Like the hyponychium at the front of the nail the eponychium is living tissue that protects the base of the nail. In iron deficiency anemia the nails become thin brittle and spoon shaped koilonychia.
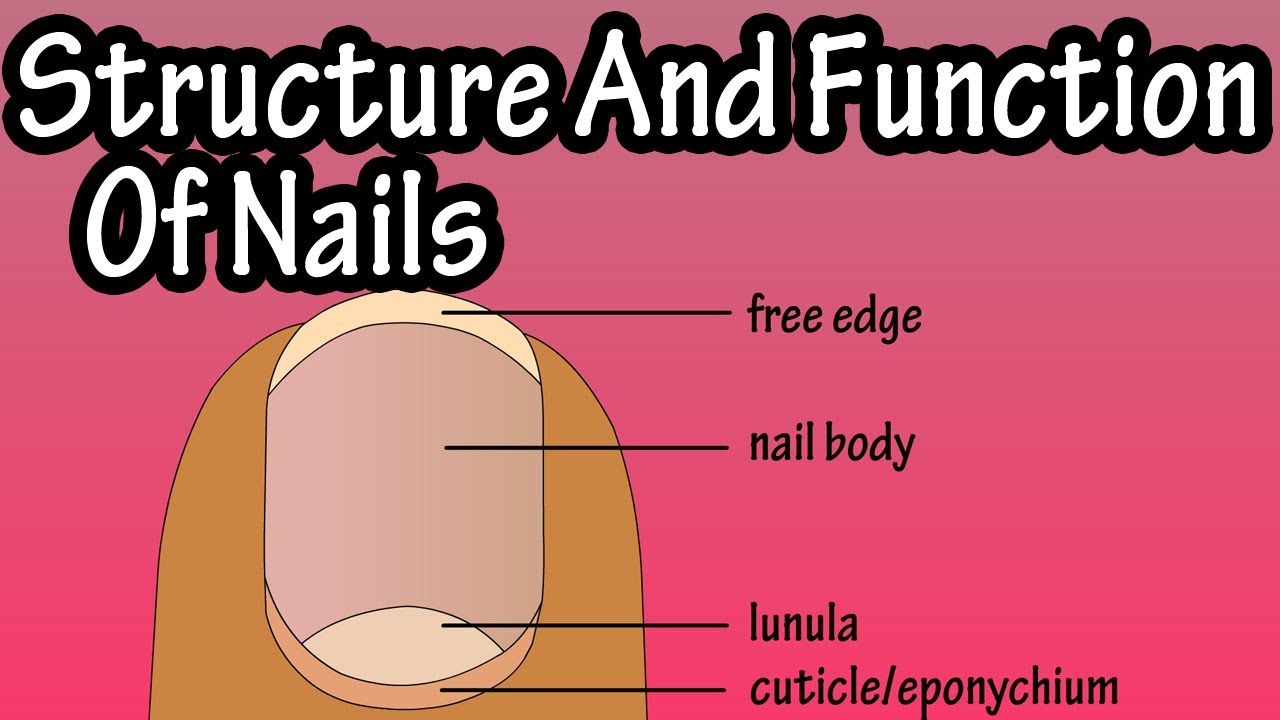 Structure Of Nails Function Of Nails Anatomy Of Nails Why Do We Have Nails
Structure Of Nails Function Of Nails Anatomy Of Nails Why Do We Have Nails
People with thick nails have a large matrix and have more than 50 layers.
Anatomy of the nail. A nail is a horn like keratinous envelope covering the tips of the fingers and toes in most primates. Disturbances of nail growth due to. The average person has 50 layers of keratin cells that make up the nail plate.
Nail structure nail root. In anemia the nails are pale and white. Clinical anatomy of nail.
It contains blood vessels that supply nutrients to the fingertip. A professional primer on the parts of the nail. Nail in the anatomy of humans and other primates horny plate that grows on the back of each finger and toe at its outer end.
The nail plate is the actual fingernail and its made of translucent keratin. The nail bed is the skin underneath the nail plate. Sometimes people confuse the nail bed with the nail plate as in oh you have such pretty nail beds but the compliment is likely meant for the nail plate.
This is the skin that we gently push back during a nail service to provide more nail estate to paint or extend onto. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough protective protein called alpha keratin which is found in the hooves hair claws and horns of vertebrates. The nail is a platelike keratinous translucent structure that consists of highly specialized epithelial cells.
The root of the nail is also known as the germinal matrix. Hypertrophy of the nail bed clubbing occurs in chronic suppurative disease lung abscess. Anatomy of a finger nail cuticle nail bed nail plate hyponychium nail matrix game.
The nails are composed largely of keratin a hardened protein that is also in skin and hair. The nail bed is also referred to as the sterile matrix. Picture of fingernail anatomy.
The eponychium is more commonly known as. It corresponds to the claw hoof or talon of other vertebrates. The thickness of your nails is determined by the size of your matrix.
As new cells grow in the matrix the older cells are pushed out compacted and take on the familiar flattened hardened form of the fingernail. People with thin nails have a small matrix and will have less than 50 layers. The average growth rate.
Fingernails grow from the matrix. Not everyones matrix is the same size. Anatomy of a finger nailanatomy.
The nail plate should not be confused with the nail bed. Nails evolved from claws found in other animals.
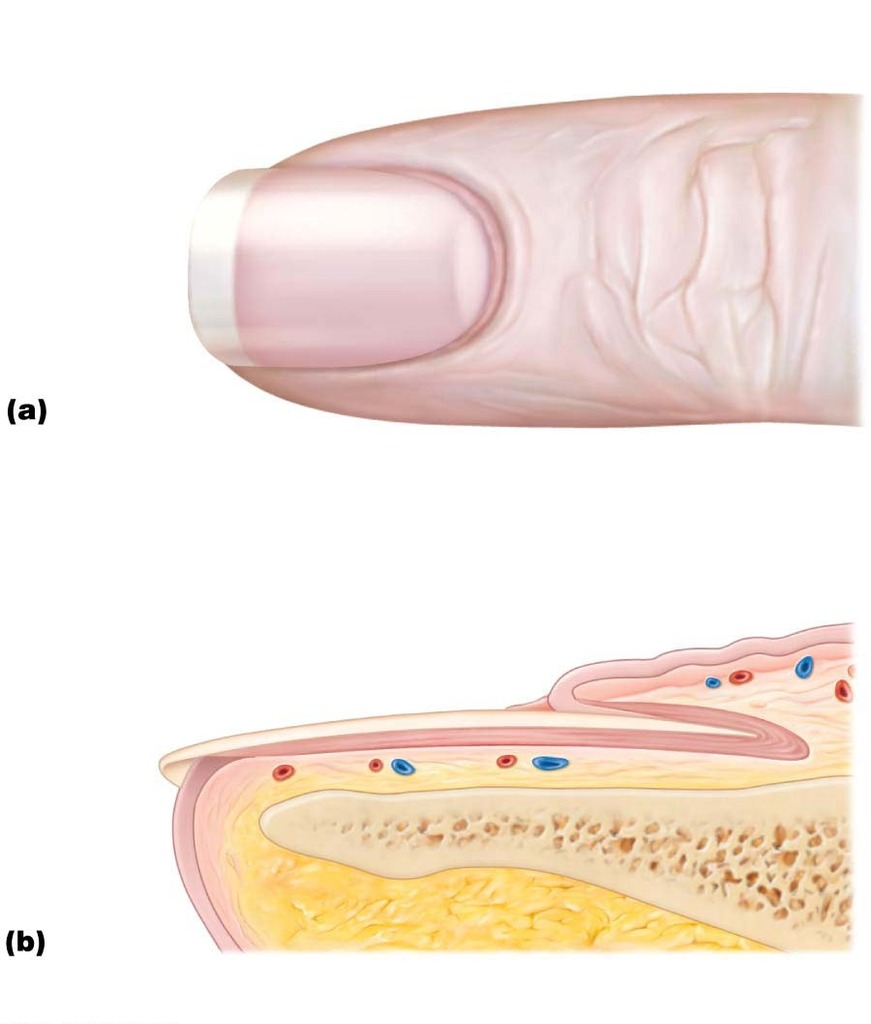 Anatomy Physiology I Chapter 5 Nail Structure Diagram
Anatomy Physiology I Chapter 5 Nail Structure Diagram
Nail Anatomy Debbie Page Wood Nails Make Up
 A Little Bit Of Nail Anatomy Beauty By Wanji
A Little Bit Of Nail Anatomy Beauty By Wanji
 Opi Nail Anatomy Education Opi
Opi Nail Anatomy Education Opi
 Figure Gross Anatomy Of Nail Unit Picture Contributed By
Figure Gross Anatomy Of Nail Unit Picture Contributed By
 Nail Matrix Anatomy Function Injuries And Disorders
Nail Matrix Anatomy Function Injuries And Disorders
 Acute And Chronic Paronychia American Family Physician
Acute And Chronic Paronychia American Family Physician
 Nail Disorders And Systemic Disease What The Nails Tell Us
Nail Disorders And Systemic Disease What The Nails Tell Us
 The Nail Bed Part I The Normal Nail Bed Matrix Stem Cells
The Nail Bed Part I The Normal Nail Bed Matrix Stem Cells
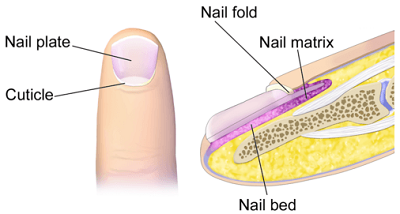 13 4 Hair And Nails Biology Libretexts
13 4 Hair And Nails Biology Libretexts
 Finger Nail Anatomy Stock Photos Finger Nail Anatomy Stock
Finger Nail Anatomy Stock Photos Finger Nail Anatomy Stock
 Nail Anatomy School Nails Colorful Nail Designs Nail Art
Nail Anatomy School Nails Colorful Nail Designs Nail Art
Nail Anatomy Different Parts Of Fingernail Bliss Kiss
 Fingernail Anatomy Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Fingernail Anatomy Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
 What S New In Nail Anatomy The Latest Facts Schoon
What S New In Nail Anatomy The Latest Facts Schoon
![]() Skin And Nail Barrier Function Structure And Anatomy
Skin And Nail Barrier Function Structure And Anatomy
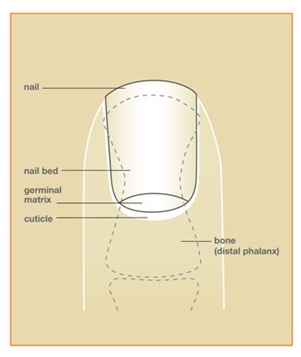 Nail Bed Injuries Hand Injuries Houston Tx
Nail Bed Injuries Hand Injuries Houston Tx
Nail Anatomy Different Parts Of Fingernail Bliss Kiss

Nail Disorders Anatomy Pathology Therapy
 Nail Finger Anatomy Vector Photo Free Trial Bigstock
Nail Finger Anatomy Vector Photo Free Trial Bigstock
 The Structure Of A Nail In 2019 School Nails Human Body
The Structure Of A Nail In 2019 School Nails Human Body
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Fingertip Musculoskeletal Key
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Fingertip Musculoskeletal Key
 How To Treat Fungal Nail Effectively Learning Article
How To Treat Fungal Nail Effectively Learning Article
 Exam 3 Nail Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
Exam 3 Nail Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
 Nail Matrix Anatomy Function Injuries And Disorders
Nail Matrix Anatomy Function Injuries And Disorders

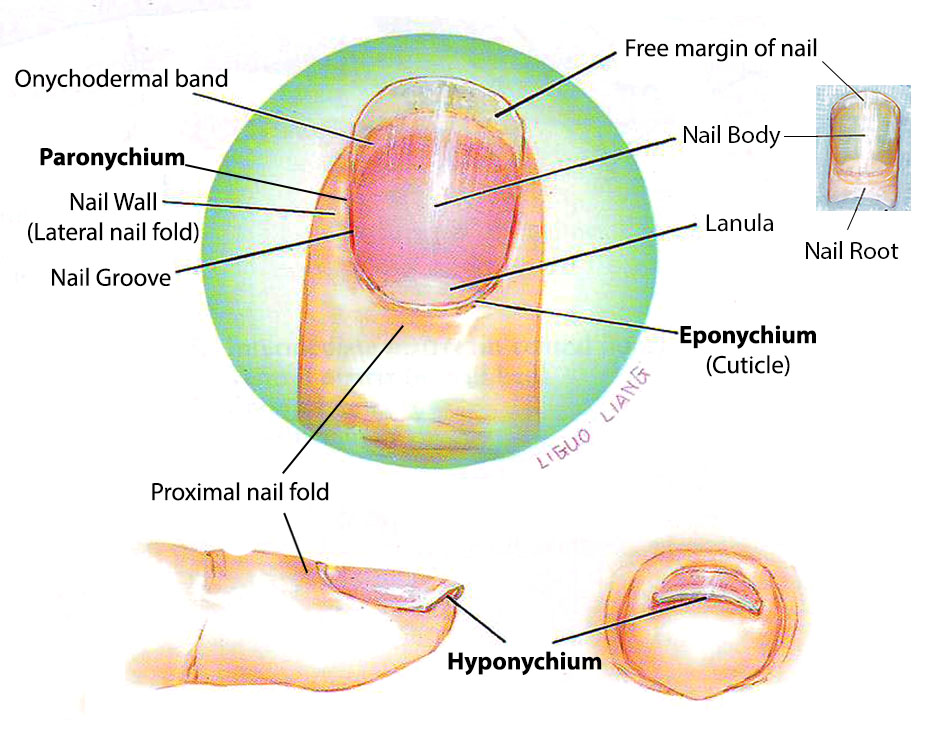




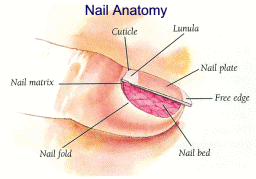
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar