If a fiber primarily produces atp through aerobic pathways then it is classified as oxidative. The strength of a muscle contration is determinded not only by the frequency of stimulation but also by the number and size of motor units recruited the number of motor units that are recruited is determined by the number of motor neurons that are stimulated by the central nervous system.
 Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
In the deep fascia around the muscles are several large arteries veins and nerves.
Muscle fiber anatomy definition. Skeletal muscle fiber location and arrangement. Any of the elongated cells characteristic of muscle. Used for forceful and rapid contractions over short periods of time.
They are red in colour due to the presence of large volumes of myoglobin and so oxygen and high numbers of mitochondria. Muscle fiber any of the cells of skeletal or cardiac muscle tissue. Muscle fs fast twitch paler colored muscle fibers of larger diameter than slow twitch fibers and having less sarcoplasm and more prominent cross striping.
Muscle cell muscle fibre. About half of the skeletal muscle fibers in adults are slow fibers. Fibre fiber any of several elongated threadlike cells especially a muscle fiber or a nerve fiber muscle musculus one of the contractile organs of the body.
Skeletal muscle is comprised from a series of bundles of muscle fibers surrounded by protective membranes. Nouna muscle cell especially one of the cylindrical multinucleate cells that make up skeletal muscles and are composed of numerous myofibrils that contract when stimulated. More atp can be produced during each metabolic cycle making the fiber more resistant to fatigue.
Type i muscle fibres type i fibre are also known as slow twitch fibre. The primary metabolic pathway used by a muscle fiber determines whether the fiber is classified as oxidative or glycolytic. Skeletal muscle is a specialized contractile tissue found in animals which functions to move an organisms body.
Branches of these vessels and nerves penetrate each muscle close to its midpoint then extend into the epimysium and perimysium layers. Muscle fiber an elongated contractile cell that forms the muscles of the body. Medical definition of muscle fiber.
In the endomysium individual muscle fibers cells are supported by nearby capillaries and nerve cells. Mammalian skeletal muscle fibers are characterized by d their morphological traits such as total number of fibers tnf and cross sectional area of fibers csaf and fiber e type characteristics such as contractile and metabolic f properties lee et al.
 10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology
10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology
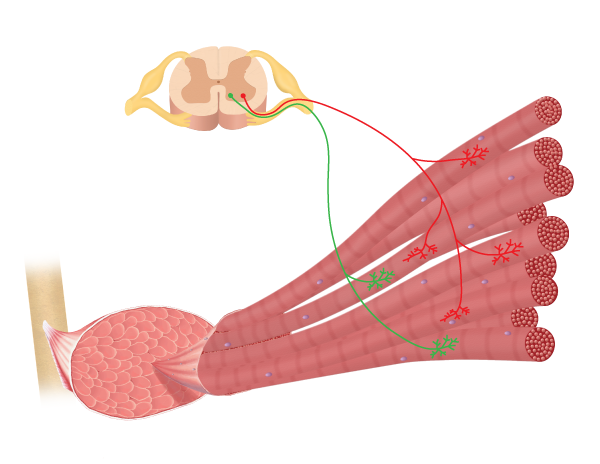 Motor Units And Muscle Twitches
Motor Units And Muscle Twitches
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Anatomy And Cell Biology 104
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Anatomy And Cell Biology 104
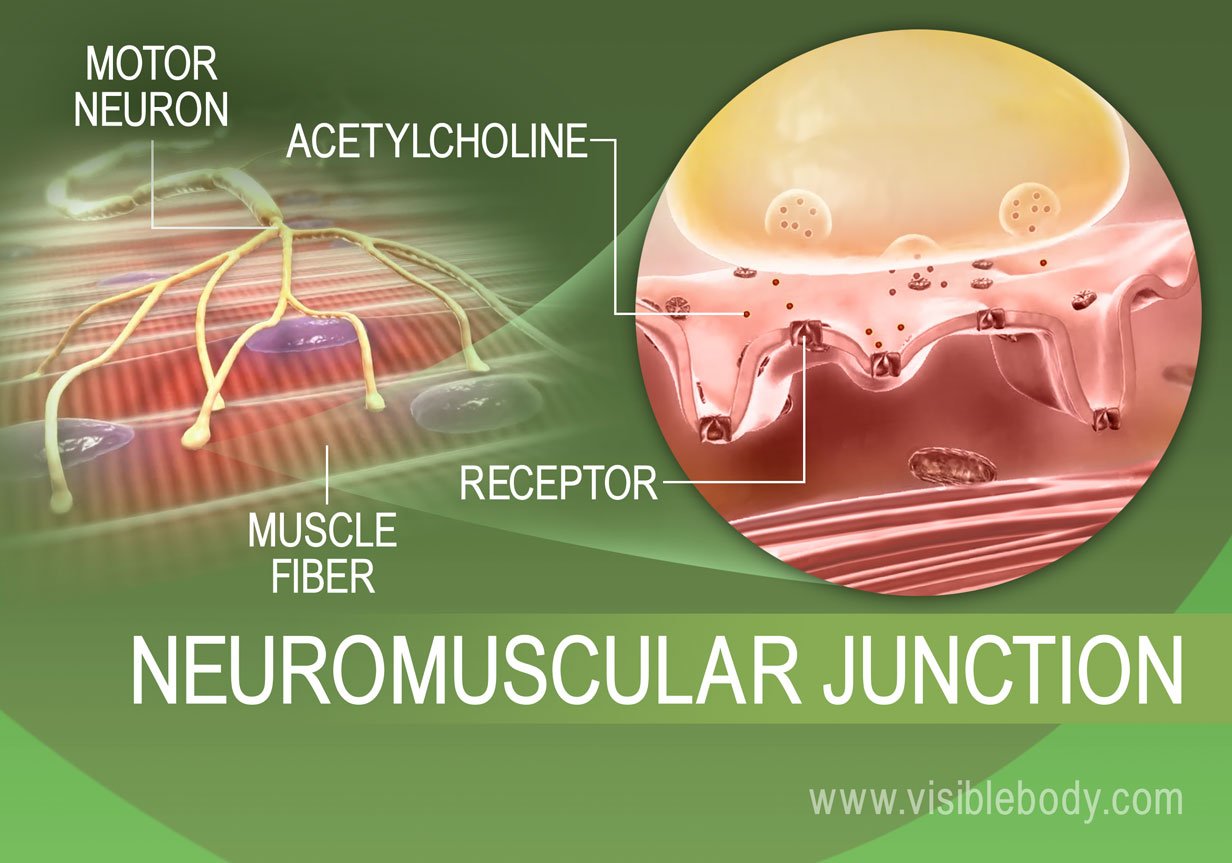 Muscle Contractions Learn Muscular Anatomy
Muscle Contractions Learn Muscular Anatomy
 Muscular System 3 Types Of Muscle Skeletal Muscle Aka
Muscular System 3 Types Of Muscle Skeletal Muscle Aka
 Skeletal Muscles Complete Anatomy
Skeletal Muscles Complete Anatomy
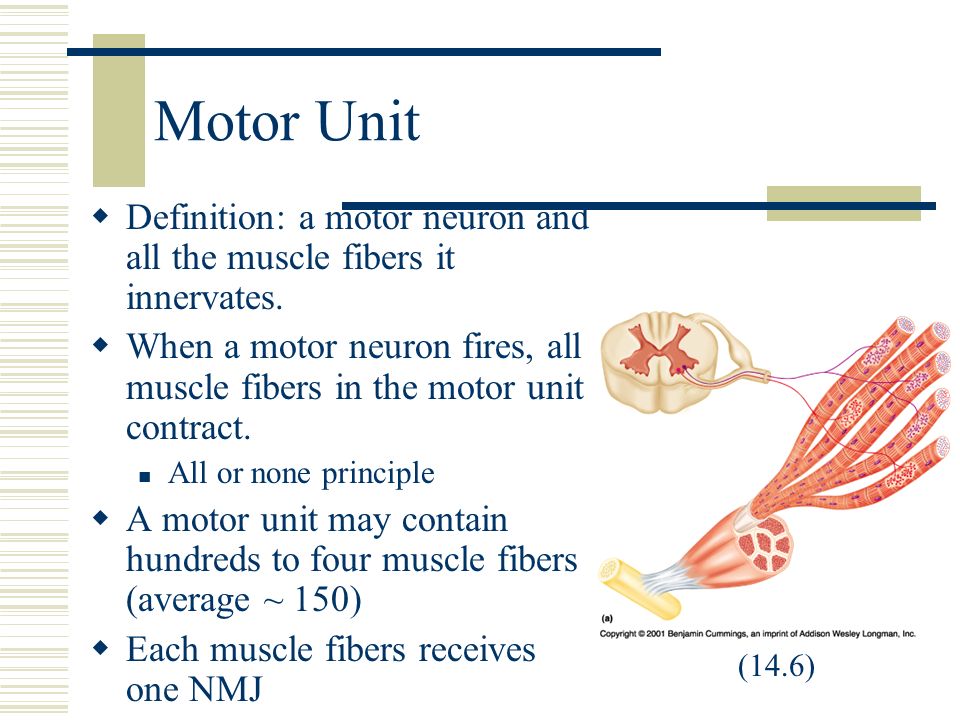 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue Functions Movement
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue Functions Movement
 Biology For Kids Muscular System
Biology For Kids Muscular System
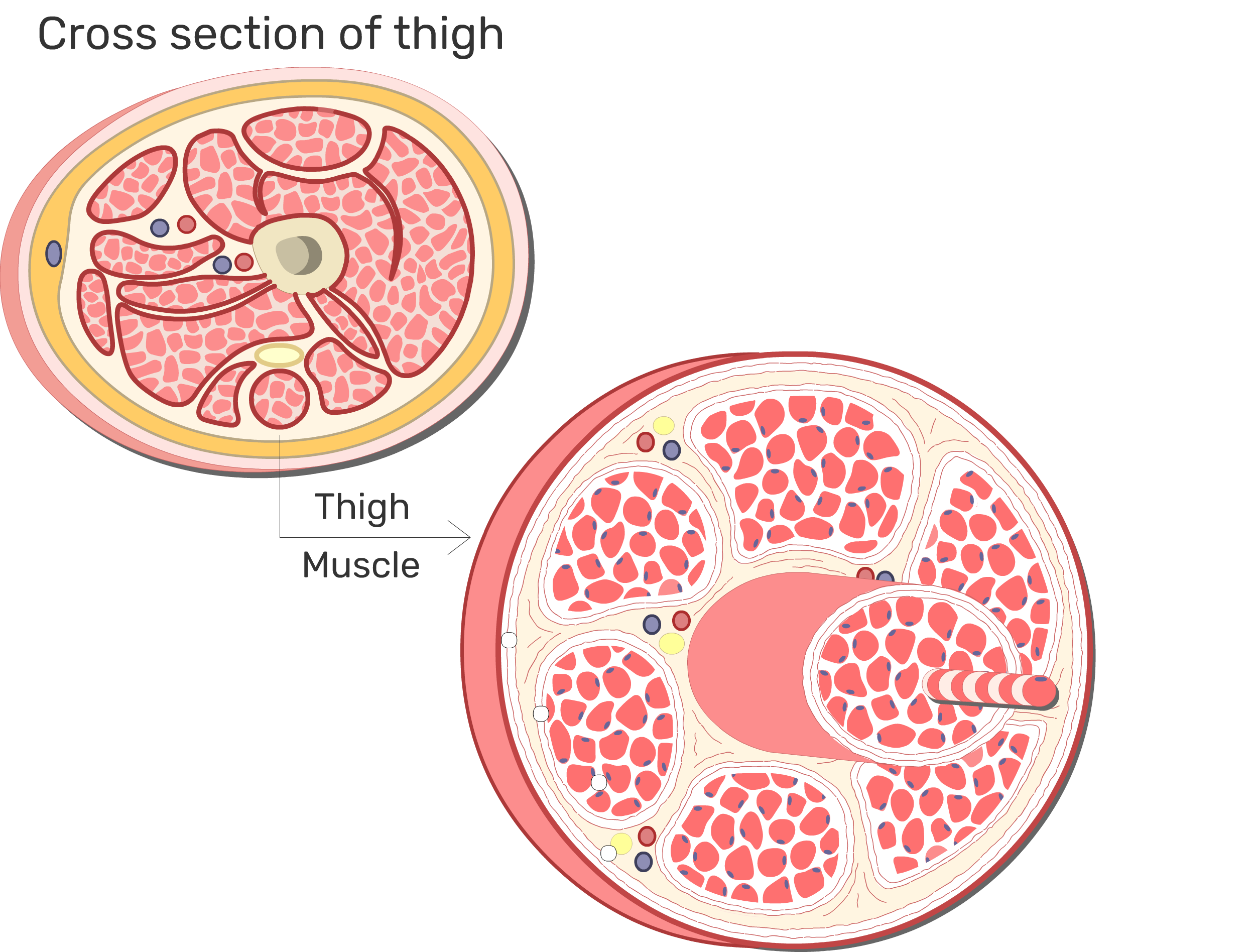 Muscle Physiology An Introduction
Muscle Physiology An Introduction
 Skeletal Muscle Structure And Function Musculoskeletal
Skeletal Muscle Structure And Function Musculoskeletal
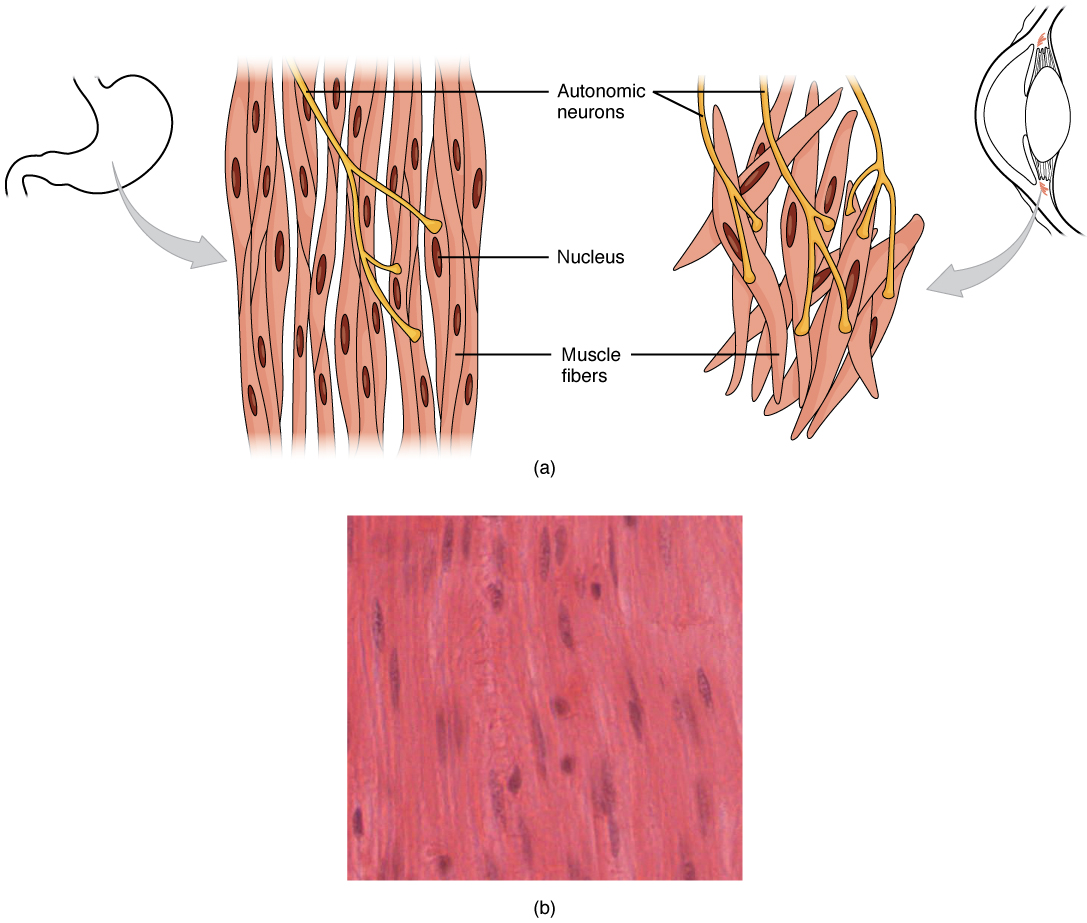 10 8 Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology
10 8 Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology
 Muscle Spindle Muscle Stretch Reflex
Muscle Spindle Muscle Stretch Reflex
 Myofibril Definition Function And Structure Biology
Myofibril Definition Function And Structure Biology
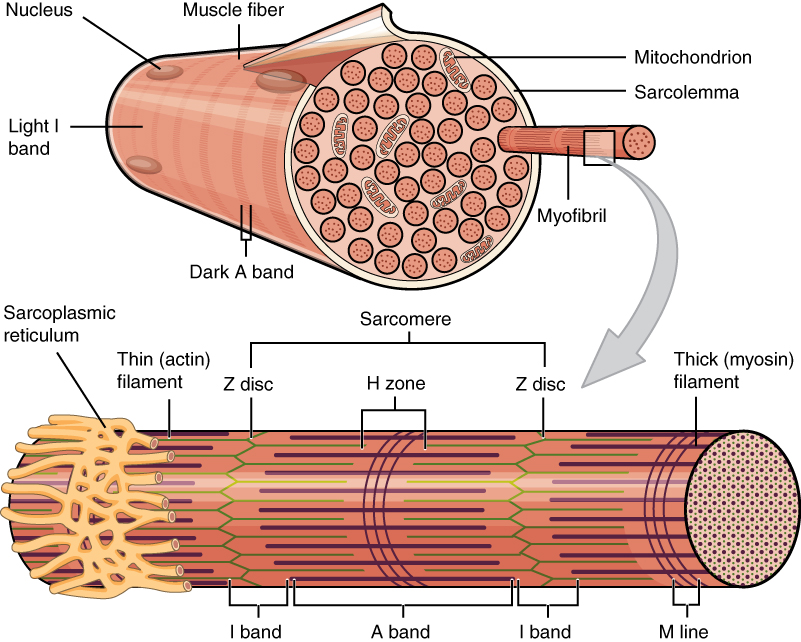 10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology
10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology
 Endomysium Anatomy Of Muscle Structure
Endomysium Anatomy Of Muscle Structure
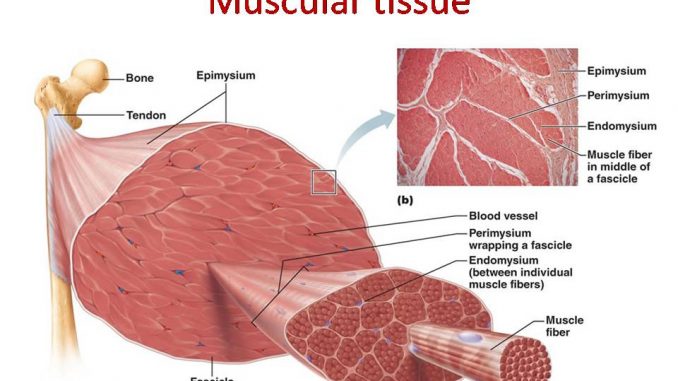 Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle
Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle
 Kondo Lab 4 Muscle Set Biology 200 With Kondo At Citrus
Kondo Lab 4 Muscle Set Biology 200 With Kondo At Citrus
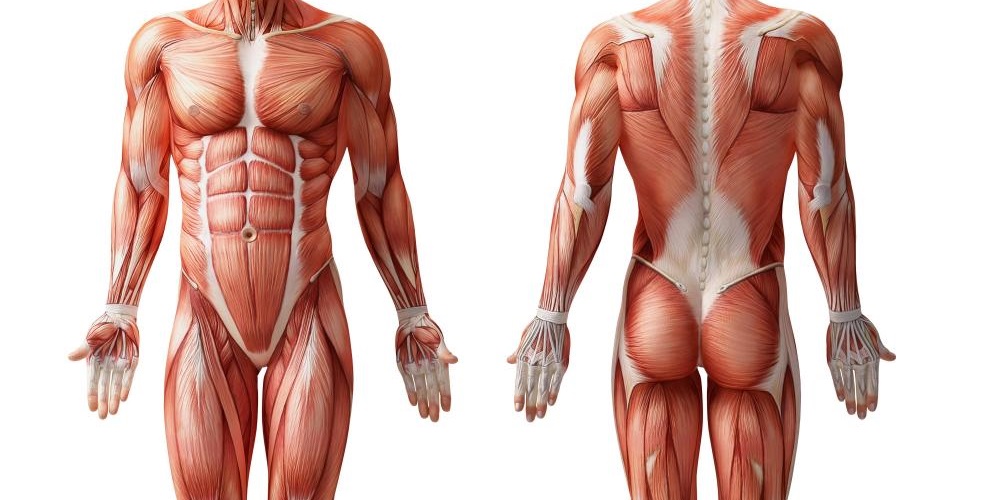 Micro Tears In Muscles Explaining How Muscle Growth Works
Micro Tears In Muscles Explaining How Muscle Growth Works
 Cardiac Muscle Definition Function Structure Britannica
Cardiac Muscle Definition Function Structure Britannica
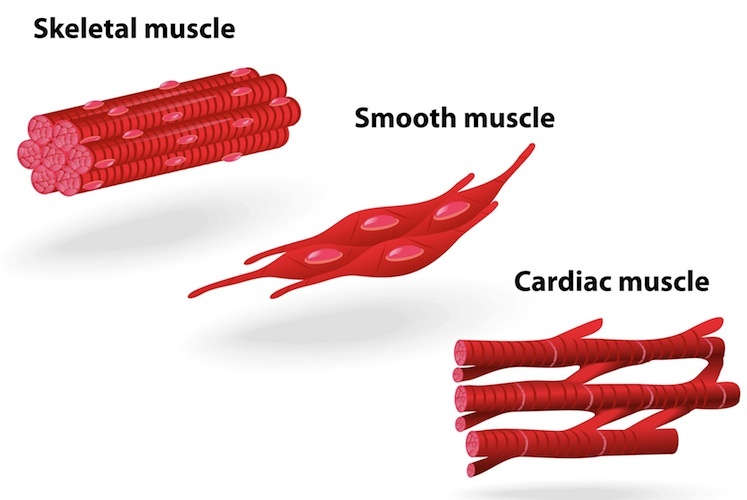 Muscle Structure Muscle Under The Microscope Science
Muscle Structure Muscle Under The Microscope Science
 Muscle Fibre Types Fast Twitch Slow Twitch Teachpe Com
Muscle Fibre Types Fast Twitch Slow Twitch Teachpe Com
 Muscular Dystrophy Symptoms Treatment Types And Causes
Muscular Dystrophy Symptoms Treatment Types And Causes
 Neuromuscular Junctions And Muscle Contractions Anatomy
Neuromuscular Junctions And Muscle Contractions Anatomy
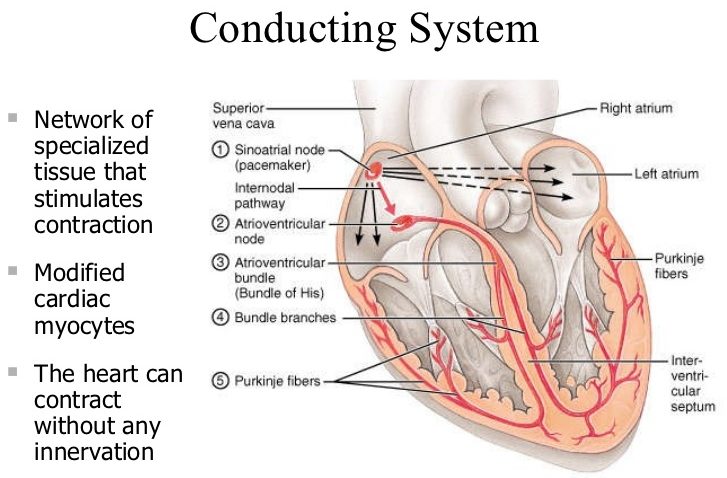 Purkinje Fibers Anatomy Location Function Anatomy Info
Purkinje Fibers Anatomy Location Function Anatomy Info


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar