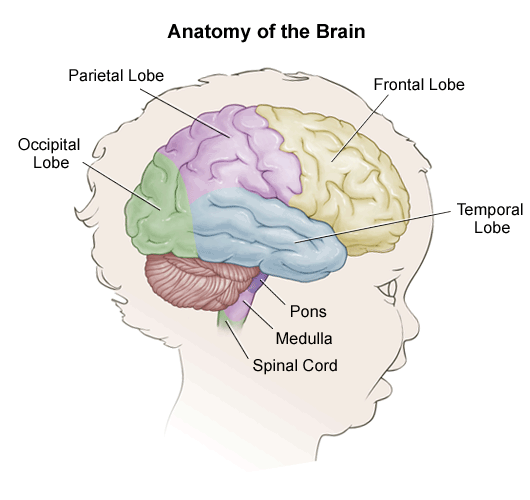
The caudal border of the medulla is the 1 st cervical spinal nerves. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum.
The upper portion of the dorsal medulla forms the lower region of the fourth ventricle a fluid filled cavity formed by the expansion of the central canal of the spinal cord upon entering the brain.

Medulla anatomy. Urine passes into this pelvis from the collecting tubules. As the ureter enters the kidney it enlarges into a cavity the renal pelvis. Three levels of the medulla are typically discussed inferior superior.
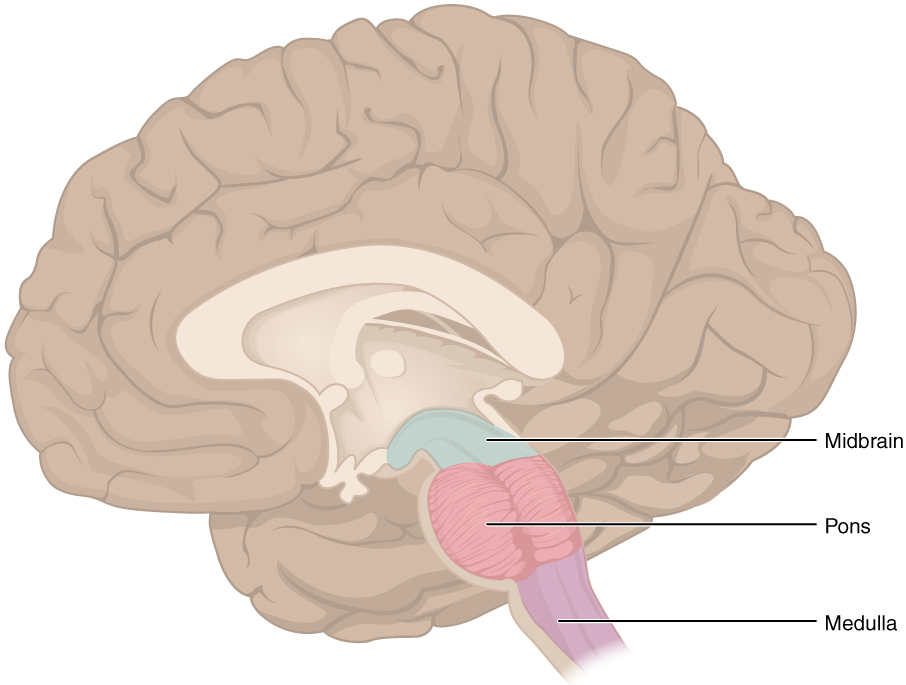
There are several main venous drainage routes for the medulla. Gross anatomy gross structure. The medulla oblongata or medulla is a long stem like structure which makes up part of the brainstem.
The medulla oblongata is a funnel shaped structure that constitutes. The myelencephalon portion of the rhombencephalon or hindbrain becomes the medulla. Motor and sensory neurons from the midbrain and forebrain travel through the medulla.
Nephrons are numerous 20000 in a mouse. Level of the olives. The medulla oblongata is an integral part of the brain that manages and controls various voluntary and involuntary functions of the brain.
The medulla is approximately 3 cm in length and 2 cm in greatest diameter 2. It is not possible to live without medulla as it performs a plethora of crucial tasks like breathing speaking eating blood pressure and more. It is a cone shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic involuntary functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing.
The medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic functions such as breathing digestion heart and blood vessel function swallowing and sneezing. Medulla oblongata gross anatomy. Somewhat striated inner section the medulla containing the loops of henle and the collecting tubules.
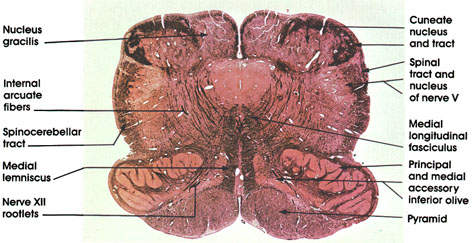
Level of decussation of the medial lemnisci. Medulla anatomy with mri this photo gallery presents the anatomy of medulla by means of mri t1 weighted sagittal axial and coronal views. Similar to the spinal cord the fourth ventricle is surrounded by white matter on the outside with the gray matter on the inside.
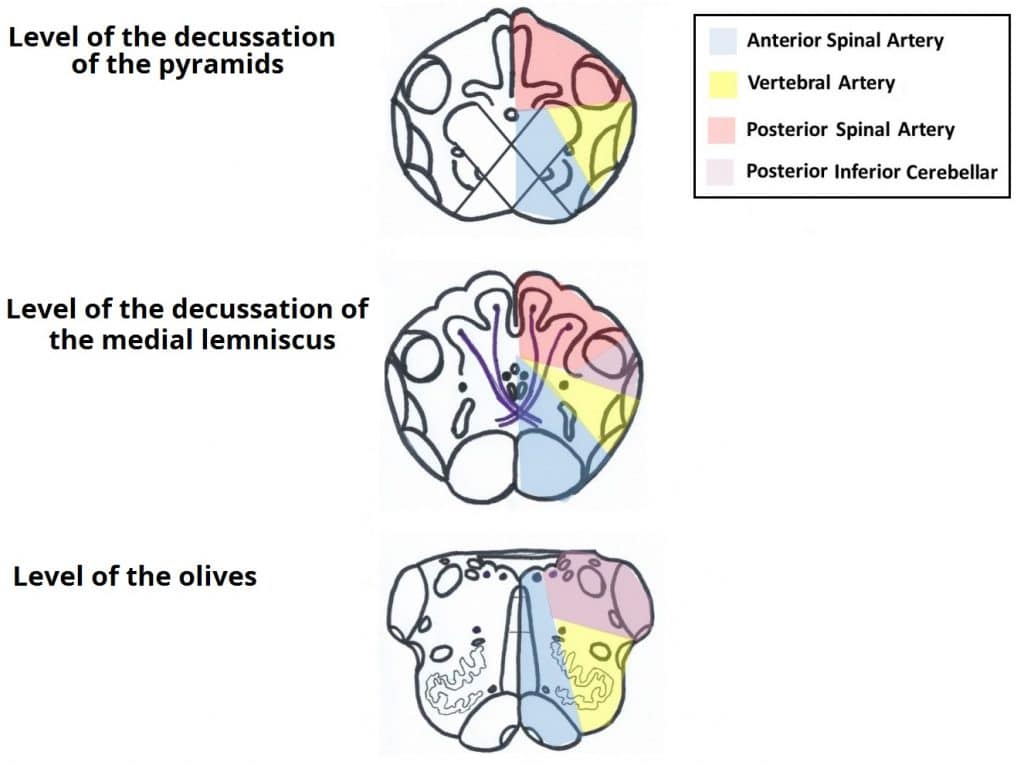
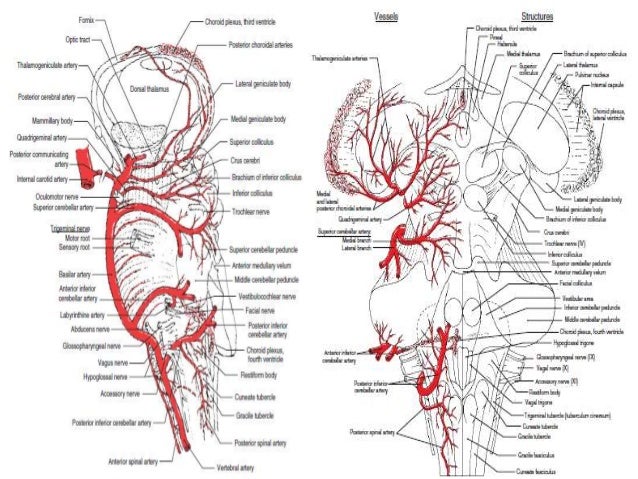
Medulla oblongata contains the vital autonomic cardiovascular and respiratory centers controlling heart rate blood pressure and breathing. Level of decussation of the pyramids. The vertebrobasilar system is responsible for supplying the medulla oblongata.
Medulla oblongata is the transition from the spinal cord to the brain it ends at the foramen magnum or the uppermost rootlets of the first cervical nerve and to which cranial nerves vi to xii are attached.
 The Medulla Oblongata Internal Structure Vasculature
The Medulla Oblongata Internal Structure Vasculature
 Medulla Oblongata Human Brain Anatomy Brain Anatomy Brain
Medulla Oblongata Human Brain Anatomy Brain Anatomy Brain
 The Spinal Cord Or Medulla Spinalis Human Anatomy
The Spinal Cord Or Medulla Spinalis Human Anatomy
 Detailed Anatomy Of The Medulla
Detailed Anatomy Of The Medulla
 Easy Notes On Medulla Oblongata Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Easy Notes On Medulla Oblongata Learn In Just 4 Minutes
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4053/WU0POdK93YLDIPco3Rwb7g_image1_medial.png) Medulla Oblongata Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Medulla Oblongata Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
 Image Result For Transverse Section Of Medulla Oblongata
Image Result For Transverse Section Of Medulla Oblongata
 What Is The Medulla Definition Function Location
What Is The Medulla Definition Function Location
 Anatomy Atlases Atlas Of Microscopic Anatomy Section 1 Cells
Anatomy Atlases Atlas Of Microscopic Anatomy Section 1 Cells
 The Spinal Cord Or Medulla Spinalis Human Anatomy
The Spinal Cord Or Medulla Spinalis Human Anatomy
 Medulla Oblongata Simplified Sections Of Internal Structure
Medulla Oblongata Simplified Sections Of Internal Structure
Brainstem I The Medulla Organization Of The Central
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4059/6CV3St7SuBfzjaQGU4w_Gracile_tubercle_02.png) Medulla Oblongata Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Medulla Oblongata Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
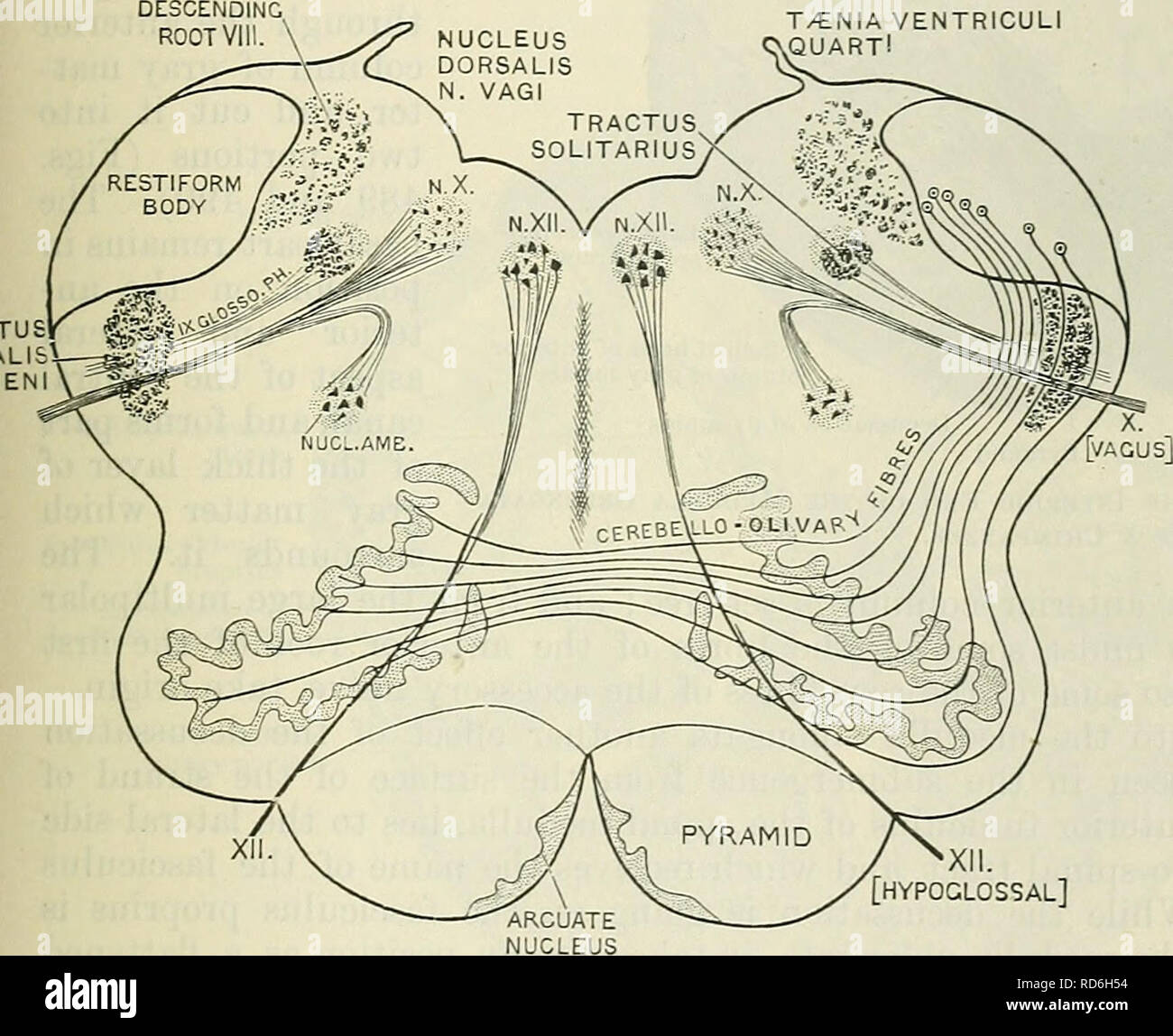 Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Internal
Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Internal
 Medulla Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
Medulla Anatomy Diagram Quizlet

Difference Between Pons And Medulla Difference Between
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11465/anatomy-brainstem-anterior-view_english.jpg) Cerebellum And Brainstem Anatomy And Functions Kenhub
Cerebellum And Brainstem Anatomy And Functions Kenhub
 14 3 Brainstem The Medulla Oblongata Relays Signals
14 3 Brainstem The Medulla Oblongata Relays Signals
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4054/VXmKXqtV3M38bosYiH1Lw_Canalis_centralis_medullae_spinlalis_m02.png) Medulla Oblongata Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Medulla Oblongata Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
 Medulla Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Medulla Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar