In addition the muscles tighten the joint capsule preventing a pinch during shoulder movements. The rotator cuff is a collection of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder giving it support and allowing a wide range of motion.
As a result the rotator cuff indirectly connects the arm to the chest wall through its attachments to the shoulder blade.

Anatomy of a shoulder rotator cuff. Anatomy of the rotator cuff. When the muscles that make up the rotator cuff shorten. They are important in shoulder movements and maintaining stability of this joint.
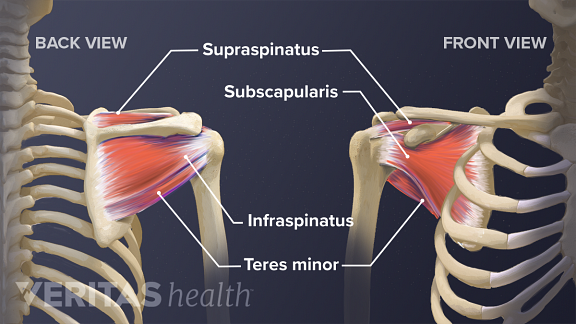
The rotator cuff are a group of muscles which are important in supporting the glenohumeral joint. The rotator cuff refers to a group of four tendons and muscles that form a cuff to stabilize the shoulder joint and keep the arm in the shoulder socket while allowing it to move in different directions. Your rotator cuff is made up of muscles and tendons that keep the ball head of your upper arm bone humerus in your shoulder socket.
The rotator cuff always pops up in exam questions. This is a tutorial on the rotator cuff. In anatomy the rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion.
The shoulder can easily slip out of alignment by a few millimeters become weak due to regular wear and tear or become completely dislocated during a fall. The shoulder blade is attached to the chest wall by additional muscles. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles four make up the rotator cuff.
Rotator cuff and shoulder anatomy the shoulder has an incredible range of motion but this means that it is also very prone to injury. The shoulder joint is stable because of the rotator cuff but it is also relatively weak. The main function of the rotator cuff is to stabilize and center the humeral head in the joint socket the glenoid cavity.
It also helps you raise and rotate your arm. The rotator cuff. As a group the rotator cuff muscles are responsible for stabilizing the shoulder joint.
The bursa is a small sac of fluid that cushions and. They keep the head of the humerus into the small glenoid fossa of the scapula in order to enlarge the range of motion in the glenohumeral joint and avoid mechanical obstruction. The rotator cuff is important for normal shoulder function.
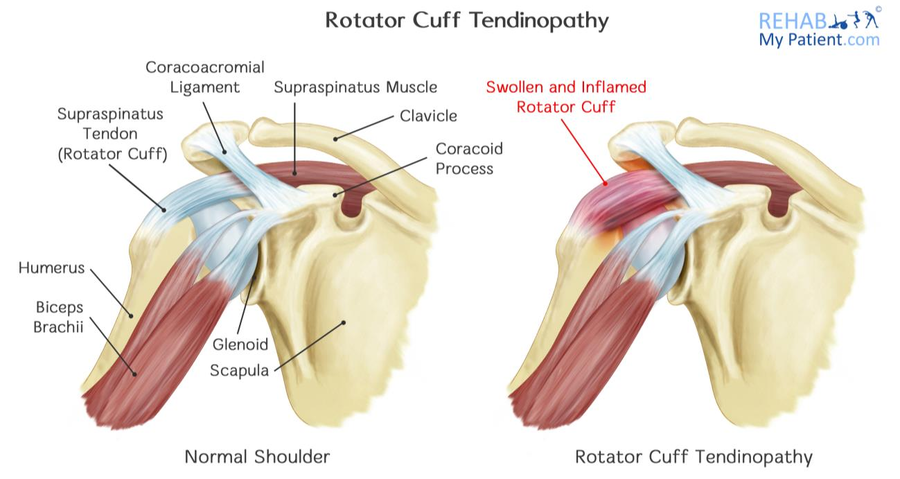 Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy Rehab My Patient
Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy Rehab My Patient
 Rotator Cuff Injury Explained Including Rotator Cuff Tear
Rotator Cuff Injury Explained Including Rotator Cuff Tear
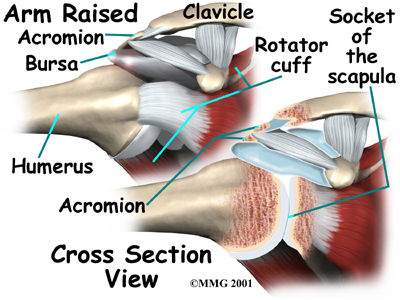 Physical Therapy In Columbia For Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tears
Physical Therapy In Columbia For Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tears
 Rotator Cuff Injuries Treatment How To Manage The Pain Heal
Rotator Cuff Injuries Treatment How To Manage The Pain Heal
 Rotator Cuff Shoulder Pain Exercise Is As Effective As Surgery
Rotator Cuff Shoulder Pain Exercise Is As Effective As Surgery
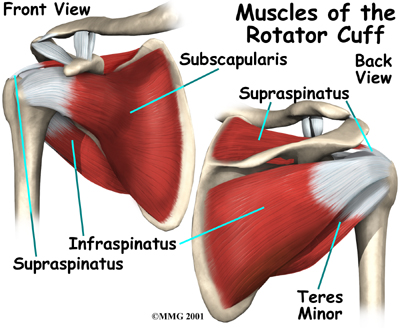 Anatomy Lessons Rotator Cuff Healing Touch Charlotte
Anatomy Lessons Rotator Cuff Healing Touch Charlotte
 Rotator Cuff Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Rotator Cuff Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
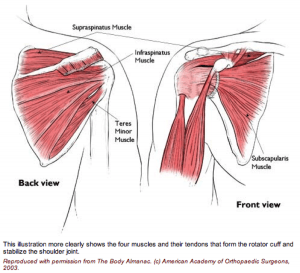 Rotator Cuff Tears Dr Franklin Orthopedic Specialists
Rotator Cuff Tears Dr Franklin Orthopedic Specialists
 Shoulder Impingement Boise Rotator Cuff Tendons Boise
Shoulder Impingement Boise Rotator Cuff Tendons Boise
Cost Effective Stock Medical Exhibits New Rotator Cuff
 Anatomy Of The Shoulder And Rotator Cuff Doctor Stock
Anatomy Of The Shoulder And Rotator Cuff Doctor Stock
Frozen Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis Orthoinfo Aaos
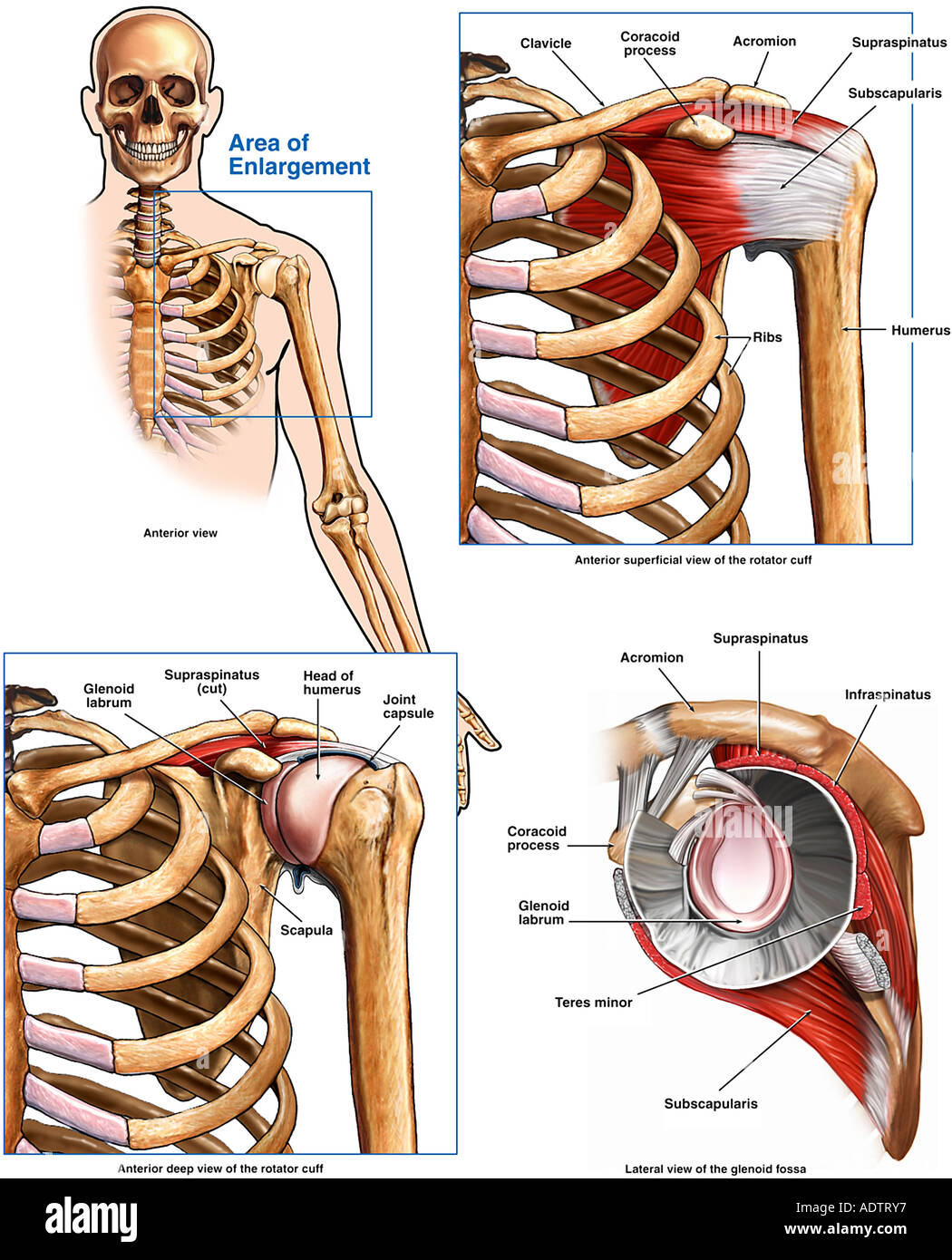 Anatomy Of The Shoulder And Rotator Cuff Stock Photo
Anatomy Of The Shoulder And Rotator Cuff Stock Photo
 Shoulder Pain Learn About The Rotator Cuff Salvation Wellness
Shoulder Pain Learn About The Rotator Cuff Salvation Wellness
Shoulder Anatomy Rotator Cuff Repair
Rotator Cuff Inpigiment Sports Medicine Naples
 Rotator Cuff Tears Physiopedia
Rotator Cuff Tears Physiopedia
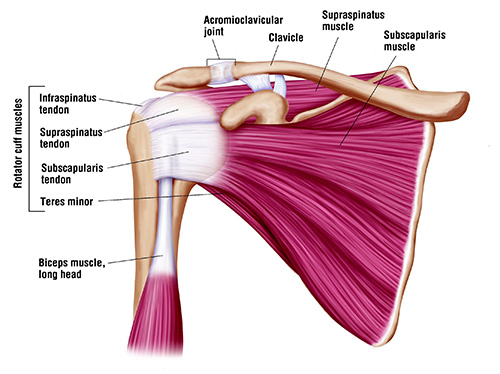 Rotator Cuff Doctor Chicago Shoulder Specialist Chicago
Rotator Cuff Doctor Chicago Shoulder Specialist Chicago
 Rotator Cuff Anatomy Illustration Common Problems
Rotator Cuff Anatomy Illustration Common Problems
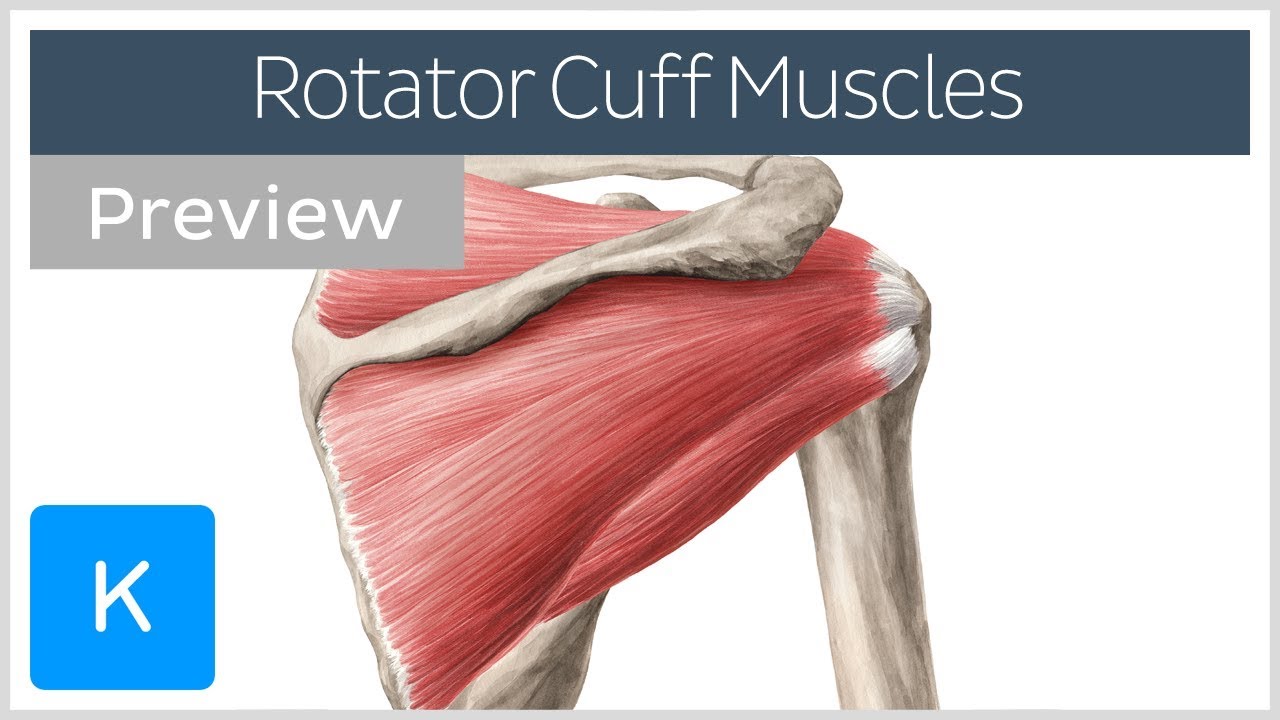 Rotator Cuff Muscles Overview Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
Rotator Cuff Muscles Overview Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
 Cables Crescents And Suspension Bridges The Unique Anatomy
Cables Crescents And Suspension Bridges The Unique Anatomy
 Rotator Cuff Tendinitis Lurie Children S
Rotator Cuff Tendinitis Lurie Children S
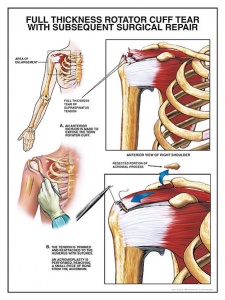 Rotator Cuff Tears Physiopedia
Rotator Cuff Tears Physiopedia
 Left Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tear Doctor Stock
Left Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tear Doctor Stock
 Rotator Cuff Muscles Of The Left Shoulder Stock Trial Exhibits
Rotator Cuff Muscles Of The Left Shoulder Stock Trial Exhibits
 Rotator Cuff Injury Tear And Strain Treatment Guidelines
Rotator Cuff Injury Tear And Strain Treatment Guidelines
 Mayo Clinic Q And A Treating Rotator Cuff Tears Mayo
Mayo Clinic Q And A Treating Rotator Cuff Tears Mayo
 Preventing Rotator Cuff Injury Capital Area Pt Wellness
Preventing Rotator Cuff Injury Capital Area Pt Wellness
 Rotator Cuff Tears Orthoinfo Aaos
Rotator Cuff Tears Orthoinfo Aaos
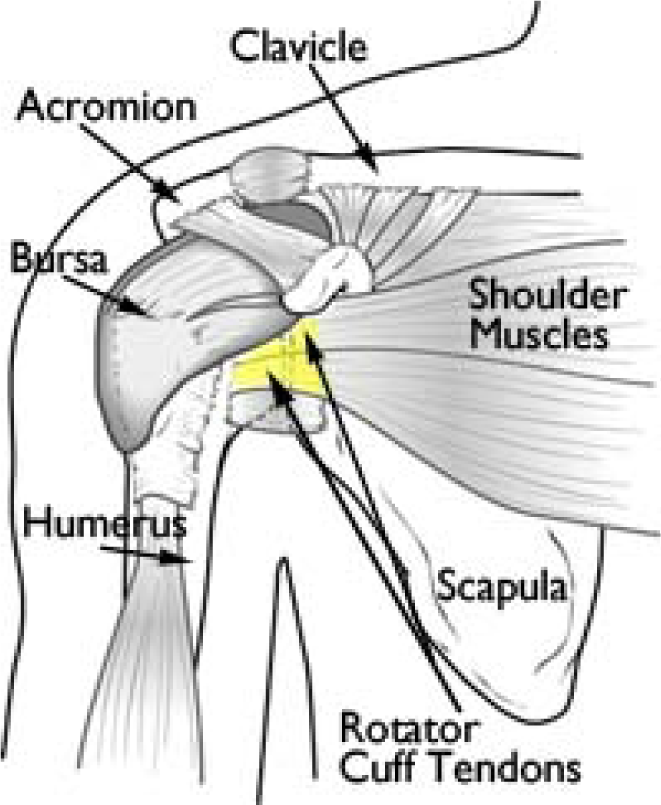 Rotator Cuff Repair Brisbane Knee And Shoulder
Rotator Cuff Repair Brisbane Knee And Shoulder
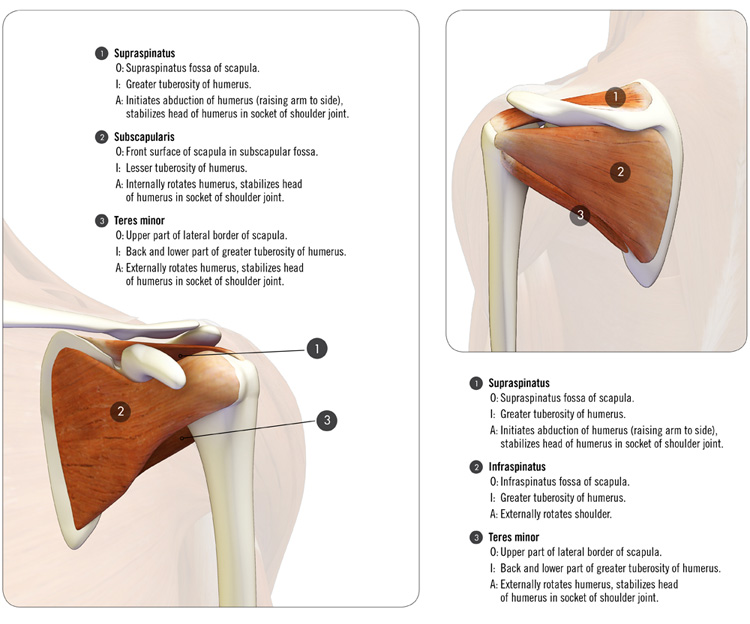

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar