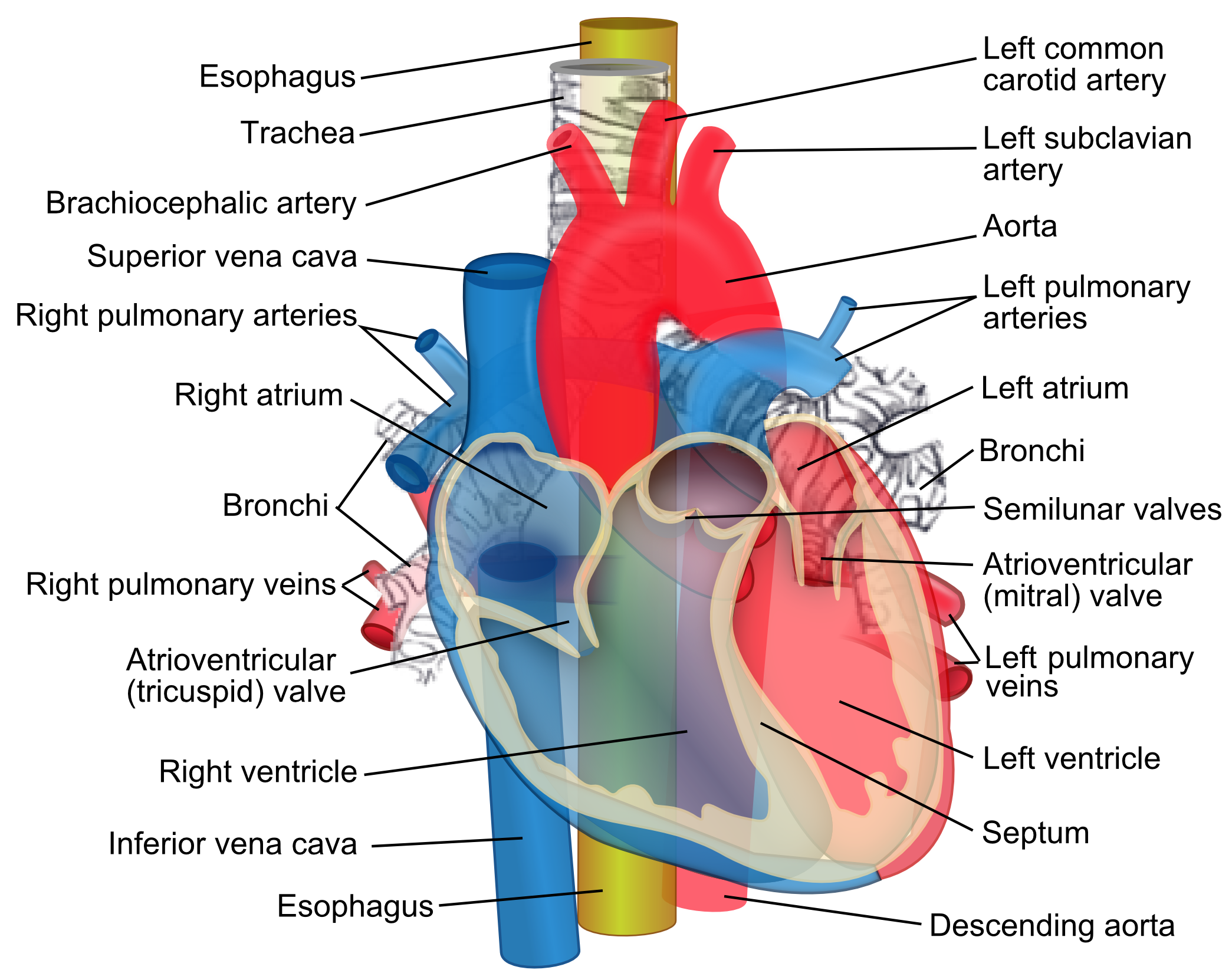
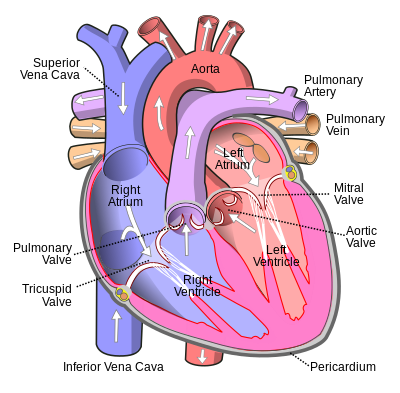
It collects blood from veins serving the tissues inferior to the heart and returns this blood to the right atrium of the heart. The ivc enters the right atrium inferior to the entrance of the superior vena cava svc.
De oxygenated blood means most of the oxygen has been removed by tissues and therefore the blood is darker.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12506/Horseshoe_kidney.png)
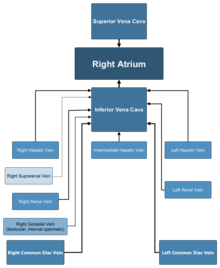
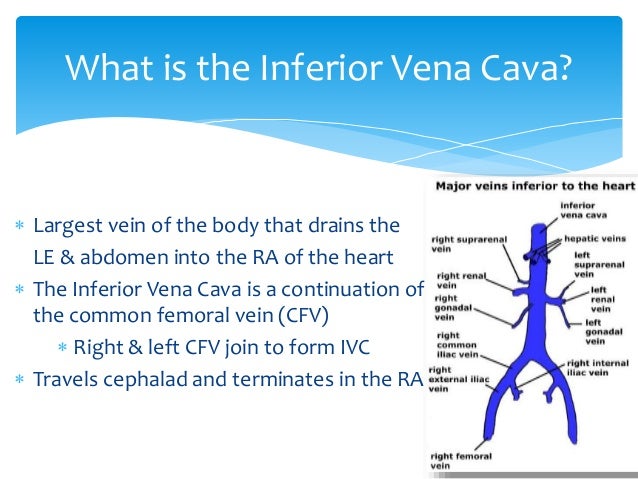
Inferior vena cava anatomy. The inferior vena cava is formed by the coming together of the two major veins from the legs the common iliac veins at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra just below the small of the back. The diagram below summarises the arrangement. The inferior vena cava or ivc is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart.
The ivcs function is to carry the venous blood from the lower limbs and abdominopelvic region to the heart. The inferior vena cava also known as ivc or the posterior vena cava is a large vein that carries blood from the torso and lower body to the right side of the heart. From there the blood is pumped to the lungs to get oxygen before going to the left side of the heart to be pumped back out to the body.
The function of the inferior vena cava is carrying de oxygenated blood also known as dark blood which is blood that has had all oxygen removed from it and has a dark bluish purple color. Its very difficult to find nice images of a normal. The inferior vena cava empties into the right atrium of the heart.
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries de oxygenated blood from the lower body to the heart. Its walls are rigid and it has valves so the blood does not flow down via gravity. Inferior vena cava ivc anatomy the ivc in a nutshell.
The ivc is formed by the union of the right and left common iliac veins. Tributaries of the inferior vena cava. This blood comes from the legs and the lower torso of the body.
Unlike the superior vena cava it has a substantial number of tributaries between its point of origin and its terminus at the heart. The inferior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body. The inferior vena cava ivc is a large retroperitoneal vessel formed by the confluence of the right and left common iliac veins.
It is located at the posterior abdominal wall on the right side of the aorta. The inferior vena cava is a vein in your body which carries blood from the lower extremities and the bottom half of the body to the heart. The inferior vena cava ivc is the largest vein of the human body.
Although the vena cava is very large in diameter its walls are incredibly thin due to the low pressure exerted by venous blood.
 Difference Between Superior And Inferior Vena Cava Compare
Difference Between Superior And Inferior Vena Cava Compare
 Inferior Vena Cava Branches With Organs Google Search
Inferior Vena Cava Branches With Organs Google Search
 Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement Vascular Ultrasound
Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement Vascular Ultrasound
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/heart_and_major_vessels-5820b6ba3df78cc2e887becd.jpg) Superior And Inferior Venae Cavae
Superior And Inferior Venae Cavae
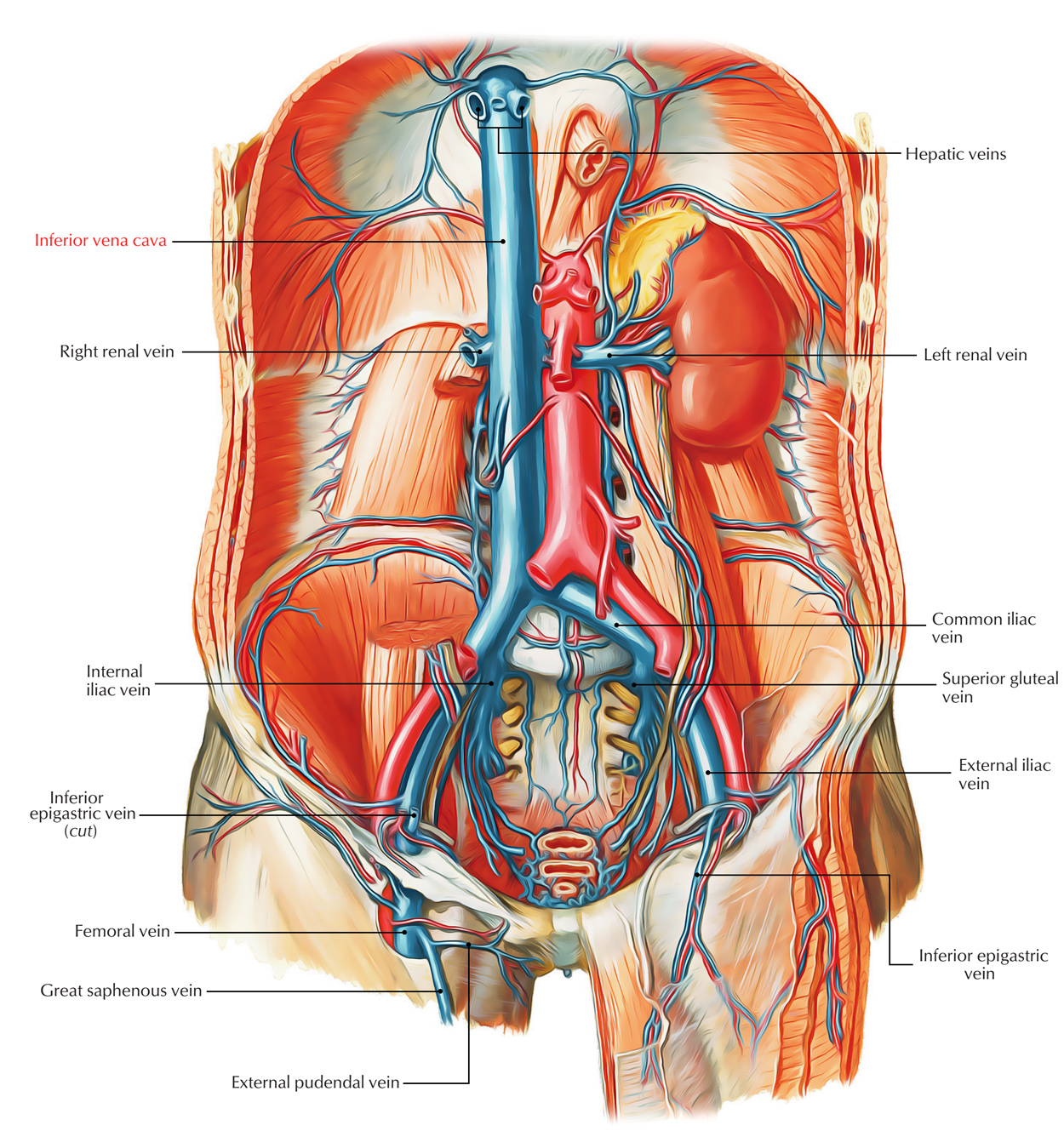 Easy Notes On Inferior Vena Cava Ivc Learn In Just 3
Easy Notes On Inferior Vena Cava Ivc Learn In Just 3
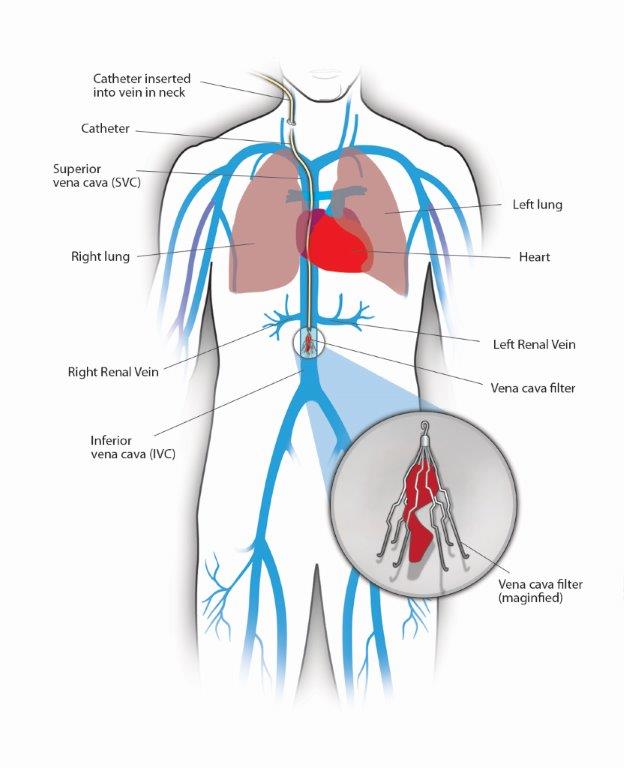 Inferior Vena Cava Filters Center For Vein Care
Inferior Vena Cava Filters Center For Vein Care
 Definition Of Inferior Vena Cava
Definition Of Inferior Vena Cava
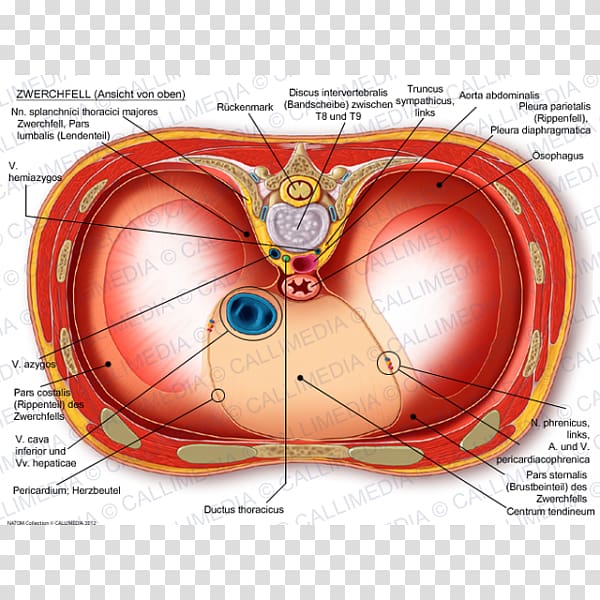 Thoracic Diaphragm Anatomy Inferior Vena Cava Thorax
Thoracic Diaphragm Anatomy Inferior Vena Cava Thorax
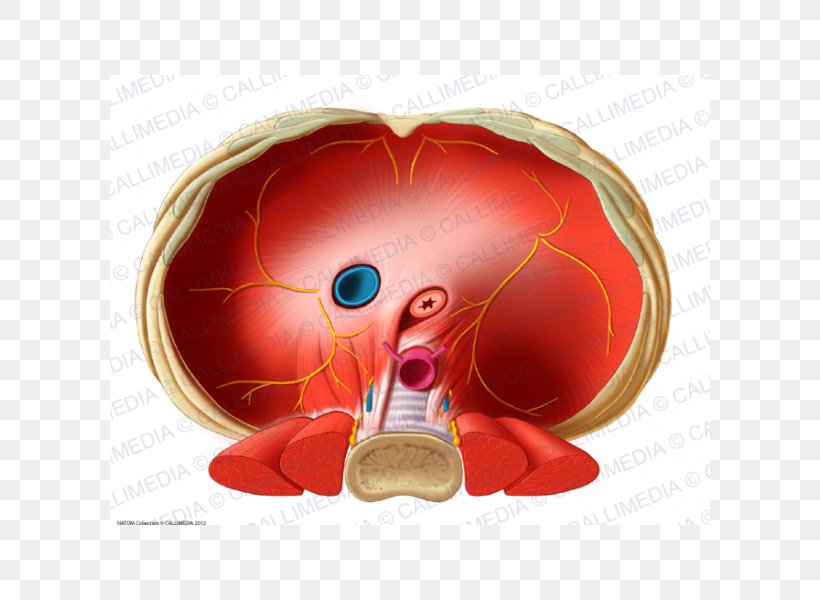 Thoracic Diaphragm Inferior Vena Cava Human Anatomy
Thoracic Diaphragm Inferior Vena Cava Human Anatomy
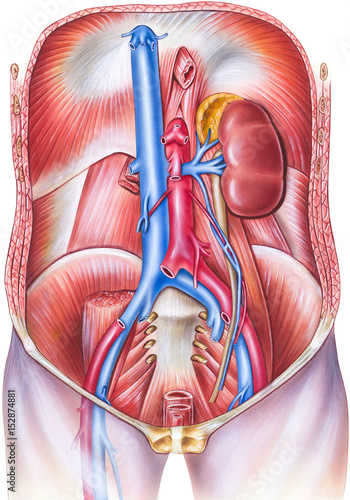 Human Anatomy Of Vasculature Of The Torso Frontal Sub
Human Anatomy Of Vasculature Of The Torso Frontal Sub
 Tributaries Of Inferior Vena Cava Diagram Quizlet
Tributaries Of Inferior Vena Cava Diagram Quizlet
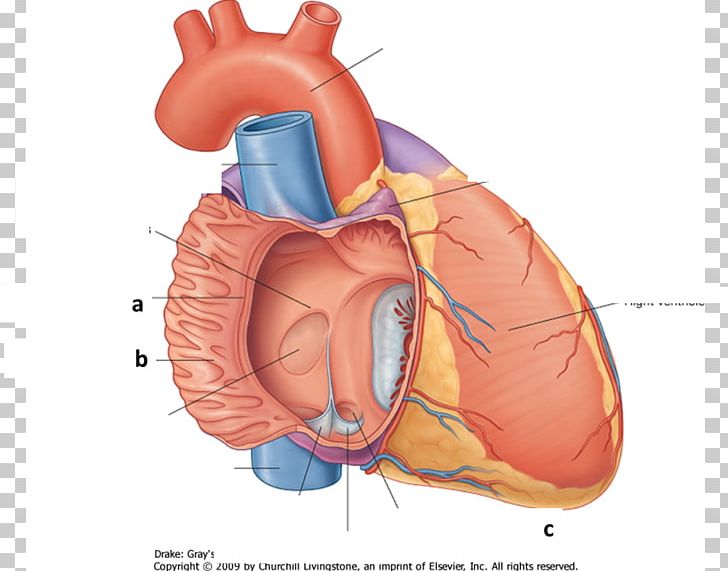 Crista Terminalis Atrium Heart Pectinate Muscles Inferior
Crista Terminalis Atrium Heart Pectinate Muscles Inferior
 Inferior Vena Cava And Its Tributaries Anatomy Tutorial
Inferior Vena Cava And Its Tributaries Anatomy Tutorial
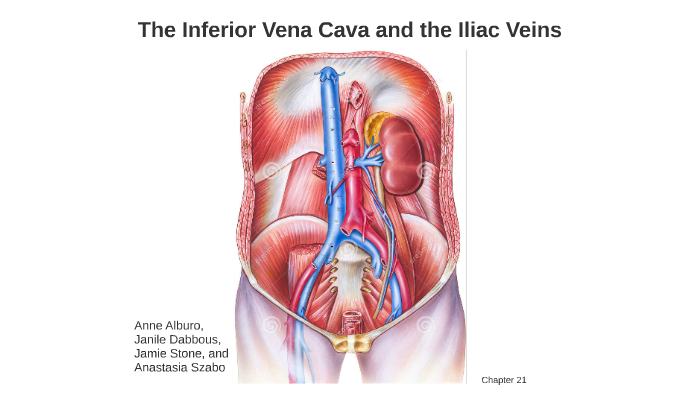 The Inferior Vena Cava And The Iliac Veins By Janile Dabbous
The Inferior Vena Cava And The Iliac Veins By Janile Dabbous
 Inferior Vena Cava Chapter 33 Atlas Of Surgical
Inferior Vena Cava Chapter 33 Atlas Of Surgical
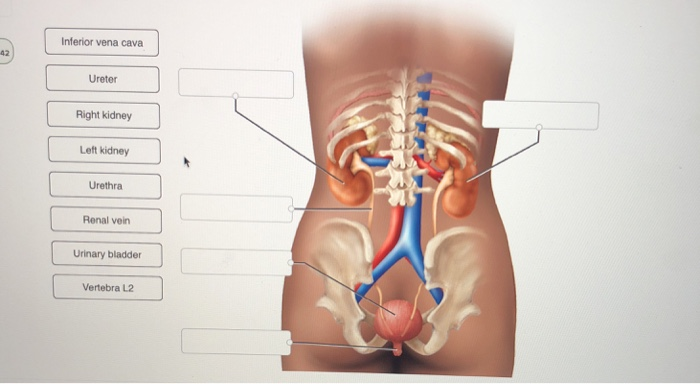 Solved Inferior Vena Cava 42 Ureter Right Kidney Left Kid
Solved Inferior Vena Cava 42 Ureter Right Kidney Left Kid
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/642/9s1xBqe3Yx69sd9UimS8w_veins-of-the-small-intestine_english.jpg) Inferior Vena Cava Anatomy And Function Kenhub
Inferior Vena Cava Anatomy And Function Kenhub

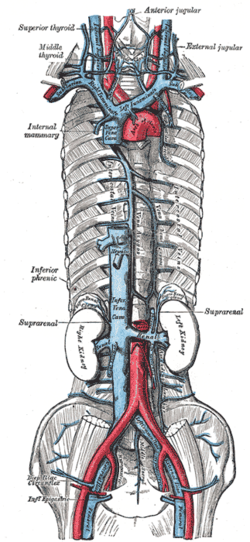
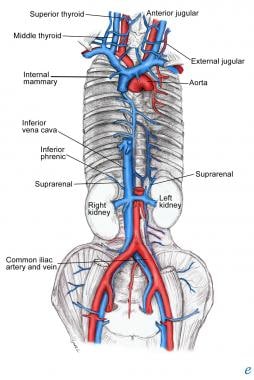 What Is The Anatomy Relevant To Inferior Vena Caval
What Is The Anatomy Relevant To Inferior Vena Caval
 The Main Veins And Arteries Of The Lower Body Including The
The Main Veins And Arteries Of The Lower Body Including The
 Main Veins Leg Foot Inferior Vena Stock Vector Royalty Free
Main Veins Leg Foot Inferior Vena Stock Vector Royalty Free
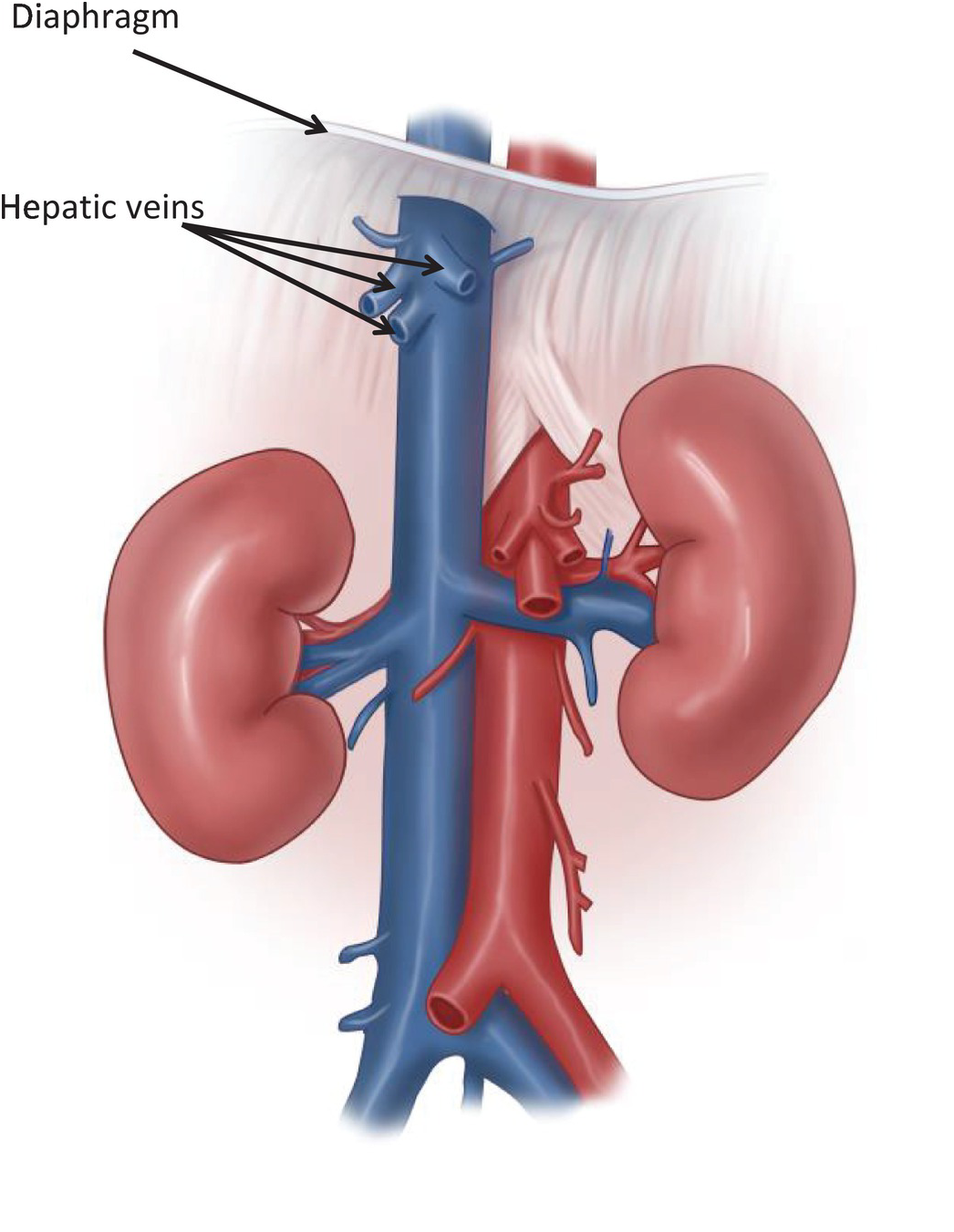
 Attachments Of The Diaphragm To The Body Wall Ivc
Attachments Of The Diaphragm To The Body Wall Ivc
 Figure 7 From Congenital Absence Of Inferior Vena Cava
Figure 7 From Congenital Absence Of Inferior Vena Cava
 Anatomy Of Major Abdominal Veins Inferior Vena Cava
Anatomy Of Major Abdominal Veins Inferior Vena Cava
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12506/Horseshoe_kidney.png) Inferior Vena Cava Anatomy And Function Kenhub
Inferior Vena Cava Anatomy And Function Kenhub
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar