Considered part of lower thoracic esophagus. Gross anatomy relationships of the esophagus.

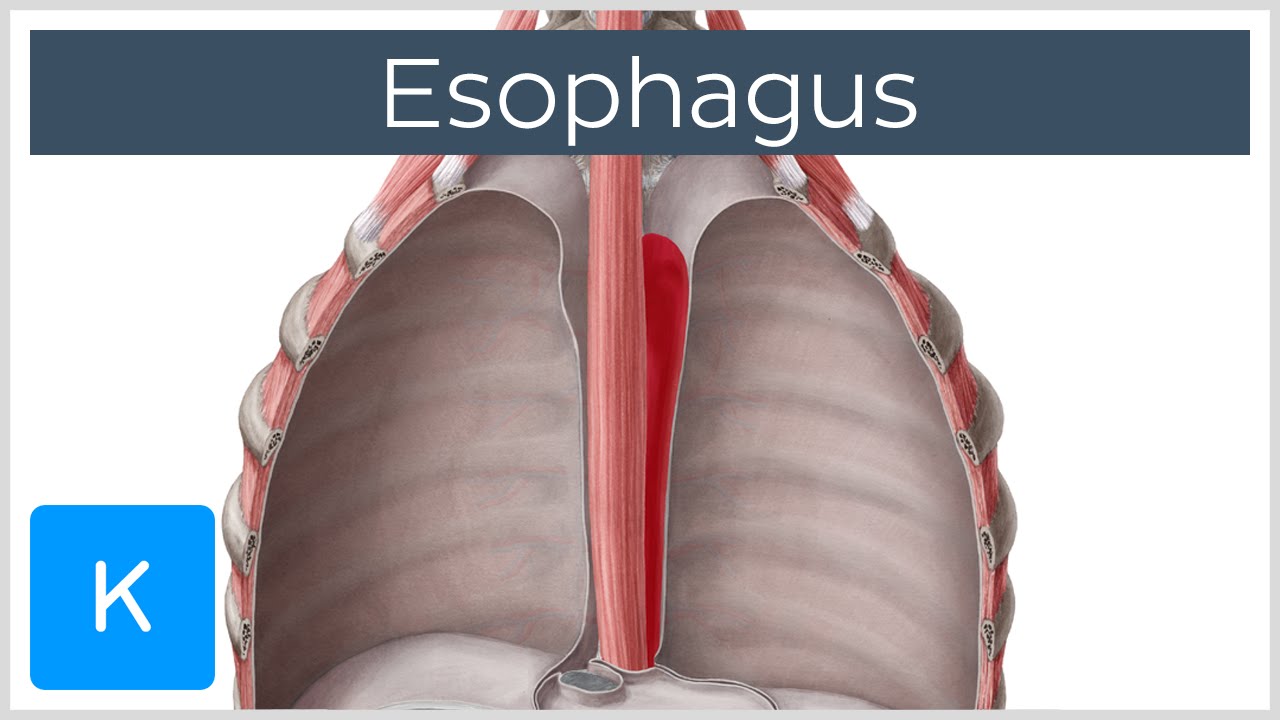
Anatomically it lies behind the trachea and heart and in front of the spinal column.

Esophagus anatomy. The esophagus has 2 types of lymphatic vessels. At the start of the esophagus where the laryngopharynx joins the esophagus. Sub site description 1 cervical.
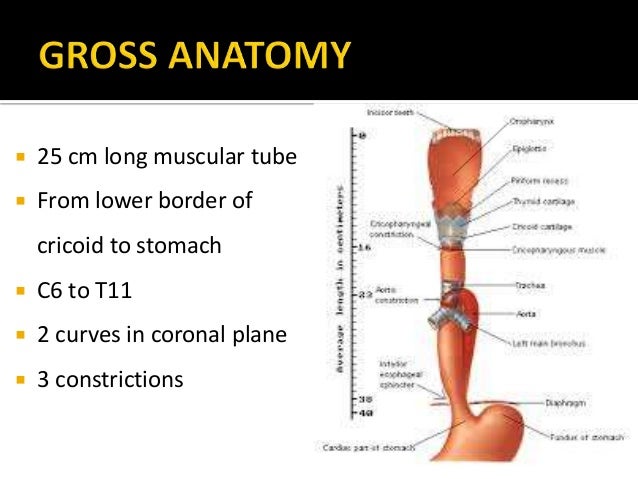
It originates at the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage c6 extending to the cardiac orifice of the stomach t11. It passes through the muscular diaphragm before entering the stomach. The esophagus is a muscular tube connecting the throat pharynx with the stomach.
The trachea lies anterior to the esophagus. The esophagus is about 8 inches long and is lined by moist pink tissue called mucosa. The esophagus can contract or expand to allow for the passage of food.
The esophagus is a muscular tube that conveys food and fluids from the pharynx to the stomach. From thoracic inlet to level of tracheal bifurcation. Esophagus also spelled oesophagus relatively straight muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach.
Where the esophagus is compressed by the left main bronchus in the posterior mediastinum. Where it is crossed on the front by the aortic arch in the superior mediastinum. Cervical begins at the lower end of pharynx.
The esophagus is a long thin and muscular tube that connects the pharynx throat to the stomach. Just before entering the stomach the esophagus passes through the diaphragm. The esophagus runs behind the windpipe trachea and heart and in front of the spine.
Venous blood from the esophagus drains into a submucosal plexus. The esophagus is a hollow muscular tube that transports saliva liquids and foods from the mouth to the stomach. In this article we shall examine the anatomy of the oesophagus its structure.
It forms an important piece of the gastrointestinal tract and functions as the conduit for food and liquids that have been swallowed into the pharynx to reach the stomach. The esophagus is a long fibromuscular tube that runs in the thoracic cavity and connects the pharynx with the stomach. The oesophagus is a fibromuscular tube approximately 25cm in length that transports food from the pharynx to the stomach.
This article will highlight the main anatomical features of the esophagus including its constrictions and sphincters its histological layers and the main pathological changes that may ail this particular organ.
 Figure 7 Esophagus Anatomy And Development Gi Motility
Figure 7 Esophagus Anatomy And Development Gi Motility
 Anatomy Of Cervical Esophageal Cancer
Anatomy Of Cervical Esophageal Cancer
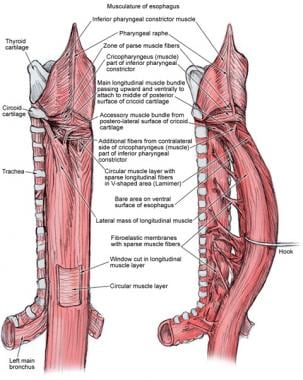 Esophagus Anatomy Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy
Esophagus Anatomy Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy
 Figure 9 Esophagus Anatomy And Development Gi Motility
Figure 9 Esophagus Anatomy And Development Gi Motility
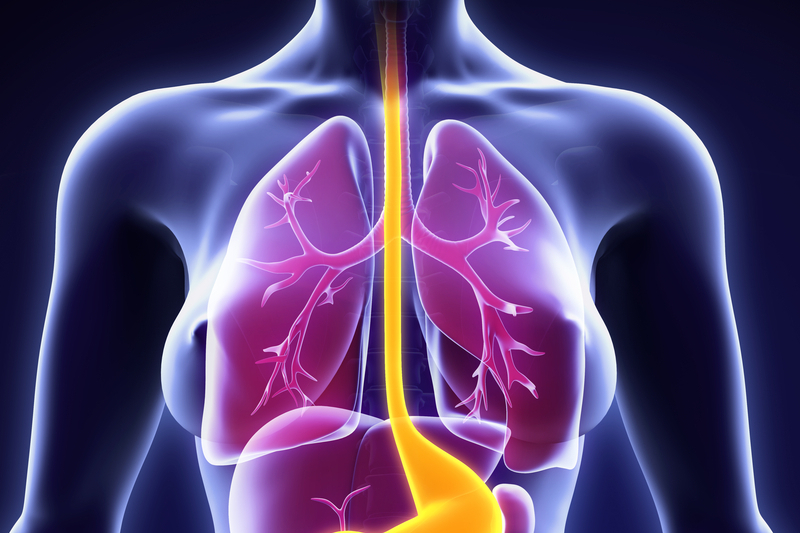 Esophagus Facts Functions Diseases Live Science
Esophagus Facts Functions Diseases Live Science
 Surgical Anatomy Of Esophagus Semantic Scholar
Surgical Anatomy Of Esophagus Semantic Scholar
 Throat Esophagus Anatomy Album On Imgur
Throat Esophagus Anatomy Album On Imgur
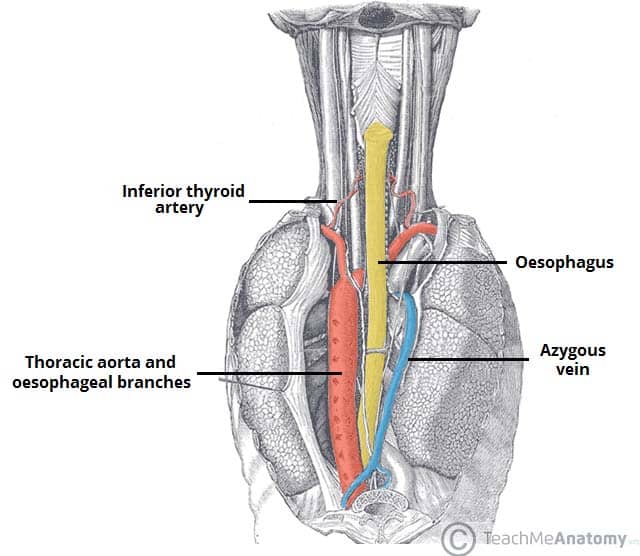 The Oesophagus Location Sphincters Teachmeanatomy
The Oesophagus Location Sphincters Teachmeanatomy
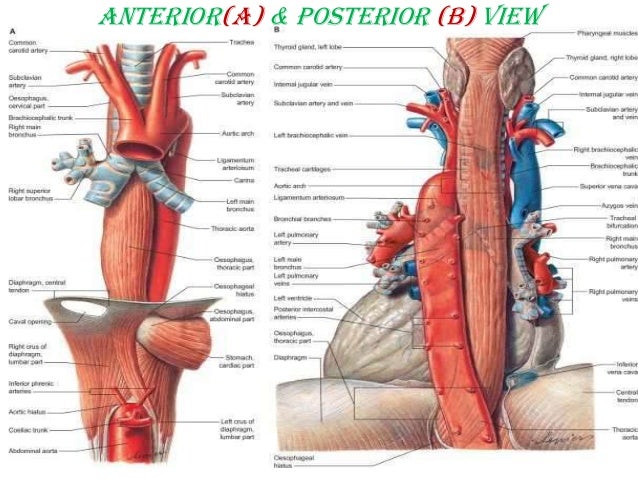 Anatomy Of Esophagus Dr Neeraj Kumar Banoria
Anatomy Of Esophagus Dr Neeraj Kumar Banoria
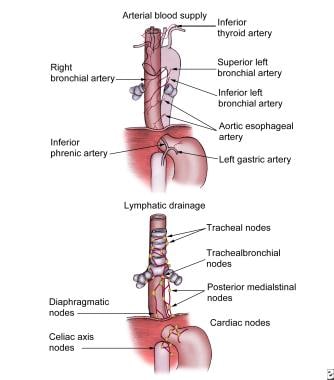 How Is Blood Supplied To The Esophagus In The Anatomy Of
How Is Blood Supplied To The Esophagus In The Anatomy Of
 Anatomy Of The Esophagus Bucher Illustration
Anatomy Of The Esophagus Bucher Illustration
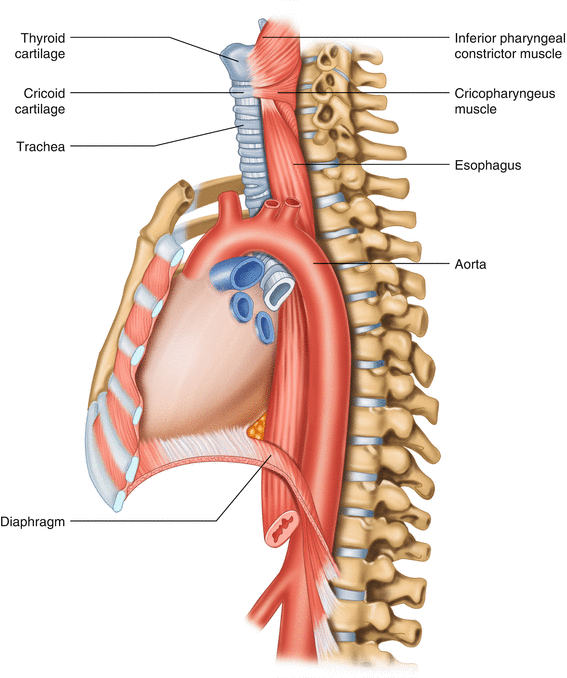 Surgical Anatomy Of The Esophagus And Esophagogastric
Surgical Anatomy Of The Esophagus And Esophagogastric
Esophageal Disease Surgery Specialists In General Surgery
 Esophagus Blood Supply Cervical Esophagus Anatomy Gallery
Esophagus Blood Supply Cervical Esophagus Anatomy Gallery
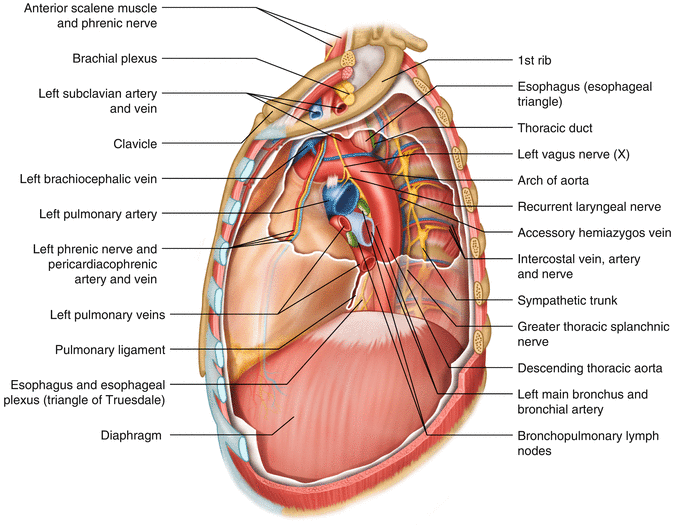 Surgical Anatomy Of The Esophagus And Esophagogastric
Surgical Anatomy Of The Esophagus And Esophagogastric
 Poses For The Throat Chakra Prajna Yoga
Poses For The Throat Chakra Prajna Yoga
 What Are Esophagus And Trachea Why Are They Located Close
What Are Esophagus And Trachea Why Are They Located Close
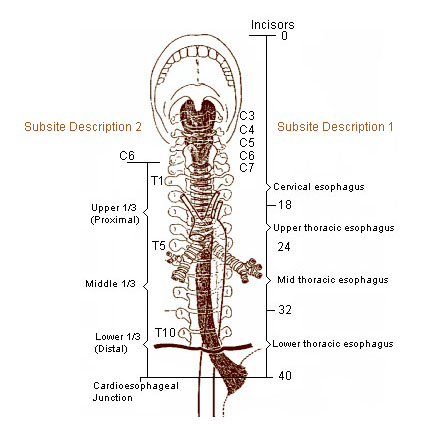 Seer Training Anatomy Of The Esophagus
Seer Training Anatomy Of The Esophagus
 Esophagus Definition Function And Structure Human Anatomy Kenhub
Esophagus Definition Function And Structure Human Anatomy Kenhub
 Anatomy Of Cervical Esophageal Cancer
Anatomy Of Cervical Esophageal Cancer
 Esophagus Anatomy Google Search Gross Anatomy
Esophagus Anatomy Google Search Gross Anatomy
 Esophagus Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Esophagus Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar