A prime mover is the muscle that has the most influence in one direction on the joint it acts on. A muscle that acts directly to produce a desired movement amid other muscles acting simultaneously to produce the same movement indirectly.
 Agonist Prime Mover Produces A Partial Movement Biceps
Agonist Prime Mover Produces A Partial Movement Biceps
Hip flexion keeps the upper body from falling backwards when standing erect.
Prime mover anatomy. An antagonist muscle is in opposition to a prime mover in that it provides some resistance andor reverses a given movement. L primus movere to move. Most movements of the body require the combined action of numerous muscles.
Pectoralis minor trapezius upper fibres. You are able to move your shoulder joints thanks to the deltoid muscles in each of them. These muscles do not act alone.
Compare antagonist fixation muscle synergist. You are likely to know the pectoralis major as simply pectorals. Prime movers are the agonist muscles and they are assisted by the synergistic muscles.
Prime movers anatomy lab 232. Trapezius middle fibres serratus anterior. It is still the agonist because while resisting gravity during relaxing the triceps brachii continues to be the prime mover or controller of the joint action.
The latissimus dorsi covers the broad area that makes up your. Prime mover muscles are the muscles that initiate the source of movement during physical action. A muscle that provides the major force for producing a specific movement.
Muscles that are prime movers pectoralis major. Agonists are also interchangeably referred to as prime movers since they are the muscles considered primarily responsible for generating or controlling a specific movement. They act simultaneously with other muscles recruited to perform the.
Muscles retracting the pectoral should muscles protracting the pectoral shoul muscles elevating the pectoral shoulde muscles depressing the pectoral should rhomboid minor. The fixator muscles assist the movement of the other three groups by holding the bones associated with the muscle groups. The antagonistic muscles are the muscles that oppose the primer mover by slowing it down.
For example the prime mover in extension of the forearm is the triceps. The prime mover sometimes called the agonist is the muscle that provides the primary force driving the action.
 Solved Post Lab Assignments Posib Quizzes Are Also Assign
Solved Post Lab Assignments Posib Quizzes Are Also Assign
%2C445%2C291%2C400%2C400%2Carial%2C12%2C4%2C0%2C0%2C5_SCLZZZZZZZ_.jpg) Prime Mover A Natural History Of Muscle Steven Vogel
Prime Mover A Natural History Of Muscle Steven Vogel
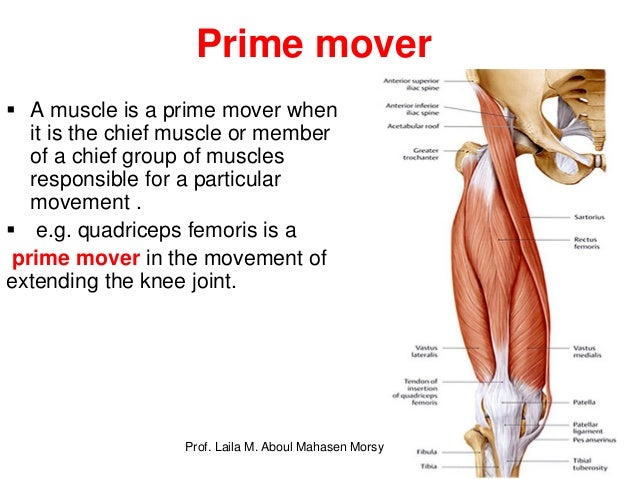 Prof Laila Muscular System 2018
Prof Laila Muscular System 2018
 Muscle Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
Muscle Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
 Muscles Of The Pectoral Girdle And Upper Limbs Anatomy And
Muscles Of The Pectoral Girdle And Upper Limbs Anatomy And
Prime Mover Anatomy Marvelous Prime Mover Lo Otive Anatomy Of
 Muscle Roles Synergist Agonist Antagonist Stabilizer
Muscle Roles Synergist Agonist Antagonist Stabilizer
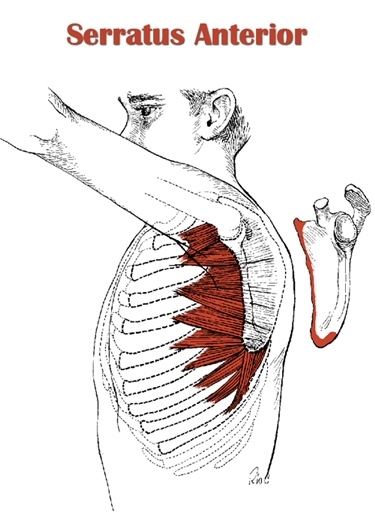 The Definitive Guide To Serratus Anterior Anatomy Exercises
The Definitive Guide To Serratus Anterior Anatomy Exercises
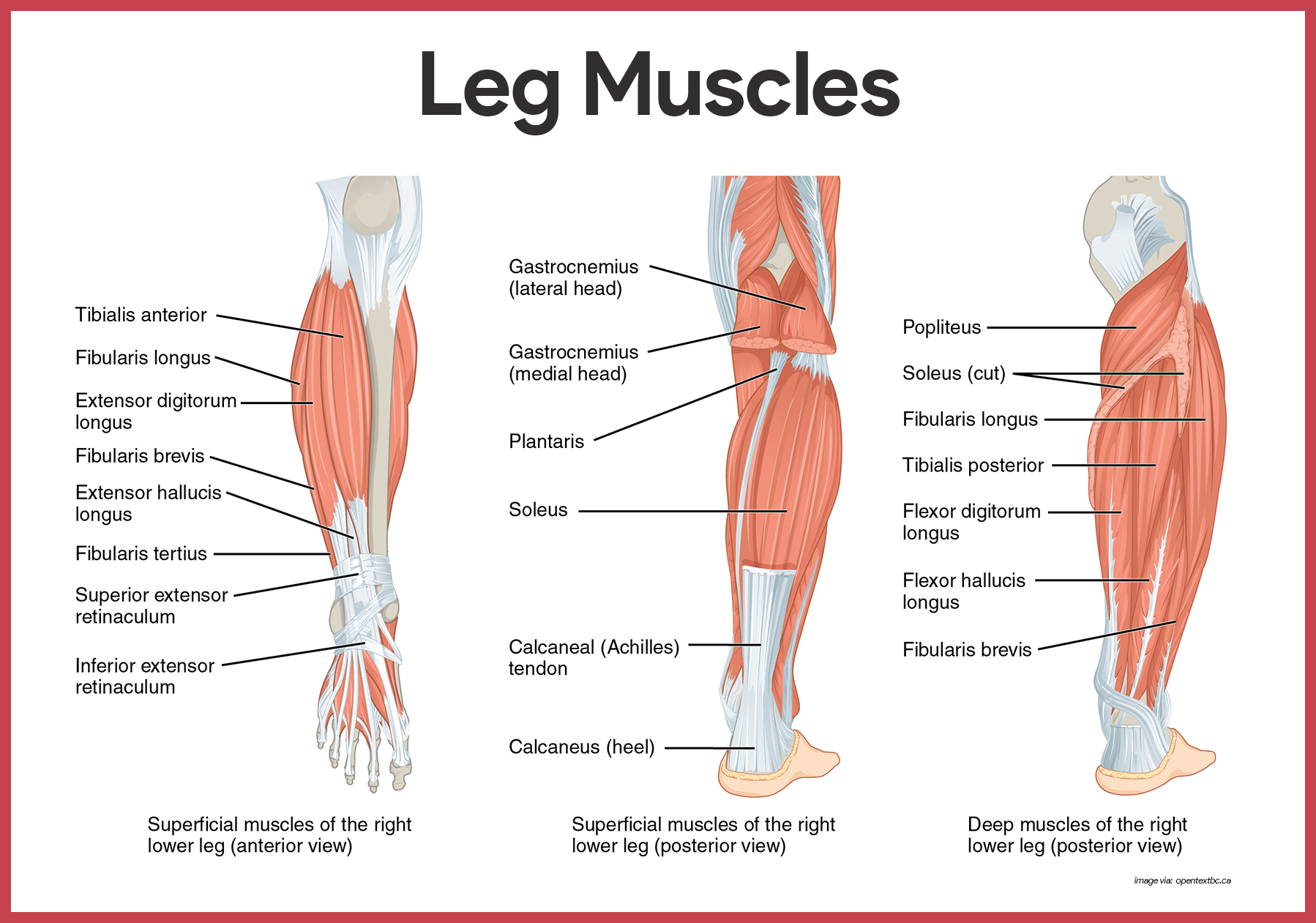 Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 The Runner In Motion Running Anatomy Sports Anatomy
The Runner In Motion Running Anatomy Sports Anatomy
 Chapter 6 Objectives The Muscular System
Chapter 6 Objectives The Muscular System
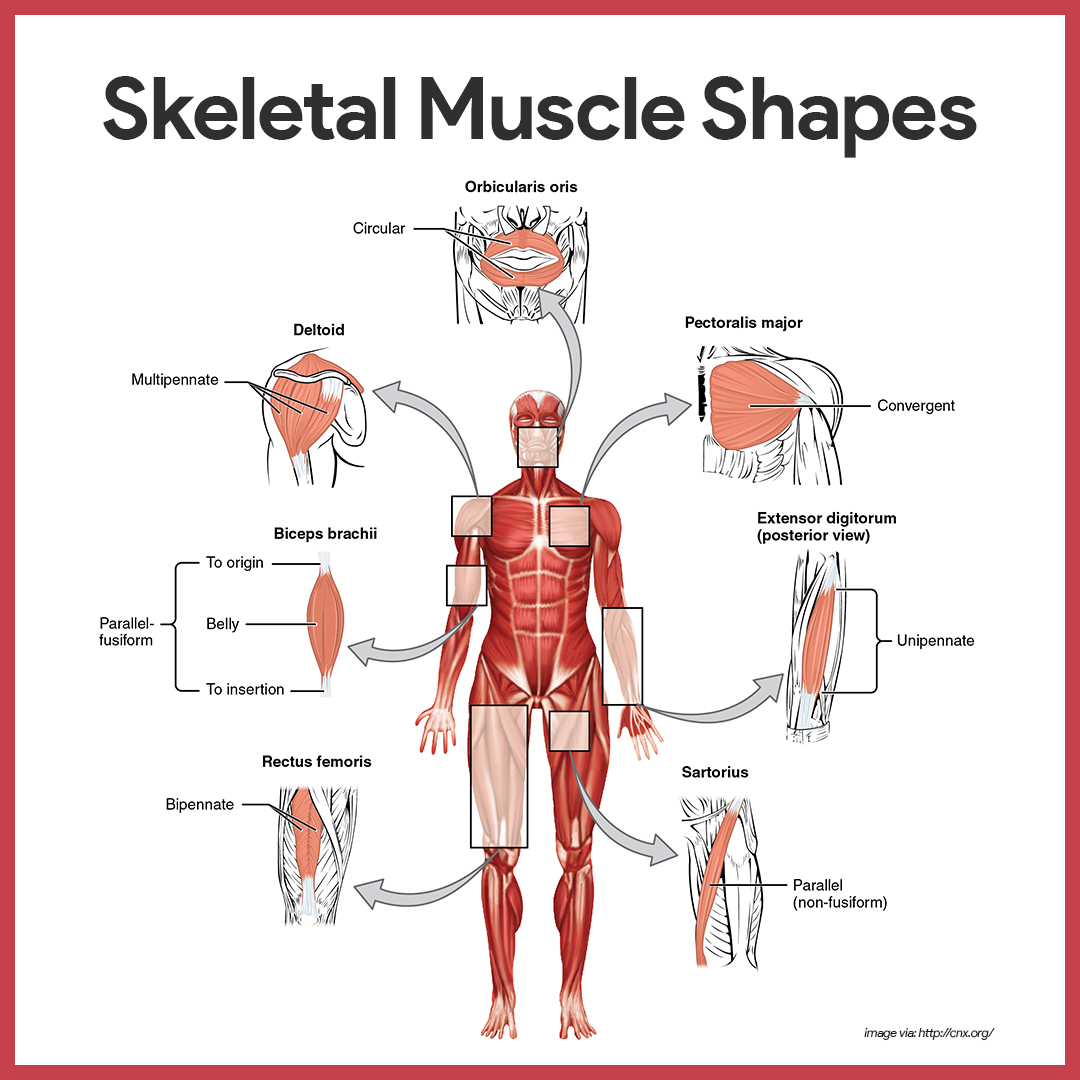 Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Functional Roles Of Muscles Prime Mover Synergist Antagonist Neutralizer Stabilizer Fixator
Functional Roles Of Muscles Prime Mover Synergist Antagonist Neutralizer Stabilizer Fixator
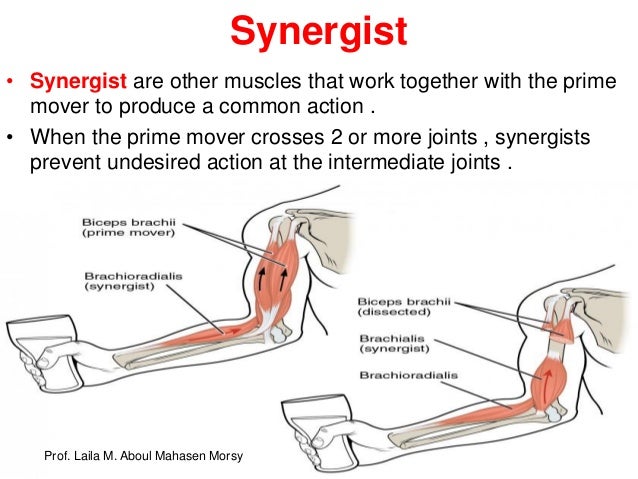 Prof Laila Muscular System 2018
Prof Laila Muscular System 2018
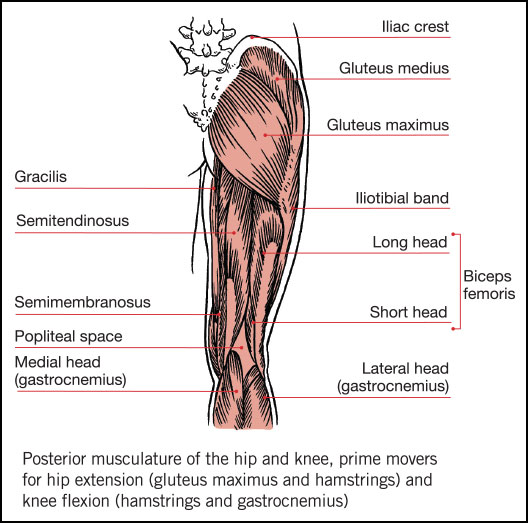 Hamstrings Anatomy And Fitness Training Ace Prosource
Hamstrings Anatomy And Fitness Training Ace Prosource
 Topic 5 Anatomy Of The Muscular System Part 1 Pdf Topic
Topic 5 Anatomy Of The Muscular System Part 1 Pdf Topic
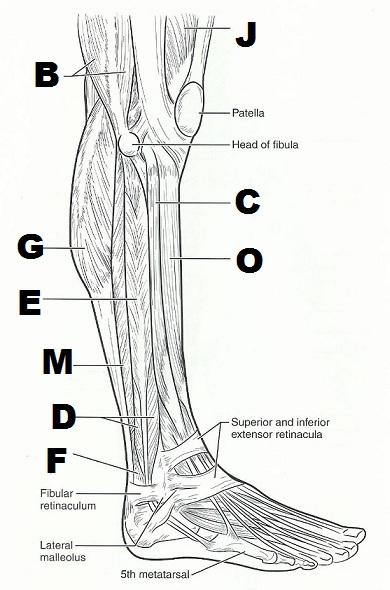
 Exercise 15 Gross Anatomy Of The Muscular System Flashcards
Exercise 15 Gross Anatomy Of The Muscular System Flashcards
 Prime Movers Of The Shoulder Girdle From Cilincal
Prime Movers Of The Shoulder Girdle From Cilincal
 Ex 13 Gross Anatomy Of The Muscular System Anatomy
Ex 13 Gross Anatomy Of The Muscular System Anatomy
 Chapter 10 Vocabulary Anatomy Physiology Honors Flashcards
Chapter 10 Vocabulary Anatomy Physiology Honors Flashcards
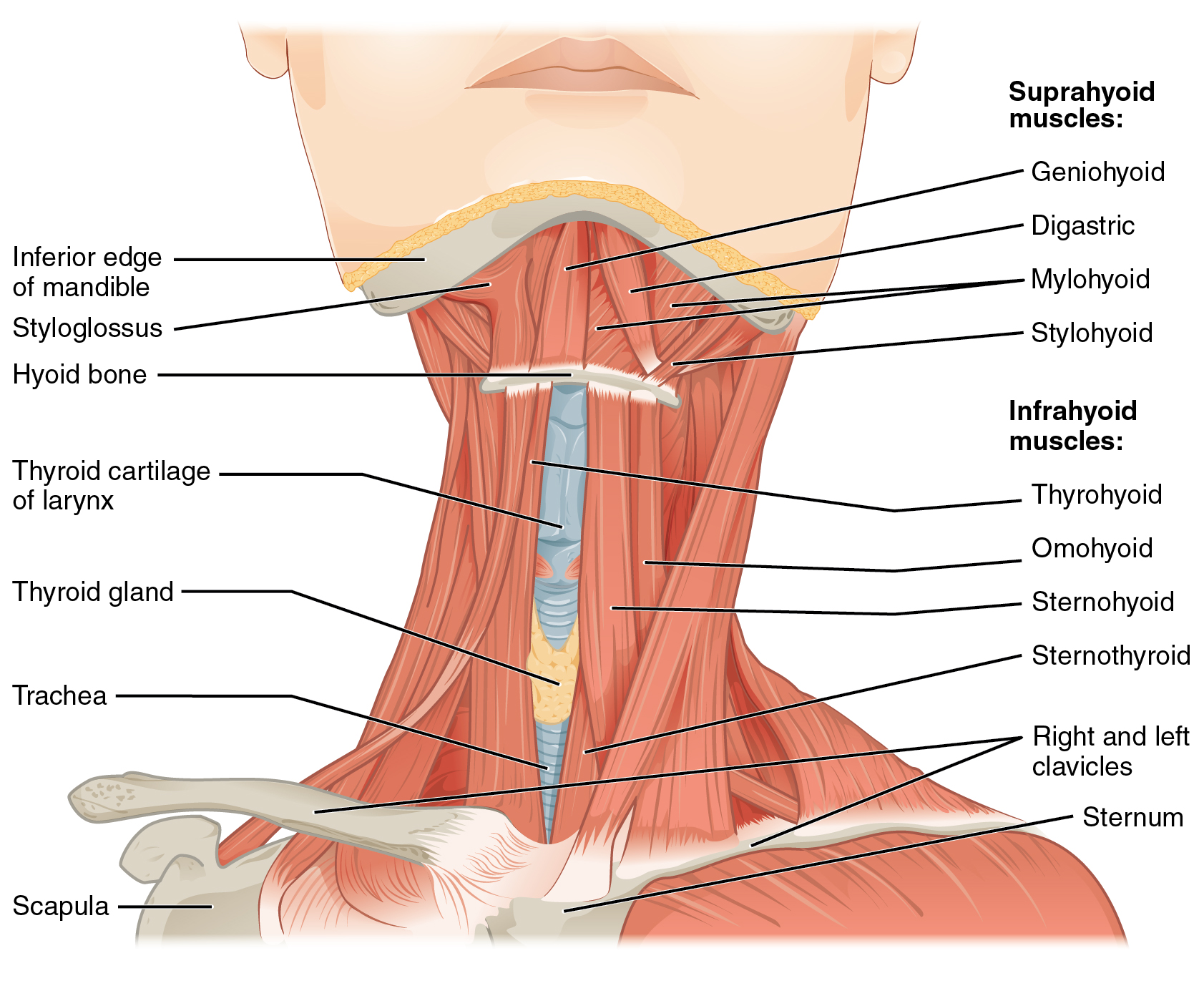 11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
 The Muscular System Gross Anatomy Over 600 Human Skeletal
The Muscular System Gross Anatomy Over 600 Human Skeletal
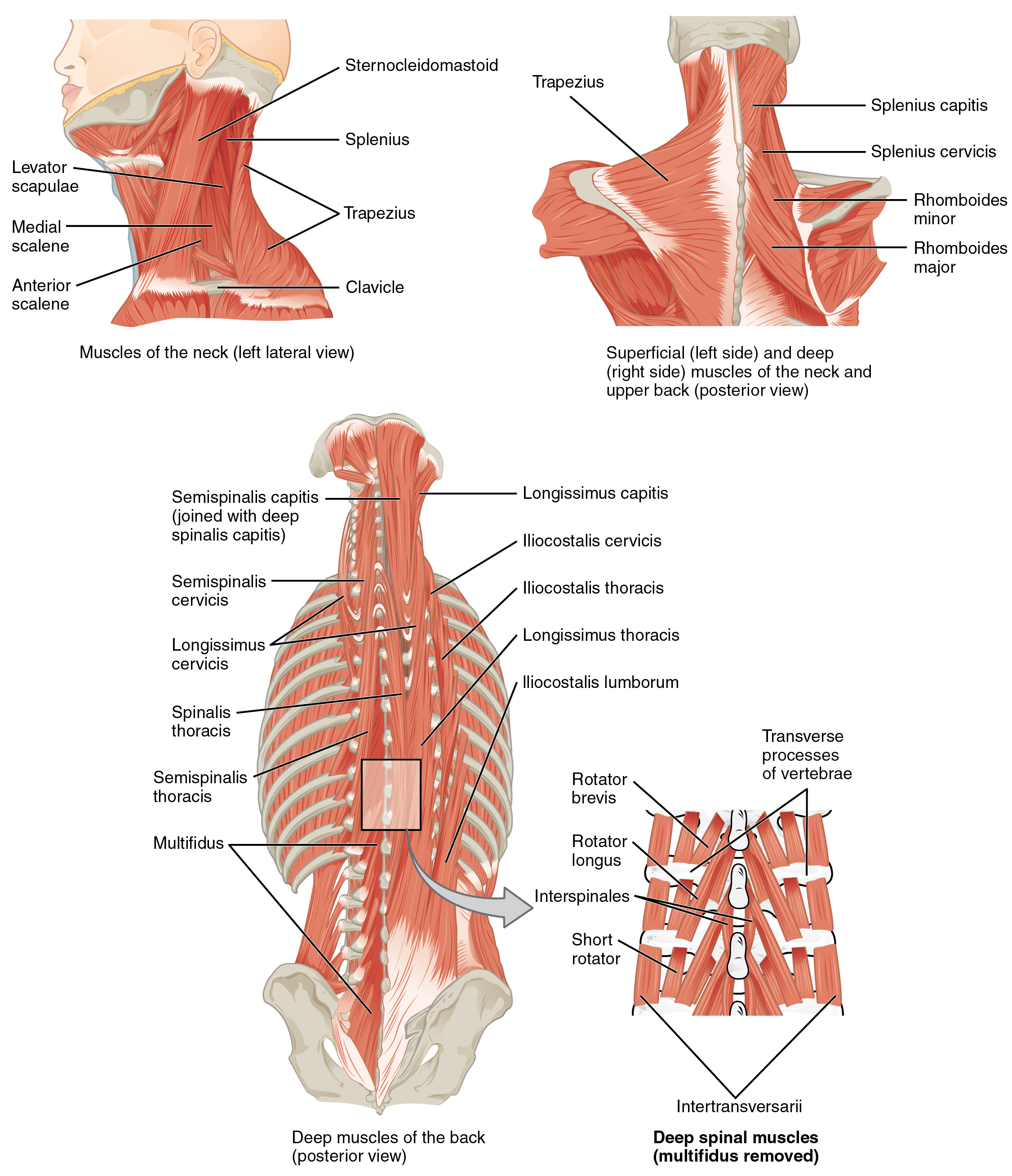 11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
 The Knee Anatomy And Function Part 3 Muscles Slahm
The Knee Anatomy And Function Part 3 Muscles Slahm

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar