The perineum below the pelvic floor. There are four articulations within the pelvis.
 3b Scientific H20 3 Female Pelvis W Ligaments 4 Part 3b Smart Anatomy
3b Scientific H20 3 Female Pelvis W Ligaments 4 Part 3b Smart Anatomy
This joint and its ability to rotate in many angles is one of many pieces of anatomy that allows humans to walk.
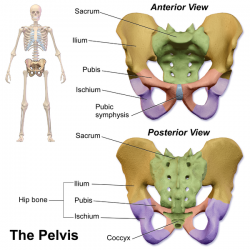
Anatomy of the pelvis. Pubic symphysis between the pubis bodies of the two hip bones. The pelvis is the lower part of the torso. The pelvis is formed by four bones which include a pair of hip bones otherwise known as innominate bones.
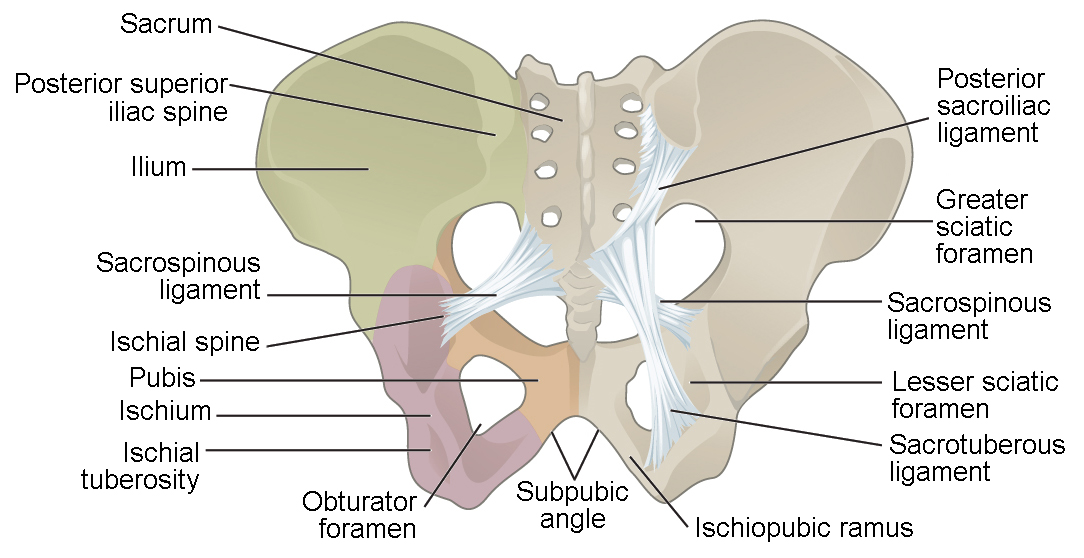
The pelviss frame is made up of the bones of the pelvis which connect the axial skeleton to the femurs and therefore acts in weight bearing of the upper body. The two main ligaments of the pelvis are the sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The sacrum and two innominate bones.
The male urethra and the penis the male urethra is a muscular tube that runs through the prostate perineal membrane. Anatomy of bony pelvis the pelvis is a ring structure made up of three bones. The hip joint is a ball and socket joint created by the femur and a part of the pelvis called the acetabulum.
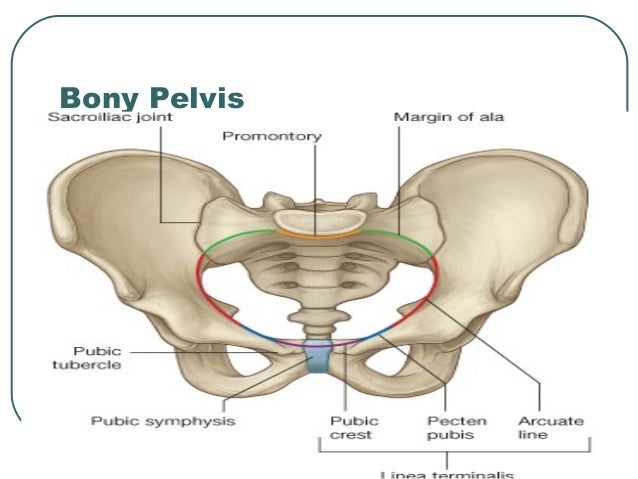
The three bones and three joints composing the pelvic ring have no inherent stability without vital ligamentous structures. Its located between the abdomen and the legs. Each hip bone in turn is firmly joined to the axial skeleton via its attachment to the sacrum of the vertebral column.
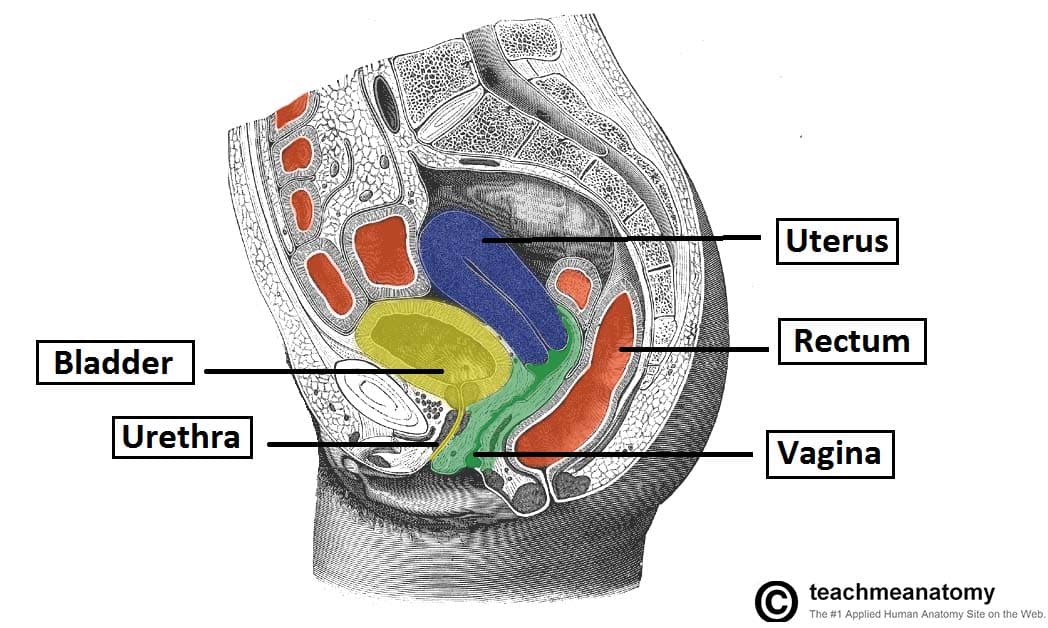
Structure the pelvic cavity typically defined as a small part of the space enclosed by the bony pelvis. They also include the vagina which is the entryway to the uterus. The testicles and scrotum are also important male structures.
The pelvic girdle hip girdle is formed by a single bone the hip bone or coxal bone coxal hip which serves as the attachment point for each lower limb. These foramina are created by the positioning of bony. Sacroiliac joints x2 between the ilium of the hip bones and the sacrum.
The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm below the pelvic cavity. Sacrococcygeal symphysis between the sacrum and the coccyx. The anatomy of the female pelvis by david terfera shereen jegtvig the female pelvic organs include the egg producing ovaries and the uterine tubes that carry the eggs into the uterus for potential fertilization by male sperm.
The anatomy of the pelvis varies depending on whether you are male or female. The external male genitals include the penis scrotum and testicles. The pelvis is the lower portion of the trunk located between the abdomen and the lower limbs.
The male pelvic organs include the penis and various glands and ducts. This area provides support for the intestines and also contains the bladder and reproductive organs.
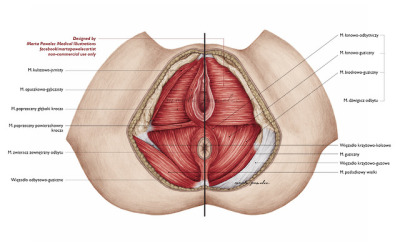
 The Ureters Anatomical Course Neurovascular Supply
The Ureters Anatomical Course Neurovascular Supply
Pelvic Floor Anatomy Beyond Basics Physical Therapy New
 Anatomy Specific Parts Of The Os Coxae Pelvis Left Vs Right
Anatomy Specific Parts Of The Os Coxae Pelvis Left Vs Right
 Anatomy The Pelvic Floor Pittsburgh Pelvic Health
Anatomy The Pelvic Floor Pittsburgh Pelvic Health
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11894/female-pelvic-viscera-and-perineum_english.jpg) Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
 Anatomy Of Human Pelvic Bone Greeting Card By Stocktrekimages
Anatomy Of Human Pelvic Bone Greeting Card By Stocktrekimages
 Pelvis Definition Anatomy Diagram Facts Britannica
Pelvis Definition Anatomy Diagram Facts Britannica
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11895/male-pelvic-viscera-and-perineum_english.jpg) Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
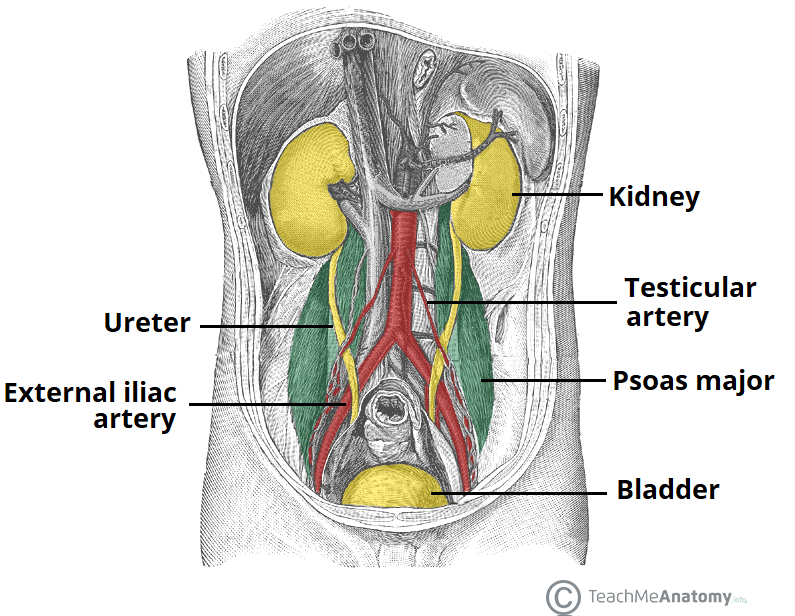
 Bony Pelvis Anatomy Bone And Spine
Bony Pelvis Anatomy Bone And Spine
 Hypertonic Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Vaginismus The
Hypertonic Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Vaginismus The
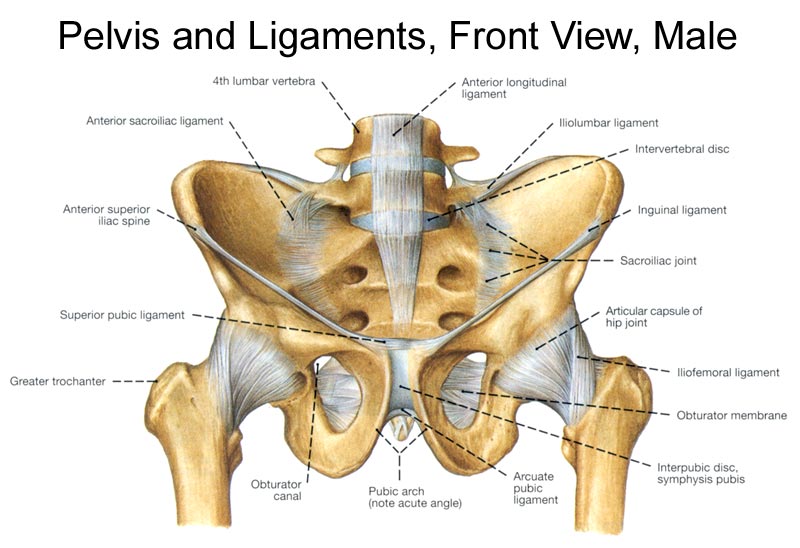
 The Pelvic Girdle And Pelvis Anatomy And Physiology I
The Pelvic Girdle And Pelvis Anatomy And Physiology I
 Pelvic Floor Anatomy Physiopedia
Pelvic Floor Anatomy Physiopedia
Pelvic Floor Anatomy Beyond Basics Physical Therapy New
Pelvis Anatomy Pelvis Anatomy Flashcards Memorang
 A Anatomy 1 Bony Pelvis Anatomy Pelvic Fracture And
A Anatomy 1 Bony Pelvis Anatomy Pelvic Fracture And
 Hip Anatomy Pelvis Diagram Quizlet
Hip Anatomy Pelvis Diagram Quizlet
 Pubic Bone Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Pubic Bone Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Anatomy Pelvis And Thorax Medical Vector Illustration On White
Anatomy Pelvis And Thorax Medical Vector Illustration On White
 Anatomy Of The Male And Female Pelvis Comprehensive
Anatomy Of The Male And Female Pelvis Comprehensive
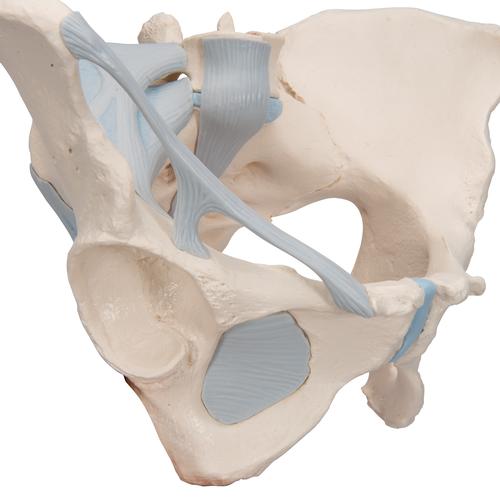 Female Pelvis Skeleton Model With Ligaments 3 Part 3b Smart Anatomy
Female Pelvis Skeleton Model With Ligaments 3 Part 3b Smart Anatomy




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar