Pediatric airways are often challenging due to the size of the patient. The beginning of the respiratory tract the nasal cavity and oropharynx.
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
With a smaller body size comes an increase in the precision needed to successfully maintain airway patency if any injury or insult to the airway occurs.
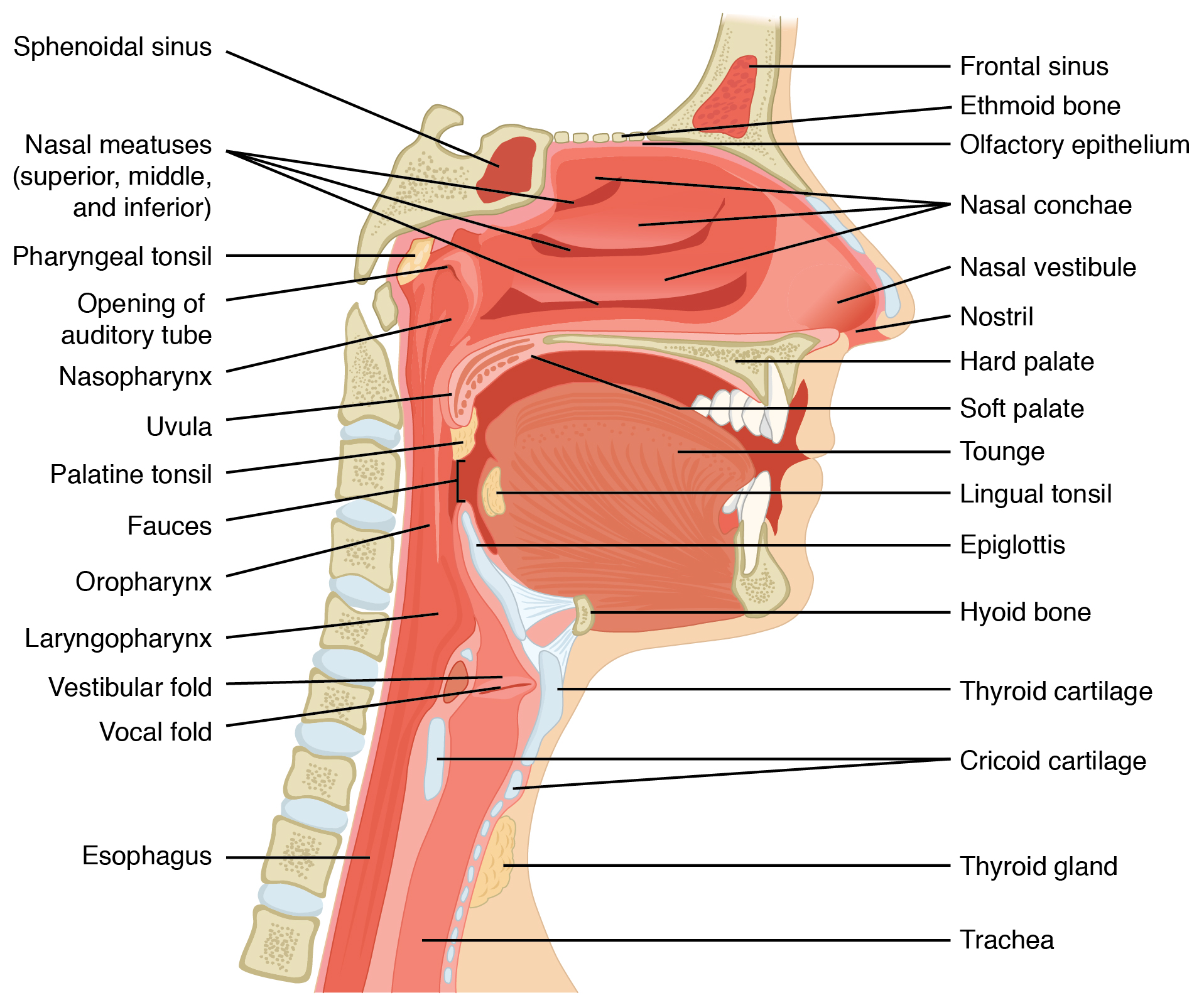
Airways anatomy. The nose is composed of bone and cartilage which are in turn attached to the facial skeleton. The medical terms for these are the nasopharynx and oropharynxlarynx. Upper airway anatomy functions warm filter and humidify air nasal cavity and nasopharynx formed by union of facial bones nasal floor towards ear not eye lined with mucous membranes cilia tissues are delicate vascular adenoids lymph tissue filters bacteria commonly infected.
Oral cavity consists of mouth palate teeth and tongue. Airway anatomy can be divided into the upper airway and the lower airway. The epiglottis is one of the main anatomic landmarks in the.
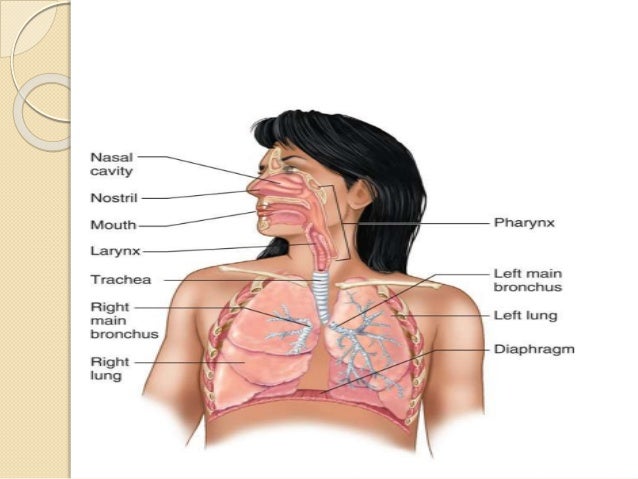
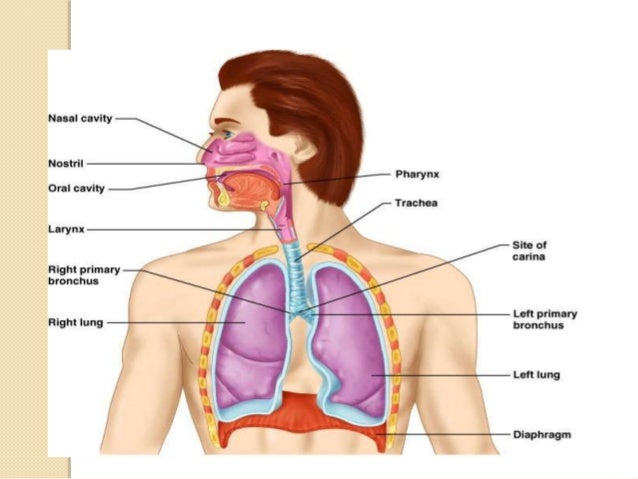
The upper airways or upper respiratory tract includes the nose and nasal passages paranasal sinuses the pharynx and the portion of the larynx above the vocal folds cords. First responders need to be familiar with respiratory system anatomy in order to keep patients healthy breathing and adequately ventilated. The upper airway 211.
The nose originates in the cranial ectoderm and is composed. The anatomy of the upper airway can be broken down into the nose mouth and throat. The upper airway consists of the pharynx and the nasal cavities.
Predictably these differences are most pronounced at birth and the most unfamiliar non adult like airway is encountered in neonates and infants under 1 year of age. Anatomy and physiology ap of the upper airway nasopharynx. The space behind the nostrils the nasopharynx is filled with blood rich tissue covered in mucus which warms and cleans incoming air.
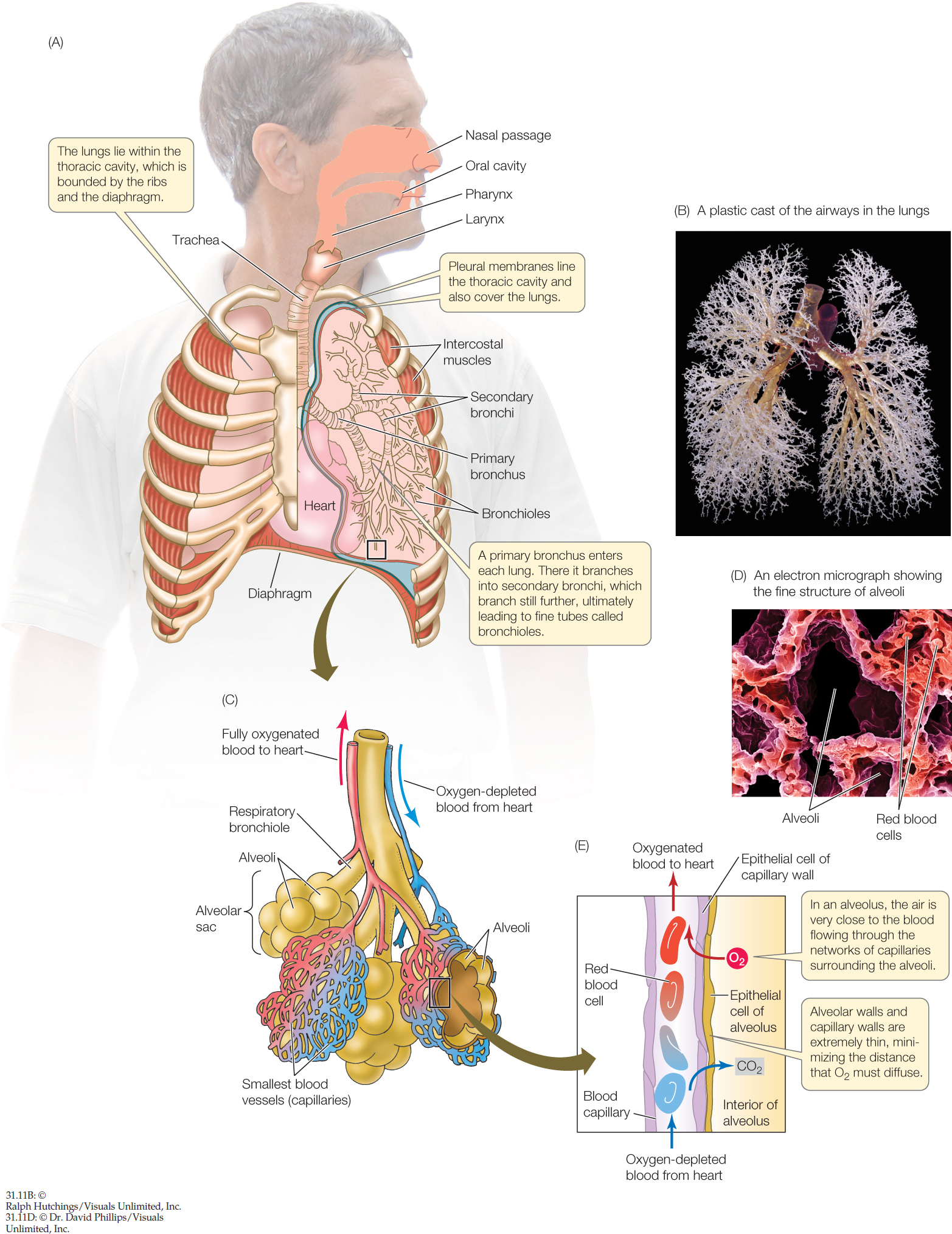
The tracheobronchial airways form. The airway of the pediatric patient differs in many ways which impact the anesthesiologists management of the airway. The pharynx is can be divided into the nasopharynx oropharynx and laryngopharynx.
The teeth are the first obstruction we meet in the oral part of the airway. The lower airways or lower respiratory tract includes the portion of the larynx below the vocal folds trachea bronchi and bronchioles. However some authors include the larynx and trachea as well.
Upper airway anatomy in order to open the paediatric airway and gain the best view of the laryngeal inlet the oral pharyngeal and tracheal axes must be brought into alignment. Below are detailed graphics of both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. The nose is the primary airway used by most conscious adults to breathe.
This requires suitable patient positioning during preparation for intubation and differs based on the age of the child.
 Airway Airway Anatomy Basic Airway Anatomy
Airway Airway Anatomy Basic Airway Anatomy
 Anatomy Of Upper Airway Doctor Stock
Anatomy Of Upper Airway Doctor Stock
Anatomy Of A Child S Lung Pediatric Pulmonologists
 Applied Functional Anatomy Of The Airway Manual Of
Applied Functional Anatomy Of The Airway Manual Of
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12572/anatomy-of-respiratory-system_english.jpg) Respiratory System Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
Respiratory System Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
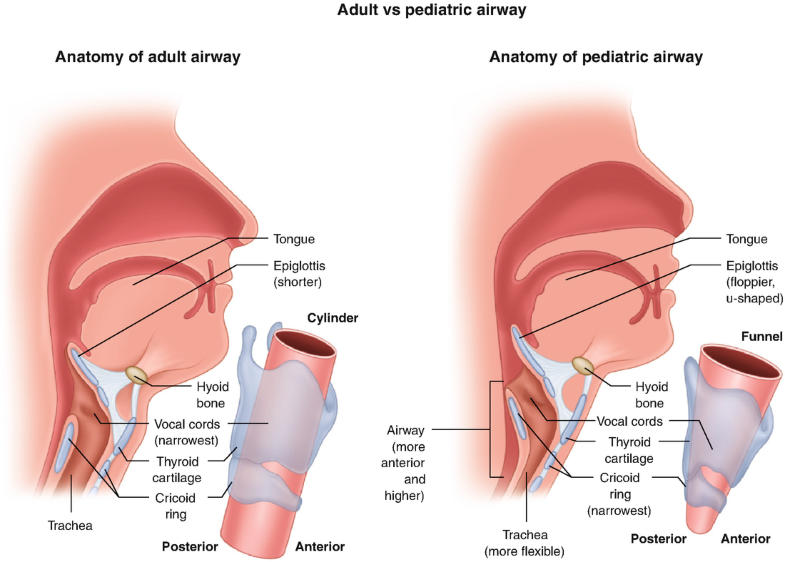 Airway Pediatric Anatomy Infants And Children Springerlink
Airway Pediatric Anatomy Infants And Children Springerlink
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12575/bronchioles-alveoli-anatomy_english.jpg) Respiratory System Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
Respiratory System Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
 Comparative Anatomy Of The Upper Airways In Adults And
Comparative Anatomy Of The Upper Airways In Adults And
 Paediatric Airway Anatomy Paediatric Emergencies
Paediatric Airway Anatomy Paediatric Emergencies
 Airway Anatomy Anatomy Respiratory Therapy Respiratory
Airway Anatomy Anatomy Respiratory Therapy Respiratory
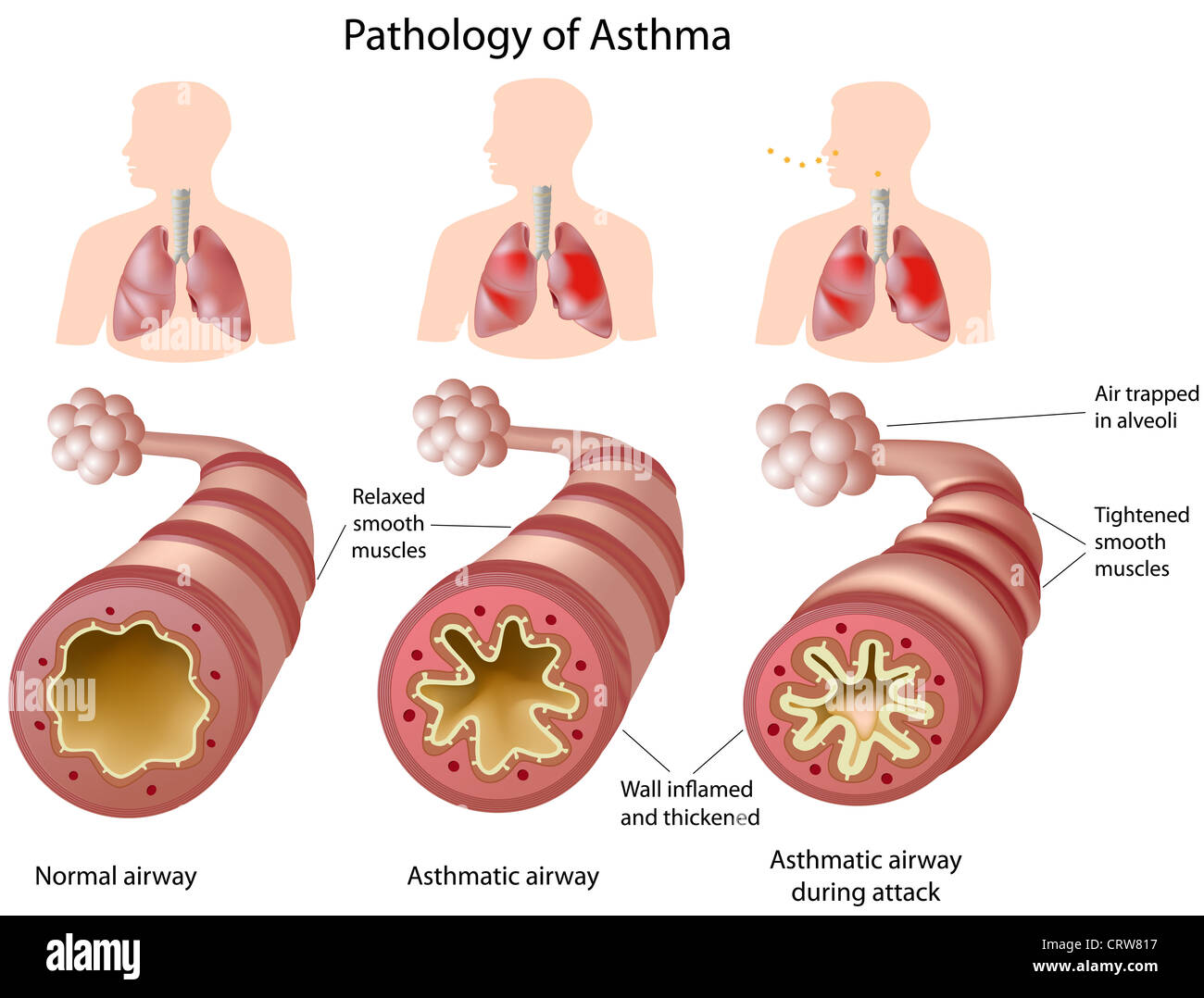 Anatomy Of Asthma Healthy Airways Versus Asthmatic Airways
Anatomy Of Asthma Healthy Airways Versus Asthmatic Airways
 Airway And Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Of The
Airway And Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Of The
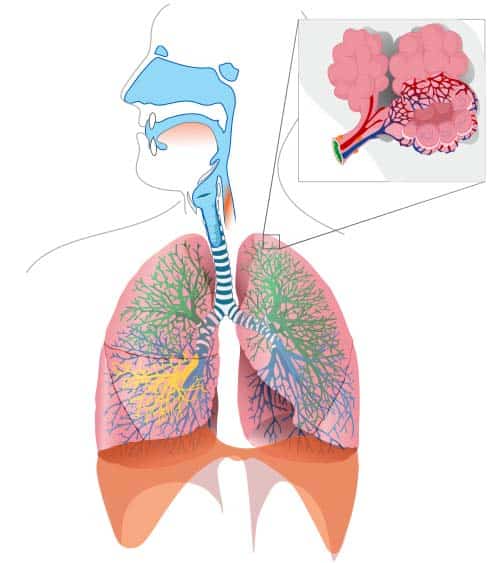 The Tracheobronchial Tree Trachea Bronchi Teachmeanatomy
The Tracheobronchial Tree Trachea Bronchi Teachmeanatomy
 22 1 Organs And Structures Of The Respiratory System
22 1 Organs And Structures Of The Respiratory System
 Anatomy 101 Learning About Airway Walls Asthma Net
Anatomy 101 Learning About Airway Walls Asthma Net
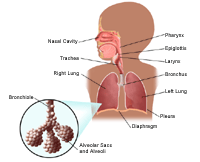 Anatomy Of The Respiratory System In Children
Anatomy Of The Respiratory System In Children
 Respiratory Conditions Lung Disease Professional Medical
Respiratory Conditions Lung Disease Professional Medical
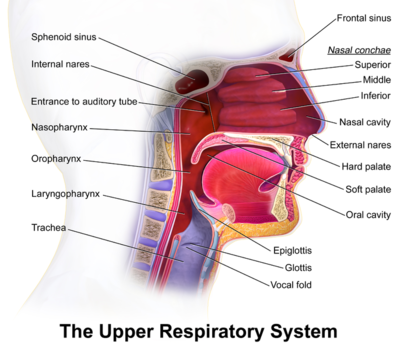 Upper Respiratory Airways Physiopedia
Upper Respiratory Airways Physiopedia
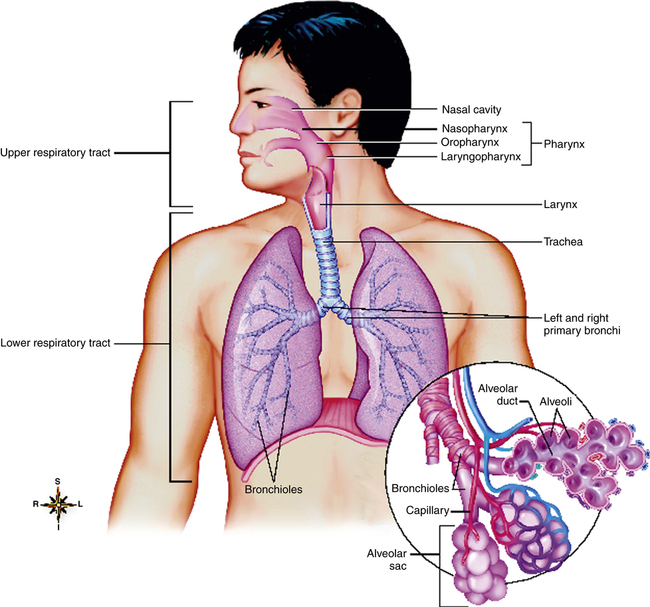 The Airways And Alveoli Clinical Gate
The Airways And Alveoli Clinical Gate
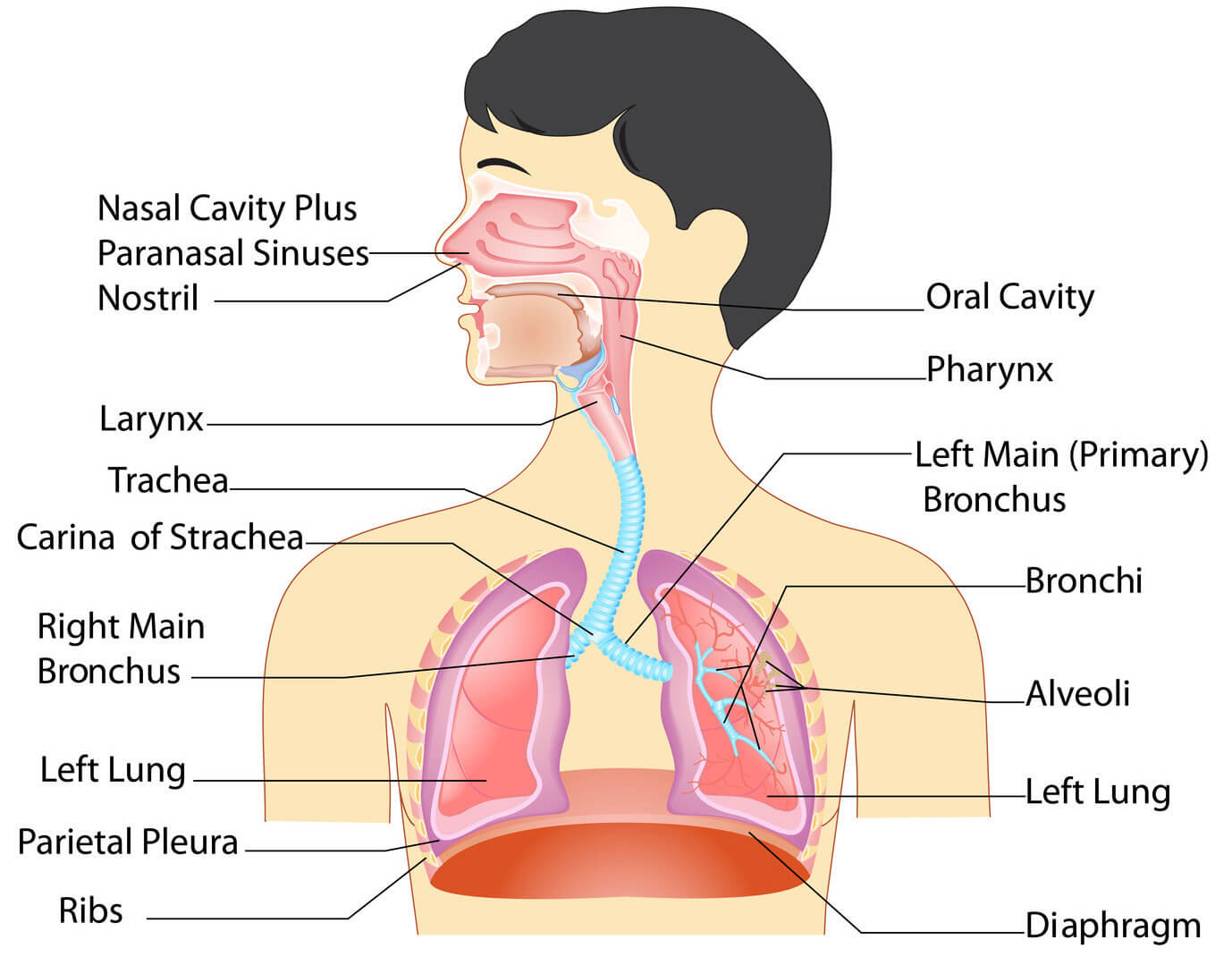 Anatomy Of The Respiratory System
Anatomy Of The Respiratory System
Anatomy Physiology Of The Respiratory System
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
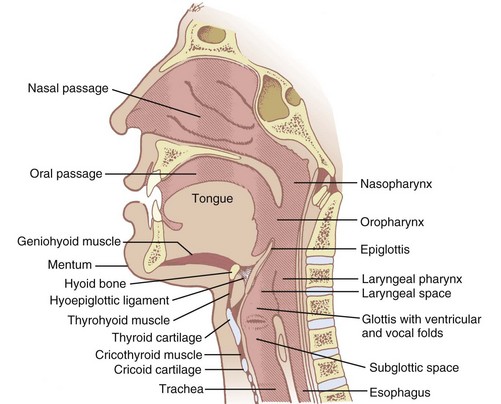 Nonintubation Management Of The Airway Airway Maneuvers And
Nonintubation Management Of The Airway Airway Maneuvers And
 Anatomy Of The Airway Springerlink
Anatomy Of The Airway Springerlink
 Respiratory Epithelium Wikipedia
Respiratory Epithelium Wikipedia
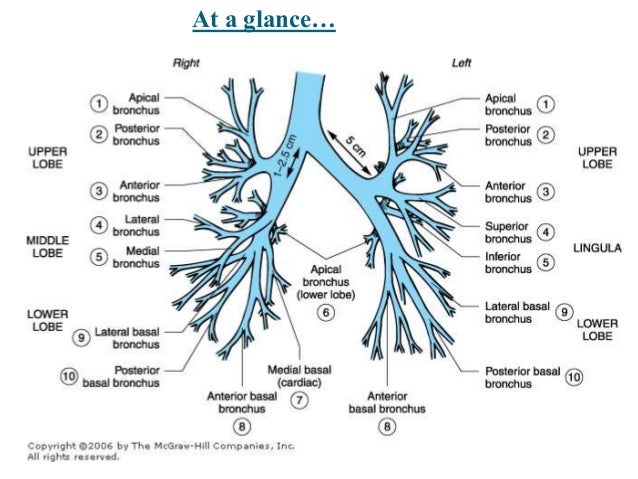


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar