Together with the joint capsule ligaments and shoulder labrum the rotator cuff muscles are important dynamic stabilizers and movers of the shoulder joint. Tests for a rotator cuff tear may include.
This is the main muscle that lets you rotate and extend your shoulder.
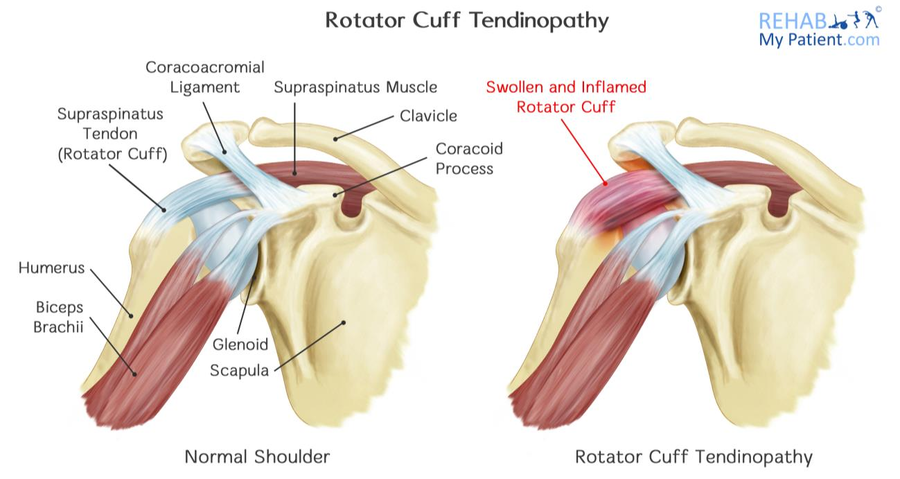
Rotator cuff anatomy. It helps you make all the motions of your arm and shoulder. Arthrogram a special type of x ray that uses dye injected into a joint to more clearly see detail in the tendons and muscles. The rotator cuff of the shoulder is made up of four muscles whose tendons come together to form a covering around the head of the humerus upper arm bone and top of the shoulder.
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that hold your upper arm in place in your shoulder. The most common signs of rotator cuff injuries are. The rotator cuff tendons cover the head of the humerus upper arm bone helping you to raise and rotate your arm.
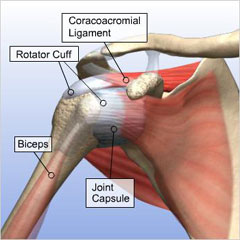
Rotator cuff and shoulder anatomy the shoulder has an incredible range of motion but this means that it is also very prone to injury. This is the smallest rotator cuff. This holds your humerus in place and keeps your upper arm stable.
In the human body the rotator cuff is a functional anatomical unit located in the upper extremity. There is a lubricating sac called a bursa between the rotator cuff and the bone on top of your shoulder acromion. Pain may or may not be present.
Mri magnetic resonance imaging. The head of your upper arm bone also. Ive just added in the muscles here and well just take a look at the muscles that make up the rotator cuff and a look at their function.
The rotator cuff muscles are a group of muscles that originate on the scapula and insert onto the head of the humerus and provide stability across this joint. Each one of these muscles is part of the rotator cuff and plays an important role. Can be localized to anterior lateral aspect of the shoulder with referred pain down the upper arm lateral aspect.
Painful range of motion. The bursa allows the rotator cuff tendons to glide freely when you move your arm. Its function is related to the glenohumeral joint where the muscles of the cuff function both as the executors of the movements of the joint and the stabilization of the joint as well.
The shoulder can easily slip out of alignment by a few millimeters become weak due to regular wear and tear or become completely dislocated during a fall.
 Significance Of Upper Scapular Rotation On Rotator Cuff
Significance Of Upper Scapular Rotation On Rotator Cuff
 Rotator Cuff Pain Tears And Other Injures Treatments
Rotator Cuff Pain Tears And Other Injures Treatments
 Rotator Cuff Surgery Summit Orthopedics Treatment Guide
Rotator Cuff Surgery Summit Orthopedics Treatment Guide
 Cables Crescents And Suspension Bridges The Unique Anatomy
Cables Crescents And Suspension Bridges The Unique Anatomy
 Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tear Ucla Orthopaedic Surgery Los
Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tear Ucla Orthopaedic Surgery Los
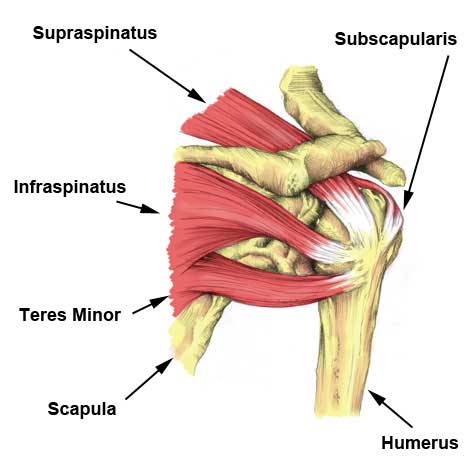 Rotator Cuff Strain Symptoms Causes Treatment And
Rotator Cuff Strain Symptoms Causes Treatment And
 Pin By Heather Wagner On Our Bodies Shoulder Anatomy
Pin By Heather Wagner On Our Bodies Shoulder Anatomy
 Rotator Cuff Anatomy Illustration Common Problems
Rotator Cuff Anatomy Illustration Common Problems
 Anatomy And Function Of Rotator Cuff Muscles Anterior
Anatomy And Function Of Rotator Cuff Muscles Anterior
Why Did I Injured My Rotator Cuff Naples Orthopedic
 What Are The Causes Of Rotator Cuff Pathology
What Are The Causes Of Rotator Cuff Pathology
Anatomy 101 The Rotator Cuff The Handcare Blog

 Rotator Cuff Muscles Msk Learning Portfolio Helen Wismer
Rotator Cuff Muscles Msk Learning Portfolio Helen Wismer
 Rotator Cuff Tears Orthoinfo Aaos
Rotator Cuff Tears Orthoinfo Aaos
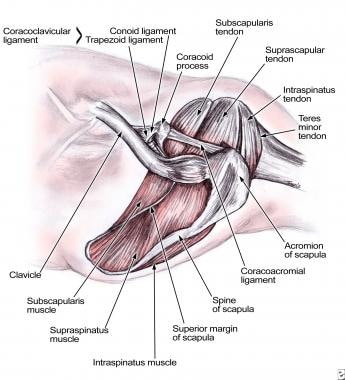 Rotator Cuff Pathology Background Anatomy Pathophysiology
Rotator Cuff Pathology Background Anatomy Pathophysiology
 What Is The Rotator Cuff And Why It S Important To Shoulder
What Is The Rotator Cuff And Why It S Important To Shoulder
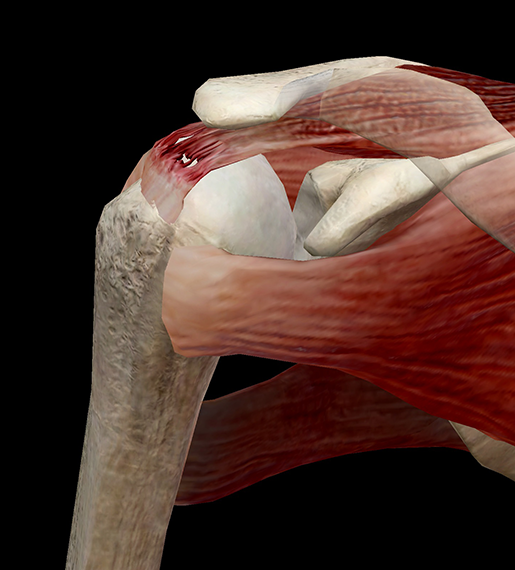 Learn Muscle Anatomy Of Dads And Rotator Cuff Injuries
Learn Muscle Anatomy Of Dads And Rotator Cuff Injuries
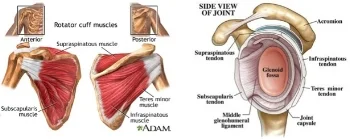
 Baton Rouge Shoulder Doctors Rotator Cuff Baton Rouge
Baton Rouge Shoulder Doctors Rotator Cuff Baton Rouge
 Rotator Cuff Syndrome Rotator Cuff Tear Rotator Cuff
Rotator Cuff Syndrome Rotator Cuff Tear Rotator Cuff
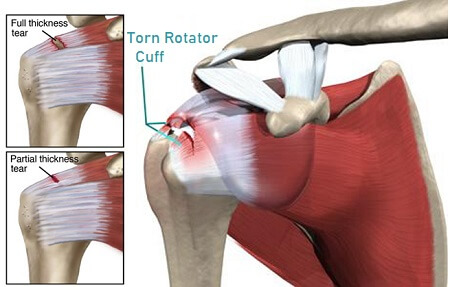 Torn Rotator Cuff Symptoms And Treatment Shoulder Pain
Torn Rotator Cuff Symptoms And Treatment Shoulder Pain
 Rotator Cuff Injury Msk Medbullets Step 1
Rotator Cuff Injury Msk Medbullets Step 1
 Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy Rehab My Patient
Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy Rehab My Patient
 Rotator Cuff Tear Rapid Recovery Paul C Murphy Md
Rotator Cuff Tear Rapid Recovery Paul C Murphy Md


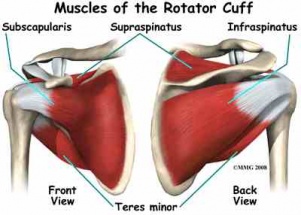
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar