The ventral or anterior pons consists of white matter tracts eg. The pons like the cerebellum is another metencephalic derivative of the rhombencephalon.
Ascending medial lemniscus tracts.
Anatomy of pons. Although it is small at approximately 25 centimeters long it serves several important. Ipsilateral pain and temperature deficits from face due to damage tothe spinal trigeminal nucleus and tract4. The pons is composed of two significant segments ventral pons and the tegmentum.
Lower down in the pons. This 25 cm long structure is aptly named for its resemblance of a bridge as it forms a communication pathway between the left and right hemispheres of the cerebellum. Vertigo nausea nystagmus deafness tinitus vomiting due todamage to vestibular and cochlear nuclei and nerves3.
Lower down in the pons. The pons is a portion of the hindbrain that connects the cerebral cortex with the medulla oblongata. Anatomy of the pons.
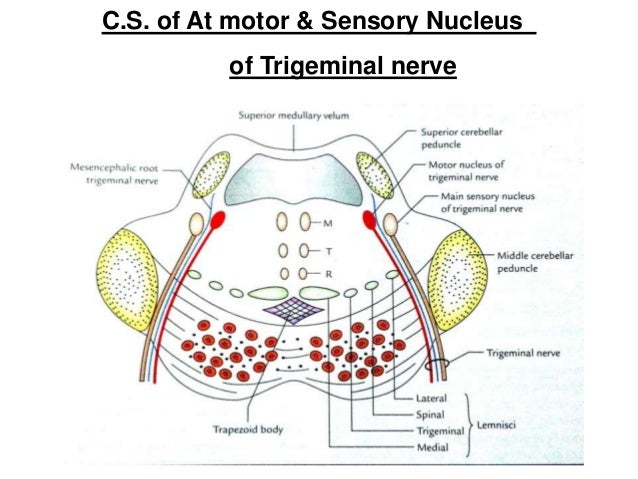
The basilar pons contains a complex combination of tracts bundles of axons and nuclei collections of cell bodies of neurons. The motor nucleus for the trigeminal nerve v. Facial nerve nucleus.
The anterior surface of the. A number of cranial nerve nuclei are present in the pons. Anterior and lateral corticospinal corticobulbar and corticopontine tracts with transverse fibres contributing to the bulk of the pons.
It is also the point of origin or termination for four of pons portion of the brain lying above the medulla oblongata and below the cerebellum and the cavity of the fourth ventricle. Descending corticospinal tracts responsible for voluntary motor control of the body. It also serves as a communications and coordination center between the two hemispheres of the brain.
Pons anatomy internal anatomy. The basilar pons and the pontine tegmentum contain nuclei and tracts. The pons is a broad horseshoe shaped mass of transverse nerve fibres that connect the medulla with the cerebellum.
Contralateral loss of pain and temperature sense from the bodydue to damage to the anterolateral system spinothalamic5. The chief or pontine nucleus of the trigeminal nerve sensory nucleus v. Ascending medial lemniscus tracts.
The rest of the pons is made up of tracts passing through the pons including. The pons has a bulbous shape and has two main components the ventral pons and the dorsal tegmentum. The pons consists of a the basilar pons in the front ventral portion and b the pontine tegmentum in the back dorsal portion.
The pons is a portion of the brain stem located above the medulla oblongata and below the midbrain. Descending corticobulbar tracts responsible for voluntary motor control of face head and neck.

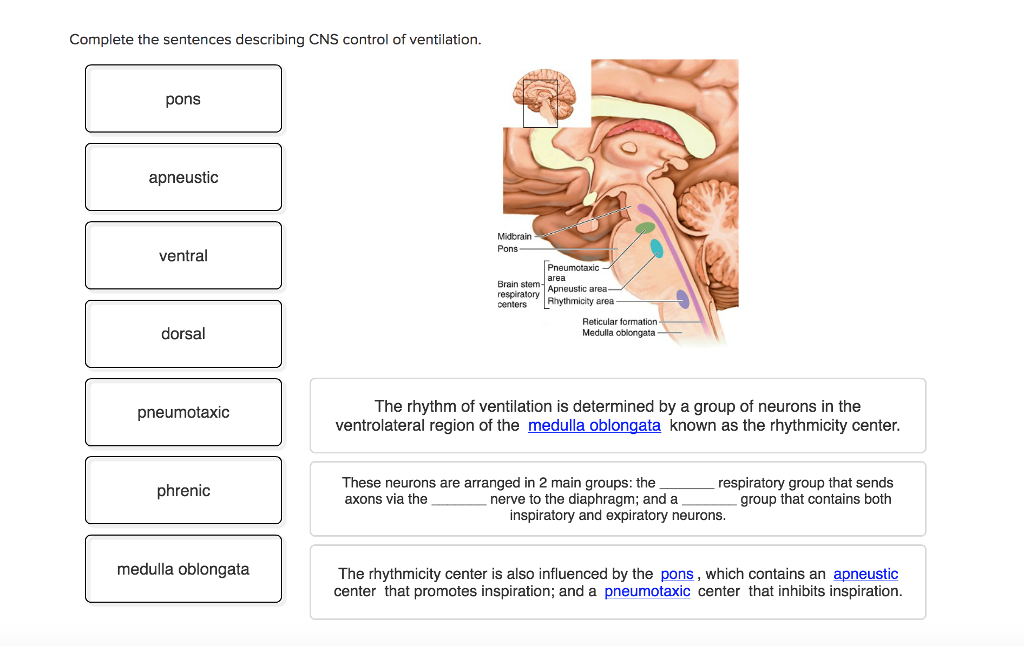 Solved Complete The Sentences Describing Cns Control Of V
Solved Complete The Sentences Describing Cns Control Of V
 Functional Anatomy Of The Facial Nerve Facial Nucleus Is In
Functional Anatomy Of The Facial Nerve Facial Nucleus Is In
 Figure Anatomy Of The Inside Of Pdq Cancer
Figure Anatomy Of The Inside Of Pdq Cancer
 Pons An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Pons An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
/cranial-nerves-56a09b4a3df78cafdaa32f16.jpg) Names Functions And Locations Of Cranial Nerves
Names Functions And Locations Of Cranial Nerves
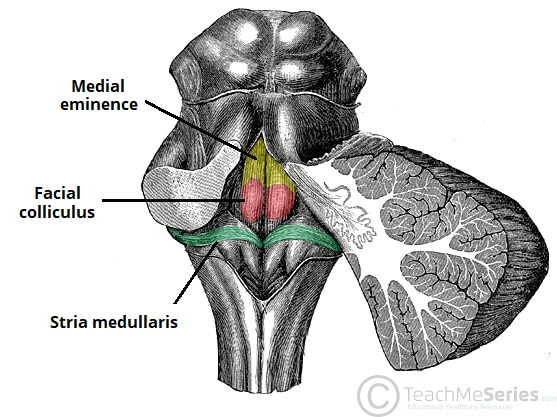 The Pons Function Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
The Pons Function Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
 Pons Anatomy Location Function Anatomy Info
Pons Anatomy Location Function Anatomy Info
 Brain Anatomy Brain Pons Cross Section Stock Photo
Brain Anatomy Brain Pons Cross Section Stock Photo
Brainstem Ii Pons And Cerebellum Part 1
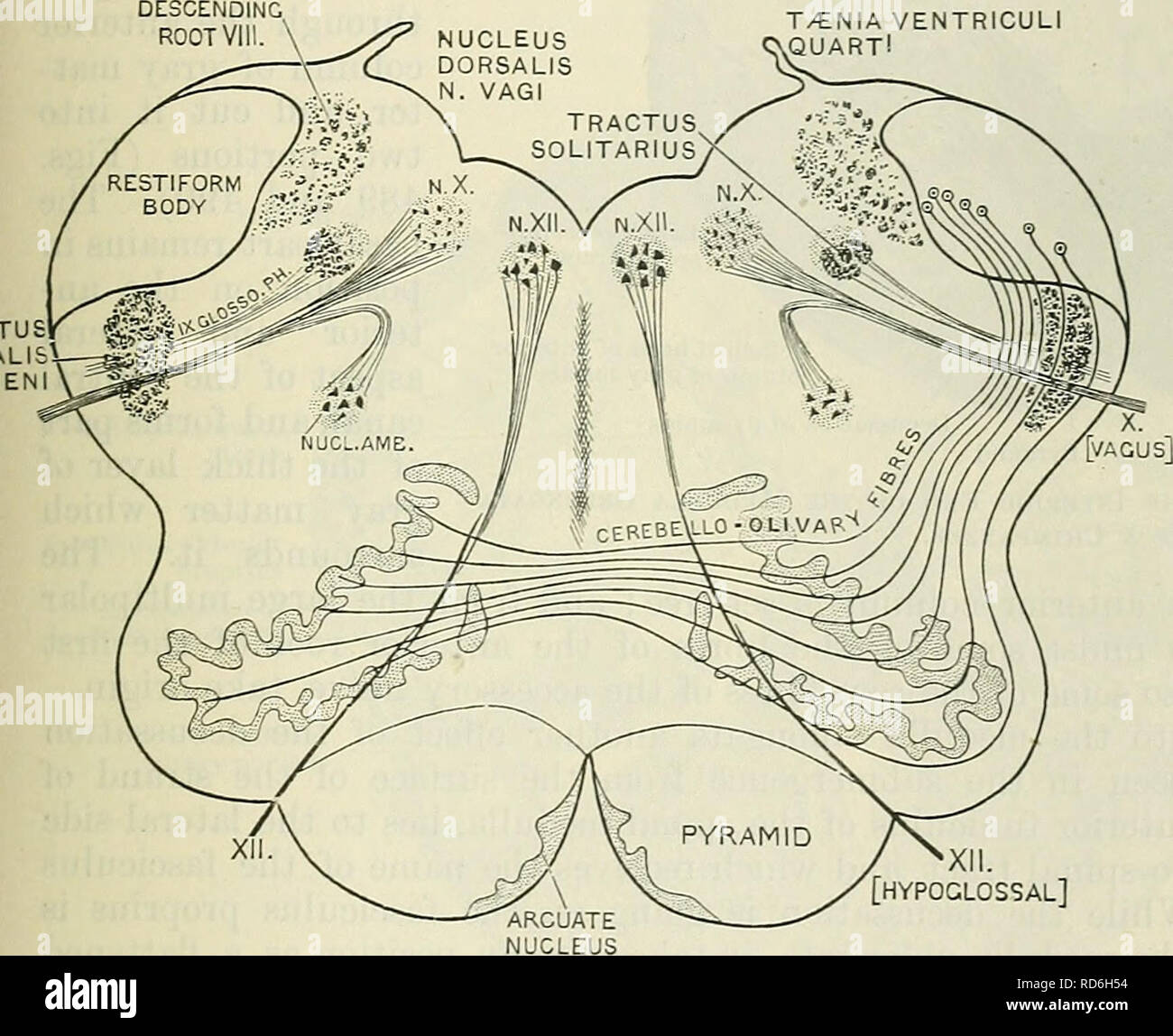 Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Internal
Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Internal
 The Brain Stem Midbrain Pons Medulla Oblongata Ppt
The Brain Stem Midbrain Pons Medulla Oblongata Ppt
 Pons Internal Structure Of Brainstem
Pons Internal Structure Of Brainstem

Virtualmedstudent Com The Pons
Brain Stem Structures Reticular Formation Pattern
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7515/Midbrain_01.png) Midbrain And Pons Anatomy Location Parts Definition Kenhub
Midbrain And Pons Anatomy Location Parts Definition Kenhub
 Pons Medulla Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Pons Medulla Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Know Your Brain Pons Neuroscientifically Challenged
 Parts Of The Brain Stem The Medulla Oblongata And Pons
Parts Of The Brain Stem The Medulla Oblongata And Pons
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/1384/pons_2_large_DgHioI4tVQsDjLdNDKew.png) Midbrain And Pons Anatomy Location Parts Definition Kenhub
Midbrain And Pons Anatomy Location Parts Definition Kenhub
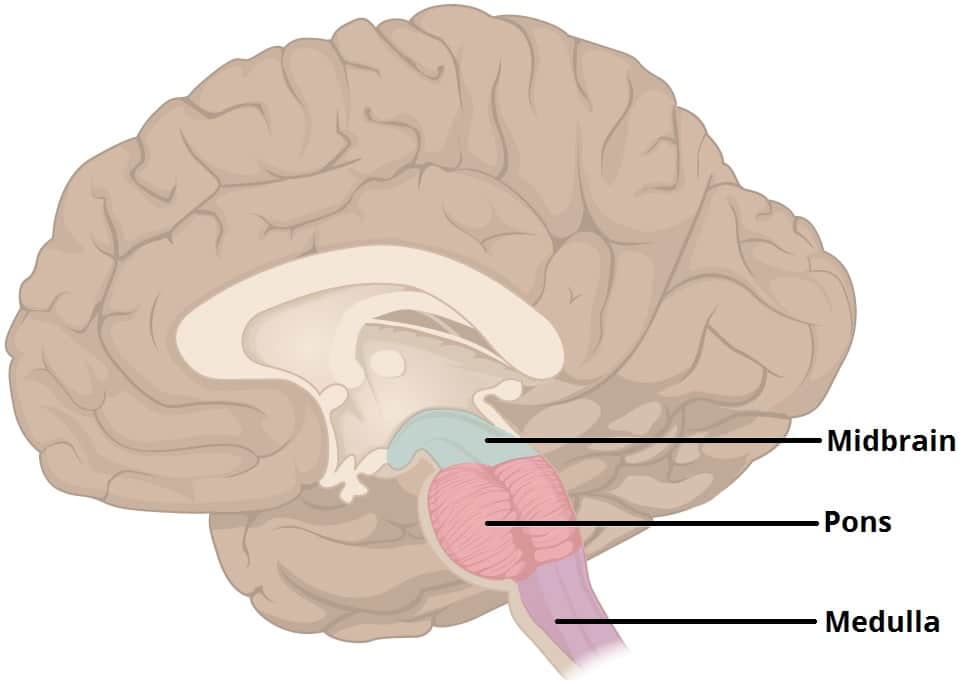 The Pons Function Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
The Pons Function Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
 Image From Page 599 Of Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy
Image From Page 599 Of Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar