The t cells are like soldiers who search out and destroy the targeted invaders. Take a journey into the cell and learn about various cell types cellular anatomy and cellular processes.
Sarcomere a unit of striated muscle tissue that contains the filaments actin and myosin.
Cell anatomy definition. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Plant cells have special organelles called chloroplasts which create sugars via photosynthesis. Science tech math science.
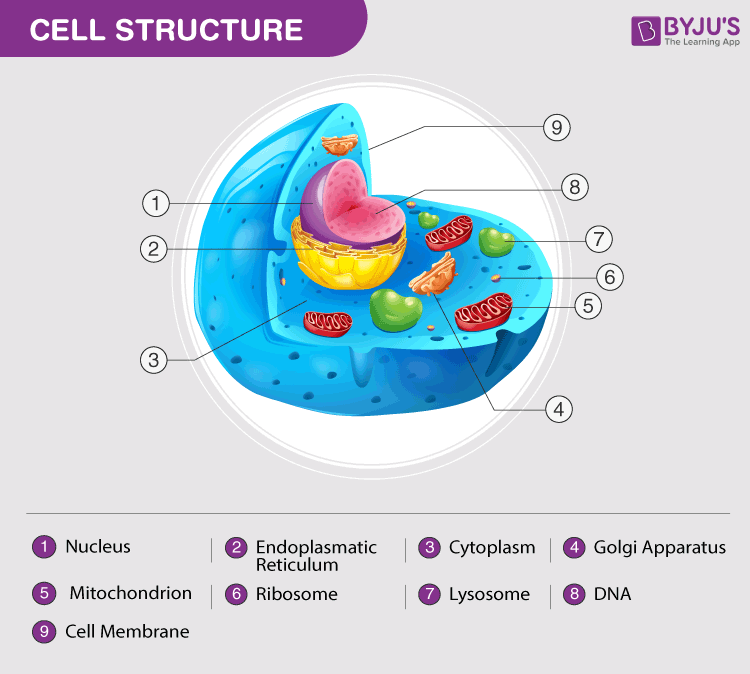
A type of white blood cell that is of key importance to the immune system and is at the core of adaptive immunity the system that tailors the bodys immune response to specific pathogens. The nucleus contains a nucleolus and is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope. Cells are often called the building blocks of life.
2 any small compartment. The cell from latin cella meaning small room is the basic structural functional and biological unit of all known organisms. 3 biology the smallest unit of an organism that is able to function independently.
Plant cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom plantae. The study of cells is called cell biology cellular biology or cytology. Protects cell from toxic hydrogen peroxide planthelps with chemical reactions.
The cells of a honeycomb. The individual cell is the unit of structure of all living things. Chro all cells contain a semifluid substance where organelles are s found only in eukaryotic cells and are absent from the cells o the for principle parts of an animal ce nucleus cytosol.
The cell is structural and functional unit of all living things. Cell the basic biological unit of living things. The nucleus contains the cells dna a type of nucleic acid.
Groups of them form tissues. It consists of a nucleus containing the genetic material surrounded by the cytoplasm in which are mitochondria lysosomes ribosomes and other organelles. Immature t cells termed t stem cells.
Consists of three parts. An entire organism may consist of a single cell which is called unicellular or many cells which is called multicellular. The for principle parts of an animal ce nucleus cytosol organelles cell membrane directs metabolism contains dna.
They are eukaryotic cells which have a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions. Organ a self contained group of tissues that performs a specific function in the body. Medical definition of t cell.
The major parts of a cell are the nucleus cytoplasm and cell membrane.
 Islets Of Langerhans Definition Function Location
Islets Of Langerhans Definition Function Location
 Purkinje Cell Anatomy Britannica
Purkinje Cell Anatomy Britannica
 Leaf Cell Definition And Types Biology Dictionary
Leaf Cell Definition And Types Biology Dictionary
 Kupffer Cells In Liver Definition Anatomy Functions
Kupffer Cells In Liver Definition Anatomy Functions
 Mitochondrion Definition Structure And Function Biology
Mitochondrion Definition Structure And Function Biology
 What Is A Cell Definition Structure Types Functions
What Is A Cell Definition Structure Types Functions
 Cell Nucleus Plant Animal Definition And Function
Cell Nucleus Plant Animal Definition And Function
 Skin Cancer Anatomy Headandneckcancerguide Org
Skin Cancer Anatomy Headandneckcancerguide Org
 Seer Training Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
Seer Training Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
 Organelle Definition Function Types And Examples
Organelle Definition Function Types And Examples
 Animal Cell Structure Function And Types Of Animal Cells
Animal Cell Structure Function And Types Of Animal Cells
 Cell Definition Functions Types And Examples Biology
Cell Definition Functions Types And Examples Biology
 Glial Cells Neuroanatomy Basics Anatomy Tutorial
Glial Cells Neuroanatomy Basics Anatomy Tutorial
 The Cell Plant Cell The Anatomy Definition Functions Structure Types Part 24
The Cell Plant Cell The Anatomy Definition Functions Structure Types Part 24
 A Definition Of Endocytosis With Steps And Types
A Definition Of Endocytosis With Steps And Types
 Prokaryotic Cells Structure Function And Definition
Prokaryotic Cells Structure Function And Definition
 Prokaryotic Cells Structure Function And Definition
Prokaryotic Cells Structure Function And Definition
 11 Different Types Of Cells In The Human Body
11 Different Types Of Cells In The Human Body
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar