You can also use these slides to help explain to patients and others what makes up each layer of skin and show how they work together. They are usually closely associated with the afferent myelinated nerve fibres arranged in a plate like structure with the base of the merkel cell.
 Skin And Integumentary System Physiology And Anatomy
Skin And Integumentary System Physiology And Anatomy
These are part of the sensory apparatus of the skin and are located within the stratum basale of the epidermis where they act as slow adapting mechanoreceptors.

Skin anatomy and physiology. Anatomy and physiology of the skin 3 or stratum spinosum murphy 1997. It performs many vital functions including protection against external physical chemical and biologic assailants as well as prevention of excess water loss from the body and a role in thermoregulation. Its health and surface appearance are determined by environmental factors as well as the function of the components that comprise the layers below.
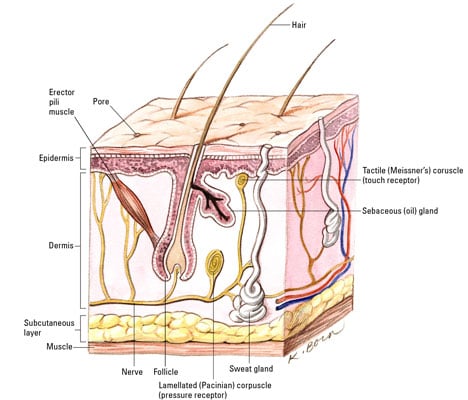
The epidermis the outermost layer of skin provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. Skin has three layers. The skin is the largest organ of the body with a total area of about 20 square feet.
To maintain beautiful skin and slow the rate at which it ages the structures and functions of the skin must be supplemented and protected. The skin is the largest organ of the body accounting for about 15 of the total adult body weight. Cells of the epidermis.
The squamous layer is composed of a variety of cells that differ in shape structure and subcellular properties depending on their location. Skin anatomy physiology the skin is the bodys largest organ and it serves as a protective barrier. Skin anatomy and physiology beautiful healthy skin is determined by the healthy structure and proper function of components within the skin.
Skin anatomy physiology from medline industries use this handy slide share presentation to review the basics of skin anatomy and physiology. Supra basal spinous cells for example are polyhedral in shape and have a rounded nucleus whereas cells of the upper spinous. The skin protects us from microbes and the elements helps regulate body temperature and permits the sensations of touch heat and cold.
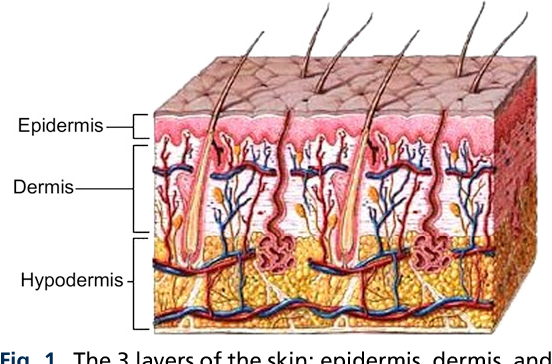 Aging Skin Histology Physiology And Pathology Semantic
Aging Skin Histology Physiology And Pathology Semantic
 Lecture 7 Integumentary System Skin Anatomy Human
Lecture 7 Integumentary System Skin Anatomy Human
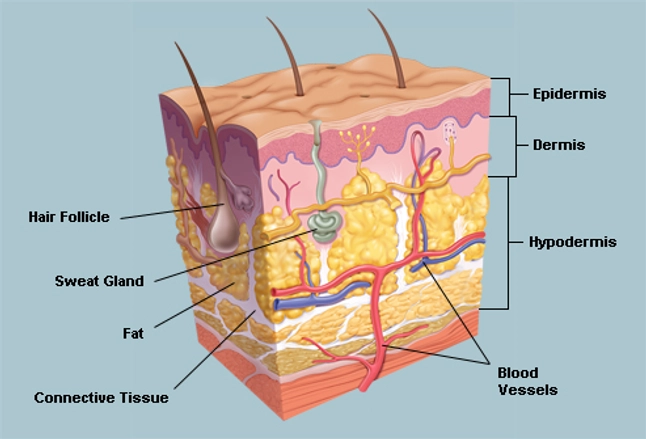 The Skin Human Anatomy Picture Definition Function And
The Skin Human Anatomy Picture Definition Function And
 Principles Of Human Anatomy And Physiology 11e1 Chapter 5
Principles Of Human Anatomy And Physiology 11e1 Chapter 5

 Anatomy Physiology Skin Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy Physiology Skin Flashcards Quizlet
 Integumentary System Skin Anatomy Medical Terminology
Integumentary System Skin Anatomy Medical Terminology
 Integumentary System Human Body Human Anatomy Physiology
Integumentary System Human Body Human Anatomy Physiology
 Skin Anatomy And Physiology Research Developments Human
Skin Anatomy And Physiology Research Developments Human
 Skin Integumentary System Review For Anatomy Physiology
Skin Integumentary System Review For Anatomy Physiology
 Human Anatomy And Physiology For Skin And Scuba Diving
Human Anatomy And Physiology For Skin And Scuba Diving
Hypodermis Of The Skin Anatomy And Physiology
The Integumentary System Lessons Tes Teach
 The Skin Canadian Cancer Society
The Skin Canadian Cancer Society
 Human Anatomy Skin And Hair Diagram Complexion Physiology
Human Anatomy Skin And Hair Diagram Complexion Physiology
 Skin Epidermis Anatomy Healthengine Blog
Skin Epidermis Anatomy Healthengine Blog
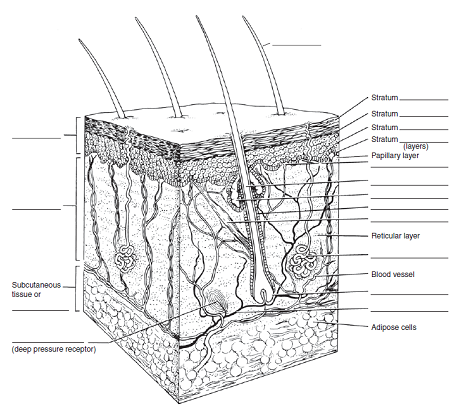 Solved Label The Skin Structures And Areas Indicated In The
Solved Label The Skin Structures And Areas Indicated In The
Anatomy And Physiology Diploma Course Assignment 2
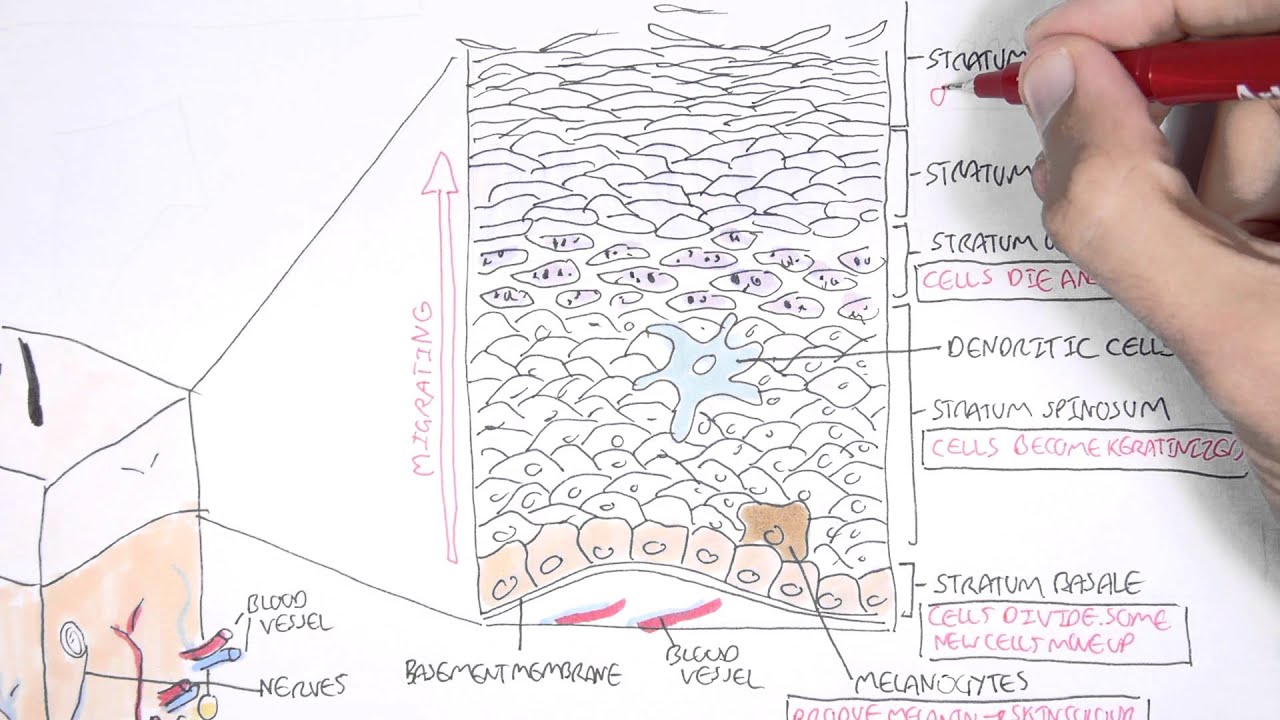 The Skin Anatomy Physiology And Microbiology
The Skin Anatomy Physiology And Microbiology
Integumentary System Bergenology A Tool For Anatomy And
 Mblex Review Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology
Mblex Review Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar