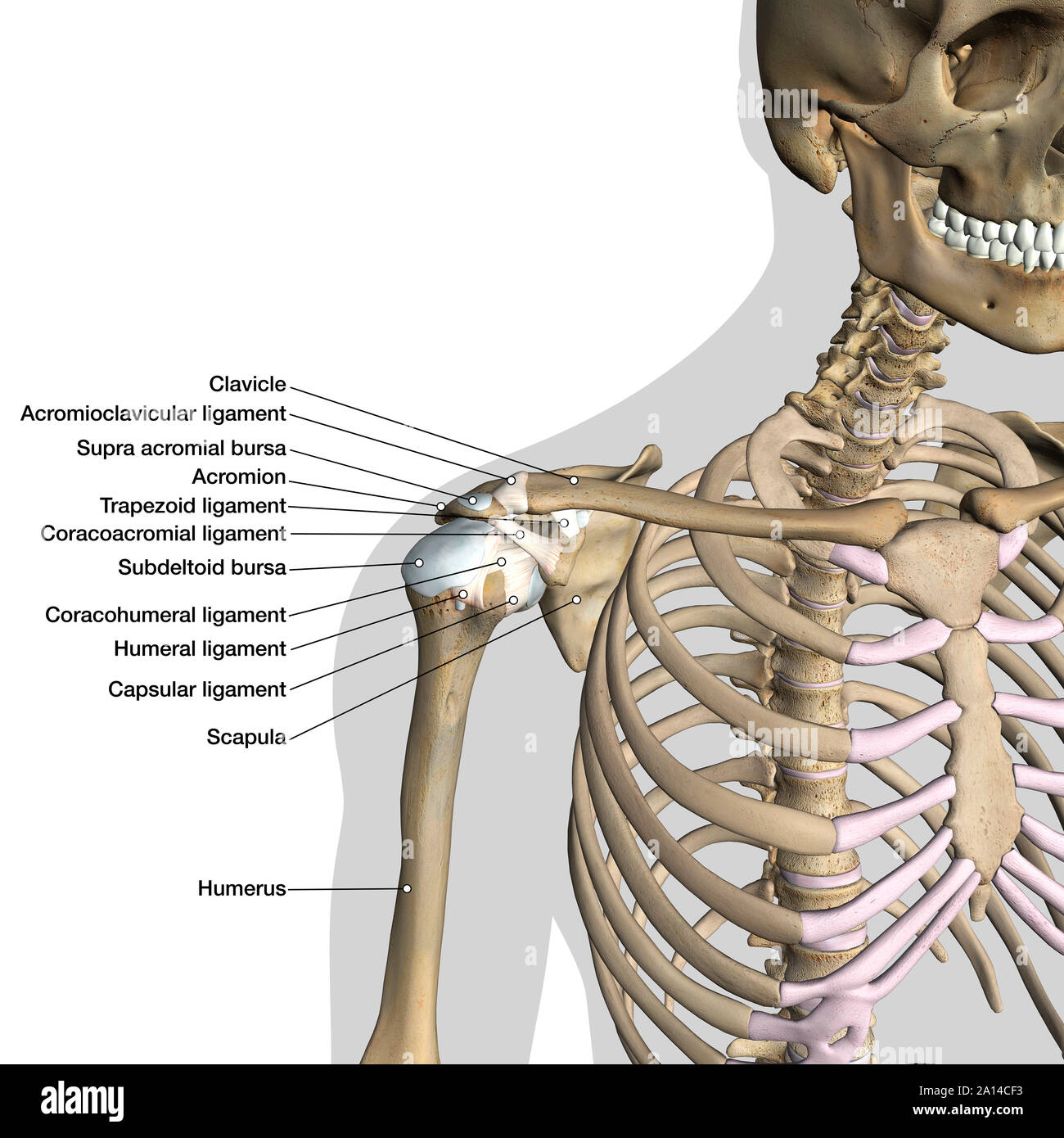 Labeled Anatomy Chart Of Shoulder Ligaments On White
Labeled Anatomy Chart Of Shoulder Ligaments On White



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar