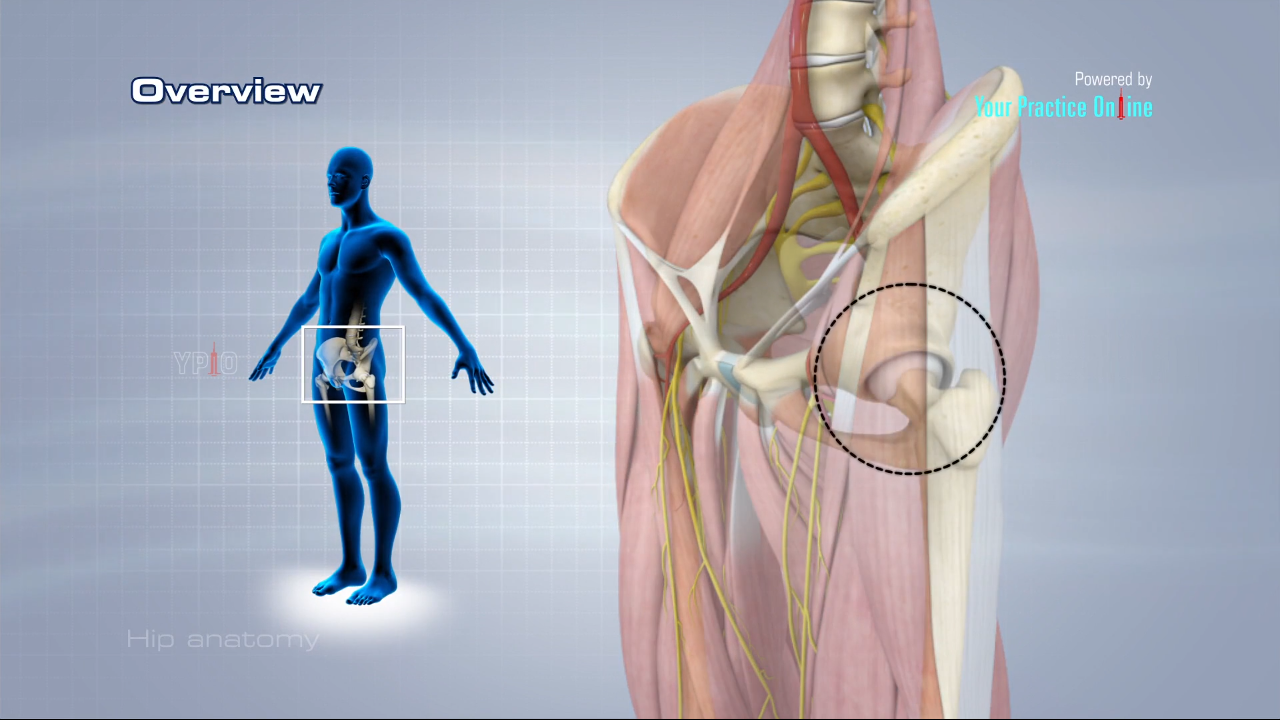
The hip joint see the image below is a ball and socket synovial joint. In vertebrate anatomy hip or coxa in medical terminology refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
 Anatomy Of The Hip Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
Anatomy Of The Hip Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
It bears our bodys weight and the force of the strong muscles of the hip and leg.

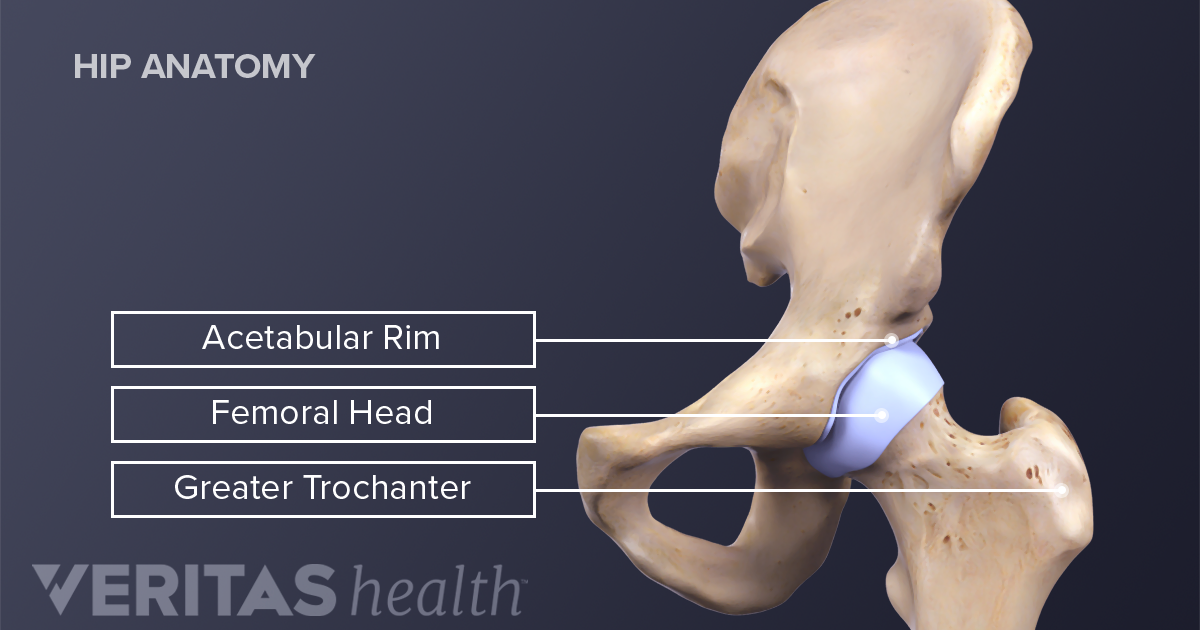
Anatomy of the hip. Iliopsoas muscle a hip flexor muscle that attaches to the upper thigh bone. The rounded head of the femur thighbone forms the ball which fits into the acetabulum a cup shaped socket in the pelvis. Anatomy of the hip an inside look at the structure of the hip.
The round head of the femur rests in a cavity the acetabulum that allows free rotation of the limb. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region inferior to the iliac crest and overlying the greater trochanter of the femur or thigh bone. It is a ball and socket joint at the juncture of the leg and pelvis.
Yet the hip joint is also one of our most flexible joints and allows a greater range of motion than all other joints in the body except for the shoulder. The femur or thighbone is the longest bone in the body. One of the bodys largest weight bearing joints the hip is where the thigh bone meets the pelvis to form a ball and socket joint.
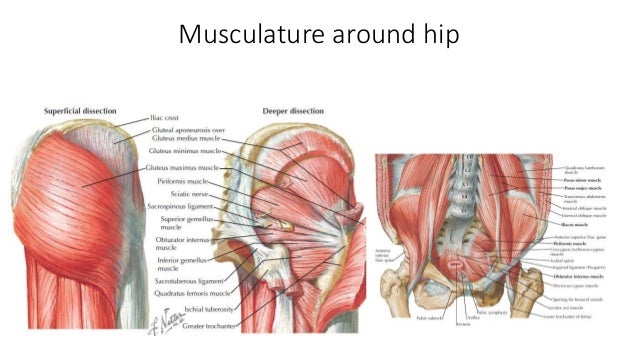
It allows us to walk run and jump. Nerves and vessels supply the muscles and bones of the hip. Rectus femoris muscle one of the quadriceps muscles on the front of your thigh.
Muscles play an important role in the health and well being. The hip joint is the articulation of the pelvis with the. Hip in anatomy the joint between the thighbone femur and the pelvis.
Anatomy of the hip. The hip joint consists of two main parts. Adductor muscles on the inside of your thigh.
The ball is the femoral head and the socket is the acetabulum. Hip problems occur when any one of these components starts to degenerate or is in some way compromised or irritated. And synovial membrane and fluid which encapsulates the hip joint and lubricates it respectively.
Hip ligaments and tendons tough fibrous tissues that bind bones to bones and muscles to bones. The hip is the bodys second largest weight bearing joint after the knee. Also the area adjacent to this joint.
The surface of the acetabulum is the only part of the pelvis replaced in either hip replacement or resurfacing. On the upper side of the pelvis hip bone is the acetabulum or socket of the ball in socket joint. Some of the other muscles in the hip are.
The hip joint is a ball and socket joint. If you think of the hip joint in layers the deepest layer is bone then ligaments of the joint capsule and the tendons and muscles are on top. Its the need for such a high degree of stabilization of the joint that limits movement.
The hip joint is one of the most important joints in the human body. Amphibians and reptiles have relatively weak pelvic girdles and the femur extends horizontally.
 The Hip Anatomy And Physiology
The Hip Anatomy And Physiology
 Hip Anatomy Diagram From Bones To Joints Science Trends
Hip Anatomy Diagram From Bones To Joints Science Trends
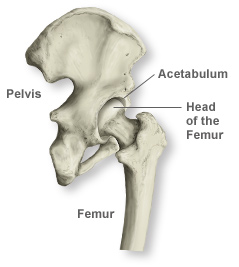 Anatomy Of The Hip Southern California Orthopedic Institute
Anatomy Of The Hip Southern California Orthopedic Institute
 Muscles Of The Hip And Thigh Human Anatomy Kenhub
Muscles Of The Hip And Thigh Human Anatomy Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11031/bones-pelvis-femur_english.jpg) Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
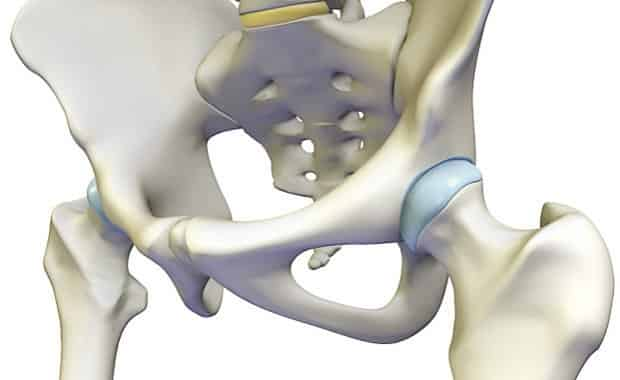 Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles
Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles
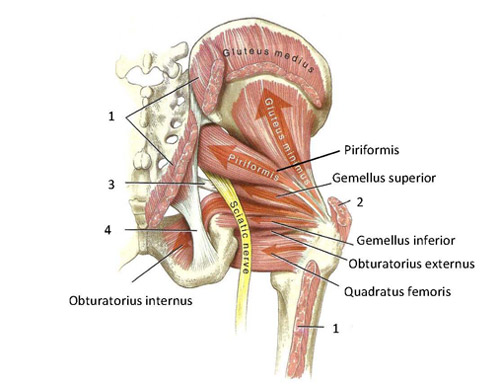 Functional Anatomy Of The Small Pelvic And Hip Muscles
Functional Anatomy Of The Small Pelvic And Hip Muscles
 Anatomy And Injuries Of The Hip Anatomical Chart
Anatomy And Injuries Of The Hip Anatomical Chart
 What Is The Anatomy Of The Hip Flexors Quora
What Is The Anatomy Of The Hip Flexors Quora
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/747/2iEeCHPsxbas46QC7ze0g_muscles-pelvis-hip-femur_english.jpg) Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip Dislocation Orthoinfo Aaos
 Anatomy Of Iliopsoa Also Known As The Dorsal Hip Muscles Canvas Art Stocktrek Images 28 X 29
Anatomy Of Iliopsoa Also Known As The Dorsal Hip Muscles Canvas Art Stocktrek Images 28 X 29
 Yoga For Hip Stability Understanding Hypermobility
Yoga For Hip Stability Understanding Hypermobility
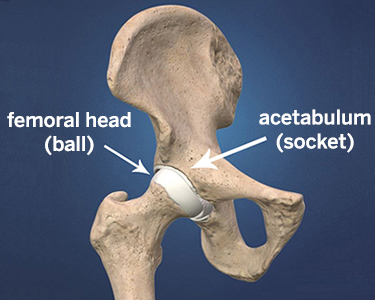 Dislocated Hip Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatments Hss
Dislocated Hip Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatments Hss
 Why People Have To Squat Differently The Movement Fix
Why People Have To Squat Differently The Movement Fix
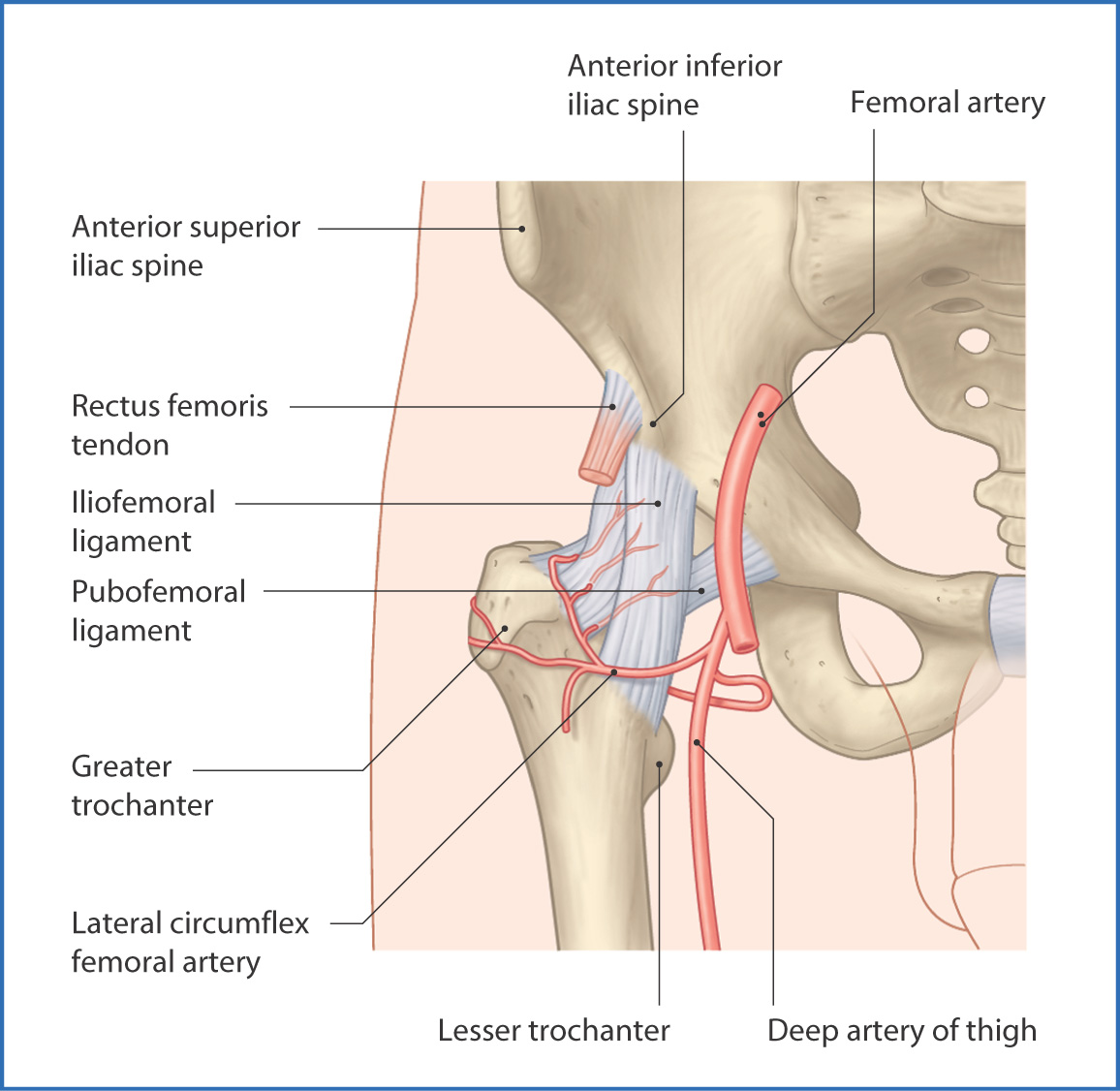 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
 5 Hip Flexor Stretches Club Pilates
5 Hip Flexor Stretches Club Pilates
 Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
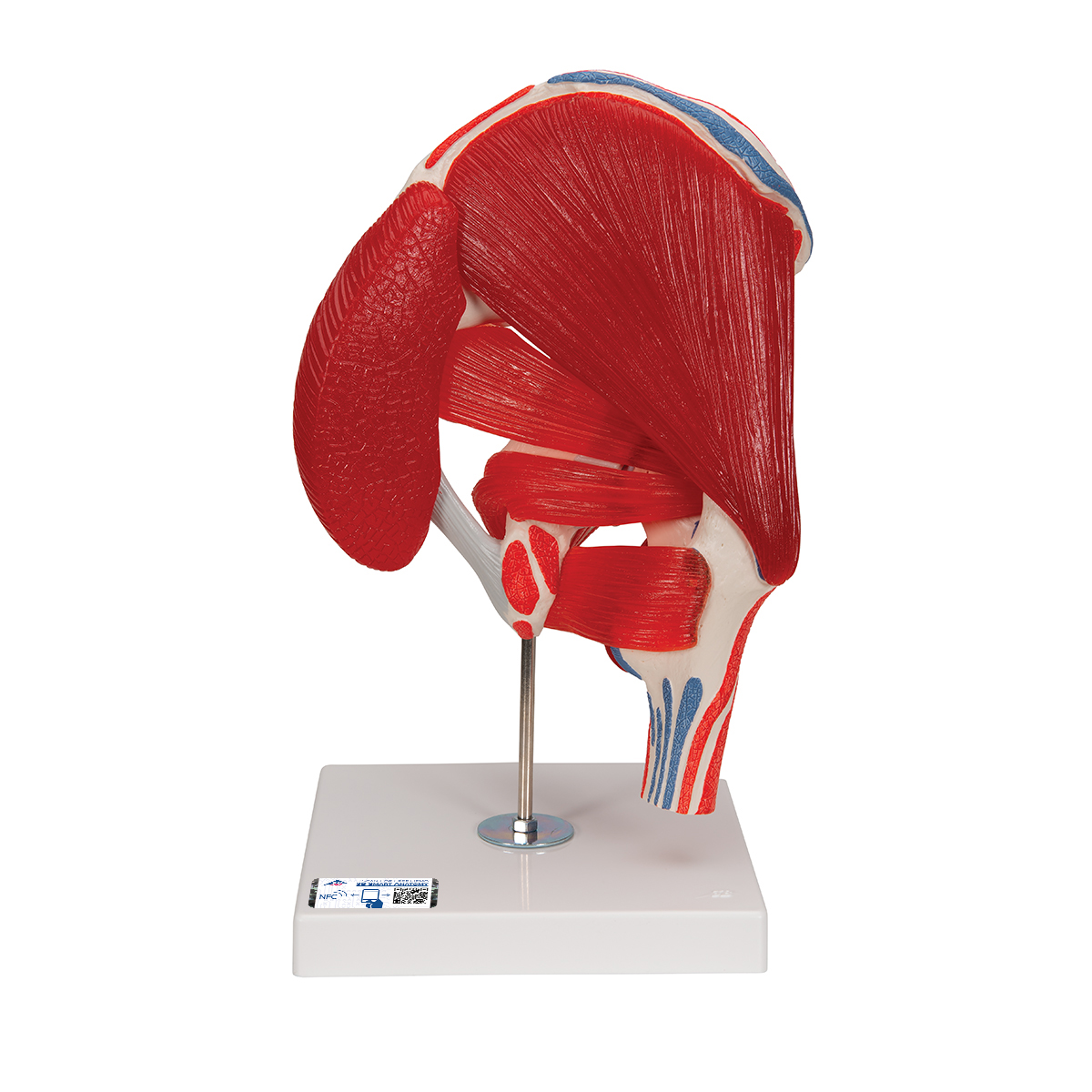 Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
 Hip Anatomy Femur And Pelvis Bones That Make Up The Hip
Hip Anatomy Femur And Pelvis Bones That Make Up The Hip
 Hip Joint Bones Ligaments Blood Supply And Innervation Anatomy Kenhub
Hip Joint Bones Ligaments Blood Supply And Innervation Anatomy Kenhub

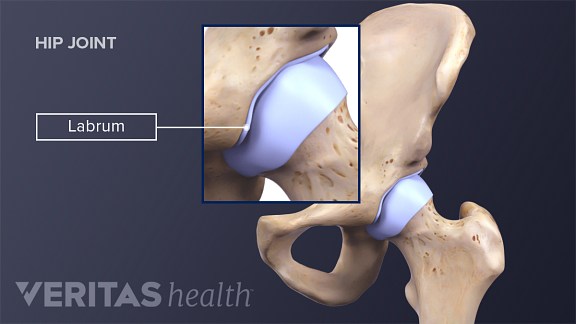
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar