The ovaries are female reproductive organs that are akin to the testes in men. The ovaries are a pair of almond shaped glands that produce ova and the female sex hormones.
In this article we will initially look at the basic function location components and clinical significance of the ovaries.
Anatomy of the ovaries. They are two nodular bodies situated one on either side of the uterus in relation to the lateral wall of the pelvis and attached to the back of the broad ligament of the uterus behind and below the uterine tubes fig. Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. They produce the ova eggs that when fertilized will develop into a fetus.
Since the anatomy and function of the ovary vary considerably at different stages in a womans life these aspects will be considered during adulthood childhood and after the menopause. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. Help begin and control follicle development by influencing hormone production.
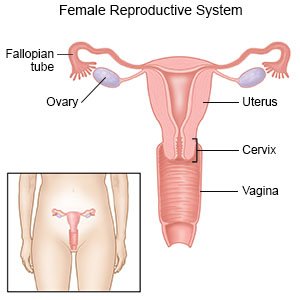
Located laterally to the left and right of the uterus and inferior to the fallopian tubes the ovaries are connected to the uterus via the ovarian ligaments. Located around and on the periphery of the ovarian follicle. The ovaries are the female pelvic reproductive organs that house the ova and are also responsible for the production of sex hormones.
Anatomy of ovaries the ovaries are the two female reproductive glands which are solid pinkish grey and almold shape entities situated on either side of the uterus and are connected to the uterus by the fallopian tube fig. There are two ovaries each of which is located within the pelvic region beside the uterus womb. They are paired organs located on either side of the uterus within the broad ligament below the uterine fallopian tubes.
Anatomy of human ovaries the ovaries develop along with other organs in the womb before birth. They also generate the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. Specifically these cells secrete androgens which are converted into estrogen by the granulosa cells.
The female gonads are called the ovaries. The ovaries are homologous with the testes in the male. The ovaries are considered the female gonads.
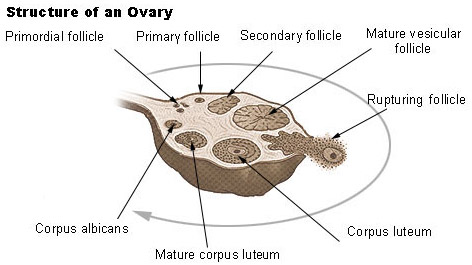
This chapter deals with the normal macroscopic microscopic and ultrastructural morphology of the human ovary and its hormonal function. The latter part of the article will cover the ligaments associated with the ovaries and their vasculature lymphatic drainage and innervation. When a female infant is born her ovaries will contain approximately 400000 egg producing follicles and for the most part her body will not produce anymore follicles for the rest of her life.
 The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
/male_female_gonads-58811e985f9b58bdb3e3dfe9.jpg) Male And Female Gonads Testes And Ovaries
Male And Female Gonads Testes And Ovaries
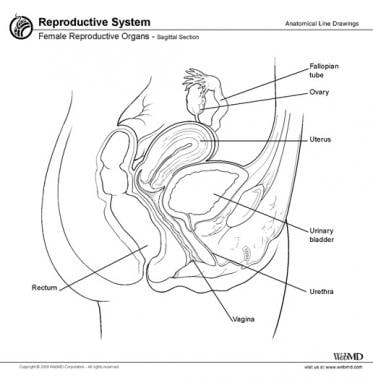
 Female Reproductive Anatomy Reproductive Medbullets Step 1
Female Reproductive Anatomy Reproductive Medbullets Step 1
Ovaries Anatomy And Physiology
 Ovary Anatomy Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy Natural
Ovary Anatomy Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy Natural
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/480/Wx4xsnGNJz0G5IjNKhXiA_uterus-and-ovaries_english.jpg) Ovaries Anatomy And Embryology Kenhub
Ovaries Anatomy And Embryology Kenhub
 Ovarian Abscess What You Need To Know
Ovarian Abscess What You Need To Know
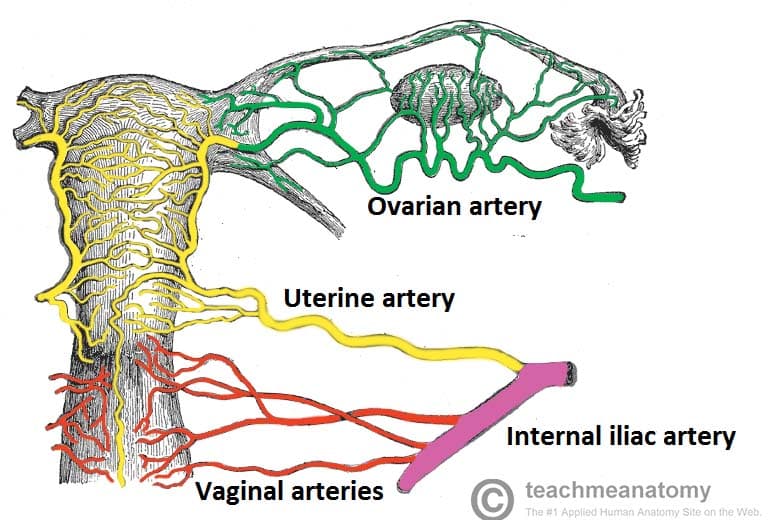
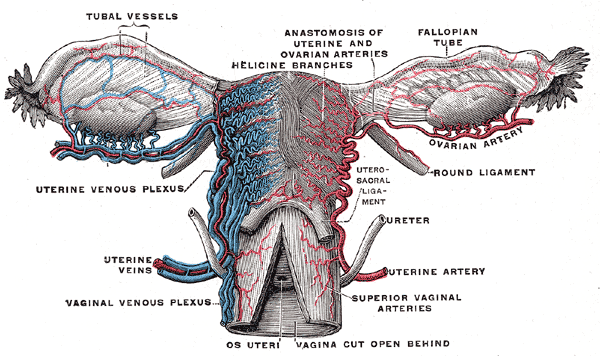
 Uterine Blood Supply Elearning
Uterine Blood Supply Elearning
 Female Reproductive System Overview Anatomy And Physiology
Female Reproductive System Overview Anatomy And Physiology
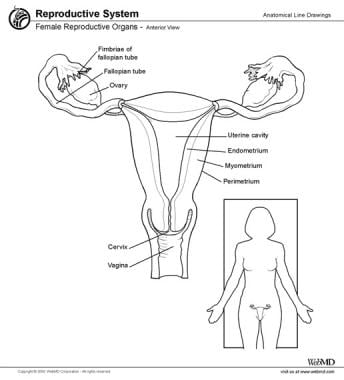 Ovary Anatomy Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy Natural
Ovary Anatomy Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy Natural
Ovarian Cancer Stage I Image Details Nci Visuals Online
 Fischer Technical Company Bs308 Uterus And Ovaries Post It
Fischer Technical Company Bs308 Uterus And Ovaries Post It
 Ovary Animal And Human Britannica
Ovary Animal And Human Britannica
 Ovarian Epithelial Cancer Treatment Mhealth Org
Ovarian Epithelial Cancer Treatment Mhealth Org
 Ovarian Epithelial Fallopian Tube And Primary Peritoneal
Ovarian Epithelial Fallopian Tube And Primary Peritoneal
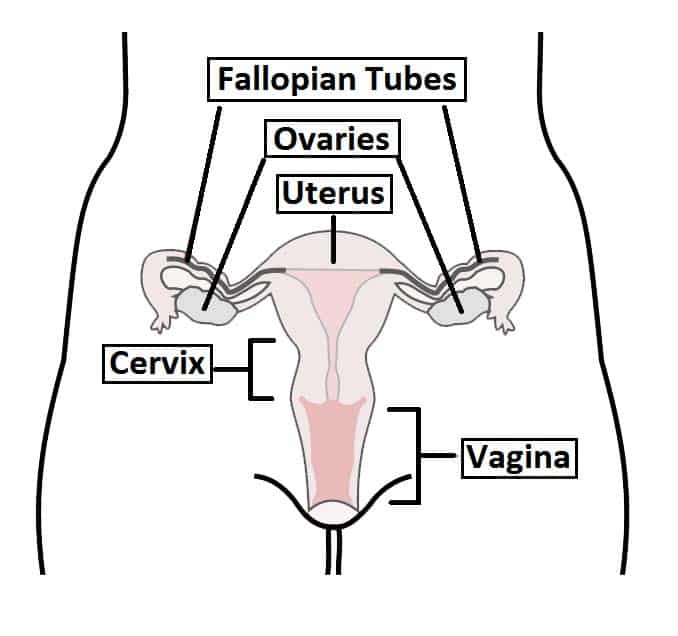 The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
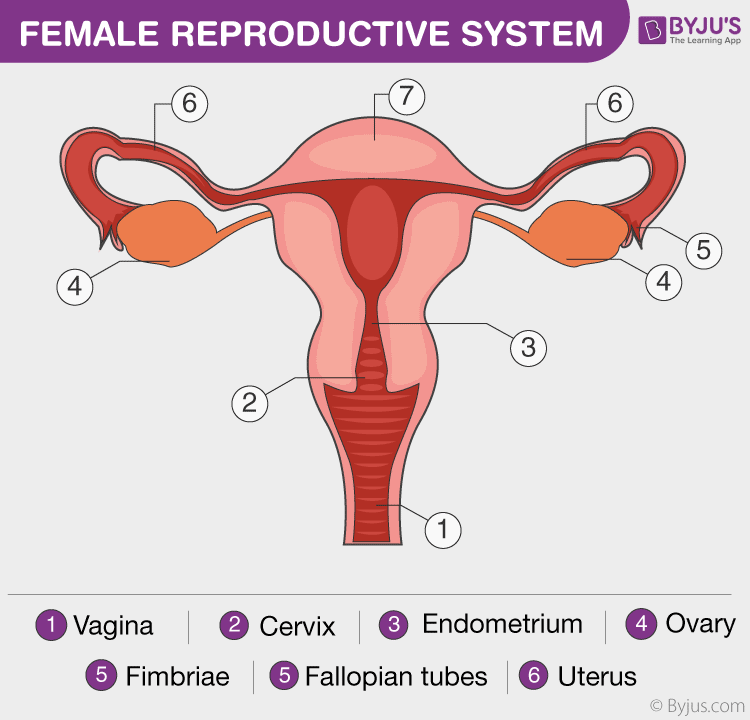
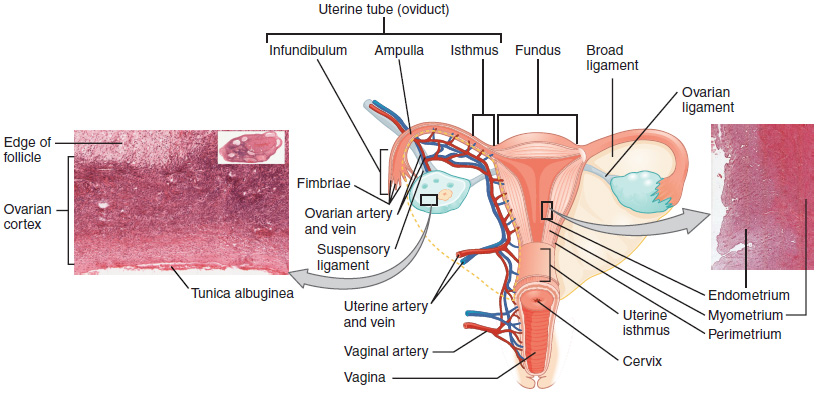 27 2 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Female Reproductive
27 2 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Female Reproductive
 The Ovaries Anatomy Of The Ovaries Anatomy Medicine Com
The Ovaries Anatomy Of The Ovaries Anatomy Medicine Com
Week 10 Female Reproductive System Anatomy Phase 1
 Female Reproductive System Gynecological Medical Banner Woman S
Female Reproductive System Gynecological Medical Banner Woman S
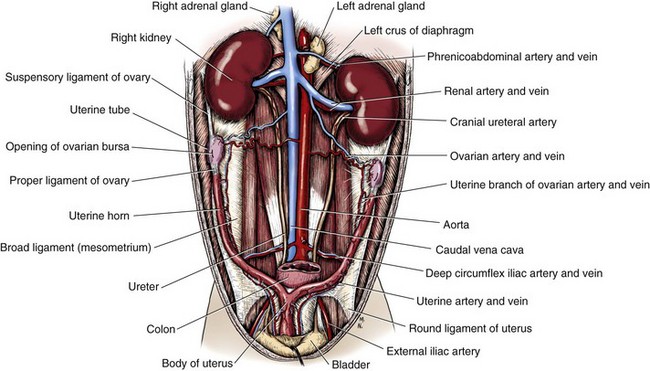 Ovaries And Uterus Veterian Key
Ovaries And Uterus Veterian Key
 The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
 Ovarian Cysts Children S Hospital Colorado
Ovarian Cysts Children S Hospital Colorado



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar