Malangoni introduction understanding the anatomic relationships of the large veins used for placement of central catheters is key to successful cannulation and avoidance of complications. It is used to administer medication or fluids that are unable to be taken by mouth or would harm a smaller peripheral vein obtain blood tests and measure central venous pressure.
 Establishing Vascular Access In The Trauma Patient Chapter
Establishing Vascular Access In The Trauma Patient Chapter
Central venous catheter cvc is a cannula placed in a central vein eg.

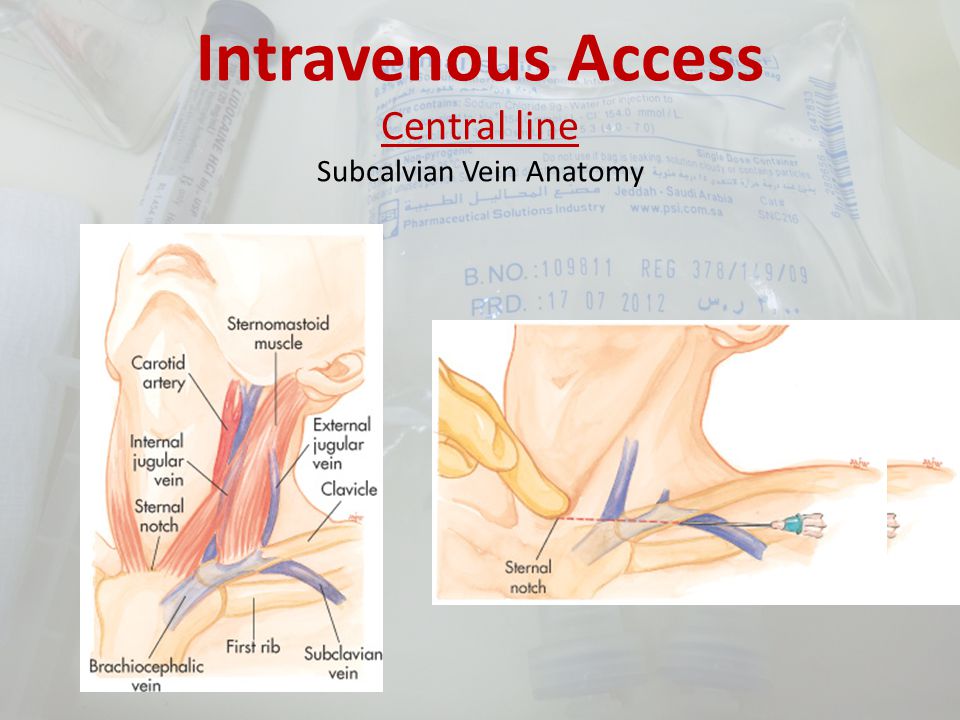
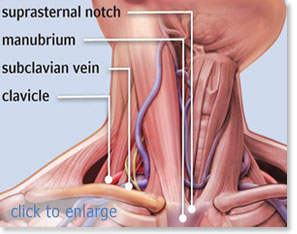
Central line anatomy. Internal jugular catheter versus subclavian catheter x ray appearances. Most commonly 34 and 5 lumen lines are inserted. Mechanical complications most often occur during insertion and are intimately related to the anatomic relationship of the central veins.
Central venous cannulation is a commonly performed procedure which facilitates resuscitation nutritional support and long term vascular access. Svc anatomy on chest x ray. Positioning of cvc in relation to the carina x ray appearances.
Chapter 40 central line anatomy mark a. Confirm what the line will be used for and how many infusions a patient has to aid your selection of the line with the correct amount of lumens. The internal jugular subclavian and femoral veins can be accessed for fluid infusion blood sampling hemodialysis cardiac pacemaker placement and measurement of.
Central lines can have multiple lumens. A central venous catheter also known as a central line central venous line or central venous access catheter is a catheter placed into a large vein. Subclavian internal jugular or femoral.
Anatomy of central venous catheter cvc insertion as seen on x ray. Central venous line placement is typically performed at four sites in the body. A long catheter may be advanced into the central circulation from the antecubital veins as well.
Catheters can be placed in veins in the neck chest groin or through veins in the arms. Alternatives include the external jugular and femoral veins. The right or left internal jugular vein ijv or the right or left subclavian vein scv.
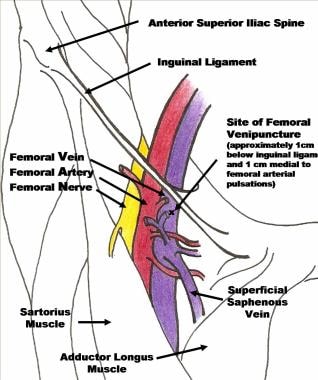 Femoral Central Venous Access Background Indications
Femoral Central Venous Access Background Indications
 Central Venous Catheters Northshore
Central Venous Catheters Northshore
 Discharge Instructions Caring For Your Peripherally Inserted
Discharge Instructions Caring For Your Peripherally Inserted
 Transparent Ultrasound Guided Central Venous Access With
Transparent Ultrasound Guided Central Venous Access With
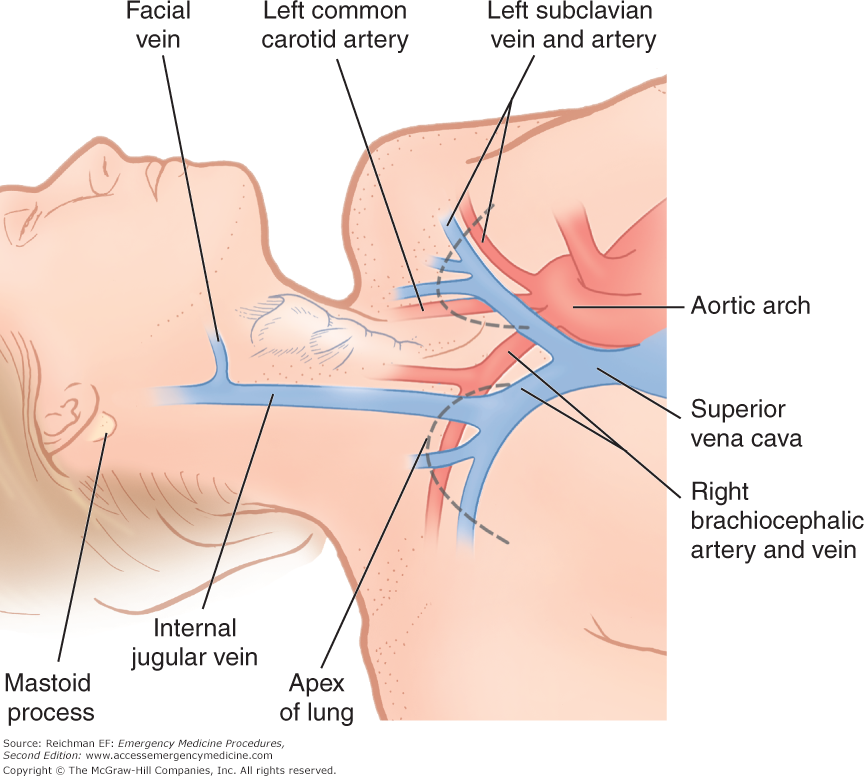 Chapter 49 Central Venous Access Emergency Medicine
Chapter 49 Central Venous Access Emergency Medicine
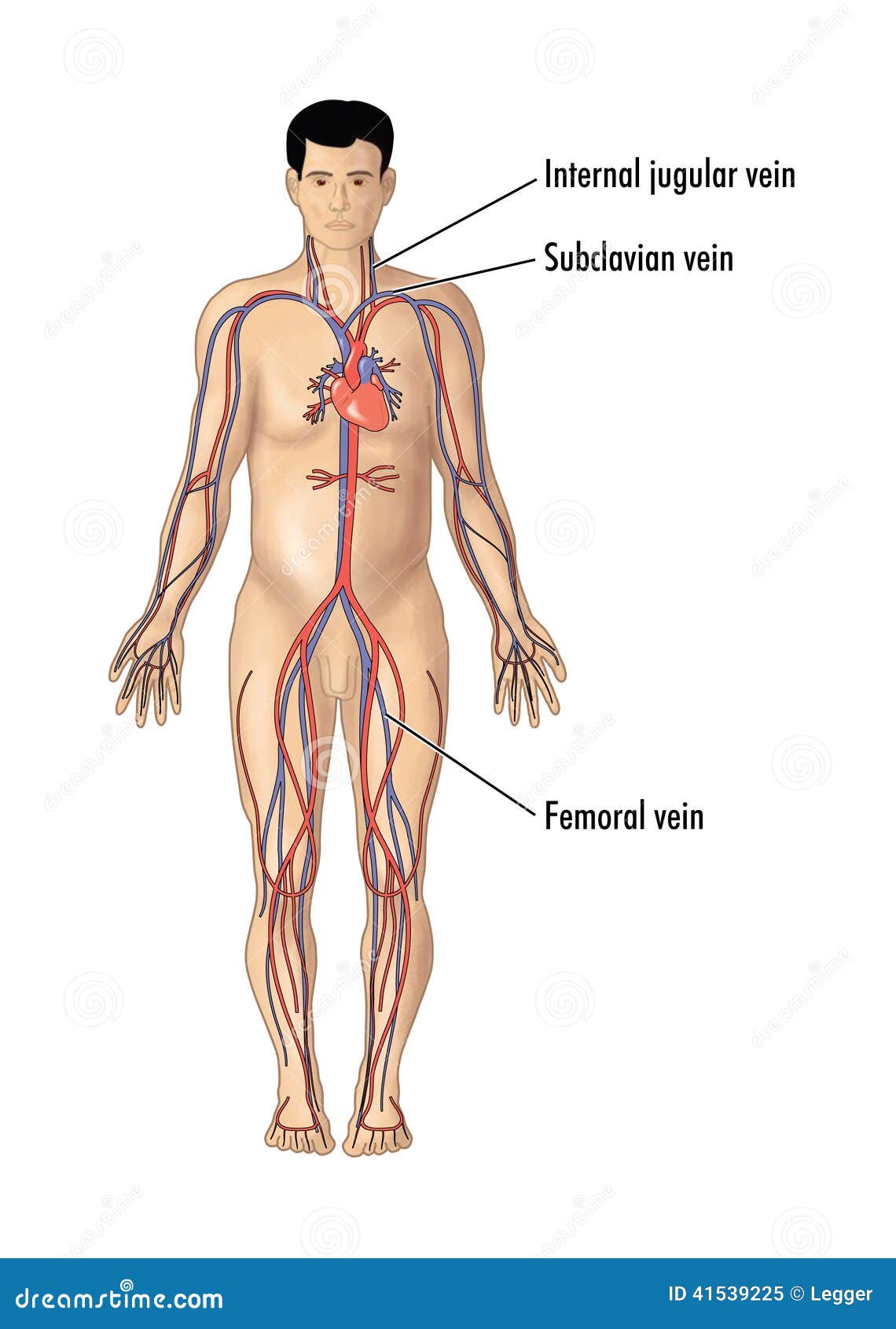 Major Blood Vessels For Central Line Insertion Stock
Major Blood Vessels For Central Line Insertion Stock
 Preventing Complications Of Central Venous Catheterization
Preventing Complications Of Central Venous Catheterization
Procguide Internal Jugular Central Line
Demo Class Pedagogy University
Procguide Internal Jugular Central Line
 New Report On Central Line Market 2018 Global Analysis By
New Report On Central Line Market 2018 Global Analysis By
Procguide Femoral Central Line
 Central Line Placement Crashing Patient
Central Line Placement Crashing Patient
 Recall Central Line Catheters Can Fracture Break Medical
Recall Central Line Catheters Can Fracture Break Medical
 The Difference Between Central Lines And Picc Lines
The Difference Between Central Lines And Picc Lines
 Chapter 49 Central Venous Access Emergency Medicine
Chapter 49 Central Venous Access Emergency Medicine
 Central Line Mrsa Infection Resulting In Endocarditis
Central Line Mrsa Infection Resulting In Endocarditis
 Intravenous Access The Ability To Obtain Intravenous Iv
Intravenous Access The Ability To Obtain Intravenous Iv
 Ultrasound Guided Central Venous Catheterization A Review
Ultrasound Guided Central Venous Catheterization A Review
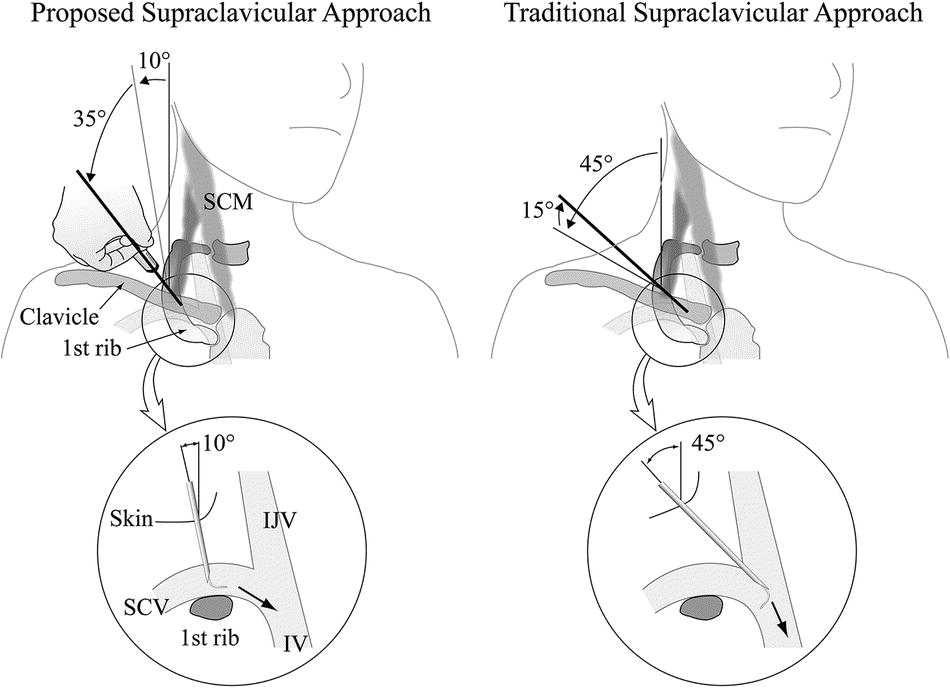
 Using The Supraclavicular Approach To Ultrasound Guided
Using The Supraclavicular Approach To Ultrasound Guided
 Section 6 Step By Step Insertion Techniques
Section 6 Step By Step Insertion Techniques
 Recommendations On The Use Of Ultrasound Guidance For
Recommendations On The Use Of Ultrasound Guidance For



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar