Managing the airway of a patient with craniofacial disorders poses many challenges to the anesthesiologist. Understanding airway anatomy is vital to proper intubation.
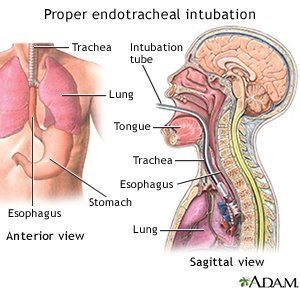 Insertion Of An Endotracheal Tube What You Need To Know
Insertion Of An Endotracheal Tube What You Need To Know
The upper airway begins in the nose though many nasal structures extend into the face and are not visible.

Airway anatomy for intubation. Endotracheal intubation can be done either nasally or orally but oral intubation is easier in most contexts. It includes the mouth the nose the palate the uvula the pharynx and the larynx. This demonstration by anthony lewis from isimulate and todd slesinger provides a brief overview of the basics of the upper airway and laryngoscopy.
Anatomical abnormalities may affect only intubation only airway management or both. A good understanding of airway and intubation is fundamental to managing a sick patient. Anatomical landmarks for intubation.
Visualizing and using your patients own anatomical landmarks during intubation may help you in your next attempt at securing an advanced airway. A quick overview is as follows. Upper airway anatomy in order to open the paediatric airway and gain the best view of the laryngeal inlet the oral pharyngeal and tracheal axes must be brought into alignment.
Thats because its easier to visualize most of the airway. This requires suitable patient positioning during preparation for intubation and differs based on the age of the child. Proficiency in airway management and tracheal intubation requires a firm foundation of knowledge in airway anatomy.
This section also describes the functional physiology of this airway. Visualize both the epiglottis and larynx but also know various positioning techniques that you can use to improve your visualization of these landmarks. This chapter provides an overview of airway anatomy for tracheal intubation with conventional laryngoscopy videolaryngoscopy glidescope and flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy.
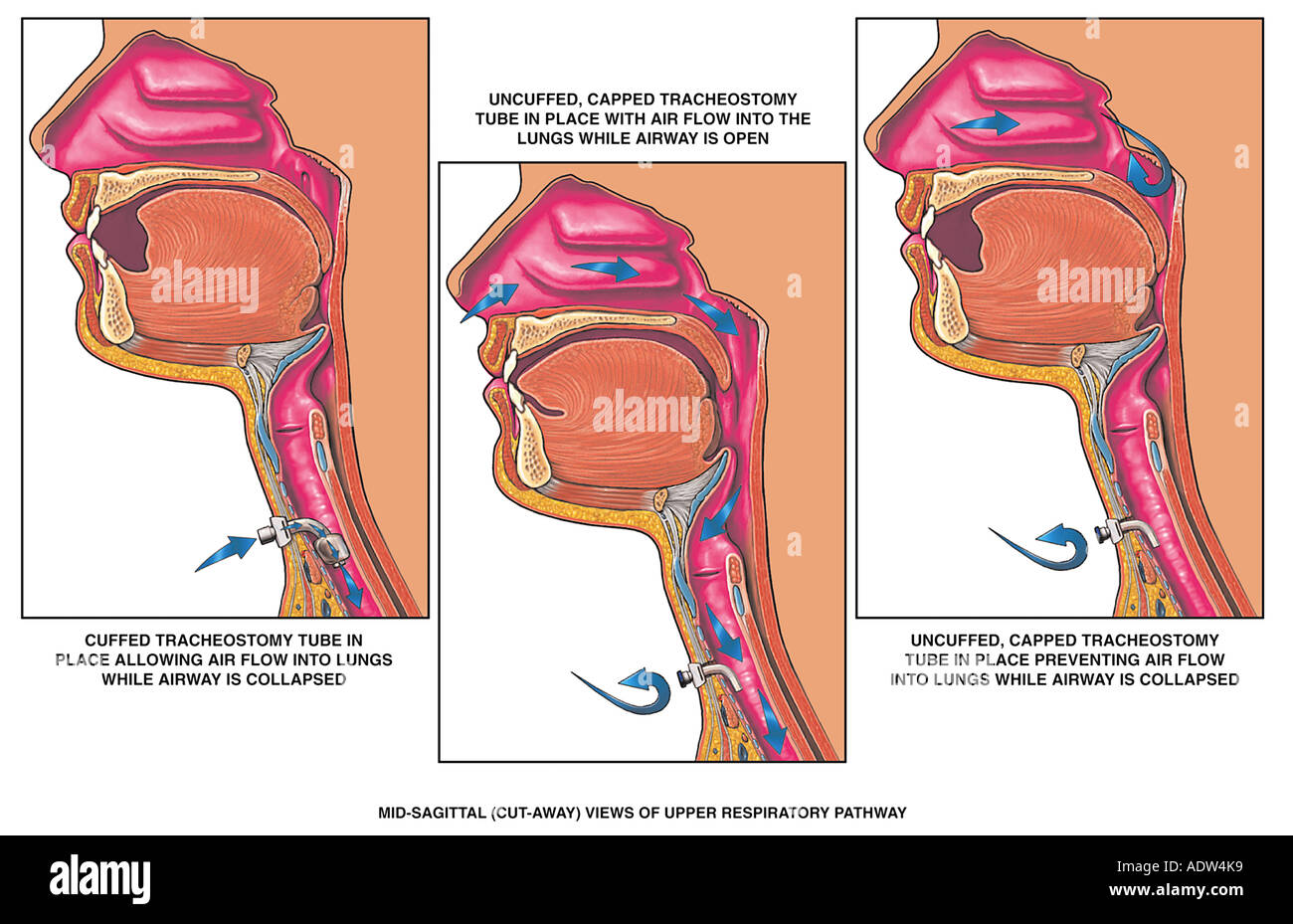 Airway Intubation Stock Photos Airway Intubation Stock
Airway Intubation Stock Photos Airway Intubation Stock
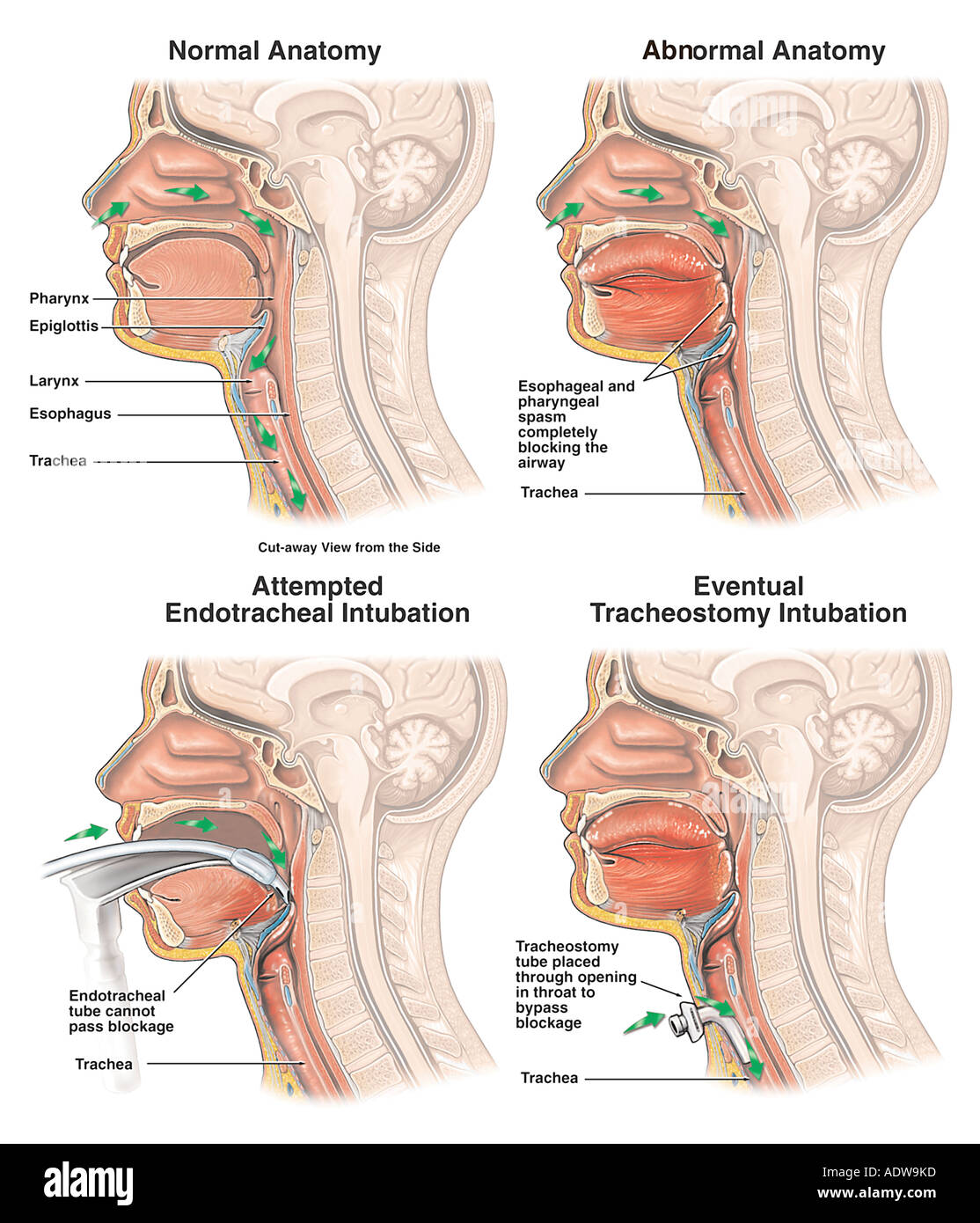 Blockage Of Airway With Attempts At Endotracheal Intubation
Blockage Of Airway With Attempts At Endotracheal Intubation
 Anatomical Differences Between Pediatric And Adult Airways
Anatomical Differences Between Pediatric And Adult Airways
 Lesson 4 Airway Airway Anatomy Upper Airway Nasal Passage
Lesson 4 Airway Airway Anatomy Upper Airway Nasal Passage
 Chapter 38 Airway Management Principles And Practice Of
Chapter 38 Airway Management Principles And Practice Of
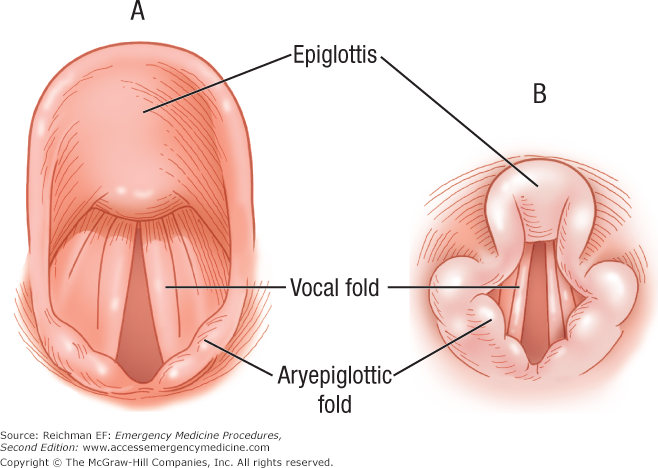 Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
 Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
 The Role Of The Lma As A Ventilating And Intubation Conduit
The Role Of The Lma As A Ventilating And Intubation Conduit
 Chapter 122 Intubation And Airway Support Principles And
Chapter 122 Intubation And Airway Support Principles And
 10 Rules For Approaching Difficult Intubation
10 Rules For Approaching Difficult Intubation
 Airway Anatomy And Endotracheal Intubation The Basics
Airway Anatomy And Endotracheal Intubation The Basics
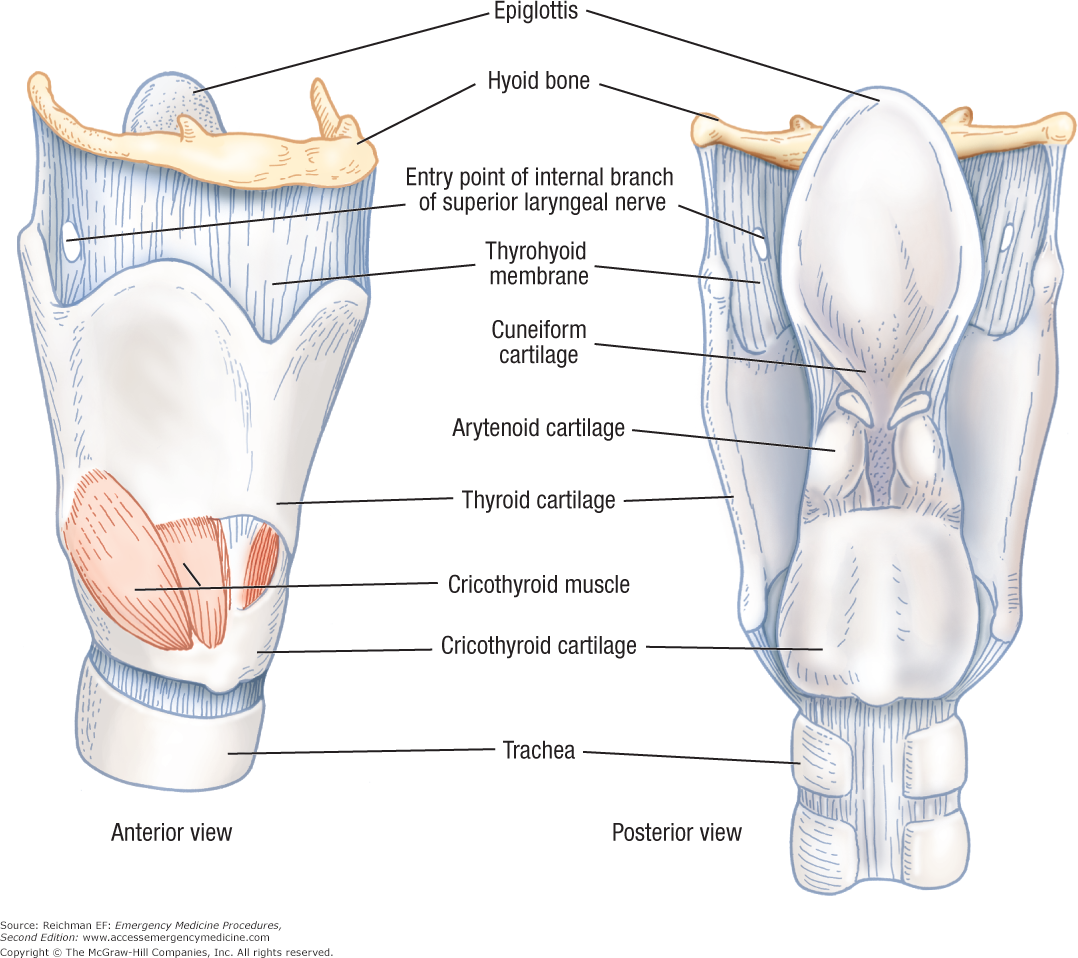 Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
Roadmap To The Glottis Ems Airway Clinic
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
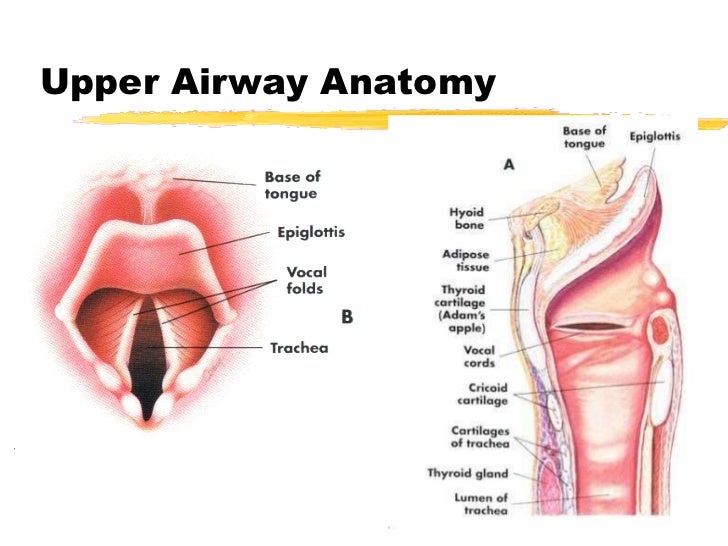
 Airway Management Outline Review Of Airway Anatomy Airway
Airway Management Outline Review Of Airway Anatomy Airway
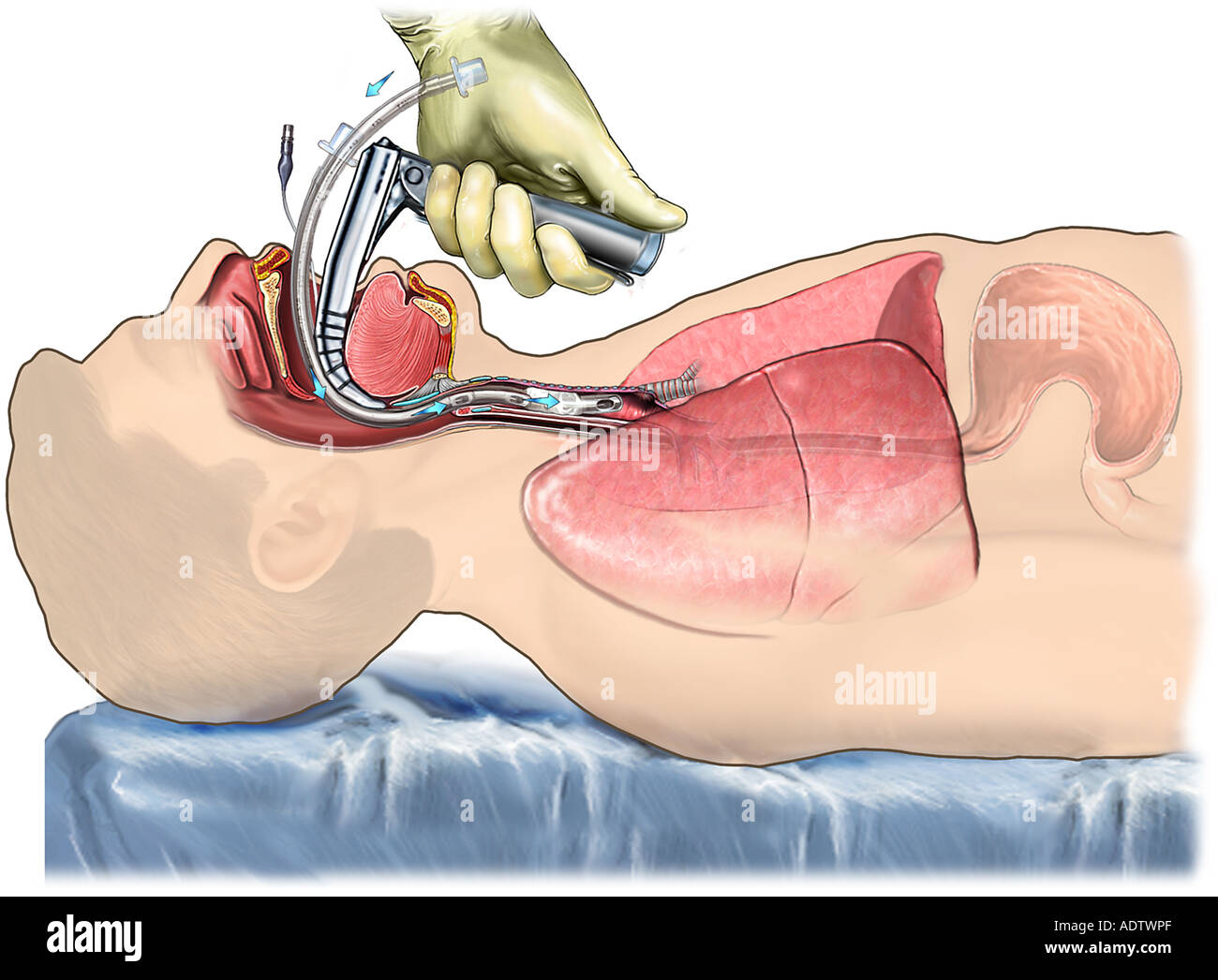 Airway Intubation Stock Photos Airway Intubation Stock
Airway Intubation Stock Photos Airway Intubation Stock
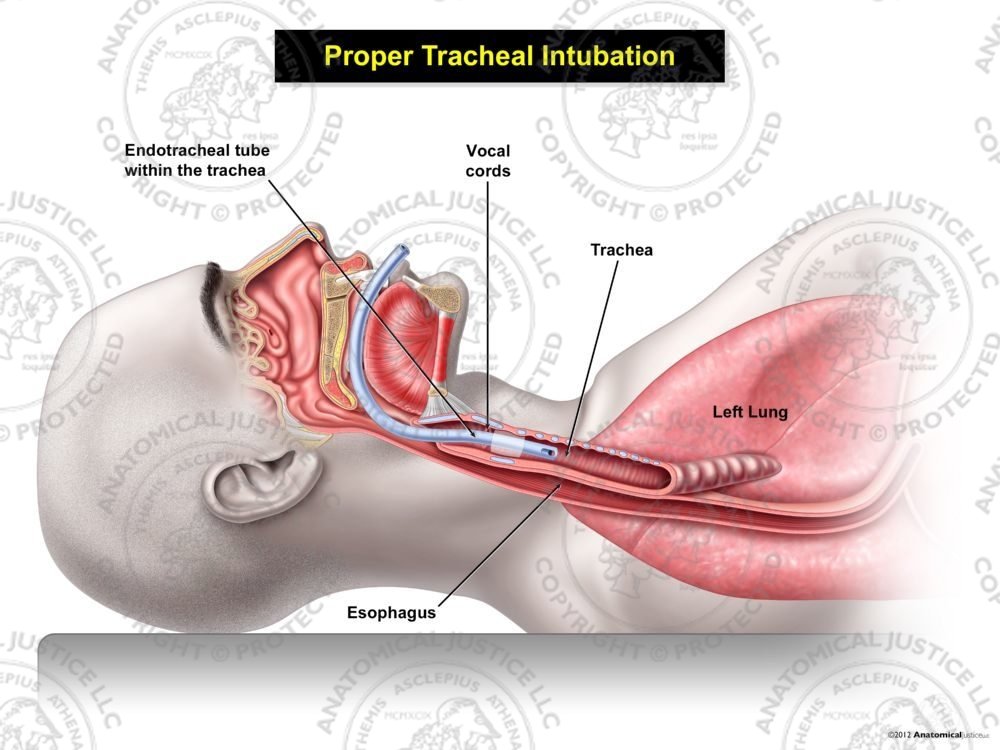 Proper Male Tracheal Intubation
Proper Male Tracheal Intubation
 Assessing And Finessing An Airway Update Emottawa
Assessing And Finessing An Airway Update Emottawa
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationtrach Travails
 Difficult Airway Management Simulator Training Model
Difficult Airway Management Simulator Training Model




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar