It uses hormones to control and coordinate your bodys metabolism energy level reproduction growth and development and response to injury stress and mood. The hypothalamus receives input from other parts of the brain and from peripheral nerves.
 The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Avian Endocrine System
The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Avian Endocrine System
And regulating cellular metabolism and energy balance.

Anatomy and physiology of endocrine system. Physiology of the endocrine system although hormones have widespread effects the major processes they control are reproduction growth and development. Anatomy of the endocrine system the endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs. Mobilizing the bodys defenses against stressors.
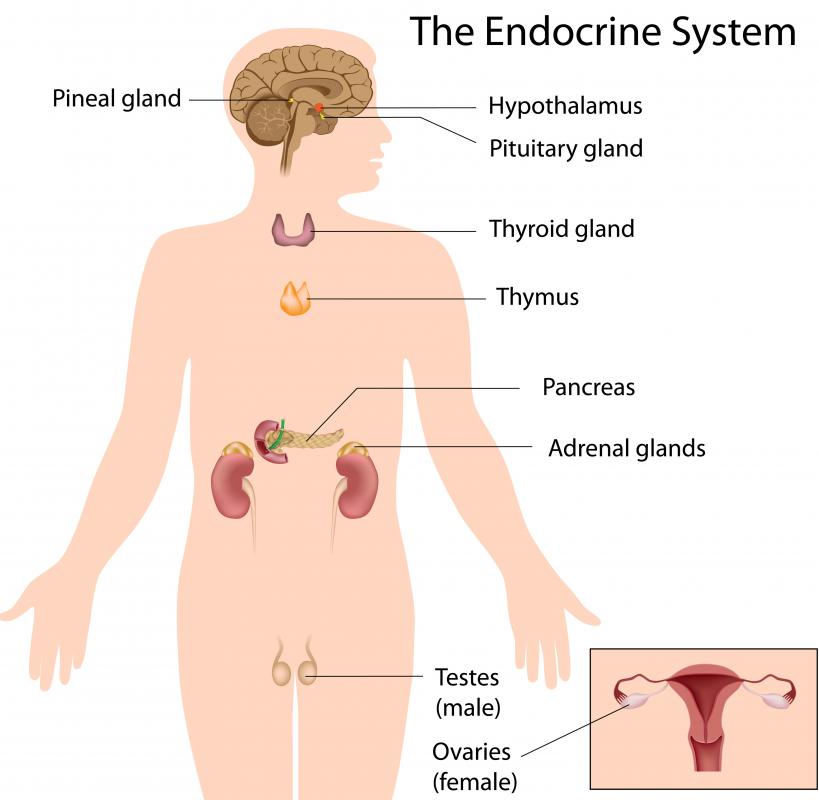
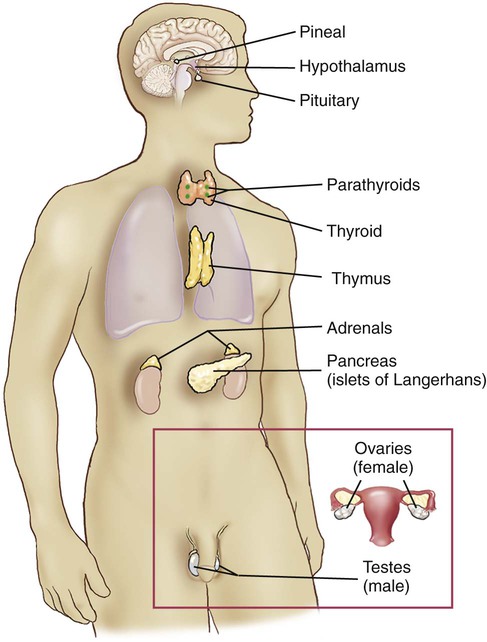
Other endocrine glands within the body include. Thyroid parathyroids adrenals pancreas ovaries and testes. The hypothalamus is located in the forebrain directly above the pituitary gland.
The major endocrine organs include the hypothalamus and the hypophysis or pituitary gland. It serves many different functions in the nervous system and is also responsible for the direct control of the endocrine system through the pituitary gland. The primary function of these ductless glands is to secrete their hormones directly into the surrounding fluid.
The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones chemical substances produced in the body that regulate the activity of cells or organs. The hypothalamus is a part of the brain located superior and anterior to the brain stem and inferior to the thalamus. The endocrine system includes the pituitary thyroid parathyroid adrenal and pineal glands figure 1.
The endocrine gland is the major player in this system. Anatomy of the endocrine system hypothalamus. The interstitial fluid and the blood vessels then transport the hormones throughout the body.
Endocrine system anatomy and physiology lecture states the function of endocrine system and physiology of endocrine system by means of hormones biochemistry that regulates the body growth and. The hypothalamus contains special cells called neurosecretory cellsneurons that secrete hormones. Maintaining electrolyte water and nutrient balance of the blood.
The following are integral parts of the endocrine system. These hormones regulate the bodys growth metabolism the physical and chemical processes of the body and sexual development and function. Anatomy and physiology of endocrine system thyroid diseases what is endocrine system pituitary hormones function of endocrine system endocrine diseases endoc.
 Ppt The Endocrine System Chapter 17 Lecture Notes
Ppt The Endocrine System Chapter 17 Lecture Notes
 Anatomy Physiology 03 07 Endocrine System By Alexis
Anatomy Physiology 03 07 Endocrine System By Alexis
Endocrine System Anatomy Physiology
 Name Period Anatomy And Physiology The Endocrine System The
Name Period Anatomy And Physiology The Endocrine System The
 03 07 Endocrine System Anatomy And Physiology What Is The
03 07 Endocrine System Anatomy And Physiology What Is The
 Anatomy And Physiology Lab 2 Exam 1 Endocrine System
Anatomy And Physiology Lab 2 Exam 1 Endocrine System
 Regulation Endocrine System Anatomy Physiology 1 With
Regulation Endocrine System Anatomy Physiology 1 With
 Endocrine System Human Anatomy And Physiology Lecture
Endocrine System Human Anatomy And Physiology Lecture
 The Endocrine System Group Activity
The Endocrine System Group Activity
 What Is The Role Of Negative Feedback In The Endocrine System
What Is The Role Of Negative Feedback In The Endocrine System
 Infographic Human Body Endocrine System Lady Things
Infographic Human Body Endocrine System Lady Things
 Free Anatomy Quiz The Endocrine System Anatomy Quiz 1
Free Anatomy Quiz The Endocrine System Anatomy Quiz 1
 Endocrine System Physiology Health Life Media
Endocrine System Physiology Health Life Media
 Endocrine System Overview Hs Anatomy And Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hs Anatomy And Physiology
 Learnhive Icse Grade 10 Biology Human Anatomy And
Learnhive Icse Grade 10 Biology Human Anatomy And
 Endocrine System Anatomy Physiology For The Mblex Mblexguide
Endocrine System Anatomy Physiology For The Mblex Mblexguide
 Anatomy And Physiology The Endocrine System Things You
Anatomy And Physiology The Endocrine System Things You
 Pdf Human Anatomy Physiology The Endocrine System Part A
Pdf Human Anatomy Physiology The Endocrine System Part A
Endocrine System Hormones Solutions
 21 Endocrine System Anatomy Physiology Educator Com
21 Endocrine System Anatomy Physiology Educator Com
 Endocrine System And Nutritional And Metabolic Diseases
Endocrine System And Nutritional And Metabolic Diseases
Endocrine System Brandon Perez Anatomy And Physiology Final
 The Endocrine System Ross And Wilson Anatomy And
The Endocrine System Ross And Wilson Anatomy And
 11 The Endocrine And Reproductive Systems Ms Buchanan S
11 The Endocrine And Reproductive Systems Ms Buchanan S
Endocrine System Anatomy And Physiology
 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System Principles Of Anatomy And
Chapter 18 The Endocrine System Principles Of Anatomy And
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar