In biology absorption pertains particularly to the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into the cell or across the tissues and organs. Absorption is the process by which digested molecules and compounds pass through the epithelial layer the skin cells that line the inside of the digestive tract as well as many other parts of.
Absorption in general sense is the act or process of absorbing or assimilating.

Absorption anatomy definition. Mediastinum definition separates the thorax into two compartments containing the right and left lungs the other thoracic organs heart esophagus etc are within it parietal. The main function of the jejunum is absorption of important nutrients such as sugars. Vitamin b12 and bile salts are absorbed in the terminal ileum.
Protects the body keeps harmful material out regulates body temperature senses and responds to the environment and creates important chemicals. Anatomy and physiology chapter 1. Chemical absorption any process by which one substance in liquid or solid form penetrates the surface of another substance.
For example intestinal absorption is the uptake of food or other substances from the digestive tract. When enzymes speed up reactions that add water hydro to chemically break up or split lysis large molecules into small molecules. Medical definition of absorption.
Digestive absorption the passage of the end products of digestion from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood and lymphatic vessels and the cells of tissues. Learn about its function and anatomy as well as the conditions that can affect it. Refers to the absorption transport use of oxygen by cells digestion occurs in specialized structures in which complex foods are broken down into simpler components that can be transported absorbed easily.
Water and lipids are absorbed by passive diffusion throughout the small intestine. Food moves through the mucous membrane lining of the small intestine into the blood. Absorption of the majority of nutrients takes place in the jejunum with the following notable exceptions.
Iron is absorbed in the duodenum.
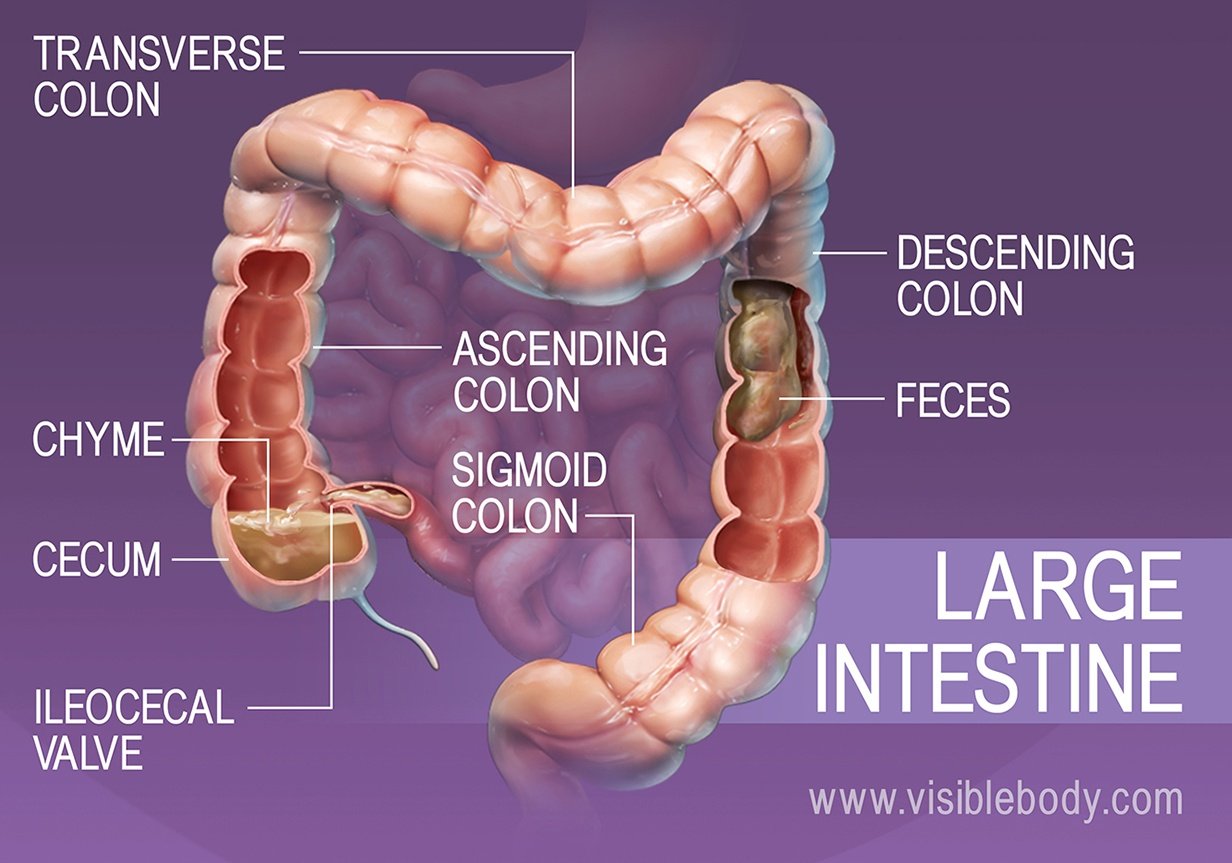 Absorption And Elimination Digestive Anatomy
Absorption And Elimination Digestive Anatomy
 Personality Iphone 7 Plus Case Iphone 8 Plus Case People Skeleton Skull High Definition Clear Bumper Soft Rubber Anti Scratch Shock Absorption
Personality Iphone 7 Plus Case Iphone 8 Plus Case People Skeleton Skull High Definition Clear Bumper Soft Rubber Anti Scratch Shock Absorption
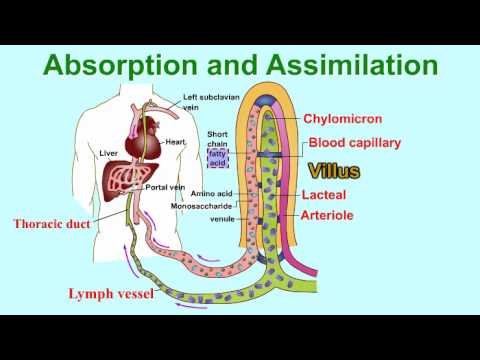 Absorption And Assimilation Villus Vitamins And Water Enter Into Body Fluids Through The Villi
Absorption And Assimilation Villus Vitamins And Water Enter Into Body Fluids Through The Villi
 Absorption Of Micronutrients And Water Into The Bloodstream
Absorption Of Micronutrients And Water Into The Bloodstream
Difference Between Digestion And Absorption Definition
 Invertebrate Digestive System Anatomy Britannica
Invertebrate Digestive System Anatomy Britannica
 Absorption Chemistry Wikipedia
Absorption Chemistry Wikipedia
 Power Absorption An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Power Absorption An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Small Intestine Parts Function Quiz Biology Dictionary
Small Intestine Parts Function Quiz Biology Dictionary
 Villi Function Definition Structure
Villi Function Definition Structure
 Absorption And Elimination Digestive Anatomy
Absorption And Elimination Digestive Anatomy
 Toxtutor Gastrointestinal Tract
Toxtutor Gastrointestinal Tract
 Small Intestine 3 Absorption Video Khan Academy
Small Intestine 3 Absorption Video Khan Academy

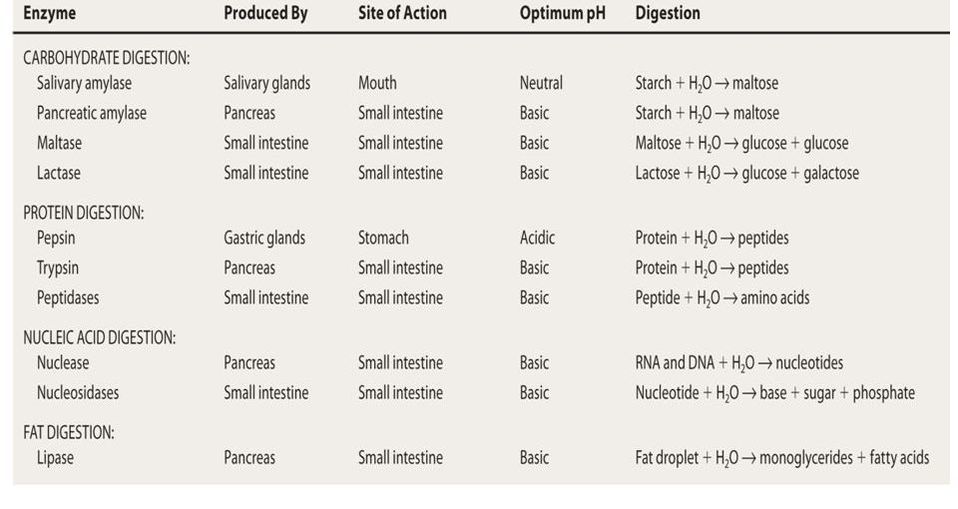 Topic 6 1 Digestion And Absorption Amazing World Of
Topic 6 1 Digestion And Absorption Amazing World Of
 Physiologic Factors Related To Drug Absorption Applied
Physiologic Factors Related To Drug Absorption Applied
 Small Intestine 1 Structure Video Khan Academy
Small Intestine 1 Structure Video Khan Academy
 Color White Light Reflection Absorption
Color White Light Reflection Absorption
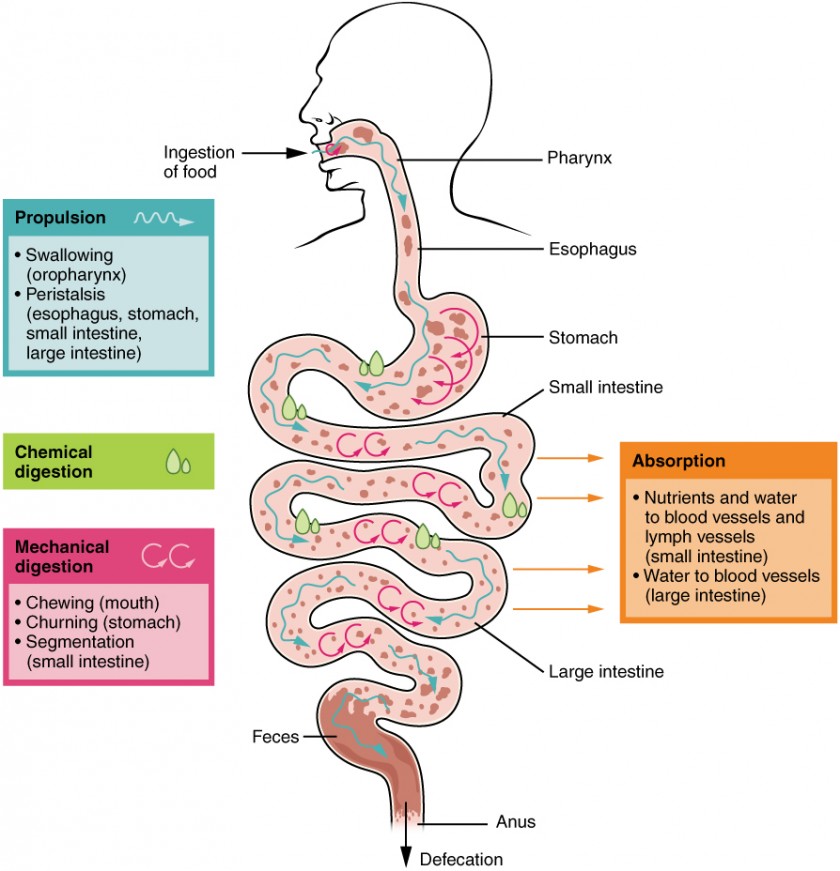 Digestive System Processes And Regulation Anatomy And
Digestive System Processes And Regulation Anatomy And
 Absorption Function Of The Small Intestine And
Absorption Function Of The Small Intestine And
 Difference Between Absorption And Adsorption With
Difference Between Absorption And Adsorption With
 Difference Between Absorption And Adsorption With
Difference Between Absorption And Adsorption With
Protein Digestion And Absorption Human Nutrition Deprecated
Factors Affecting Absorption Of Drugs Howmed



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar