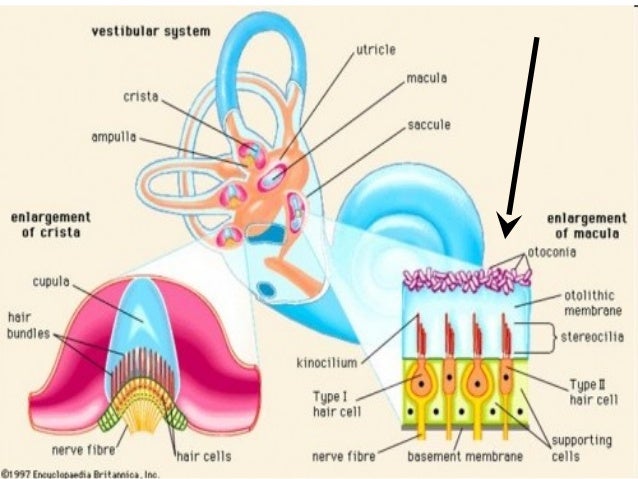
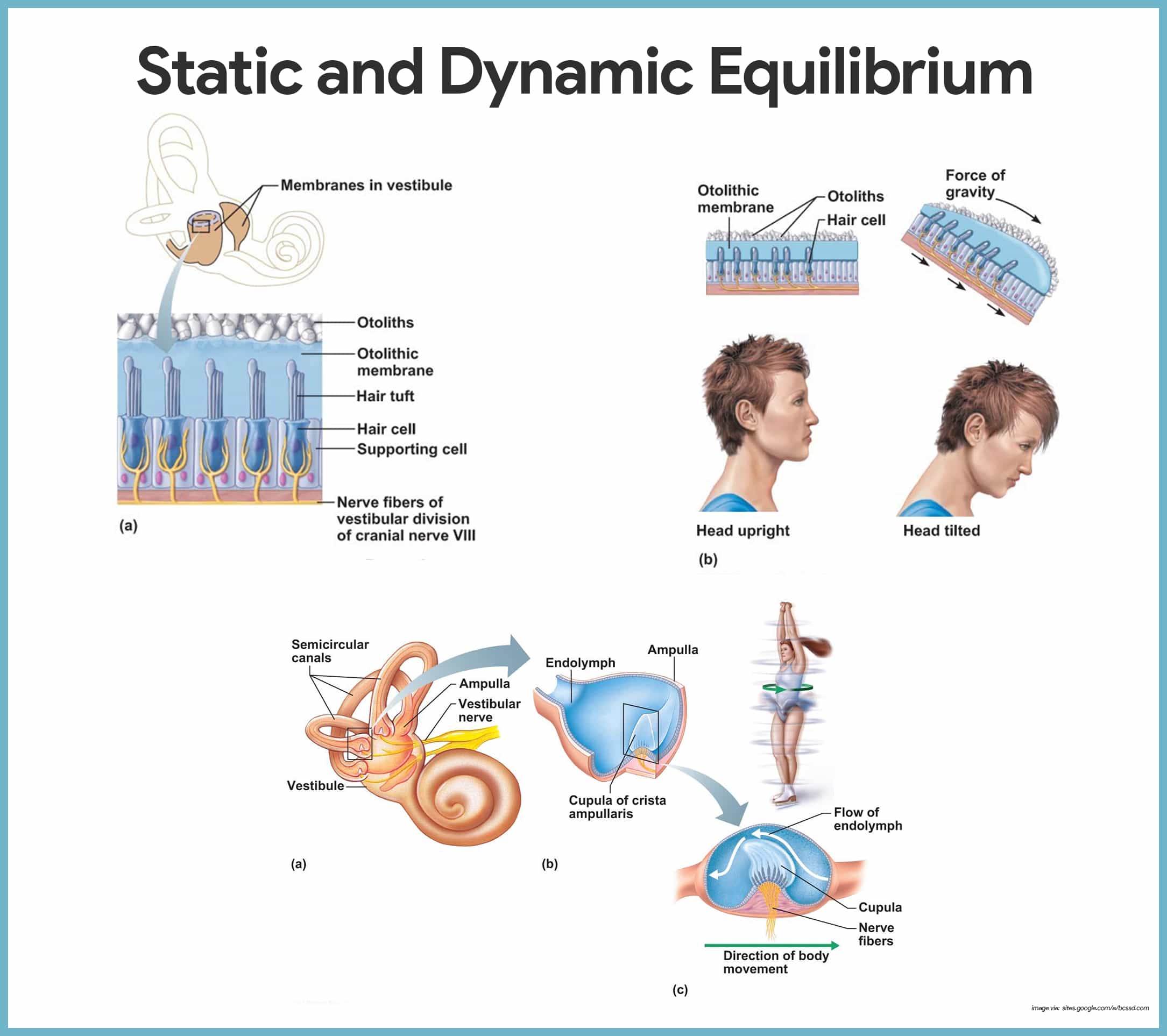
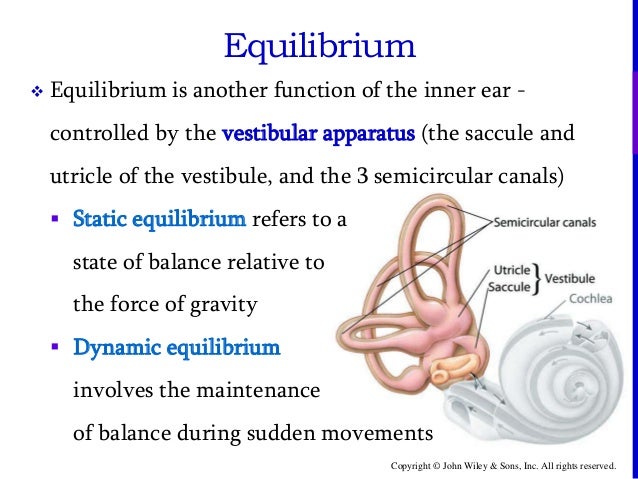
Static equilibrium inside the vestibule are two chambers. The saccule and utricle each contain a sense organ called the macula where stereocilia and their supporting cells are found.
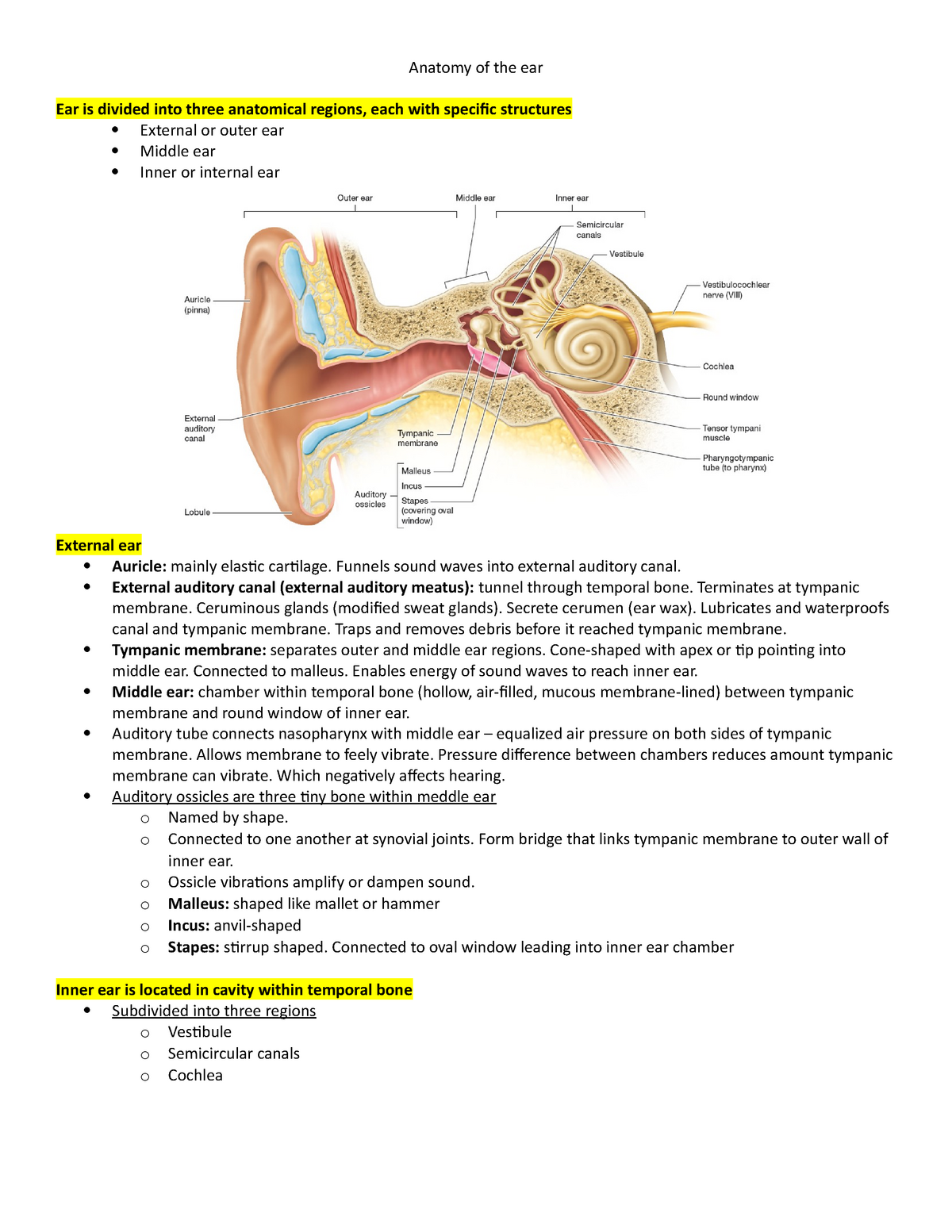 Anatomy Of The Ear Lecture Notes 23 Bio N212 Iupui
Anatomy Of The Ear Lecture Notes 23 Bio N212 Iupui
The apparently steady but actually fluctuating state which is exhibited by stable ecosystems and communities.
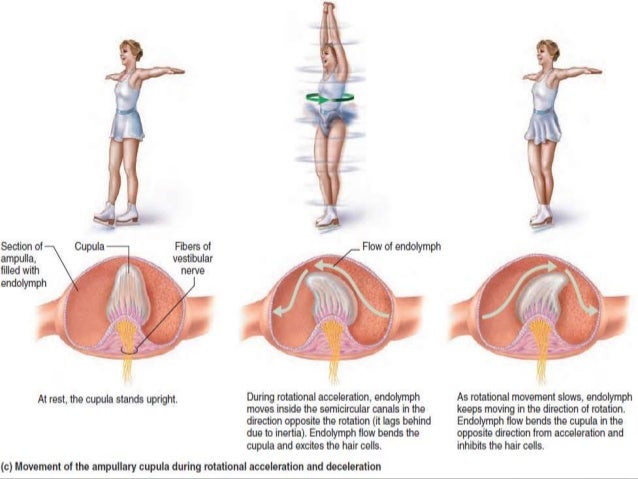
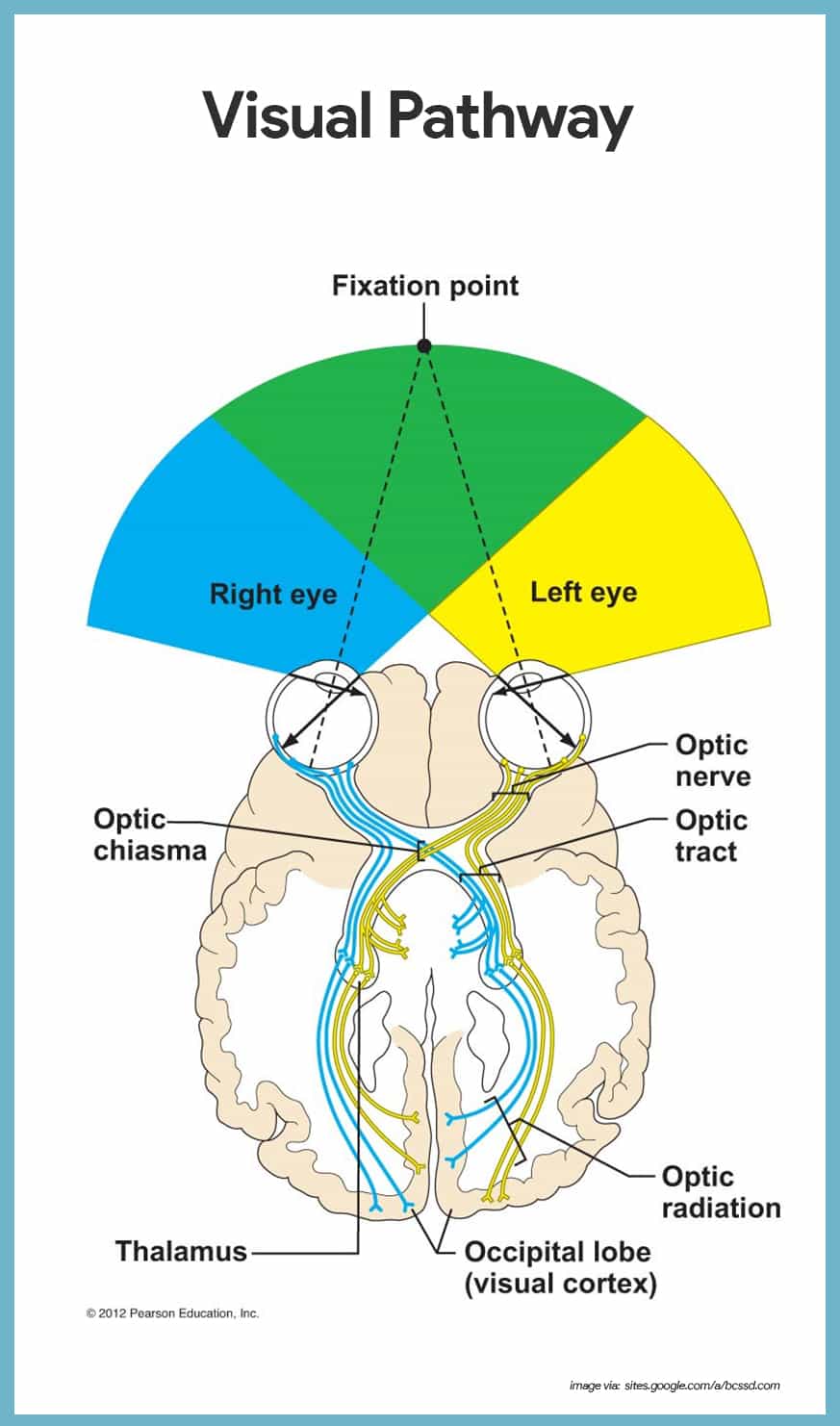
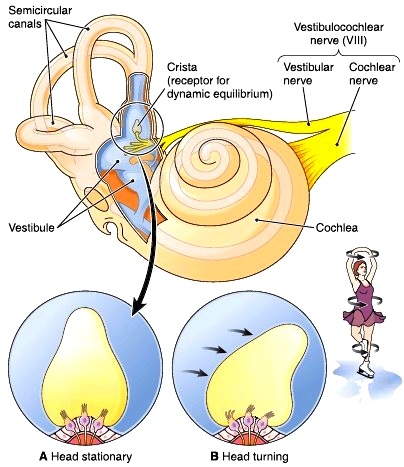
Dynamic equilibrium anatomy. The perception of equilibrium occurs in the vestibular apparatus. Sensory receptors for dynamic equilibrium are found in the cri when your body experiences acceleration or rotation the cupul hair cells respond to the motion of the cupula creating actio the nerve impulse travels down the vestibular nerve crosses o. The information for static equilibrium and linear acceleration dynamic comes from the utricle and saccule within the vestibule.
Equilibrium occurs when a reversible reaction a reaction that proceeds in both directions has an unchanging ratio of products and reactants. Dynamic equilibrium has different meanings in each science sub discipline such as biochemistry or ecology. Fluctuations occur within such systems in relation to seasons life cycles nutrient cycles energy cycles successional stages etc all within an apparently stable system.
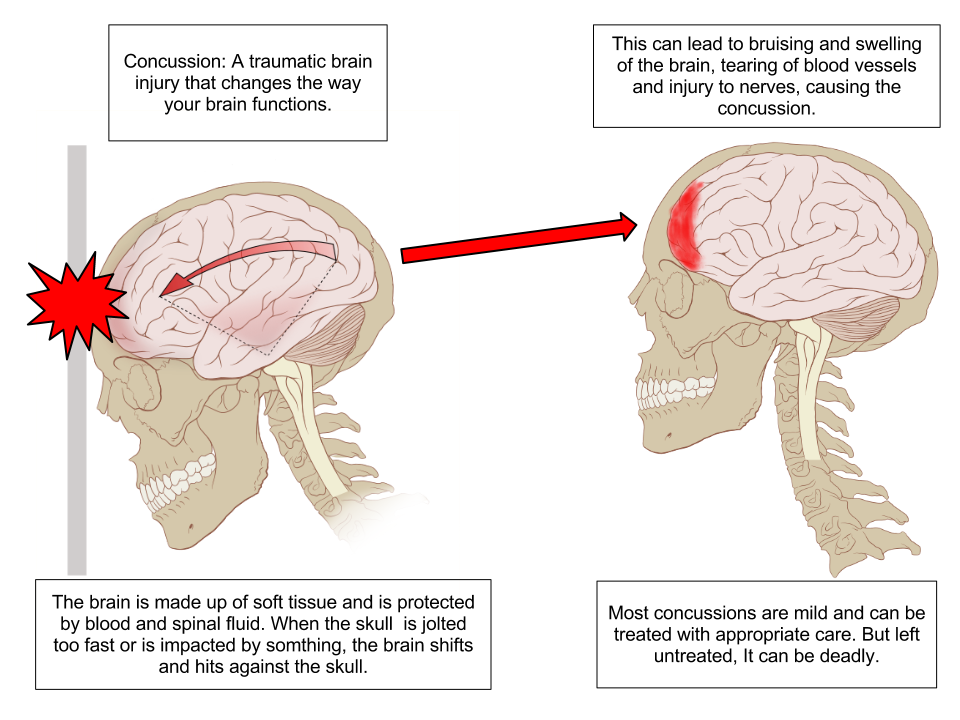
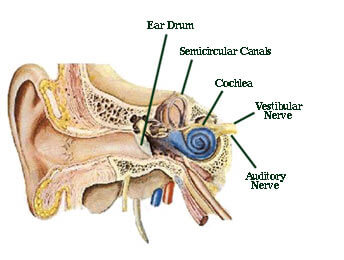
The functional components of the membranous labyrinth involved in the sensations of static and dynamic equilibrium are a system of thin walled intercommunicating tubes and ducts situated within the petrous part of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. Dynamic equilibrium maintains the position of the head in response to rotational motion of the body such as rocking as in a boat or turning. Dynamic equilibrium maintenance of the body posture mainly the head in response to sudden movements.
Equilibrium balance static equilibrium maintenance of body posture relative to gravity while the body is still. The big picture of chemical equilibrium is static as the concentration of products and reactants is constant. Dynamic equilibrium is the steady state of a reversible reaction where the rate of the forward reaction is the same as the reaction rate in the backward direction.
Tracking a moving object. Motion in the following two structures is detected as follows. Dynamic equilibrium is different from a static equilibrium in which the parts do not move once theyve reached equilibrium.
A closer look however reveals that equilibrium is actually. The vestibule is the primary detector of changes in static equilibrium. In other words the system is at rest.
There are five vestibular structures each containing a specialized mechanoreceptor a maculae within the utricle and saccule and a cristae within the ampullae of the superior horizontal and posterior semicircular canals. Static equilibrium also known as mechanical equilibrium means the reaction has stopped.
 Hearing And Equilibrium Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
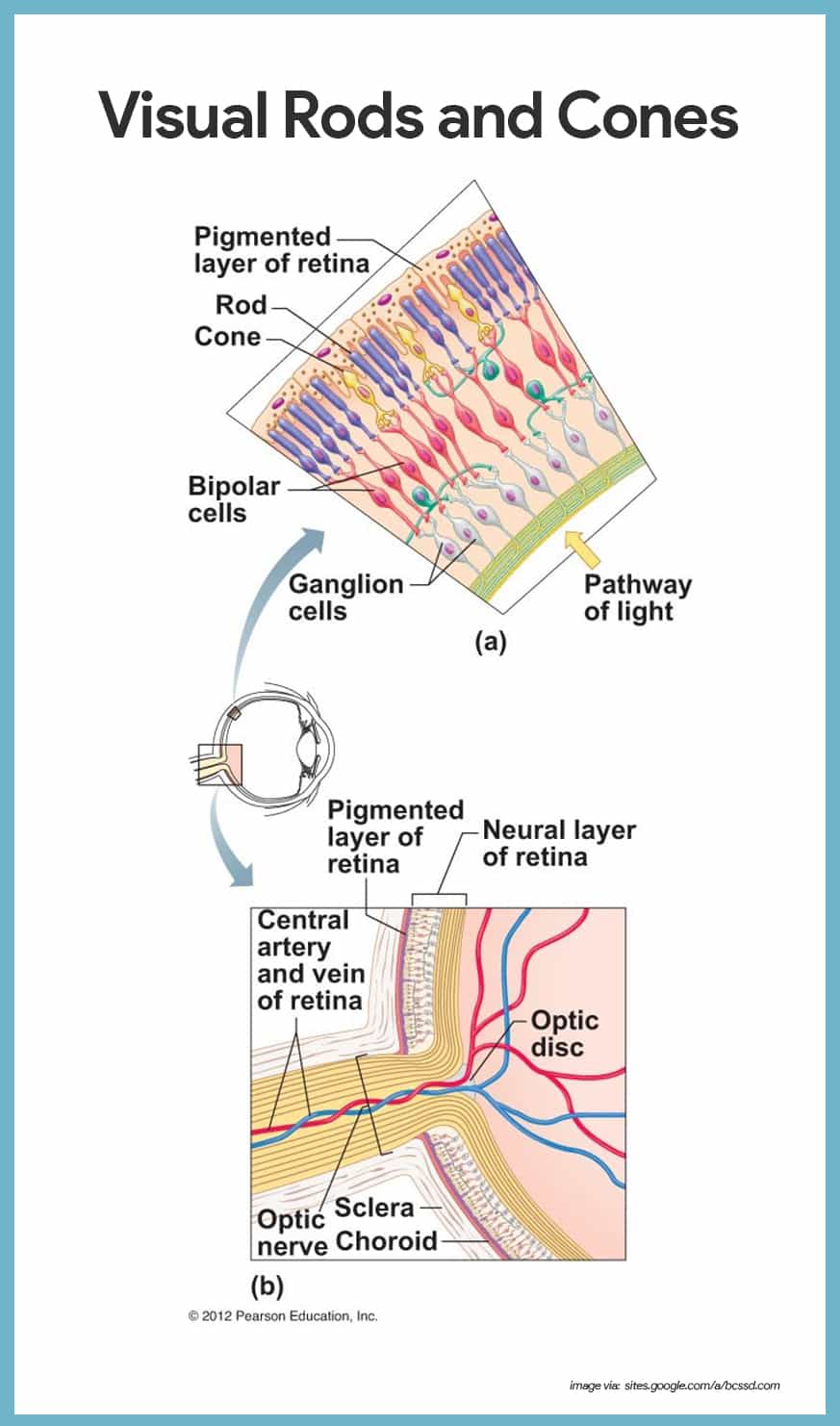
 Special Senses Equilibrium And Hearing
Special Senses Equilibrium And Hearing
 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Balance And Equilibrium 091703 Physiological Systems Studocu
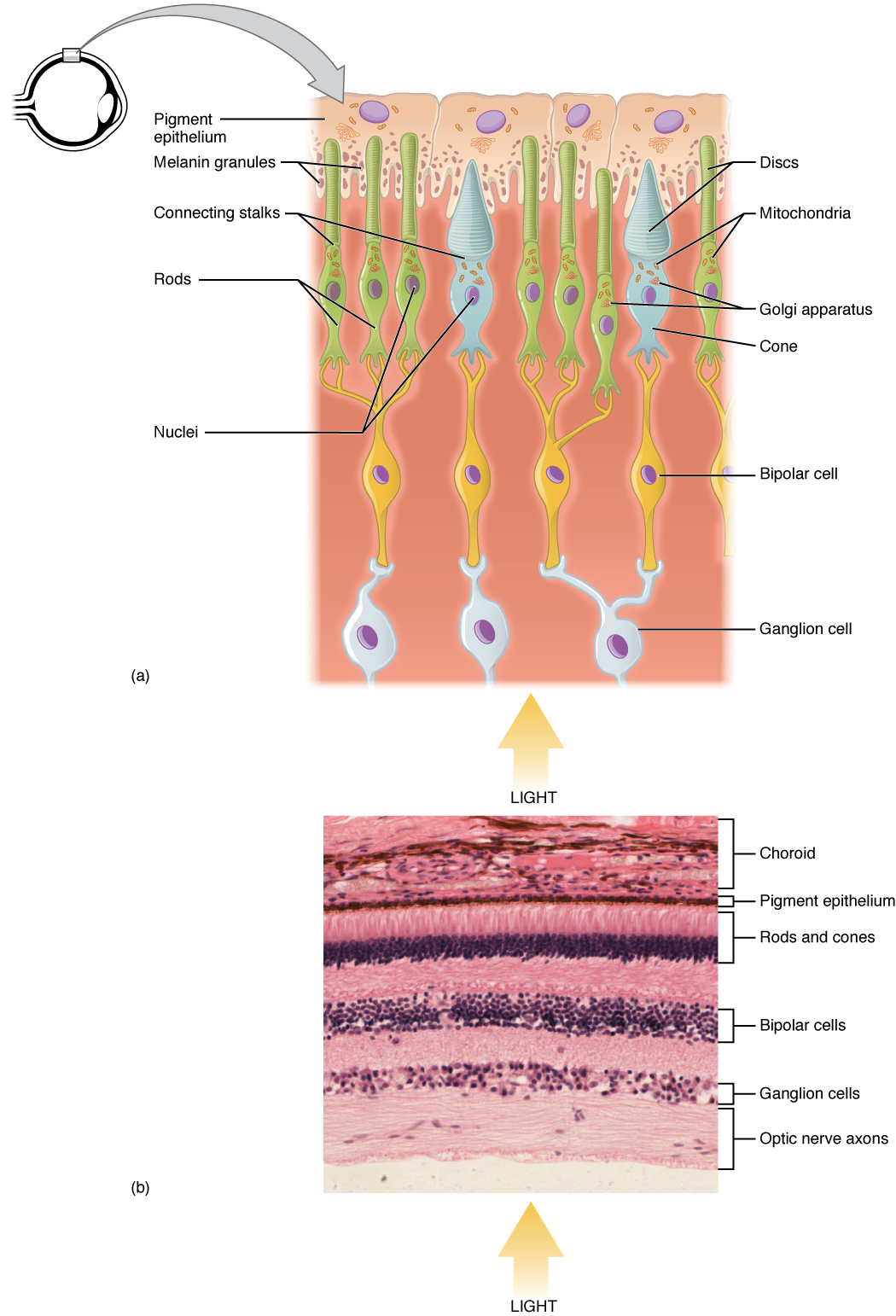 14 1 Sensory Perception Anatomy And Physiology
14 1 Sensory Perception Anatomy And Physiology
 Inner Ear Anatomy Structure Function Of Balance Hs Ls1 A
Inner Ear Anatomy Structure Function Of Balance Hs Ls1 A
 Human Ear The Physiology Of Balance Vestibular Function
Human Ear The Physiology Of Balance Vestibular Function
 Physical Model For Terminal Velocity Body Physics Motion
Physical Model For Terminal Velocity Body Physics Motion
 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Vestibular Sensory Pathway Sensory Pathways Vestibular
Vestibular Sensory Pathway Sensory Pathways Vestibular
 Chapter 8 Special Senses Hearing Equilibrium Ppt Video
Chapter 8 Special Senses Hearing Equilibrium Ppt Video
 Anatomy Unit 1 Notes Hearing Equilibrium
Anatomy Unit 1 Notes Hearing Equilibrium
 Inner Ear Vestibule Anatomy Reading Industrial Wiring Diagrams
Inner Ear Vestibule Anatomy Reading Industrial Wiring Diagrams
 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Anatomy Of The Ear Lecture Notes 23 Bio N212 Iupui
 Difference Between Static And Dynamic Equilibrium Biology
Difference Between Static And Dynamic Equilibrium Biology
Ch 15 Inner Ear Static Dynamic Equilibrium
 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Chapter 8 Special Senses Hearing Equilibrium Ppt Video
Chapter 8 Special Senses Hearing Equilibrium Ppt Video
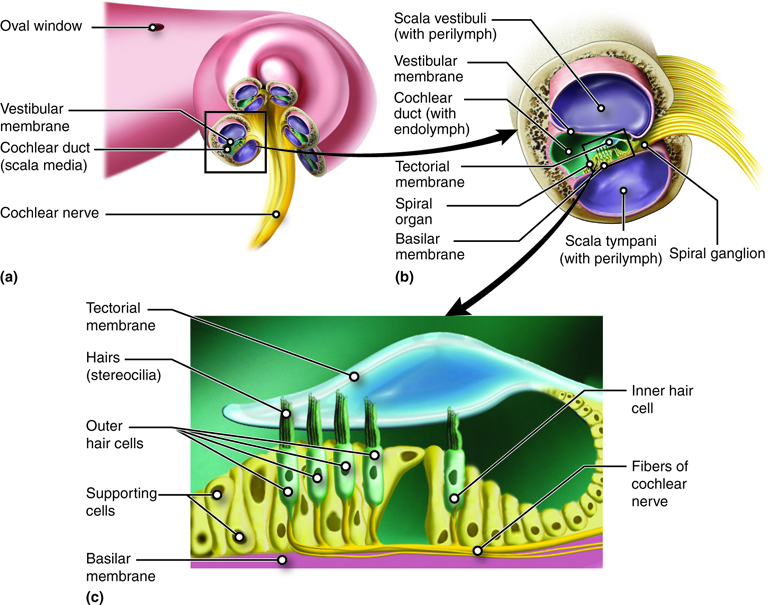 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
 Two Kinds Of Equilibrium 1 Static Equilibrium Refers To The
Two Kinds Of Equilibrium 1 Static Equilibrium Refers To The
 Balance Aging January Ppt Download
Balance Aging January Ppt Download
Special Senses Anatomy Of The Ear Oer Commons
 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
 Structure Of Human Ear And Process Of Hearing And
Structure Of Human Ear And Process Of Hearing And
 Cochlea Diagram Ear Anatomy Ear Function Eye Anatomy
Cochlea Diagram Ear Anatomy Ear Function Eye Anatomy
 Anatomy Of The Ear Human Body Anatomy Lecture Notes
Anatomy Of The Ear Human Body Anatomy Lecture Notes
Anatomy Of The Ear Diagnosis 101
 Sponge Set Up Cornell Notes On Pg 65 Topic 12 7
Sponge Set Up Cornell Notes On Pg 65 Topic 12 7
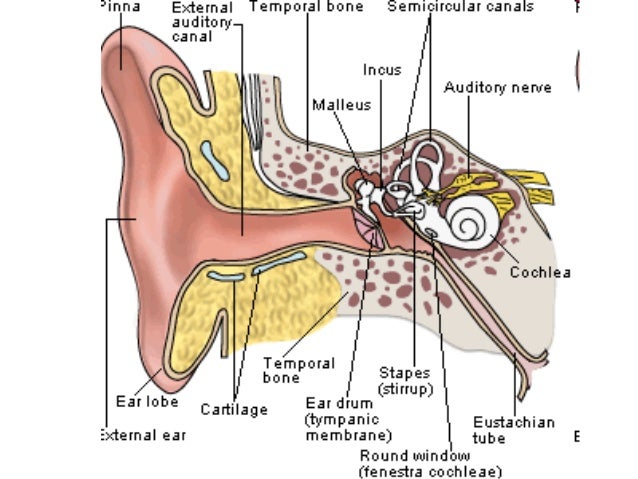 Anatomy Unit 1 Notes Hearing Equilibrium
Anatomy Unit 1 Notes Hearing Equilibrium
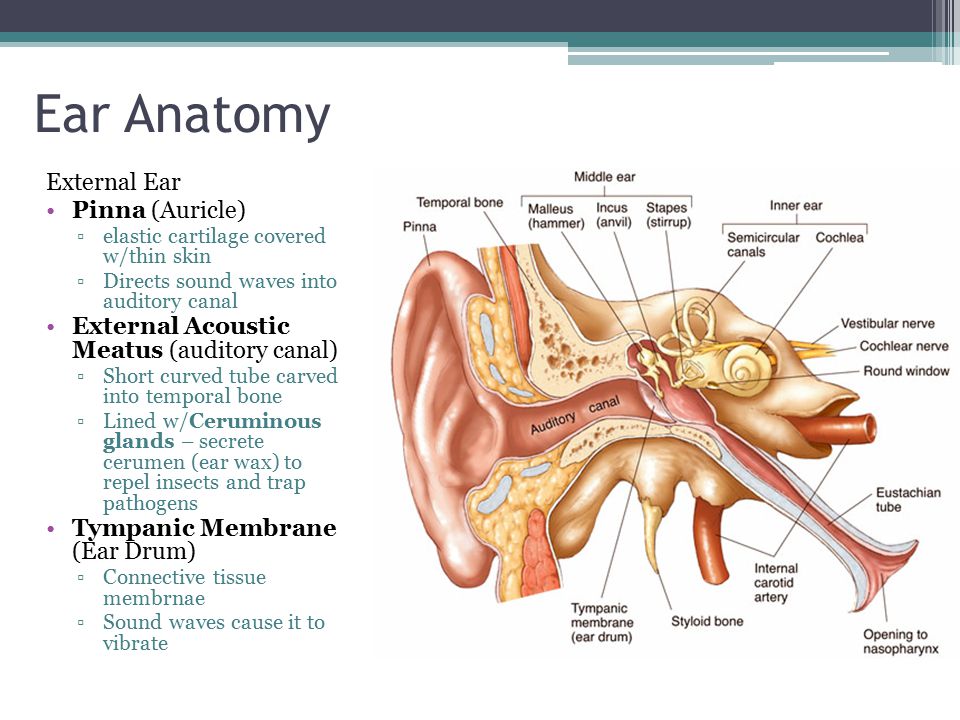 Special Senses Equilibrium Hearing Ppt Video Online
Special Senses Equilibrium Hearing Ppt Video Online
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar