Tools you will need for the dissection are. Sharks used in dissection classes are usually the dogfish.
 Dogfish Sharks What Phylum Do Sharks Belong To
Dogfish Sharks What Phylum Do Sharks Belong To
List of the 5 fins of the dogfish shark 2 dorsal pectoral pelvic caudal the depressor of the pectoral fin allows the pectoral fins to lower.

Dogfish shark anatomy. A large dissecting tray 2. Located caudal side of the pectoral fin. External and internal anatomy of a dogfish shark a cartilaginous fish.
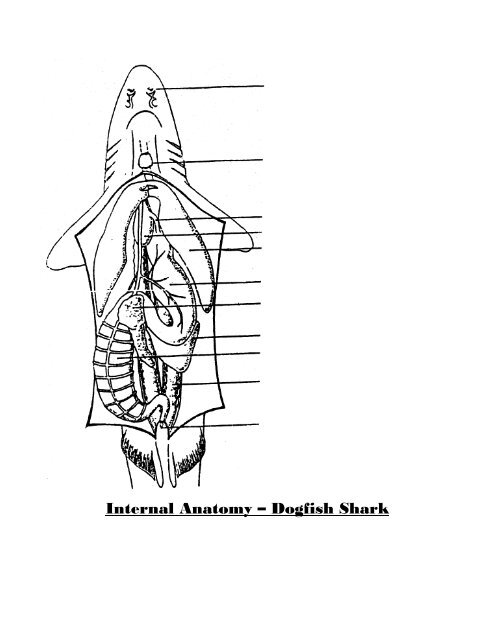
Digestive anatomy of the dogfish shark a smooth shiny membrane called peritoneum can be seen lining the inside of the body wall. A third lobe much shorter lobe contains the green gall bladder along its right edge. The shark anatomy allows them to see in dim light they can detect the contrasts of light and shadow and their pupils can dilate and contract.
The spines carry a poison secreted by glands at their base. Phylum chordata subphylum vertebrata class chondrichthyes. Spiny dogfish in the northern pacific ocean have recently been reevaluated and foun.
The anterior dorsal fin is larger than the posterior dorsal fin. The spiny dogfish has a double dorsal fin. While these common names may apply to several species squalus acanthias is distinguished by having two spines and lacks an anal fin.
It is found mostly in shallow waters and further offshore in most parts of the world especially in temperate waters. Digestive anatomy of the dogfish shark examine the photographs of the spiny dogfish shark with its body cavity slit open by clicking the blue lettered links in the column to the right. Variation observed within shark anatomy is a potential result of speciation and habitat variation skeleton.
Because of its ready availability and primitive chordate structure it is often the only fish a student will dissect in a comparative anatomy course. Shark anatomy differs from that of bony fish in a variety of ways. The spiny dogfish spurdog mud shark or piked dogfish is one of the best known species of the squalidae family of sharks which is part of the squaliformes order.
The liver largest organ 3 lobes two main lobes the right and left lobes extend from the length of the cavity. Nostrils and sense of smell the nostrils of a shark are and external part of the shark anatomy and on the ventral side of their bodies. The shark specimen in the photographs was prepared by turning it ventral side up and making a mid ventral incision just anterior to the cloacal opening.
The skeleton of a shark is mainly made of cartilage. Holds the oil that gives the shark buoyancy many digestive functions such as storing nutrients and transforming food molecules arriving from the gut gall bladder storing bile a liquid that breaks up fat droplets in the gut. The spiny dogfish has the presence two spines one immediately in front of each dorsal fin.
A species of dogfish shark. External anatomy of the dogfish shark.
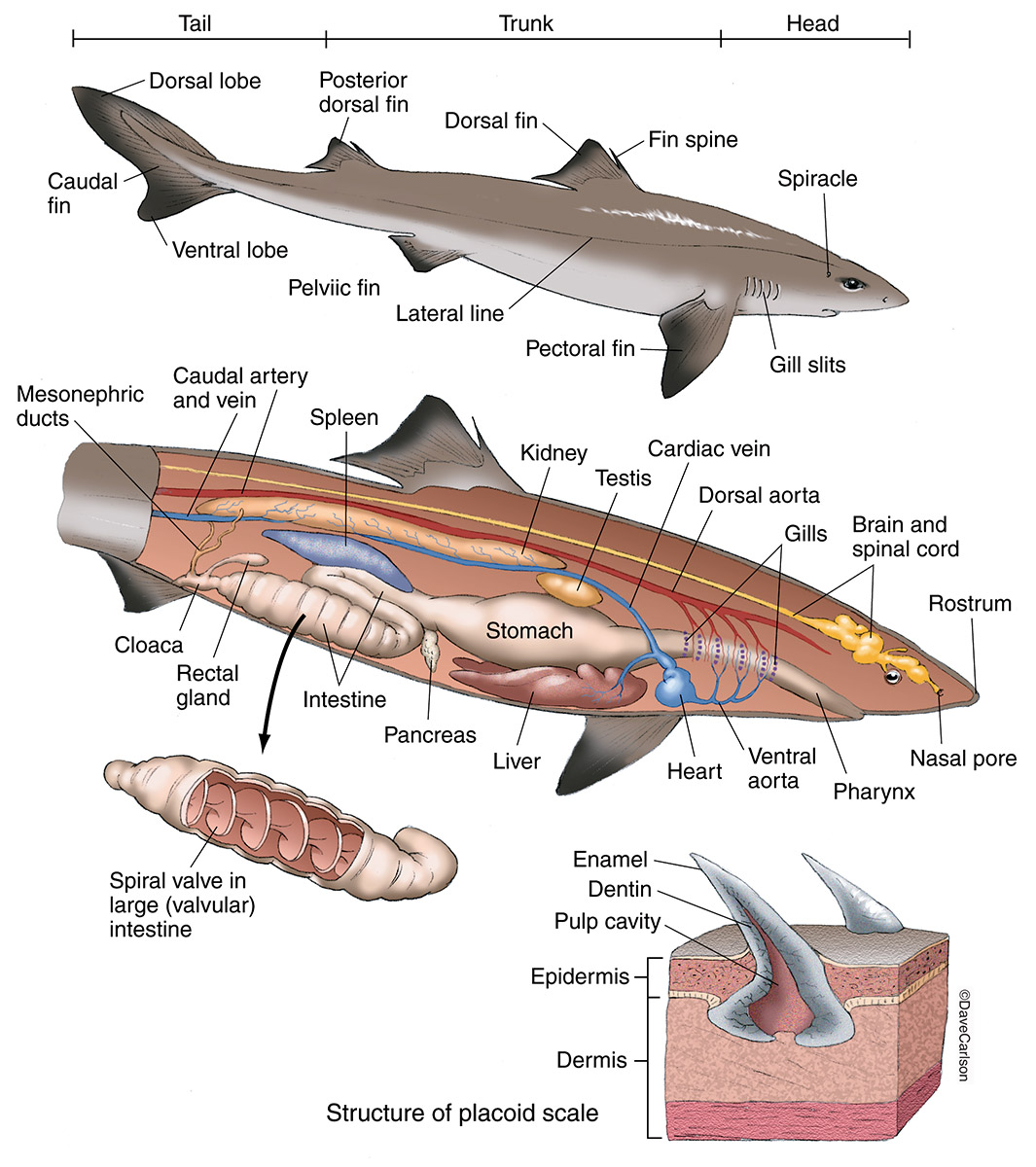 Shark Anatomy Dogfish Carlson Stock Art
Shark Anatomy Dogfish Carlson Stock Art
 Schematic Representation Of The Skeletal And Muscular
Schematic Representation Of The Skeletal And Muscular
Biology 453 Shark Cardiovascular Sys Photos
Gulf Of Maine Educational Materials Supplemental To Dogfish Dissection Guide Homologies Between Cat Felis Catus And Dogfish Shark Squalus

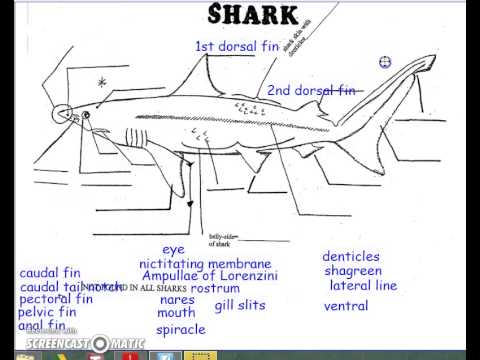 External Anatomy Of A Dogfish Shark Youtube
External Anatomy Of A Dogfish Shark Youtube
 Internal Anatomy Of The Dogfish Shark 5 Kidney 6 Rectal
Internal Anatomy Of The Dogfish Shark 5 Kidney 6 Rectal
 Oceanography Spiny Dogfish Shark Squalusacanthias Dissection
Oceanography Spiny Dogfish Shark Squalusacanthias Dissection
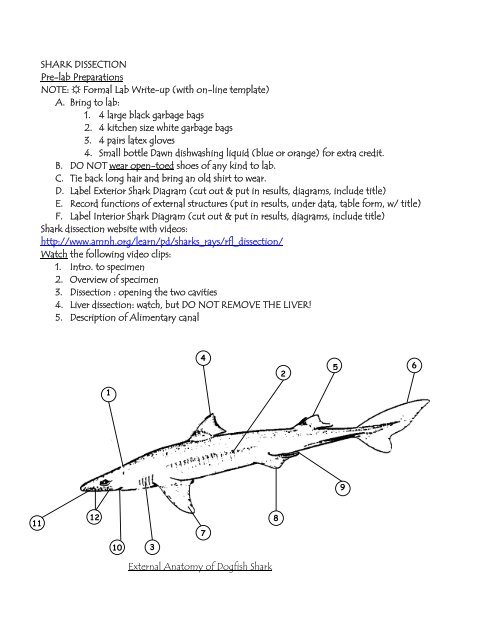 Shark Dissection Pre Lab Preparations Note Formal Lab Write
Shark Dissection Pre Lab Preparations Note Formal Lab Write
 Dogfish Anatomy Dogfish Shark Shark Anatomy
Dogfish Anatomy Dogfish Shark Shark Anatomy
Actions In Alp Ripple Effect Of The Aquatic Biome
Dissections Quincy Buickerood S Digital Portfolio
 The Dogfish Shark Structure And Function Carolina Com
The Dogfish Shark Structure And Function Carolina Com
 Ppt Dogfish Shark Squalus Acanthius Dissection
Ppt Dogfish Shark Squalus Acanthius Dissection
 Spiny Dogfish Shark Zoom Sharks Dogfish Shark Shark
Spiny Dogfish Shark Zoom Sharks Dogfish Shark Shark
 Anatomy Of The Dogfish Shark Anatomy And Scientific
Anatomy Of The Dogfish Shark Anatomy And Scientific
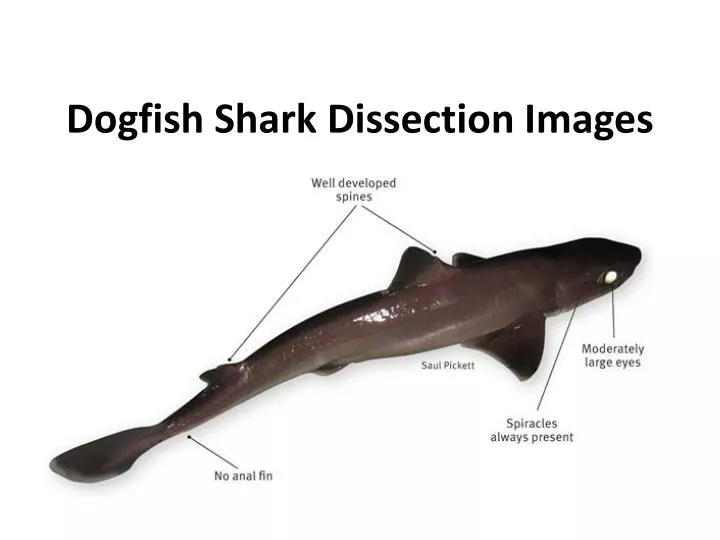 Ppt Dogfish Shark Dissection Images Powerpoint
Ppt Dogfish Shark Dissection Images Powerpoint
 Spiny Dogfish Shark Internal Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
Spiny Dogfish Shark Internal Anatomy Diagram Quizlet

 Internal Anatomy Of Dogfish Shark Diagram Quizlet
Internal Anatomy Of Dogfish Shark Diagram Quizlet
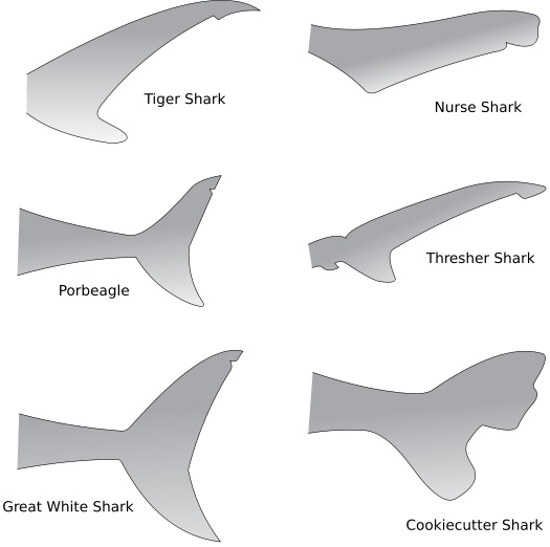 Information About Sharks And Their Anatomy Secrets Shark Sider
Information About Sharks And Their Anatomy Secrets Shark Sider



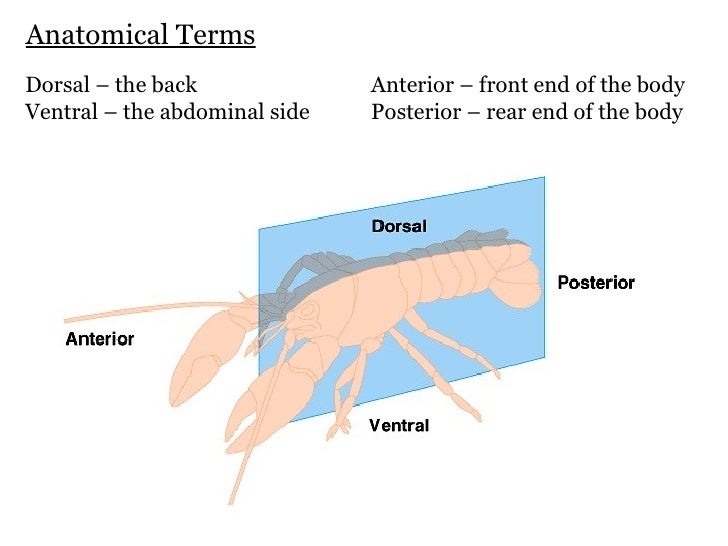
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar