Venous system overview vein structure. Anatomy of the venous system.
Urgo Medical Anatomy Of The Normal Venous System In The
Venous return vr is the volume of blood that reaches the right heart.
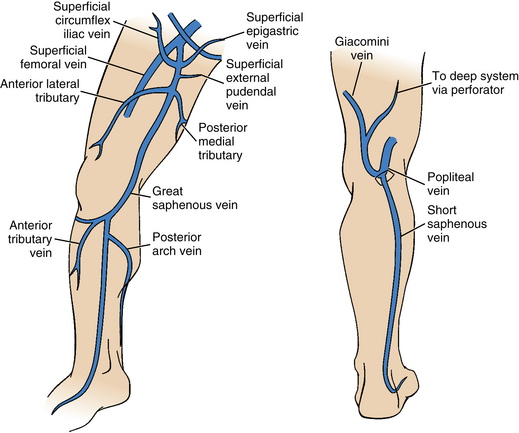
Venous anatomy. The superficial subcutaneous venous system in the legs includes the long saphenous vein and the short saphenous vein. Treatment including angioplasty and stent placement can open the vein but it tends to narrow again restenosis. This is the outer layer of the vein wall.
Veins are the blood vessels which carry the blood from peripheral tissues towards heart. We distinguish between the superficial and the deep venous systems. Sometimes vein problems can occur most commonly due to either a blood clot or a vein defect.
Venous drainage anatomy overview. They carry the deoxygenated blood which is bluish in color and for the same reason veins appear blue. Effective communication and an understanding of the treatment options require a common nomenclature as updated by an international consensus committee.
Pulmonary vein stenosis is a condition in which the pulmonary vein is thickened leading to narrowing. Varicose veins without skin changes are present in about 20 of the general population and they are slightly more frequent in women. Venous anatomy is divided into three systems.
Veins have thinner walls and larger lumina than arteries do. Veins are less muscular than arteries and are often closer to the skin. A primary characteristic of the deep veins is that they run alongside the arteries and as such often share the same name.
It is an uncommon but serious birth defect and is often combined with other heart abnormalities. The anatomy of the lower extremity venous system is complex and highly variable. Unlike the high pressure arterial system the venous system is a low pressure system that relies on muscle contractions to return blood to the heart.
Grossly the venous system is composed of venules and small and great veins. Exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. Use this interactive 3 d diagram to explore the venous system.
Chronic venous diseases cvds include a spectrum of clinical findings ranging from spider telangiectasias and varicose veins to debilitating venous ulceration. The venous system is that part of the circulation in which the blood is transported from the periphery back to the heart. Deep superficial and perforating.
In contrast to veins arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins are often categorized based on their location and any unique features. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart.
Tips for healthy.
Lower Extremity Venous Reflux Baliyan Cardiovascular
 Lower Extremity Venous Anatomy Dallas Tx Venous System
Lower Extremity Venous Anatomy Dallas Tx Venous System
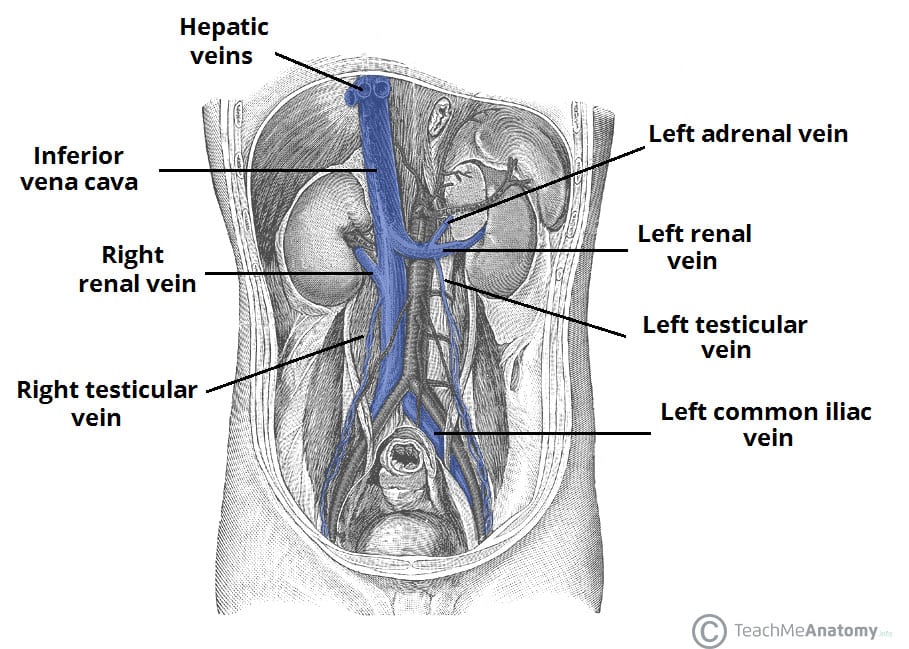 Venous Drainage Of The Abdomen Teachmeanatomy
Venous Drainage Of The Abdomen Teachmeanatomy
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcore Em
 Venous Insufficiency Redbacteria
Venous Insufficiency Redbacteria
 Venous System Stock Vectors Images Vector Art Shutterstock
Venous System Stock Vectors Images Vector Art Shutterstock
 Veins Types Venous System Clinical Significance How To
Veins Types Venous System Clinical Significance How To
 Ecr 2013 C 2631 Upper Extremity Venous Ultrasound
Ecr 2013 C 2631 Upper Extremity Venous Ultrasound
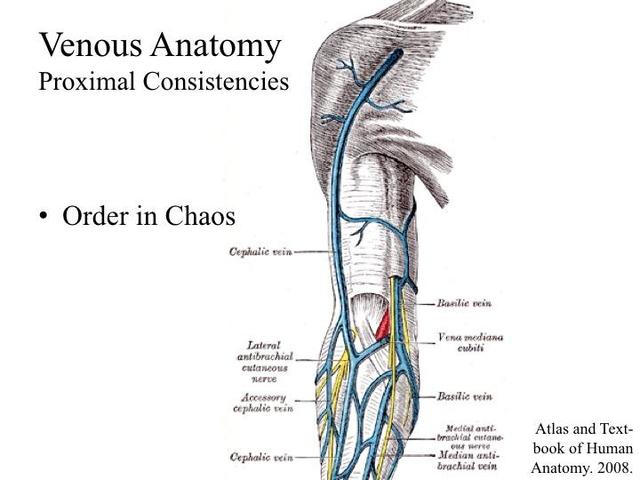
Venous Anatomy Milwaukie Vein Center
 Schematic View Of Venous Anatomy From Insightful Phlebology
Schematic View Of Venous Anatomy From Insightful Phlebology
 Science Source Venous System Of The Pelvis Artwork
Science Source Venous System Of The Pelvis Artwork
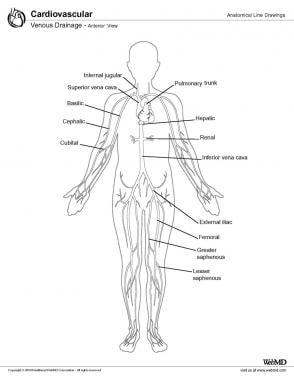 Venous Drainage Anatomy Overview Microscopic Anatomy
Venous Drainage Anatomy Overview Microscopic Anatomy
 J Neurosurgery On Twitter Neurosurgicalatlas
J Neurosurgery On Twitter Neurosurgicalatlas
 Human Venous System Diagram Quizlet
Human Venous System Diagram Quizlet
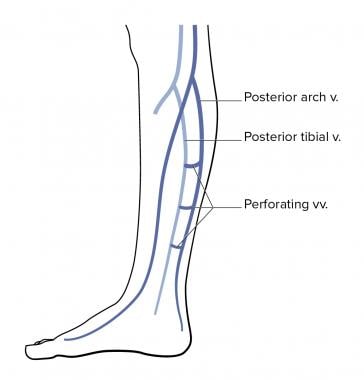 Which Three Venous Systems Are Affected By Chronic Venous
Which Three Venous Systems Are Affected By Chronic Venous
 Venous System Diagram Vintage Anatomy Greeting Card
Venous System Diagram Vintage Anatomy Greeting Card
 Lower Extremity Veins Radiology Key
Lower Extremity Veins Radiology Key
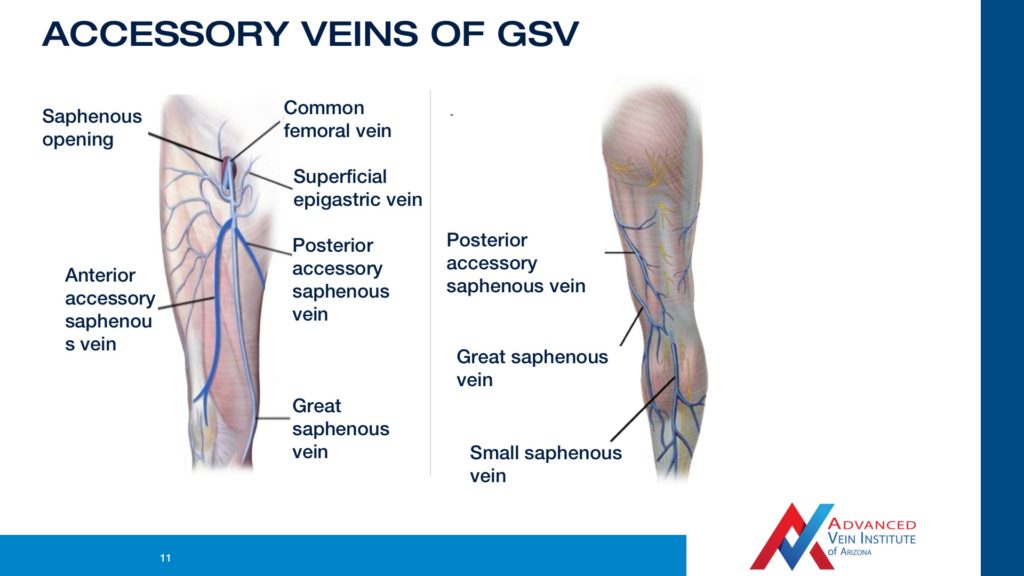 Video The Venous Anatomy Varicose Vein Treatment In Tempe
Video The Venous Anatomy Varicose Vein Treatment In Tempe
 Diagram Showing The Venous Anatomy Of The Leg
Diagram Showing The Venous Anatomy Of The Leg
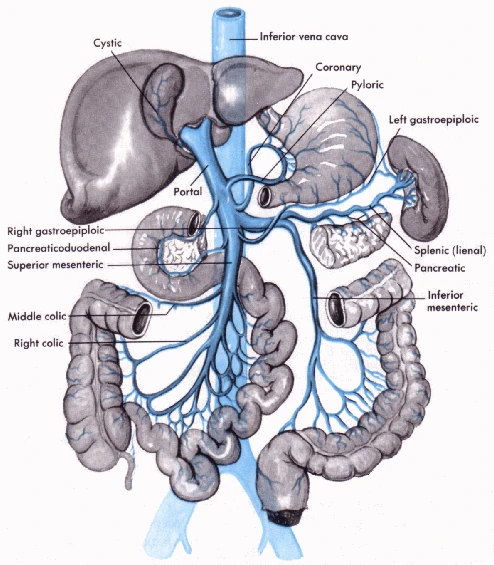 Abdomen Venous Portal System Ranzcrpart1 Wiki Fandom
Abdomen Venous Portal System Ranzcrpart1 Wiki Fandom
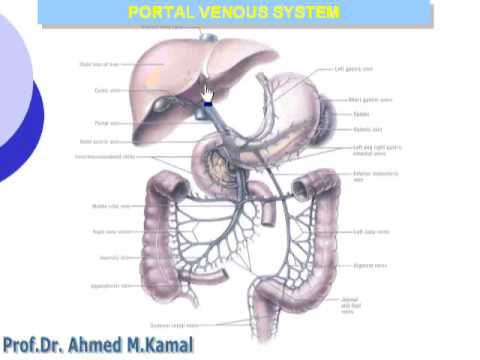


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar