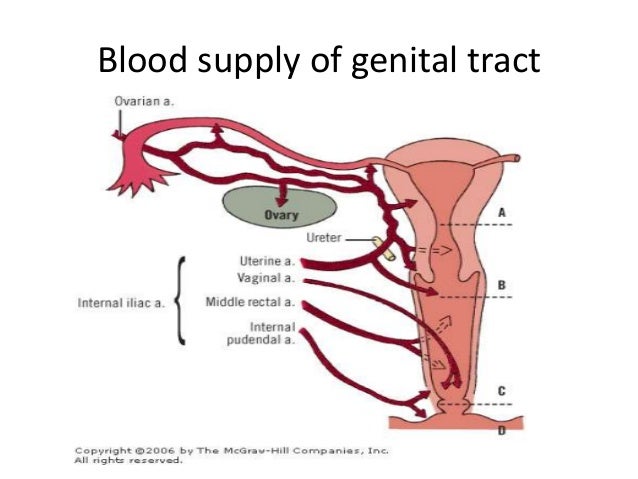
The ovaries are the female pelvic reproductive organs that house the ova and are also responsible for the production of sex hormones. Uterine veins follow the course of arteries.
/male_female_gonads-58811e985f9b58bdb3e3dfe9.jpg) Male And Female Gonads Testes And Ovaries
Male And Female Gonads Testes And Ovaries
Specifically these cells secrete androgens which are converted into estrogen by the granulosa cells.
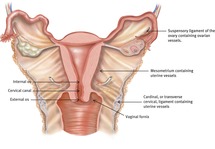
Anatomy of the uterus and ovaries. Ovaries the ovaries are a pair of oval structures about 15 inches 4 cm long on either side of the uterus in the pelvic cavity fig. Neurovascular structures enter the hilum of the ovary via the mesovarium. They are paired organs located on either side of the uterus within the broad ligament below the uterine fallopian tubes.
Anatomy of ovaries the ovaries are the two female reproductive glands which are solid pinkish grey and almold shape entities situated on either side of the uterus and are connected to the uterus by the fallopian tube fig. The ovaries develop along with other organs in the womb before birth. When a female infant is born her ovaries will contain approximately 400000 egg producing follicles and for the most part her body will not produce anymore follicles for the rest of her life.
The right ovary tends to be slightly larger than the left ones. The uterus is a fibromuscular organ that can be divided into the upper muscular uterine corpus and the lower fibrous cervix which extends into the vagina. Help begin and control follicle development by influencing hormone production.
Each ovary has average dimensions of 3 cm length 2 cm breadth and 1 cm thickness. The uterus receives vascular supply from anastomosing ovarian and uterine arteries. The ovarian ligament extends from the medial side of an ovary to the uter ine wall and the broad ligament is a fold of the peri toneum that covers the ovaries.
Structure of the ovary. Anatomy of human ovaries. Located around and on the periphery of the ovarian follicle.
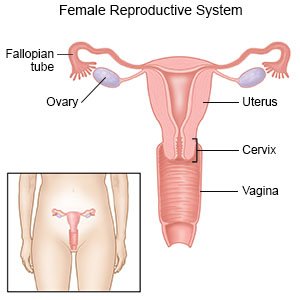
The uterine artery is a branch of the vaginal artery and enters the mesometrium at the level of the cervix close to the body of the uterus. The ovaries are a pair of almond shaped glands that produce ova and the female sex hormones. Located laterally to the left and right of the uterus and inferior to the fallopian tubes the ovaries are connected to the uterus via the ovarian ligaments.
The ovaries are almond shaped structures located on either side of the uterus and closely related to several anatomical structures in the pelvic region. Hence being smaller than its male analogue the testis. The ovaries are paired oval organs attached to the posterior surface of the broad ligament of the uterus by the mesovarium a fold of peritoneum continuous with the outer surface of the ovaries.
The upper part of the uterus above the insertion of the fallopian tubes is called the fundus.
 The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
 Ovarian Abscess What You Need To Know
Ovarian Abscess What You Need To Know
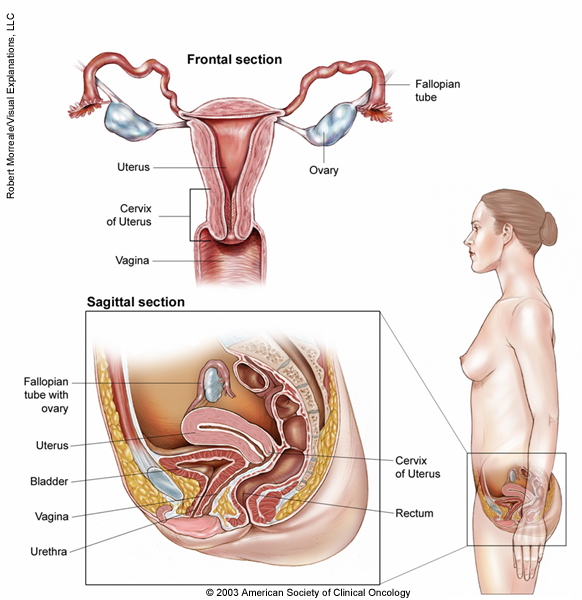
 Applied Anatomy And Imaging Of The Uterus Vagina Ovaries
Applied Anatomy And Imaging Of The Uterus Vagina Ovaries
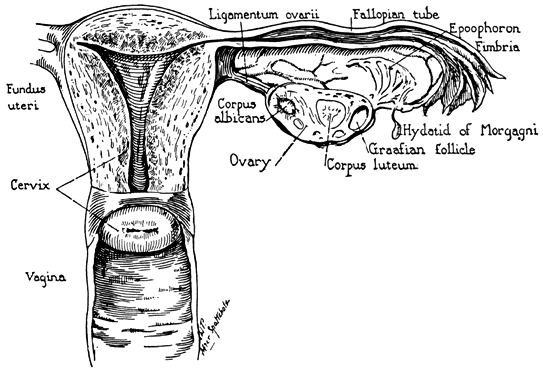 Volume 1 Chapter 2 Clinical Anatomy Of The Uterus
Volume 1 Chapter 2 Clinical Anatomy Of The Uterus
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/arteria-ovarica/gsuWNm9AbZbHVdmrjeJsQ_V._ovarii_02.png) Ligaments Of The Uterus Function And Clinical Cases Kenhub
Ligaments Of The Uterus Function And Clinical Cases Kenhub
 Ovarian Fallopian Tube And Peritoneal Cancer Medical
Ovarian Fallopian Tube And Peritoneal Cancer Medical
 What Are The Three Layers Of The Uterine Wall From The
What Are The Three Layers Of The Uterine Wall From The
 Anatomy Of Female Uterus With Ovaries Canvas Print
Anatomy Of Female Uterus With Ovaries Canvas Print
 Uterine Ligaments Diagram Human Uterus Anatomy
Uterine Ligaments Diagram Human Uterus Anatomy
Clinical Anatomy Of The Uterus Fallopian Tubes And Ovaries
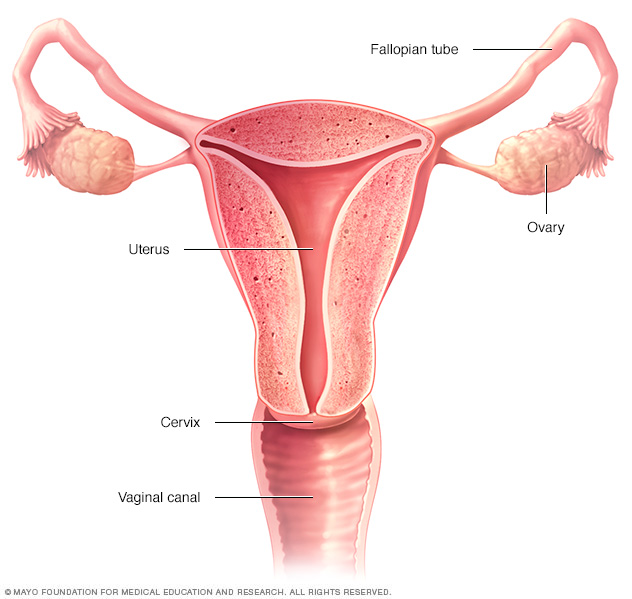 Ovarian Cysts Disease Reference Guide Drugs Com
Ovarian Cysts Disease Reference Guide Drugs Com
 Uterine Fibroid Symptoms Treatment Causes Surgery
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms Treatment Causes Surgery
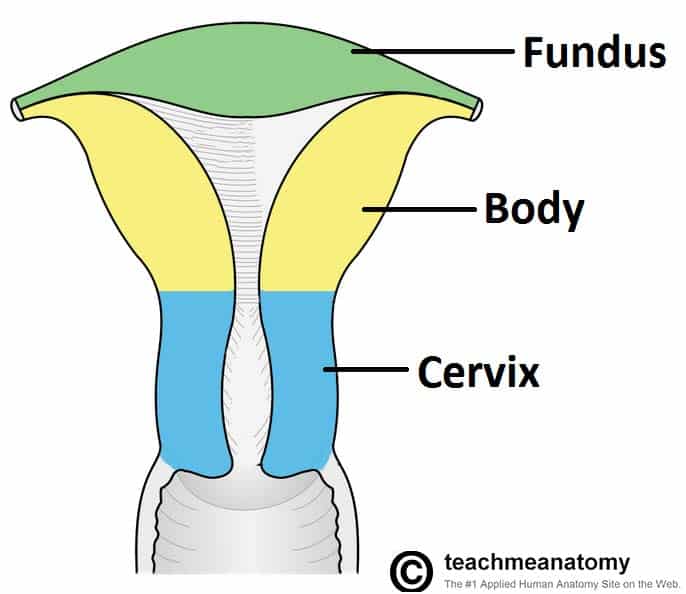 The Uterus Structure Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
The Uterus Structure Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
 Ovarian Cysts And Pelvic Masses Cigc
Ovarian Cysts And Pelvic Masses Cigc
 Amazon Com Jiulonerst Pathological Uterus Ovary Human Model
Amazon Com Jiulonerst Pathological Uterus Ovary Human Model
 Anatomy Of The Uterus And Its Surgical Removal Obgyn Key
Anatomy Of The Uterus And Its Surgical Removal Obgyn Key
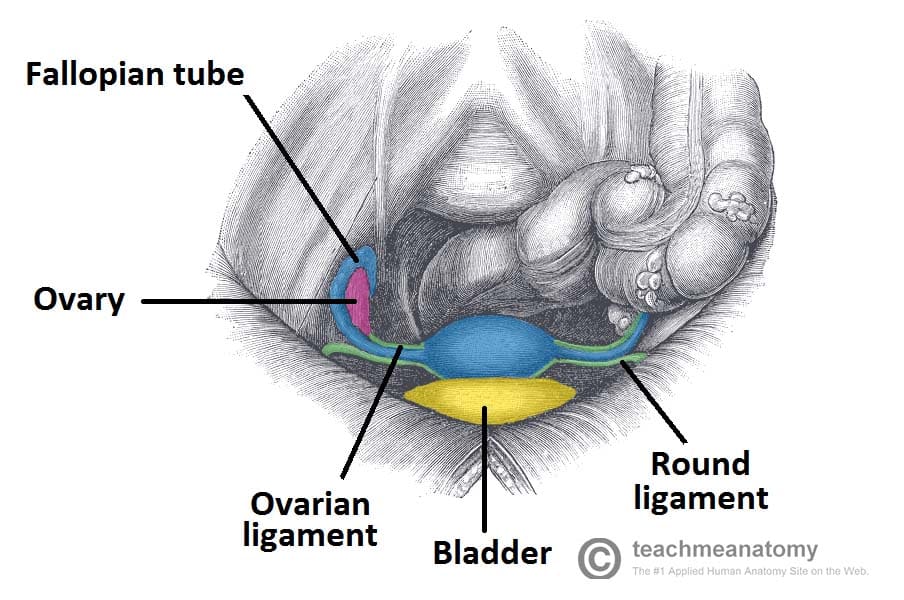 Ligaments Of The Female Reproductive Tract Teachmeanatomy
Ligaments Of The Female Reproductive Tract Teachmeanatomy
 Uterine Sarcoma Vanderbilt Ingram Cancer Center
Uterine Sarcoma Vanderbilt Ingram Cancer Center
 Uterus Ovary Anatomical Model With Pathologies
Uterus Ovary Anatomical Model With Pathologies
 Uterus And Ovary Model Labeled Bing Images Reproductive
Uterus And Ovary Model Labeled Bing Images Reproductive
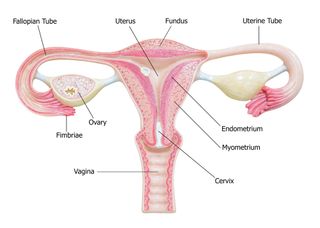 Ovaries Facts Function Disease Live Science
Ovaries Facts Function Disease Live Science
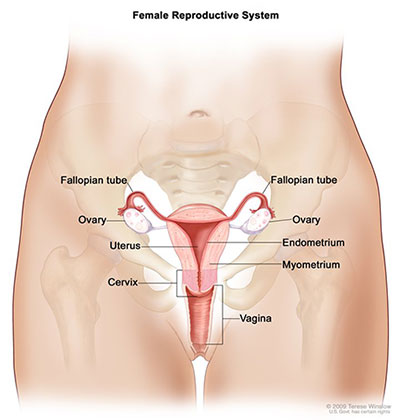 Seer Training Salpingo Ovarian Peritoneal Functional Anatomy
Seer Training Salpingo Ovarian Peritoneal Functional Anatomy
 Uterus And Ovaries Anatomy Pictures And Information
Uterus And Ovaries Anatomy Pictures And Information
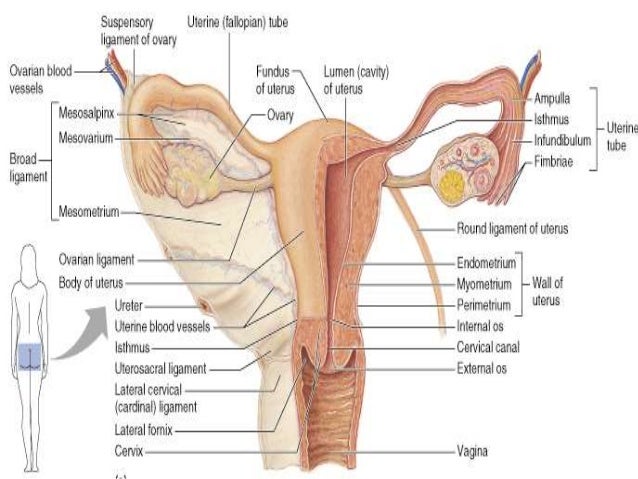 Anatomy And Physiology Of Female Reproductive System
Anatomy And Physiology Of Female Reproductive System



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar