The middle layer is the choroid. The slight bulge in the sclera at the front of the eye is a clear thin dome shaped tissue called the cornea.
Eye Anatomy And How The Eye Works
The macula is a small extra sensitive area in the retina that gives you central vision.
Anatomy of eye and functions. Light is focused primarily by the cornea the clear front surface of the eye which acts like a camera lens. Ciliary body structure containing muscle and is located behind the iris which focuses the lens. The front of the choroid is the colored part of the eye called the iris.
The outer layer of the eyeball is a tough white opaque membrane called the sclera the white of the eye. The iris or coloured part of the eye surrounds the pupil. The cornea is the transparent clear layer at the front and.
Anatomy and physiology of the eye conjunctiva. Cornea the clear front window of the eye which transmits and focuses ie. Behind the eye your optic nerve carries these impulses to the brain.
Eye color is created by the amount and type of pigment in your iris. Cornea the cornea is the outer covering of the eye. The nerve at the back of the eye that transports electric signals to the brain.
The eye has many parts which work together to accomplish vision and to keep the structures required for vision safe from infection and injury. The white part of the eye that one sees when looking at oneself in the mirror is. There are several layers of the cornea creating a tough layer that provides additional protection.
This dome shaped layer protects your eye from elements that could cause damage to the inner parts of the eye. Parts of the eye and their functions. The pupil or black dot at the centre of the eye is an opening through which light can enter.
The surface of the eye and of the inner eyelids is covered by a clear protective membrane called the conjunctiva. Eye parts and functions. The sclera or white part of the eye protects the eyeball.
Anatomy of the eye choroid layer containing blood vessels that lines the back of the eye and is located between. The conjunctiva is a thin transparent layer of tissues covering the front of the eye. The iris of the eye functions like the diaphragm of a camera controlling the amount of light reaching the back of the eye by automatically adjusting the size of the pupil aperture.
Multiple genes inherited from each parent determine a persons eye color. Light enters through the cornea past the iris through the pupil refracted by the lens and onto the retina of the eye. Light path through the eye.
The eye has many parts that must work together to produce clear vision. The transparent orb within the eye that refracts light to the retina of the eye.
 Eye Structure And Function In Dogs Dog Owners Merck
Eye Structure And Function In Dogs Dog Owners Merck
 Anatomy Of The Eye American Association For Pediatric
Anatomy Of The Eye American Association For Pediatric
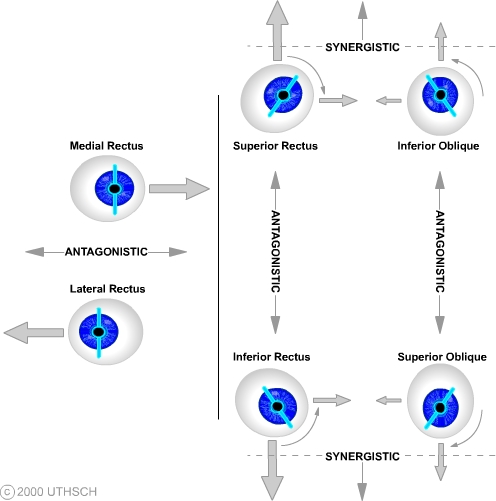 Ocular Motor Control Section 3 Chapter 8 Neuroscience
Ocular Motor Control Section 3 Chapter 8 Neuroscience
Eye Health Anatomy Of The Eye Visionaware
 Anatomy And Structure Of The Eye Brightfocus Foundation
Anatomy And Structure Of The Eye Brightfocus Foundation
 Functions And Anatomy Of The Eye
Functions And Anatomy Of The Eye
 Human Eye Anatomy And Functions Diagram Eye Anatomy
Human Eye Anatomy And Functions Diagram Eye Anatomy
 Parts Of The Eye And Their Functions Video Lesson
Parts Of The Eye And Their Functions Video Lesson
 Structure And Function Of The Eyes Eye Disorders Merck
Structure And Function Of The Eyes Eye Disorders Merck
Ocular Anatomy And Function Lab 2 7 Eye Lab Flashcards
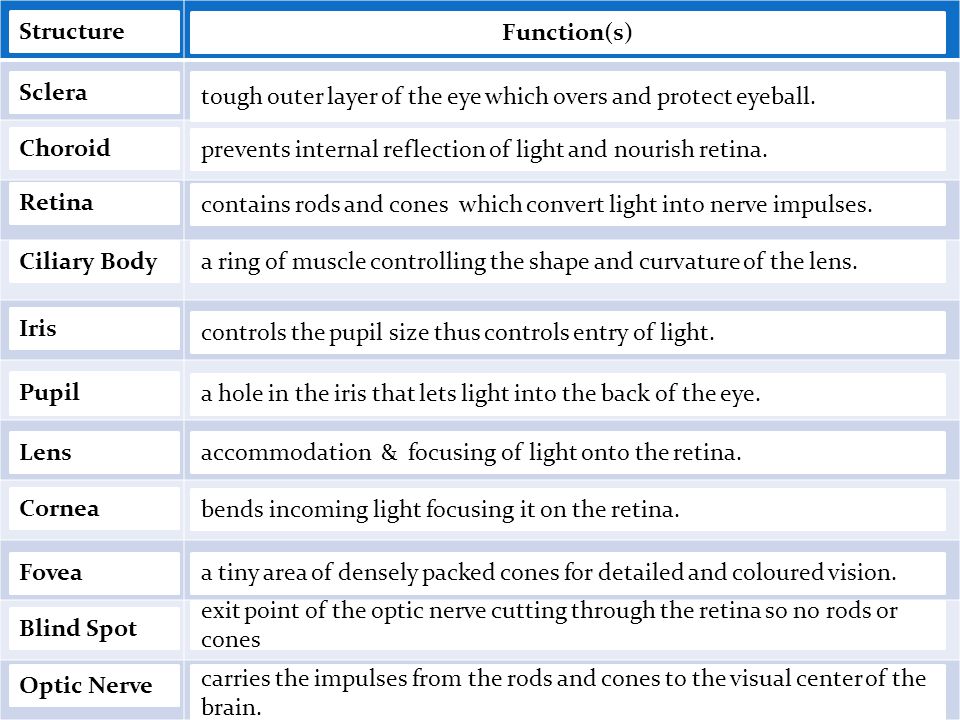 The Eye Structure Function Ppt Video Online Download
The Eye Structure Function Ppt Video Online Download
 Anatomy Of The Eye Human Eye Anatomy Owlcation
Anatomy Of The Eye Human Eye Anatomy Owlcation
![]() Review Your Eye Anatomy In Order To Understand Eye Disease
Review Your Eye Anatomy In Order To Understand Eye Disease
 Eye Anatomy Structure Function Of Vision Hs Ls1 A
Eye Anatomy Structure Function Of Vision Hs Ls1 A
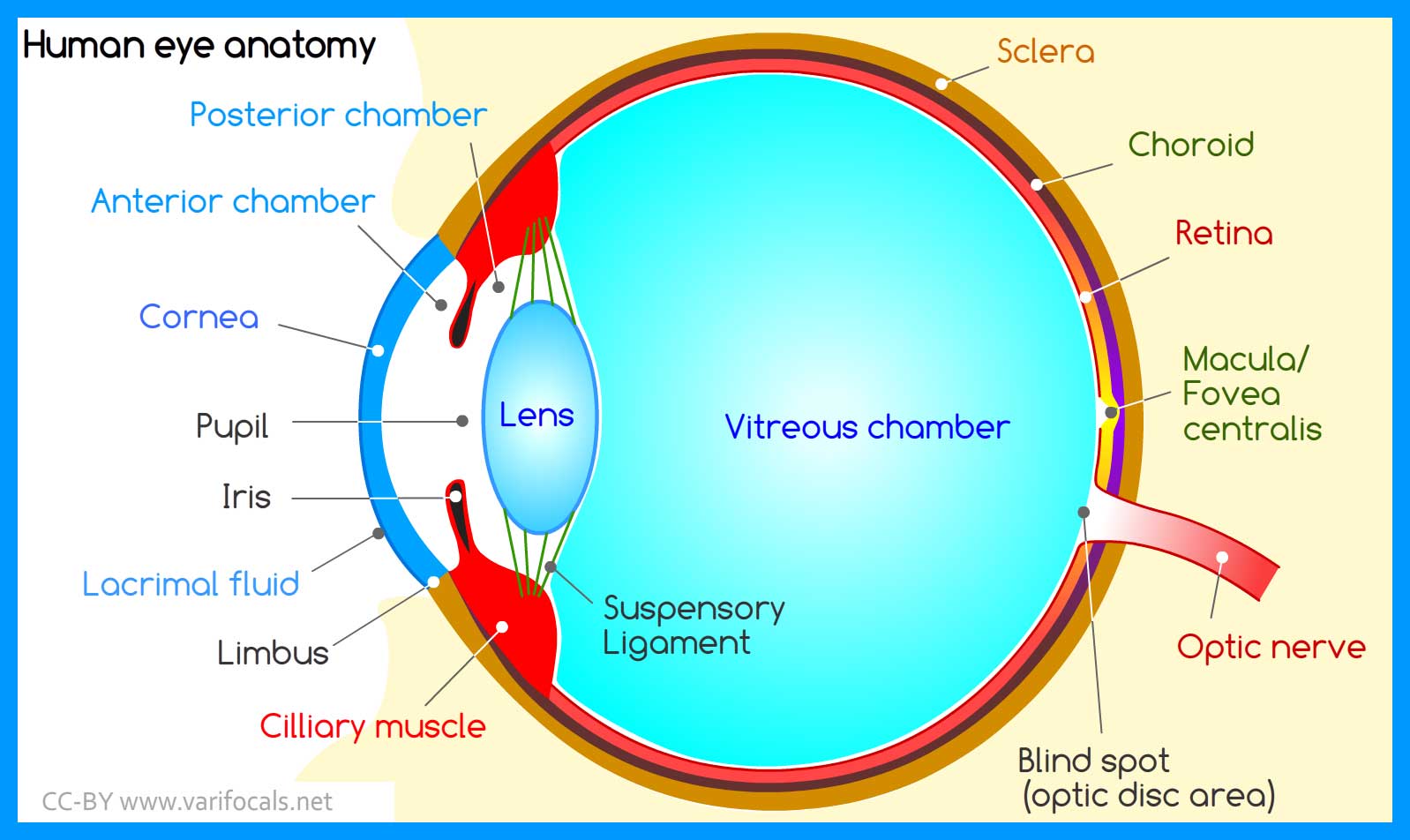 Human Eye Anatomy Structure And Function
Human Eye Anatomy Structure And Function
Basic Eye Anatomy Cataract Surgery Information
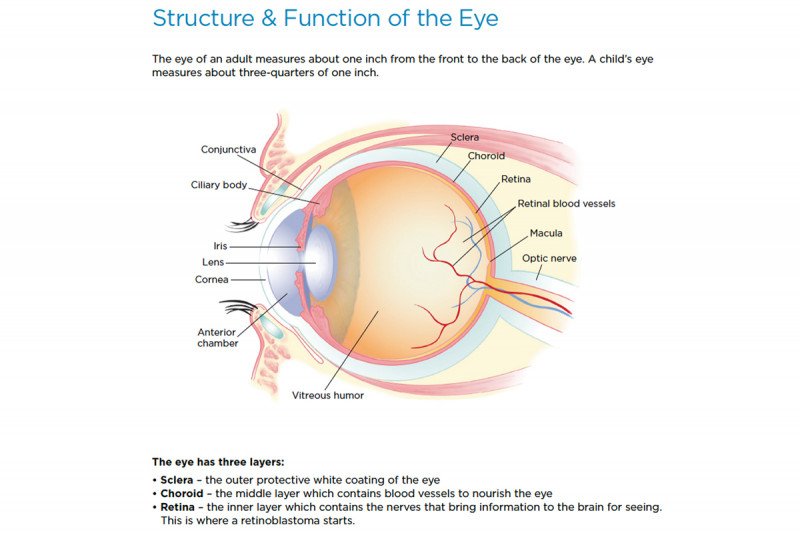 Retinoblastoma Anatomy Of The Eye Memorial Sloan
Retinoblastoma Anatomy Of The Eye Memorial Sloan
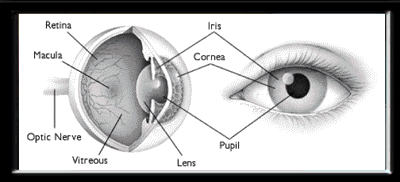 Anatomy Of The Eye The Ottawa Hospital
Anatomy Of The Eye The Ottawa Hospital
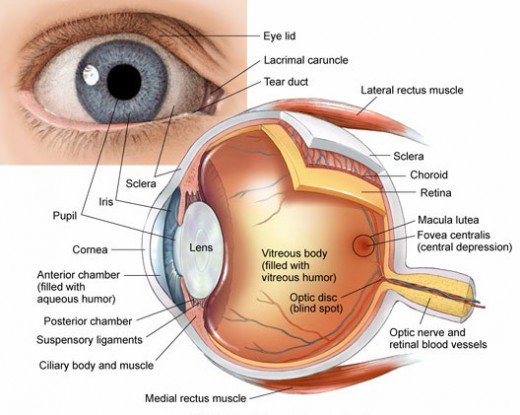 Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes
Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes
 Stuart R Winthrop M D Eye Anatomy And Function
Stuart R Winthrop M D Eye Anatomy And Function

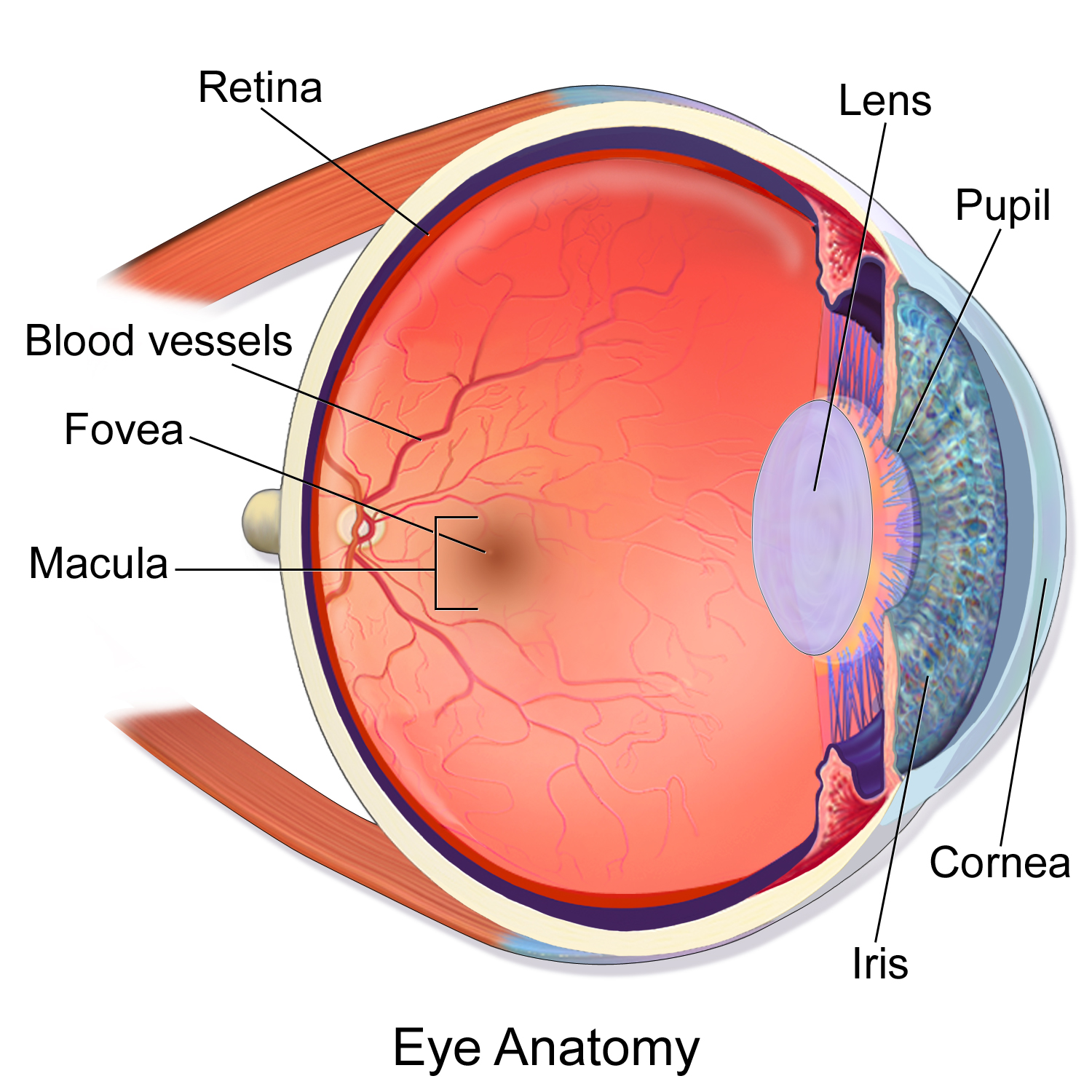


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar