43 of 1168 words 2 images. Whereas an agonist causes an action an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist and an.
 Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Online Student
Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Online Student
It be an or a particular receptor promoting a receptor mediated biological response by competing substance or substance at receptor.
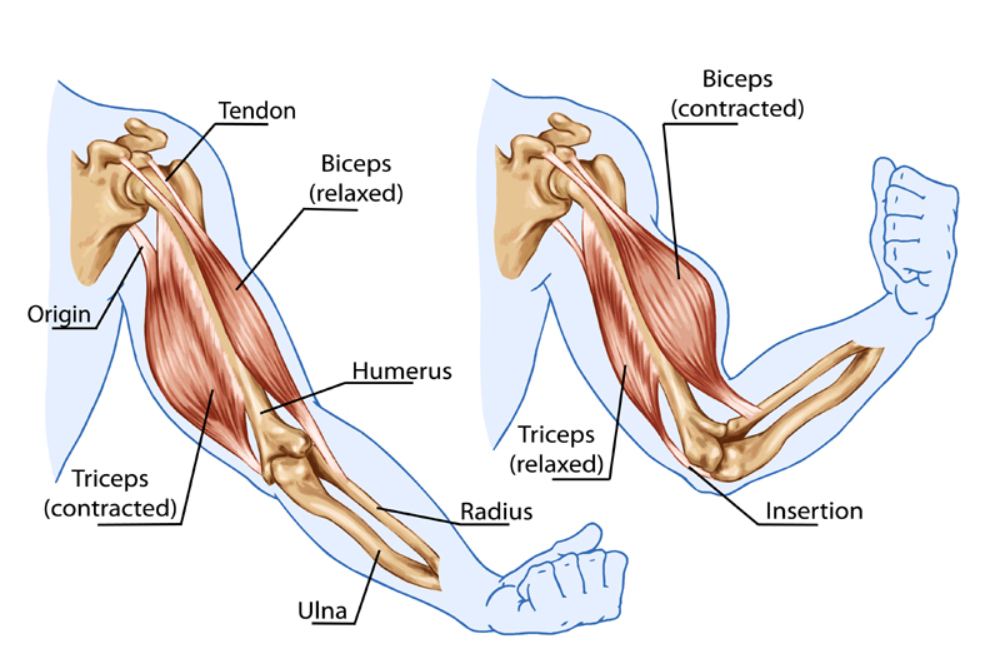
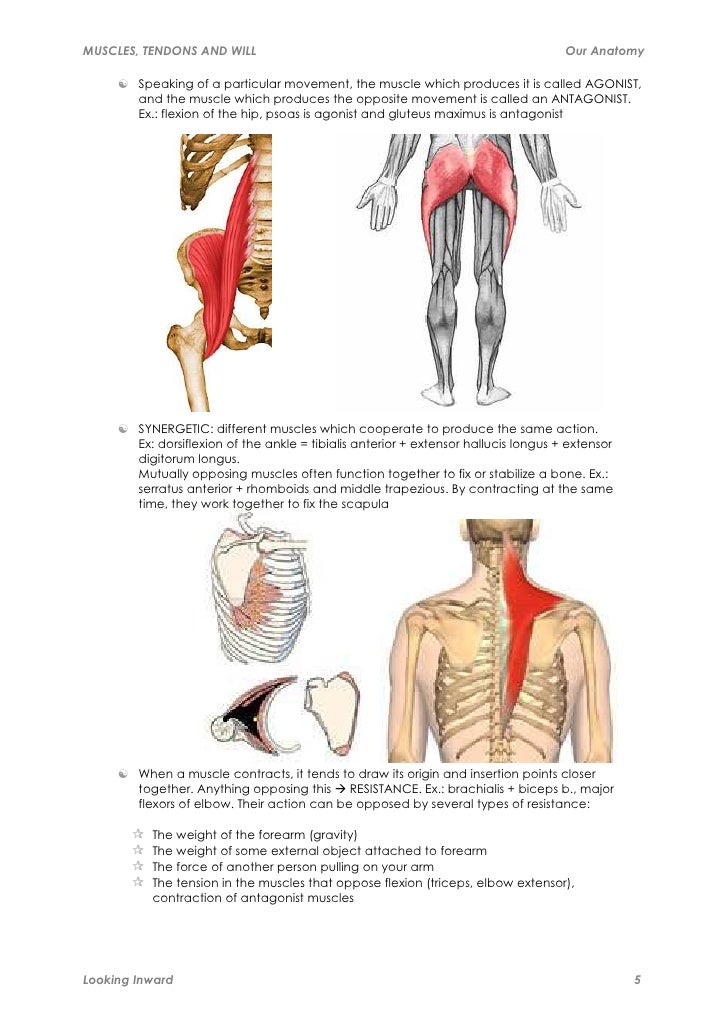
Agonist anatomy. Anatomy a a particular movement to a of movement in a by contracting. The biceps brachii is an agonist for elbow flexion. The agonist muscle group is also referred to as the prime mover because it is the muscle group that provides the main pull to create a movement.
Agonists and antagonists. Stabilizer fixator and neutralizer. A schematic of the classes of sensory receptors.
The moveable end of the muscle that attaches to the bone being pulled is called the muscles insertion and the end of the muscle attached to a fixed stabilized bone is called the origin. Sensory receptor cells differ in terms of morphology location and stimulus. A chemical that binds to some receptor of a cell and triggers a response by that cell.
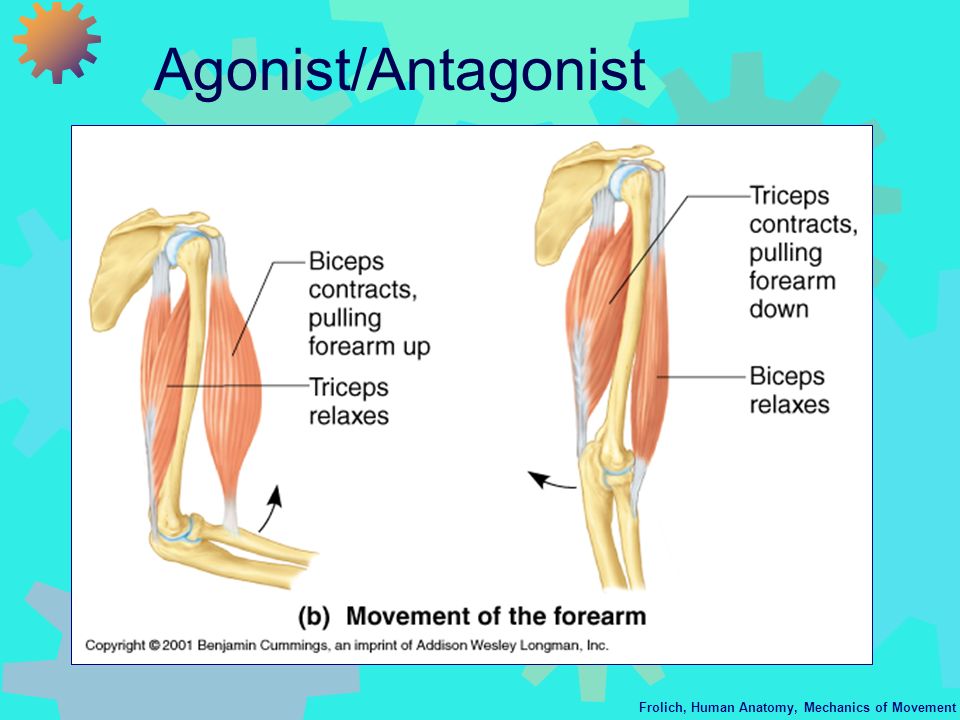
Agonist muscles and antagonist muscles refer to muscles that cause or inhibit a movement. It is the group of muscles that contract to move a. In the bicep curl which produces flexion at the elbow the biceps muscle is the agonist as seen in the image below.
Agonists often mimic the action of a naturally occurring substance. Although a number of muscles may be involved in an action the principal muscle involved is called the prime mover or agonist. Prime moverstr the muscles that are asist the prime mover or agonist.
The muscle that has the opposite action of prime mover and syn supraspinatusinfraspinatusteres minor and subscapularis is s agonist the primary muscle that involve in any action. All sensory receptors rely on one of these four capacities to detect changes in the environment but may be tuned to detect specific characteristics of each to perform a specific sensory function. For example the triceps brachii contracts producing a shortening contraction during the up phase of a push up elbow extension.
These are the agonists of elbow flexion all of which are capable of flexing the elbow joint to some extent. Agonist muscles cause a movement to occur through their own activation. The agonist in a movement is the muscle s that provides the major force to complete the movement.
Hip flexion keeps the upper body from falling backwards when standing erect. Because of this agonists are known as the prime movers. The primary muscle that involve in any action.
During the down phase of a push up the same triceps brachii actively controls elbow flexion while producing a lengthening contraction. A chemical in on or receptors receptors by structural of receptors ligand s. It is assisted by the brachialis and the brachioradialis.
 Muscles Of The Upper Arm Geeky Medics
Muscles Of The Upper Arm Geeky Medics
 Yoga Teacher Central Anatomy For Yoga Teachers
Yoga Teacher Central Anatomy For Yoga Teachers
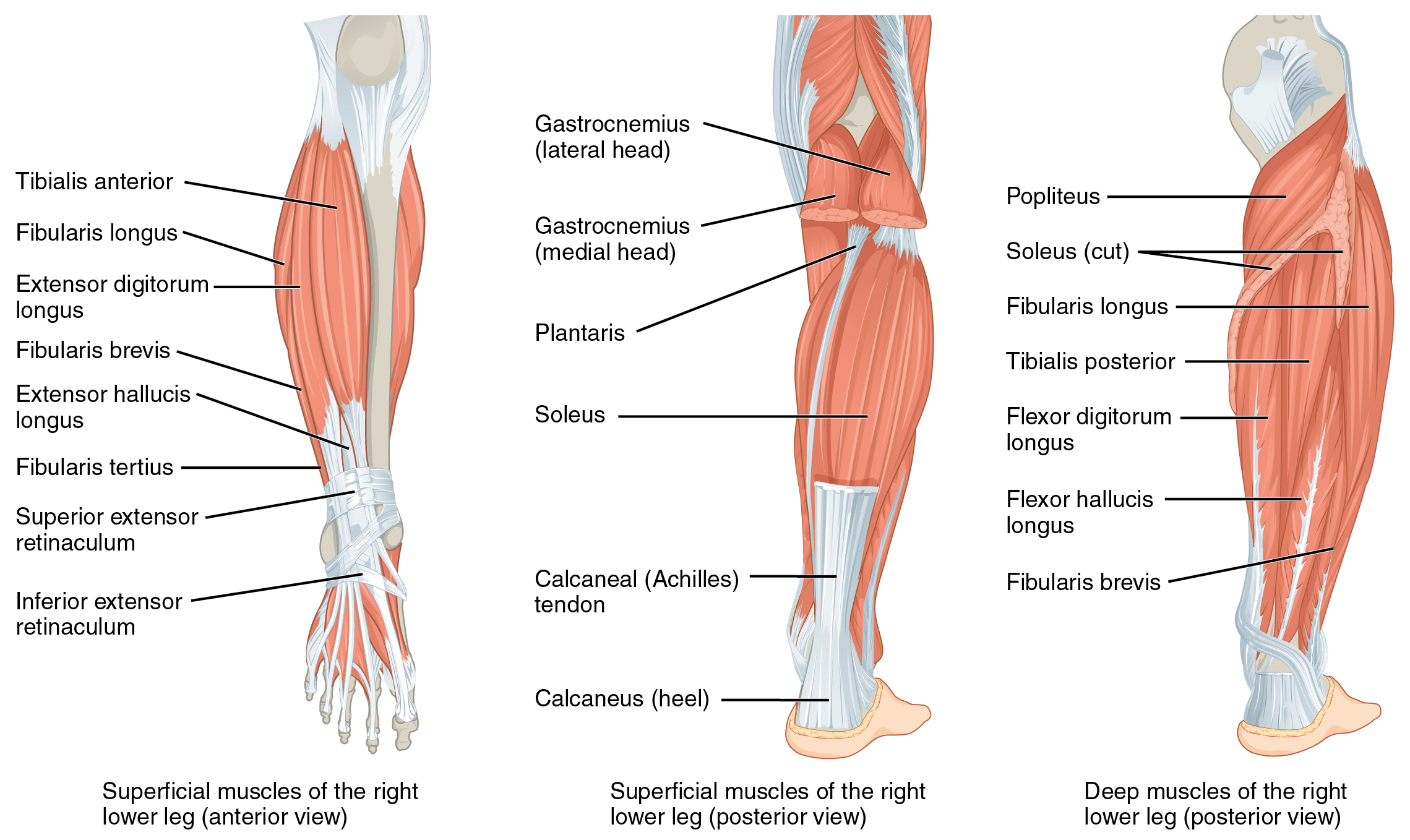
 Lower Leg Anatomy Archives The Wellness Digest
Lower Leg Anatomy Archives The Wellness Digest
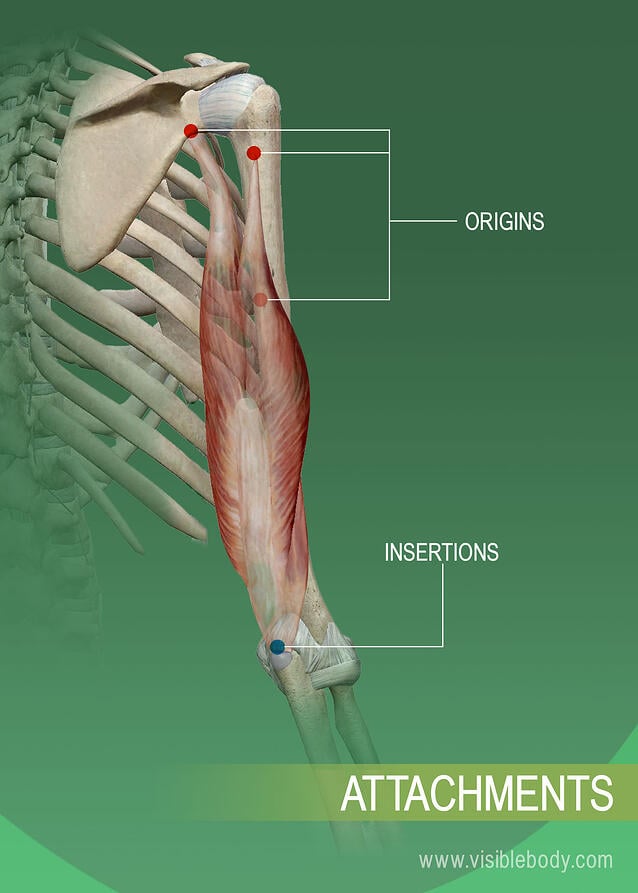 Muscle Attachments And Actions Learn Muscle Anatomy
Muscle Attachments And Actions Learn Muscle Anatomy
 Iliopsoas Anatomy Origins Insertions Actions
Iliopsoas Anatomy Origins Insertions Actions
 Agonist Muscles Anatomy Image Stock Photos Page 1 Masterfile
Agonist Muscles Anatomy Image Stock Photos Page 1 Masterfile
 Extraocular Muscles And Movements
Extraocular Muscles And Movements
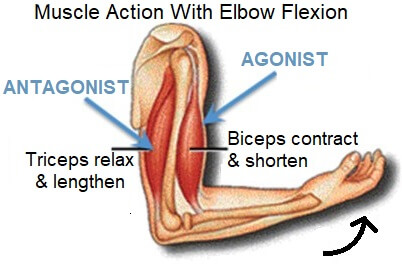 Leg Calf Cramps Causes Treatment Knee Pain Explained
Leg Calf Cramps Causes Treatment Knee Pain Explained
 The Beauty Of Bloody Fists And Broken Bones The Agonist By
The Beauty Of Bloody Fists And Broken Bones The Agonist By
Actions Of Skeletal Muscles Human Anatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12550/HeadCadavar.png) Temporal Muscle Anatomy Function And Innervation Kenhub
Temporal Muscle Anatomy Function And Innervation Kenhub

Chapter 1 The Skeletal And Muscular Systems
 Bio23 F19 S20 Complete Course Guide By Human Anatomy Issuu
Bio23 F19 S20 Complete Course Guide By Human Anatomy Issuu
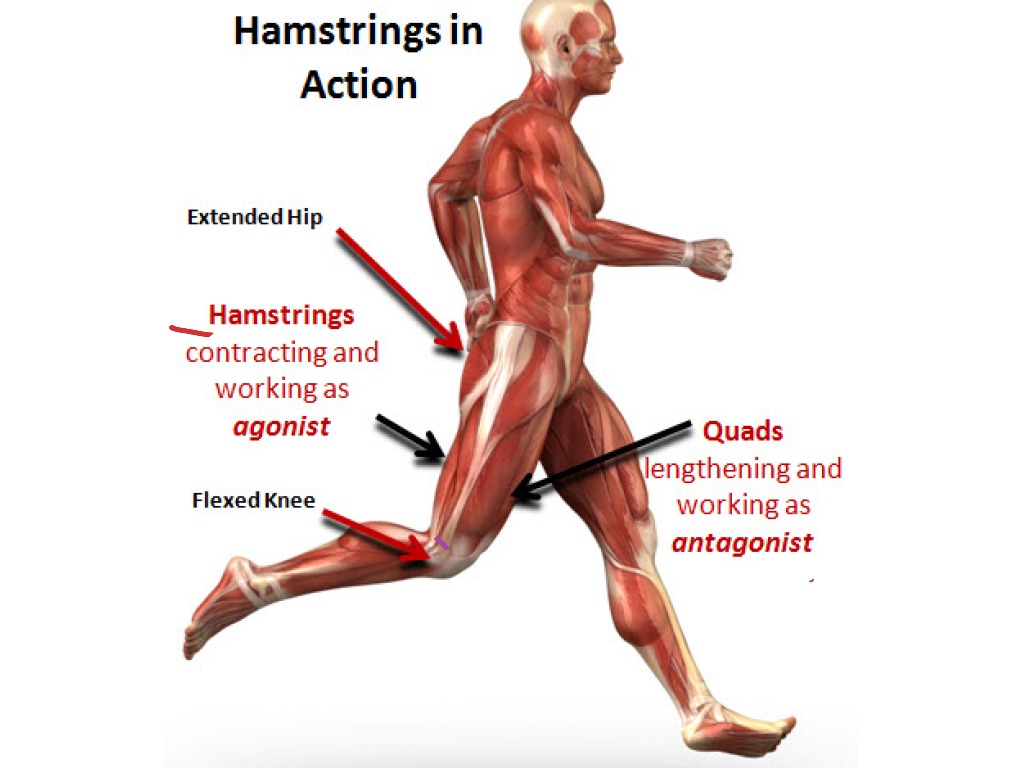 Antagonistic Muscle Action Anatomy Showme
Antagonistic Muscle Action Anatomy Showme
 Anatomical Terms Of Muscle Wikipedia
Anatomical Terms Of Muscle Wikipedia
 Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
 Agonist Muscle Definition Example
Agonist Muscle Definition Example
 Agonist Definition Types And Quiz Biology Dictionary
Agonist Definition Types And Quiz Biology Dictionary
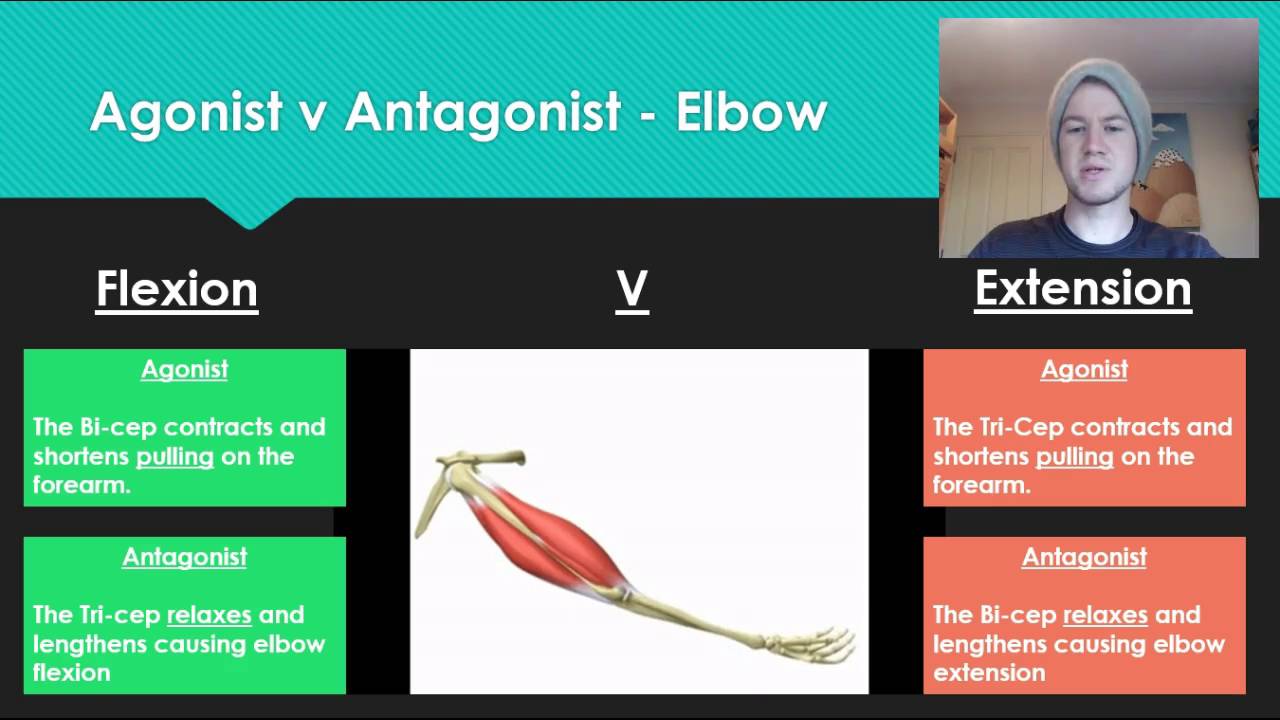 Anatomy 7 Agonist V Antagonist Muscle Pairs
Anatomy 7 Agonist V Antagonist Muscle Pairs
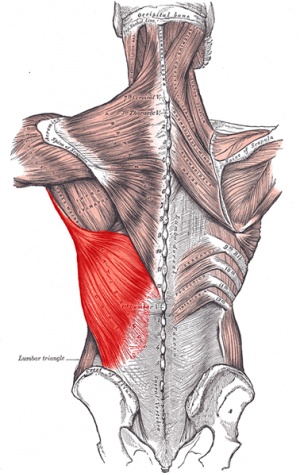 Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Physiopedia
Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Physiopedia
Yoga Anatomy Agonist Antagonist Muscle Groups Sterling
 Anatomical Terms Of Muscle Wikipedia
Anatomical Terms Of Muscle Wikipedia
 11 6 Appendicular Muscles Of The Pelvic Girdle And Lower
11 6 Appendicular Muscles Of The Pelvic Girdle And Lower
General Principles Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
 Gastrocnemius Muscle Anatomy Britannica
Gastrocnemius Muscle Anatomy Britannica
 Pin On Upper Leg Muscle Anatomy
Pin On Upper Leg Muscle Anatomy
 4 Facts You Need To Know About Muscles To Pass Your Level 2 Exam First Time
4 Facts You Need To Know About Muscles To Pass Your Level 2 Exam First Time
 Terminology Definitions Basic Definitions
Terminology Definitions Basic Definitions
 Mechanics Of Movement Ii Muscle Action Across Joints Ppt
Mechanics Of Movement Ii Muscle Action Across Joints Ppt
Anatomy Exam 300825 Uws Studocu


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar