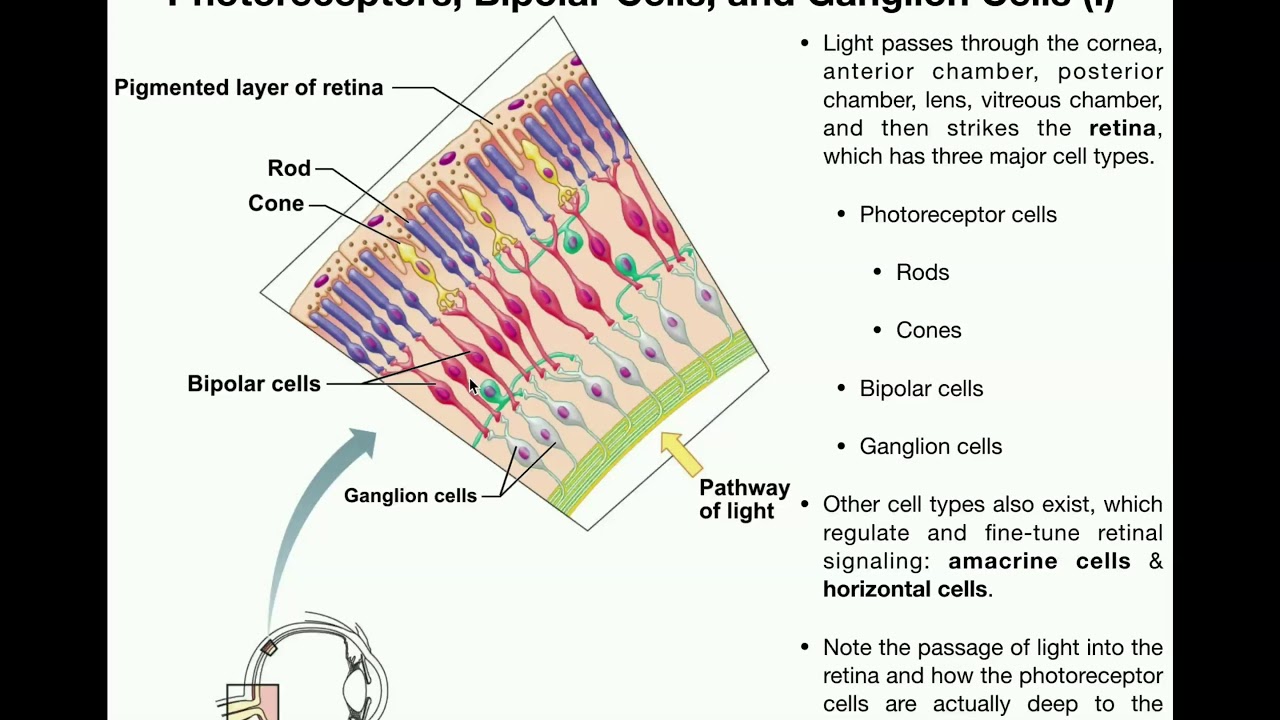
Simple anatomy of the retina by helga kolb. The optic nerve contains the ganglion cell axons running to the brain and additionally incoming blood vessels that open into the retina to vascularize the retinal layers and neurons fig.
 High Yield Topic Clinical Anatomy Of Retina
High Yield Topic Clinical Anatomy Of Retina
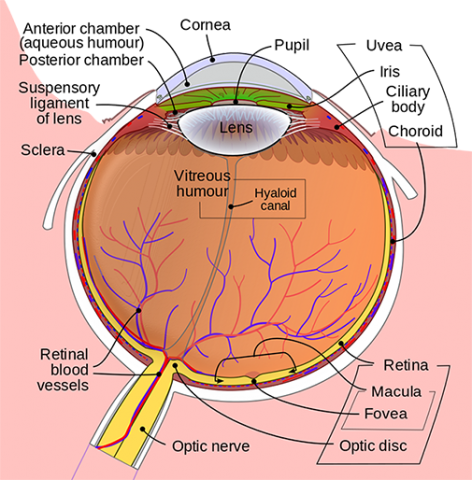
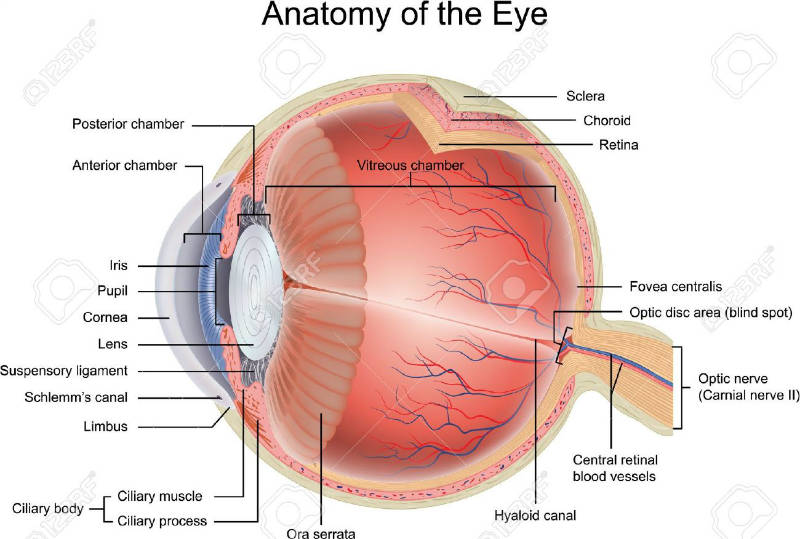
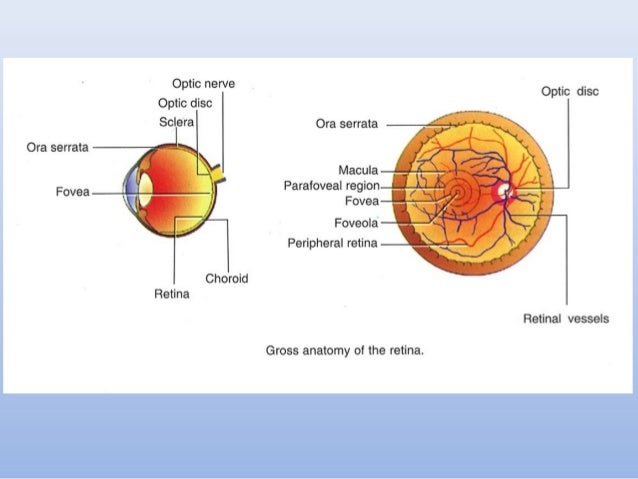
The retina is approximately 05 mm thick and lines the back of the eye.

Anatomy of retina. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses and is supported b. This page describes normal retinal anatomy. The retina is the innermost light sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs.
This fundus photograph shows the normal appearance of the retina. The red curving structures are blood vessels which enter the retina through the nerve. Anatomy of retina by drashok kumar valuroutu 2.
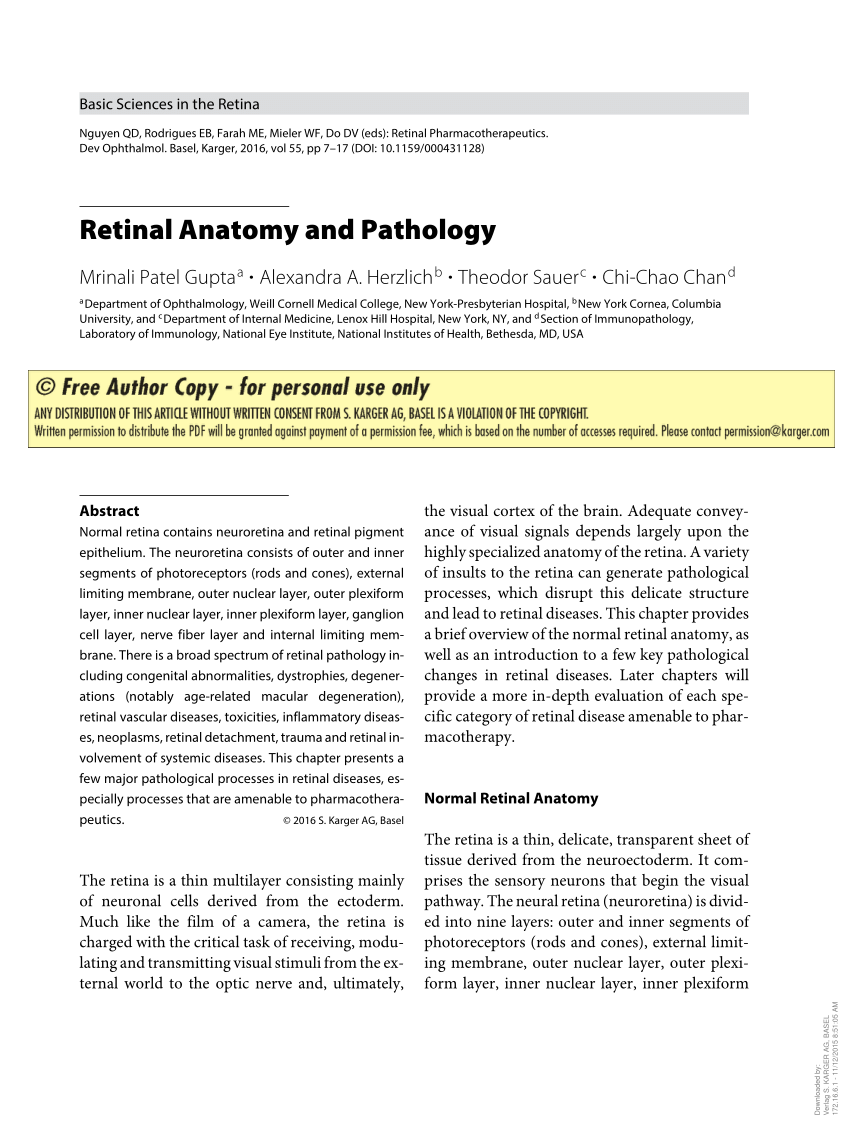
From the center of the optic nerve radiate the major blood vessels of the retina. This is a small tube that runs from the eye to the nasal cavity. In the diagram above anatomy of the eye the artery is shown in red while the vein is shown in blue.
The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye on the inside. The retina is a thin semitransparent multilayered sheet of neural tissue that lines the inner aspect of the posterior two thirds of the wall of the globe. The retina processes light through a layer.
Refer to this page for comparison with the retinal disease pages. It is located near the optic nerve. The whitish circle is the nerve that connects the retina to the brain.
The purpose of the retina is to receive light that the lens has focused convert the light into neural signals and send these signals on to the brain for visual recognition. In the center of the retina is the optic nerve a circular to oval white area measuring about 2 x 15 mm across. The central artery and vein runs through the center of the optic nerve.
The central artery supplies the retina while the central vein drains the retina. The optics of the eye create a focused two dimensional image of the visual world on the retina which translates that image into electrical neural impulses to the brain to create visual perception the retina serving a function analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera.
Normal Retinal Anatomy The Retina Reference
 Eye Conditions Florida Eye Clinic
Eye Conditions Florida Eye Clinic
 Pdf Retinal Anatomy And Pathology
Pdf Retinal Anatomy And Pathology
Simple Anatomy Of The Retina By Helga Kolb Webvision
 Anatomy Of The Eye And Arrangement Of Cells In The Retina
Anatomy Of The Eye And Arrangement Of Cells In The Retina
 Anatomy Crystal Clear Eye Surgeons
Anatomy Crystal Clear Eye Surgeons
 Anatomy Of The Eye Kellogg Eye Center Michigan Medicine
Anatomy Of The Eye Kellogg Eye Center Michigan Medicine
Eye Anatomy And How The Eye Works
Gross Anatomy Of The Eye By Helga Kolb Webvision
 Anatomy Of The Eye Moorfields Eye Hospital
Anatomy Of The Eye Moorfields Eye Hospital
Introduction Retina International S Ird Toolkit
 Anatomy Of The Eye Retina Ophthalmologist Gettysburg Pa
Anatomy Of The Eye Retina Ophthalmologist Gettysburg Pa
 The Anatomy Of Retina From Outer Layer Up To Inner Layer
The Anatomy Of Retina From Outer Layer Up To Inner Layer
Anatomy And Function Of The Structural Elements Of The Retina
 Midterm Spring Anatomy Physiology Lab With Nelson At
Midterm Spring Anatomy Physiology Lab With Nelson At
 Anatomy Vision Part 1 Retina Photoreceptors Bipolar Cells Ganglion Cells
Anatomy Vision Part 1 Retina Photoreceptors Bipolar Cells Ganglion Cells



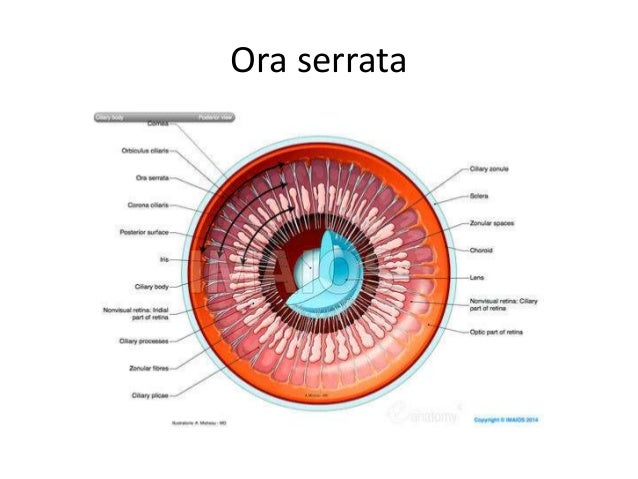
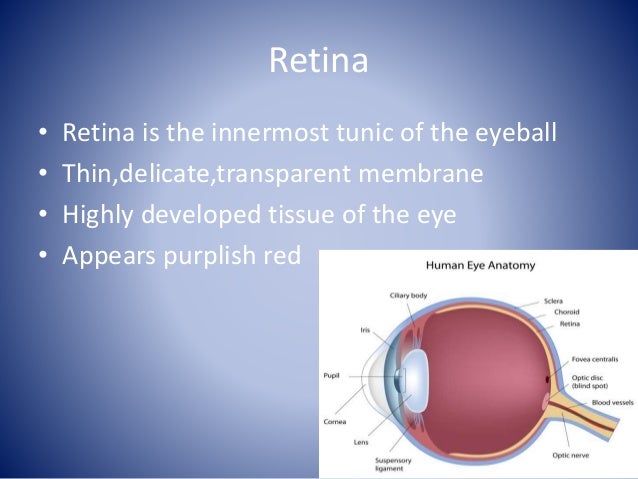
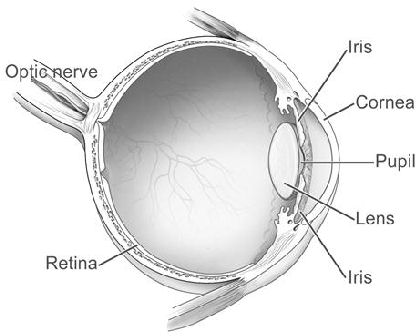
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-308783-003-56acdcd85f9b58b7d00ac8e8.jpg)

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar