Each maxilla articulates with nine bones. No arch cartilage primary cartilage center of ossification close to the cartilage of nasal capsule center of ossification in angle between division of infraorbital nerve from this center the bone formation spreads bony trough for infraorbital canal is formed posteriorly below the orbit toward the developing maxillaanteriorly toward.
 Female Maxilla Bone Image Photo Free Trial Bigstock
Female Maxilla Bone Image Photo Free Trial Bigstock
The nasal zygomatic lacrimal inferior nasal concha palatine vomer and the adjacent fused maxilla.

Maxillary bone anatomy. The frontal and ethmoid. Resorption of alveolar bone 26. Maxilla bone anatomy the two maxilla or maxillary bones maxillae plural form the upper jaw l mala jaw.
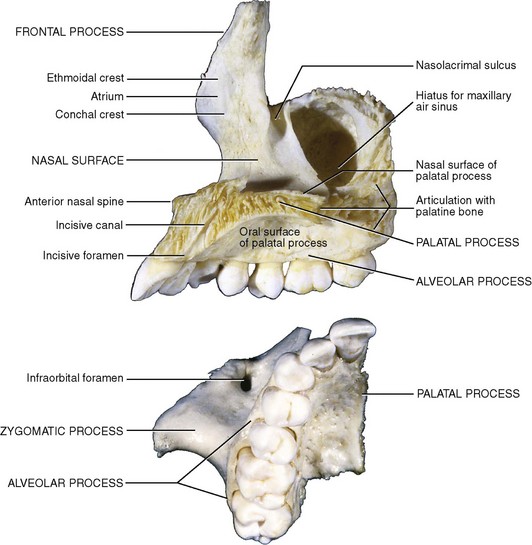
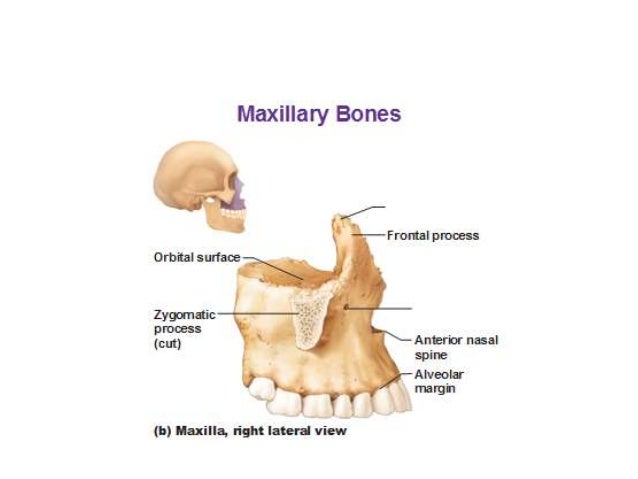
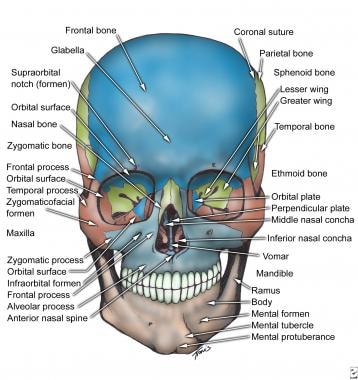
The nasal bone which makes up the bridge of your. Each maxilla has four processes frontal zygomatic alveolar and palatine and helps form the orbit roof of the mouth and the lateral walls of the nasal cavity. A small vertical midline plate termed the nasal spine of the frontal bone contributes to the nasal septum.
Le fort i fracture. Le fort ii fracture. Development of maxilla maxilla develops from ossification in mesenchyme of maxillary processof 1st arch.
Anteriorly between the orbital surfaces the frontal bone articulates with the anterior portions of the nasal bones and frontal processes of the maxilla. As the maxilla is the central bone of the midface it can fracture through various accidents most commonly the le fort fractures which are subclassified into three types. The maxilla forms the upper jaw by fusing together two irregularly shaped bones along the median palatine suture located at the midline of the roof of the mouth.
It forms the floor of the nasal cavity and parts of its lateral wall and roof the roof of the oral cavity contains the maxillary sinus and contributes most of the inferior rim and floor of the orbit. Detachment of the alveolar process from the maxilla in a rectangular form. The maxillary bones on each side join in the middle at the intermaxillary suture a fused line that is created by the union of the right and left halves of the maxilla bone.
Seven of the face. The palatine bones which make up part of the hard palate. The frontal bone which makes contact with bones in the nose.
Maxilla is a paired bone that has a body and four processes. The maxilla or maxillary bones is a pair of symmetrical bones joined at the midline which forms the middle third of the face. The zygomatic bones or cheek bones.
The maxilla or upper jaw bone latin. Two of the cranium. The maxilla is also fused together with other important bones in the skull including.
Frontal process zygomatic process palatine process and alveolar process. The two maxillary bones maxillae are fused in the midline by the intermaxillary suture to form the upper jaw.
Facial Bones Human Anatomy Organs
 Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica
Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica
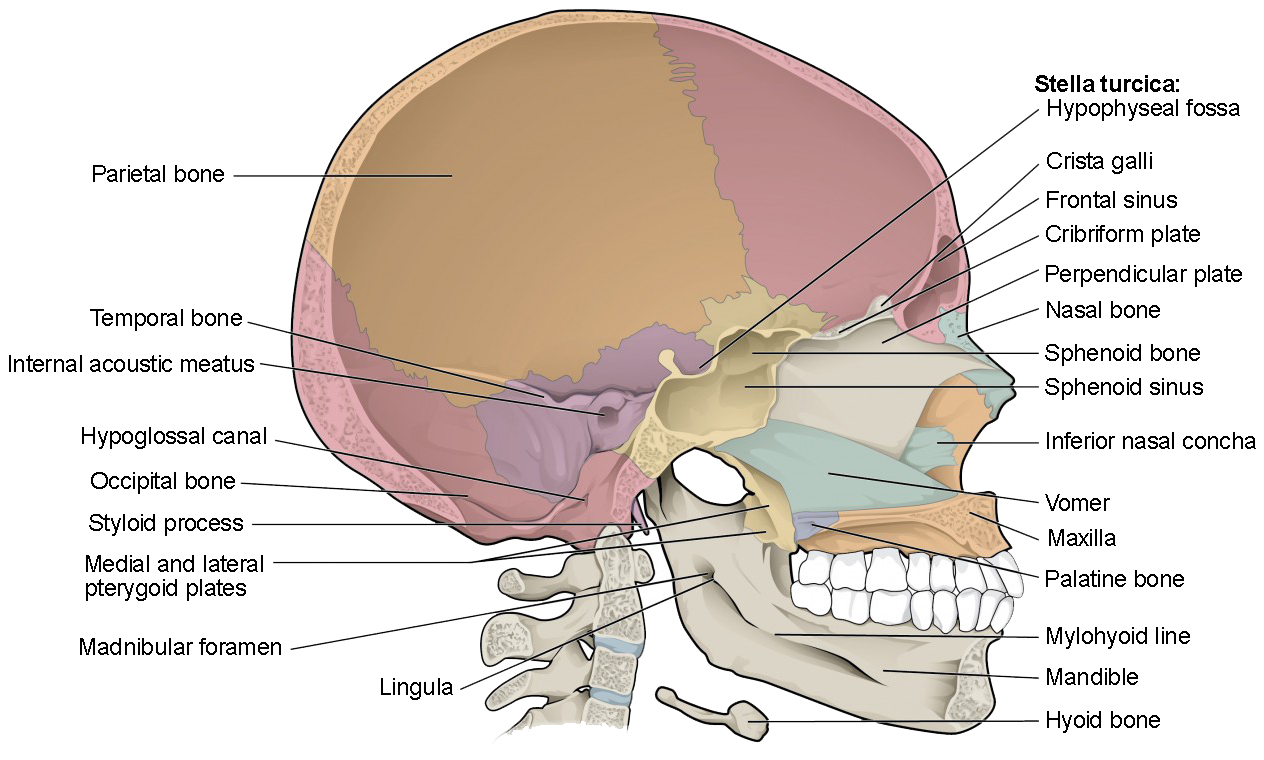 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I
The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/552/W39arzeteG61UaMYzqsYw_skull-anterior-lateral-views_english.jpg) Maxilla Anatomy Function Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Maxilla Anatomy Function Clinical Aspects Kenhub
The Skull Anatomy And Physiology Openstax
 Benefits Of Zygomatic Implants In Patients With Severe
Benefits Of Zygomatic Implants In Patients With Severe
 Maxillary Bone Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
Maxillary Bone Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
 10 Applied Surgical Anatomy Of The Head And Neck Pocket
10 Applied Surgical Anatomy Of The Head And Neck Pocket
 Quiz 2 Lab 3 Facial Bones Anatomy 214 With Woodman At
Quiz 2 Lab 3 Facial Bones Anatomy 214 With Woodman At
Anatomy Of The Maxilla And Mandible Jaw Bone Medical Chart
 Facial Fracture Management Handbook Applied Anatomy Iowa
Facial Fracture Management Handbook Applied Anatomy Iowa

 Maxilla Bone Palatine Process Alveolar Process Human
Maxilla Bone Palatine Process Alveolar Process Human
 Royalty Free Maxilla Stock Images Photos Vectors
Royalty Free Maxilla Stock Images Photos Vectors
Facial Bones Human Anatomy Organs
 Anatomy Of Maxilla And Mandible
Anatomy Of Maxilla And Mandible
 Maxilla An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Maxilla An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Maxilla Bone Cranium Bones Head Skull Stock Illustration
Maxilla Bone Cranium Bones Head Skull Stock Illustration
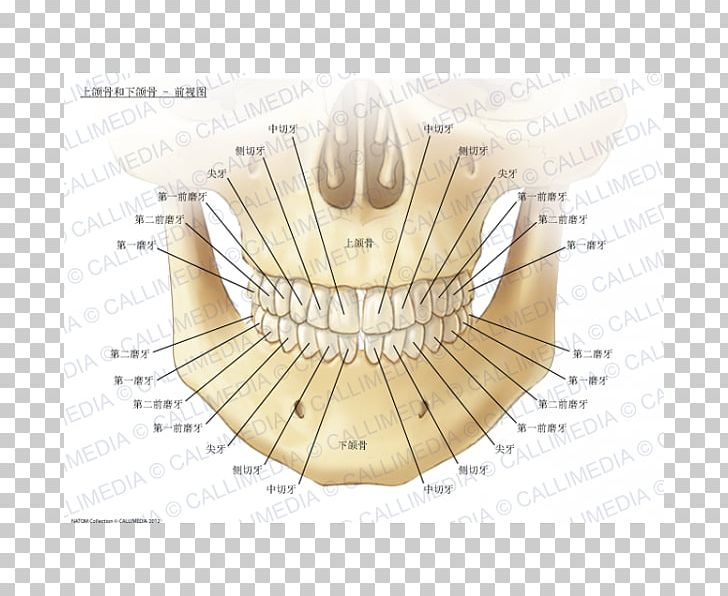 Maxilla Mandible Anatomy Human Body Bone Png Clipart
Maxilla Mandible Anatomy Human Body Bone Png Clipart
 Orbital Anatomy Plastic Surgery Key
Orbital Anatomy Plastic Surgery Key
 Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
 The Maxillae Upper Jaw Human Anatomy
The Maxillae Upper Jaw Human Anatomy


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar